Regulation of Huntingtin Gene Expression by miRNA-137, -214, -148a, and Their Respective isomiRs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
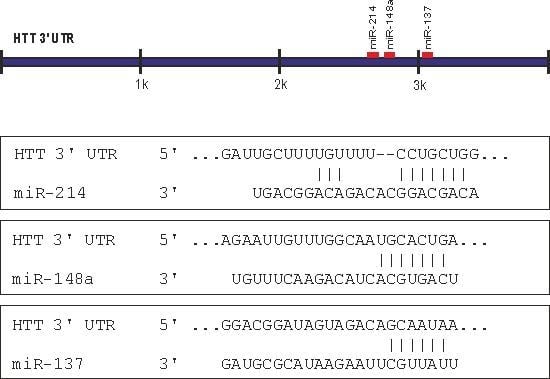
2.1. Prediction of miRNA Interactions with the HTT Transcript
2.2. Canonical miR-137, miR-214, and miR-148a Regulate the Expression of the HTT Gene
2.3. 5′-End Variants of miRNAs Are Functional and Might Regulate the Same Targets as Canonical miRNAs
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture
3.2. Plasmid Constructs and Synthetic miRNA Oligonucleotides
3.3. Cell Transfection
3.4. Luciferase Reporter Assay
3.5. RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR
3.6. Northern Blotting
3.7. Western Blotting
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Information
ijms-14-16999-s001.pdfAcknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chekulaeva, M.; Filipowicz, W. Mechanisms of miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation in animal cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol 2009, 21, 452–460. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, V.N.; Han, J.; Siomi, M.C. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2009, 10, 126–139. [Google Scholar]
- Krol, J.; Loedige, I.; Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet 2010, 11, 597–610. [Google Scholar]
- Starega-Roslan, J.; Koscianska, E.; Kozlowski, P.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. The role of the precursor structure in the biogenesis of microRNA. Cell. Mol. Life Sci 2011, 68, 2859–2871. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, J.; Jung, S.; Keller, S.; Gregory, R.I.; Diederichs, S. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat. Cell Biol 2009, 11, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Saini, H.K.; van Dongen, S.; Enright, A.J. miRBase: Tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 2008, 36, D154–D158. [Google Scholar]
- Morin, R.D.; O’Connor, M.D.; Griffith, M.; Kuchenbauer, F.; Delaney, A.; Prabhu, A.L.; Zhao, Y.; McDonald, H.; Zeng, T.; Hirst, M.; et al. Application of massively parallel sequencing to microRNA profiling and discovery in human embryonic stem cells. Genome Res 2008, 18, 610–621. [Google Scholar]
- Starega-Roslan, J.; Krol, J.; Koscianska, E.; Kozlowski, P.; Szlachcic, W.J.; Sobczak, K.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. Structural basis of microRNA length variety. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, 257–268. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, H.; Ghildiyal, M.; Zamore, P.D. Argonaute loading improves the 5′ precision of both MicroRNAs and their miRNA* strands in flies. Curr. Biol 2008, 18, 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Ye, C.; Ramirez, D.; Manjunath, N. Alternative processing of primary microRNA transcripts by Drosha generates 5′ end variation of mature microRNA. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7566. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, F.; Sonenberg, N.; Nagar, B. Structural basis for 5′-nucleotide base-specific recognition of guide RNA by human AGO2. Nature 2010, 465, 818–822. [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf, P.; Rusu, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sewer, A.; Iovino, N.; Aravin, A.; Pfeffer, S.; Rice, A.; Kamphorst, A.O.; Landthaler, M.; et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007, 129, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar]
- Ruby, J.G.; Jan, C.; Player, C.; Axtell, M.J.; Lee, W.; Nusbaum, C.; Ge, H.; Bartel, D.P. Large-scale sequencing reveals 21U-RNAs and additional microRNAs and endogenous siRNAs in C. elegans. Cell 2006, 127, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Neilson, J.R.; Kumar, P.; Manocha, M.; Shankar, P.; Sharp, P.A.; Manjunath, N. miRNA profiling of naive, effector and memory CD8 T cells. PLoS One 2007, 2, e1020. [Google Scholar]
