A Novel Colorimetric Immunoassay Utilizing the Peroxidase Mimicking Activity of Magnetic Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
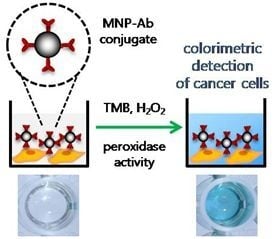
2.1. A Novel Colorimetric Immunoassay Utilizing the Peroxidase Mimicking Activity of Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.2. Colorimetric Detection of Rotavirus
2.3. Colorimetric Detection of Breast Cancer Cells
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs)
3.2. Chemical Modification of MNPs
3.3. Preparation of Antibody-Conjugated MNPs
3.4. Kinetic Analysis
3.5. Colorimetric Detection of Rotavirus
3.6. Colorimetric Detection of Breast Cancer Cells
3.7. Cytotoxicity Test
3.8. Prussian Blue Staining
3.9. Fluorescent Visualization of the Cells by Tyramide Signal Amplification (TSA)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Information
ijms-14-09999-s001.pdfAcknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Valanne, A.; Huopalahti, S.; Soukka, T.; Vainionpää, R.; Lövgren, T.; Härmä, H. A sensitive adenovirus immunoassay as a model for using nanoparticle label technology in virus diagnostics. J. Clin. Virol 2005, 33, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Dai, Q.; Austin, L.; Coutts, J.; Knowles, G.; Zou, J.; Chen, H.; Huo, Q. A one-step homogeneous immunoassay for cancer biomarker detection using gold nanoparticle probes coupled with dynamic light scattering. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2008, 130, 2780–2782. [Google Scholar]
- Lequin, R.M. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)/Enzyme-Linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin. Chem 2005, 51, 2415–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuya, T.; Tashiro, S.; Hoshino, N.; Shibata, N.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. A core-shell-type fluorescent nanosphere possessing reactive poly(ethylene glycol) tethered chains on the surface for zeptomole detection of protein in time-resolved fluorometric immunoassay. Anal. Chem 2003, 75, 6124–6132. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Hao, C.; Fei, X.; Ju, H. Flow-Injection chemiluminescent immunoassay for alpha-fetoprotein based on epoxysilane modified glass microbeads. J. Immunol. Methods 2006, 312, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith, S.J. Radioimmunoassay: Review of basic principles. Semin. Nucl. Med 1975, 5, 125–152. [Google Scholar]
- Wulff, G. Enzyme-like catalysis by molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem. Rev 2002, 102, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Fruk, L.; Niemeyer, C.M. Covalent Hemin-DNA adducts for generating a novel class of artificial heme enzymes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2005, 44, 2603–2606. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.J.; Yoo, K.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Ha, T.K. 5-(Beta-cyclodextrinylamino)-5-ceoxy-alpha-d-riboses as models for nuclease, ligase, phosphatase, and phosphorylase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2000, 39, 347–349. [Google Scholar]
- Fiammengo, R.; Jäschke, A. Nucleic acid enzymes. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 2005, 16, 614–621. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X. Label-free colorimetric immunoassay for the simple and sensitive detection of neurogenin3 using gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron 2011, 26, 4245–4248. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosi, A.; Airò, F.; Merkoçi, A. Enhanced gold nanoparticle based ELISA for a breast cancer biomarker. Anal. Chem 2010, 82, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, Y.L.; Jung, C.; Parab, H.; Li, T.; Park, H.G. Direct colorimetric diagnosis of pathogen infections by utilizing thiol-labeled pcr primers and unmodified gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron 2010, 25, 1941–1946. [Google Scholar]
- Niemeyer, C.M. Nanoparticles, proteins, and nucleic acids: Biotechnology meets materials science. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2001, 40, 4128–4158. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, Y.K.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.M.; Park, H.G. Universal colorimetric detection of nucleic acids based on polydiacetylene (PDA) liposomes. Adv. Funct. Mater 2008, 18, 701–708. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Zhuang, J.; Nie, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N.; Wang, T.; Feng, J.; Yang, D.; Perrett, S.; Xiyun, Y. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol 2007, 2, 577–583. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.S.; Kim, M.I.; Cho, D.Y.; Park, H.G. Label-Free colorimetric detection of nucleic acids based on target-induced shielding against the peroxidase-mimicking activity of magnetic nanoparticles. Small 2011, 7, 1521–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.I.; Ye, Y.; Won, B.Y.; Shin, S.; Lee, J.; Park, H.G. A highly efficient electrochemical biosensing platform by employing conductive nanocomposite entrapping magnetic nanoparticles and oxidase in mesoporous carbon foam. Adv. Funct. Mater 2011, 21, 2868–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.I.; Shim, J.; Li, T.; Lee, J.; Park, H.G. Fabrication of nanoporous nanocomposites entrapping Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and oxidases for colorimetric biosensing. Chem. A Eur. J 2011, 17, 10700–10707. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.I.; Shim, J.; Li, T.; Woo, M.A.; Cho, D.; Lee, J.; Park, H.G. Colorimetric quantification of galactose using a nanostructured multi-catalyst system entrapping galactose oxidase and magnetic nanoparticles as peroxidase mimetics. Analyst 2012, 137, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.I.; Shim, J.; Harshala, P.; Shin, S.C.; Lee, J.; Park, H.G. A convenient alcohol sensor using one-pot nanocomposite entrapping alcohol oxidase and magnetic nanoparticles as peroxidase mimetics. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol 2012, 12, 5914–5919. [Google Scholar]
- Parashar, U.D.; Hummelman, E.G.; Bresee, J.S.; Miller, M.A.; Glass, R.I. Global illness and deaths caused by rotavirus disease in children. Emerg. Infect. Dis 2003, 9, 565–572. [Google Scholar]
- Dennehy, P.H. Rotavirus vaccines: An overview. Clin. Microbiol. Rev 2008, 21, 198–208. [Google Scholar]
- Desselberger, U.; Iturriza-Gomara, M.; Gray, J.J. Rotavirus epidemiology and surveillance. Novartis Found Symp 2001, 238, 125–147. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, M.; Schulz, S.; Fischer, R.; Niemeyer, C.M. Detection of rotavirus from stool samples using a standardized immuno-PCR (“Imperacer”) method with end-pointand real-time detection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2005, 333, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.H.; Cheon, D.S.; Liu, F.; Lee, K.B.; Seo, T.S. Graphene oxide based immunobiosensor for pathogen detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2010, 49, 5708–5711. [Google Scholar]
- Ljungman, M. Targeting the DNA damage response in cancer. Chem. Rev 2009, 109, 2929–2950. [Google Scholar]
- Slamon, D.J.; Clark, G.M.; Wong, S.G.; Levin, W.J.; Ullrich, A.; McGuire, W.L. Human breast cancer: Correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 1987, 235, 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Bunn, P.A., Jr; Helfrich, B.; Soriano, A.F.; Franklin, W.A.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Hirsch, F.R.; Baron, A.; Zeng, C.; Chan, D.C. Expression of Her-2/neu in human lung cancer cell lines by immunohistochemistry and fluorescencein situ hybridization and its relationship to in vitro cytotoxicity by trastuzumab and chemotherapeutic agents. Clin. Cancer Res 2001, 7, 3239–3250. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, P.; Liu, X.; Lee, T.; Liu, L.; Barham, R.; Kirkland, R.; Leesman, G.; Kuller, A.; Ybarrondo, B.; Ng, S.C.; Singh, S. Highly sensitive proximity mediated immunoassay reveals her2 status conversion in the circulating tumor cells of metastatic breast cancer patients. Proteome Sci 2011, 9, 75–89. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, J.; DeBiasio, R.; Zhu, Z.; Giuliano, K.A.; Schmidt, B.F. Immunofluorescence signal amplification by the enzyme-catalyzed deposition of a fluorescent reporter substrate (CARD). Cytometry 1996, 23, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Bofin, A.M.; Qvigstad, G.; Waldum, C.; Waldum, H.L. Neuroendocrine differentiation in carcinoma of the breast. Tyramide signal amplification discloses chromogranin a-positive tumour cells in more breast tumours than previously realized. APMIS 2002, 110, 658–664. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, R.V.; Upadhyay, R.V.; Charles, S.W.; Ramchand, C.N. Direct binding of protein to magnetic particles. Biotechnol. Tech 1997, 11, 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Pan, B.F.; Zheng, W.M.; Ao, L.M.; Gu, H.C. Study of streptavidin coated onto PAMAM dendrimer modified magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 2005, 293, 48–54. [Google Scholar]







© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Woo, M.-A.; Kim, M.I.; Jung, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Seo, T.S.; Park, H.G. A Novel Colorimetric Immunoassay Utilizing the Peroxidase Mimicking Activity of Magnetic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9999-10014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059999
Woo M-A, Kim MI, Jung JH, Park KS, Seo TS, Park HG. A Novel Colorimetric Immunoassay Utilizing the Peroxidase Mimicking Activity of Magnetic Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(5):9999-10014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059999
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoo, Min-Ah, Moon Il Kim, Jae Hwan Jung, Ki Soo Park, Tae Seok Seo, and Hyun Gyu Park. 2013. "A Novel Colorimetric Immunoassay Utilizing the Peroxidase Mimicking Activity of Magnetic Nanoparticles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 5: 9999-10014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059999
APA StyleWoo, M.-A., Kim, M. I., Jung, J. H., Park, K. S., Seo, T. S., & Park, H. G. (2013). A Novel Colorimetric Immunoassay Utilizing the Peroxidase Mimicking Activity of Magnetic Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(5), 9999-10014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059999