- Huse, S.M.; Huber, J.A.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L.; Welch, D.M. Accuracy and quality of massively parallel DNA pyrosequencing. Genome Biol 2007, 8, R143. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, G.; Yin, X.; Luo, H.; Xu, X.; Bolund, L.; Zhang, X.; Gan, S.Q.; Li, N. Sequencing bias: Comparison of different protocols of microRNA library construction. BMC Biotechnol 2010, 10, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.Y.; Doudna, J.A. TRBP alters human precursor microRNA processing in vitro. RNA 2012, 18, 2012–2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Abe, M.; Sabin, L.R.; Hendriks, G.J.; Naqvi, A.S.; Yu, Z.; Cherry, S.; Bonini, N.M. The exoribonuclease Nibbler controls 3′ end processing of microRNAs in Drosophila. Curr. Biol 2011, 21, 1888–1893. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, C.A.; Tabrizi, S.J. Huntington’s disease: From molecular pathogenesis to clinical treatment. Lancet Neurol 2011, 10, 83–98. [Google Scholar]
- Fiszer, A.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. RNA toxicity in polyglutamine disorders: Concepts, models, and progress of research. J. Mol. Med 2013, 91, 683–691. [Google Scholar]
- Marti, E.; Pantano, L.; Banez-Coronel, M.; Llorens, F.; Minones-Moyano, E.; Porta, S.; Sumoy, L.; Ferrer, I.; Estivill, X. A myriad of miRNA variants in control and Huntington’s disease brain regions detected by massively parallel sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38, 7219–7235. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, H.R.; Schoenfeld, L.W.; Ruby, J.G.; Auyeung, V.C.; Spies, N.; Baek, D.; Johnston, W.K.; Russ, C.; Luo, S.; Babiarz, J.E.; et al. Mammalian microRNAs: Experimental evaluation of novel and previously annotated genes. Genes Dev 2010, 24, 992–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara, Y.; Megraw, M.; Kreider, E.; Iizasa, H.; Valente, L.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G.; Nishikura, K. Frequency and fate of microRNA editing in human brain. Nucleic Acids Res 2008, 36, 5270–5280. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Valverde, S.L.; Taft, R.J.; Mattick, J.S. Dynamic isomiR regulation in Drosophila development. RNA 2010, 16, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar]
- Khvorova, A.; Reynolds, A.; Jayasena, S.D. Functional siRNAs and miRNAs exhibit strand bias. Cell 2003, 115, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, D.S.; Hutvagner, G.; Du, T.; Xu, Z.; Aronin, N.; Zamore, P.D. Asymmetry in the assembly of the RNAi enzyme complex. Cell 2003, 115, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Azuma-Mukai, A.; Oguri, H.; Mituyama, T.; Qian, Z.R.; Asai, K.; Siomi, H.; Siomi, M.C. Characterization of endogenous human Argonautes and their miRNA partners in RNA silencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7964–7969. [Google Scholar]
- Cloonan, N.; Wani, S.; Xu, Q.; Gu, J.; Lea, K.; Heater, S.; Barbacioru, C.; Steptoe, A.L.; Martin, H.C.; Nourbakhsh, E.; et al. MicroRNAs and their isomiRs function cooperatively to target common biological pathways. Genome Biol 2011, 12, R126. [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys, D.T.; Hynes, C.J.; Patel, H.R.; Wei, G.H.; Cannon, L.; Fatkin, D.; Suter, C.M.; Clancy, J.L.; Preiss, T. Complexity of murine cardiomyocyte miRNA biogenesis, sequence variant expression and function. PLoS One 2012, 7, e30933. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, L.W.; Zhang, S.; Etheridge, A.; Ma, L.; Martin, D.; Galas, D.; Wang, K. Complexity of the microRNA repertoire revealed by next-generation sequencing. RNA 2010, 16, 2170–2180. [Google Scholar]
- Neilsen, C.T.; Goodall, G.J.; Bracken, C.P. IsomiRs—The overlooked repertoire in the dynamic microRNAome. Trends Genet 2012, 28, 544–549. [Google Scholar]
- Faghihi, M.A.; Zhang, M.; Huang, J.; Modarresi, F.; van der Brug, M.P.; Nalls, M.A.; Cookson, M.R.; St-Laurent, G., 3rd; Wahlestedt, C. Evidence for natural antisense transcript-mediated inhibition of microRNA function. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R56. [Google Scholar]
- Llorens, F.; Banez-Coronel, M.; Pantano, L.; Del Rio, J.A.; Ferrer, I.; Estivill, X.; Marti, E. A highly expressed miR-101 isomiR is a functional silencing small RNA. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 104. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, Y.T.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, R.J.; Kuo, H.H.; Thang, W.C.; Chiu, K.P.; Yu, A.L. Concordant and discordant regulation of target genes by miR-31 and its isoforms. PLoS One 2013, 8, e58169. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, M.; Ghose, J.; Bhattarcharyya, N.P. Micro RNA-214,-150,-146a and-125b target Huntingtin gene. RNA Biol 2011, 8, 1005–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Witkos, T.M.; Koscianska, E.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. Practical aspects of microRNA target prediction. Curr. Mol. Med 2011, 11, 93–109. [Google Scholar]
- Dweep, H.; Sticht, C.; Pandey, P.; Gretz, N. miRWalk—Database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by “walking” the genes of three genomes. J. Biomed. Inform 2011, 44, 839–847. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, S.D.; Lin, F.M.; Wu, W.Y.; Liang, C.; Huang, W.C.; Chan, W.L.; Tsai, W.T.; Chen, G.Z.; Lee, C.J.; Chiu, C.M.; et al. miRTarBase: A database curates experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, D163–D169. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, M.; Ghose, J.; Das, E.; Bhattarcharyya, N.P. Altered microRNAs in STHdh(Q111)/Hdh(Q111) cells: miR-146a targets TBP. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2010, 396, 742–747. [Google Scholar]
- Soldati, C.; Bithell, A.; Johnston, C.; Wong, K.Y.; Stanton, L.W.; Buckley, N.J. Dysregulation of REST-regulated coding and non-coding RNAs in a cellular model of Huntington’s disease. J. Neurochem 2013, 124, 418–430. [Google Scholar]
- Kiriakidou, M.; Nelson, P.T.; Kouranov, A.; Fitziev, P.; Bouyioukos, C.; Mourelatos, Z.; Hatzigeorgiou, A. A combined computational-experimental approach predicts human microRNA targets. Genes Dev 2004, 18, 1165–1178. [Google Scholar]
- John, B.; Enright, A.J.; Aravin, A.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. Human microRNA targets. PLoS Biol 2004, 2, e363. [Google Scholar]
- Krek, A.; Grun, D.; Poy, M.N.; Wolf, R.; Rosenberg, L.; Epstein, E.J.; MacMenamin, P.; da Piedade, I.; Gunsalus, K.C.; Stoffel, M.; et al. Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat. Genet 2005, 37, 495–500. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar]
- Bicchi, I.; Morena, F.; Montesano, S.; Polidoro, M.; Martino, S. MicroRNAs and molecular mechanisms of neurodegeneration. Genes 2013, 4, 244–263. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, V.; Esposito, R.; Aprile, M.; Ciccodicola, A. Non-coding RNA and pseudogenes in neurodegenerative diseases: “The (un)Usual Suspects”. Front. Genet 2012, 3, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Koscianska, E.; Baev, V.; Skreka, K.; Oikonomaki, K.; Rusinov, V.; Tabler, M.; Kalantidis, K. Prediction and preliminary validation of oncogene regulation by miRNAs. BMC Mol. Biol 2007, 8, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, D.; Villen, J.; Shin, C.; Camargo, F.D.; Gygi, S.P.; Bartel, D.P. The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 2008, 455, 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Ingolia, N.T.; Weissman, J.S.; Bartel, D.P. Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 2010, 466, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Cheng, W.C.; Chung, I.F.; Huang, T.S.; Chang, S.T.; Sun, H.J.; Tsai, C.F.; Liang, M.L.; Wong, T.T.; Wang, H.W. YM500: A small RNA sequencing (smRNA-seq) database for microRNA research. Nucleic Acids Res 2013, 41, D285–D294. [Google Scholar]
- Robins, H.; Press, W.H. Human microRNAs target a functionally distinct population of genes with AT-rich 3′ UTRs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15557–15562. [Google Scholar]
- Grimson, A.; Farh, K.K.; Johnston, W.K.; Garrett-Engele, P.; Lim, L.P.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: Determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 91–105. [Google Scholar]
- Kertesz, M.; Iovino, N.; Unnerstall, U.; Gaul, U.; Segal, E. The role of site accessibility in microRNA target recognition. Nat. Genet 2007, 39, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, S.; Tarapore, R.S.; Teslaa, J.J.; Grinblat, Y.; Setaluri, V.; Spiegelman, V.S. MicroRNA-340-mediated degradation of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor mRNA is inhibited by the coding region determinant-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem 2010, 285, 20532–20540. [Google Scholar]
- Brennecke, J.; Stark, A.; Russell, R.B.; Cohen, S.M. Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol 2005, 3, e85. [Google Scholar]
- Ebhardt, H.A.; Tsang, H.H.; Dai, D.C.; Liu, Y.; Bostan, B.; Fahlman, R.P. Meta-analysis of small RNA-sequencing errors reveals ubiquitous post-transcriptional RNA modifications. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar]
- Felice, K.M.; Salzman, D.W.; Shubert-Coleman, J.; Jensen, K.P.; Furneaux, H.M. The 5′ terminal uracil of let-7a is critical for the recruitment of mRNA to Argonaute2. Biochem. J 2009, 422, 329–341. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, S.; Cai, T.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hodges, E.; Ni, F.; Wu, L.; Li, S.; Zhou, H.; Long, C.; et al. Sorting of small RNAs into Arabidopsis argonaute complexes is directed by the 5′ terminal nucleotide. Cell 2008, 133, 116–127. [Google Scholar]
- Koscianska, E.; Starega-Roslan, J.; Czubala, K.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. High-resolution northern blot for a reliable analysis of microRNAs and their precursors. Scientific World Journal 2011, 11, 102–117. [Google Scholar]
- Koscianska, E.; Starega-Roslan, J.; Sznajder, L.J.; Olejniczak, M.; Galka-Marciniak, P.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. Northern blotting analysis of microRNAs, their precursors and RNA interference triggers. BMC Mol. Biol 2011, 12, 14. [Google Scholar]






© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozlowska, E.; Krzyzosiak, W.J.; Koscianska, E. Regulation of Huntingtin Gene Expression by miRNA-137, -214, -148a, and Their Respective isomiRs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 16999-17016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816999
Kozlowska E, Krzyzosiak WJ, Koscianska E. Regulation of Huntingtin Gene Expression by miRNA-137, -214, -148a, and Their Respective isomiRs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(8):16999-17016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816999
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozlowska, Emilia, Wlodzimierz J. Krzyzosiak, and Edyta Koscianska. 2013. "Regulation of Huntingtin Gene Expression by miRNA-137, -214, -148a, and Their Respective isomiRs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 8: 16999-17016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816999
APA StyleKozlowska, E., Krzyzosiak, W. J., & Koscianska, E. (2013). Regulation of Huntingtin Gene Expression by miRNA-137, -214, -148a, and Their Respective isomiRs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(8), 16999-17016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816999