RETRACTED: Dinitrosopiperazine-Mediated Phosphorylated-Proteins Are Involved in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Metastasis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Non-Cytotoxic Concentrations of DNP in 6-10B NPC Cells

2.2. DNP Induces the Invasion and Motility of 6-10B Cells


2.3. Proteomic Analysis of DNP-Mediated Phosphoprotein Expression

2.4. Validation of Differential Phosphoproteins
| No. | Protein Name | Uniprot Accession | Mr | pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein | P11142 | 71,082 | 5.31 |
| 2 | Keratin,type II cytoskeletal 8 | P05787 | 53,669 | 5.57 |
| 3 | TUBB protein | P07437 | 50,097 | 4.88 |
| 4 | Vimentin | P08670 | 53,679 | 5.16 |
| 5 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein k | P61978 | 51,233 | 5.22 |
| 6 | 60 kDa Heat shock protein | P10809 | 61,191 | 5.66 |
| 7 | Keratin type II cytoskeletal 8 | P05787 | 53,669 | 5.54 |
| 8 | Laminin receptor 1 | P08865 | 32,951 | 4.88 |
| 9 | Creatine kinase B-type | P12277 | 42,911 | 5.24 |
| 10 | ATP synthase D chain mitochondrial | O75947 | 18,541 | 5.22 |
| 11 | Ezrin | P003370 | 69,282 | 5.36 |
| 12 | Keratin,type II cytoskeletal 18 | P05783 | 48,031 | 5.34 |
| 13 | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A | P15531 | 17,311 | 5.79 |
| 14 | Heat shock protein β-1 | P04792 | 22,831 | 5.87 |
| 15 | Glutathione S-transferase P1 | P09211 | 23,572 | 5.49 |
| 16 | Protein DJ-1 | Q99497 | 19,889 | 6.38 |
| 17 | 3-Hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase mitochondrial precursor (3HIDH) | P31937 | 35,711 | 8.29 |
| 18 | Stathmin | P16949 | 17,199 | 5.81 |
| 19 | Annexin A3 | P12429 | 36,524 | 5.67 |
| 20 | Basic transcription factor 3 | P20071 | 17,688 | 6.77 |
| 21 | Ribosomal protein P2 | P56671 | 11,658 | 4.32 |
| 22 | Putative NF-κB-activating protein | Q34578 | 26,097 | 8.51 |
| 23 | Microtubule-associated serine | P48618 | 98,398 | 5.67 |
| 24 | c-Myc-responsive protein | O43598 | 19,321 | 5.05 |
| 25 | Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 | P62993 | 25,209 | 5.71 |
| 26 | Proliferating cell nuclear antigen | P12004 | 29,097 | 4.61 |
2.5. DNP-Mediated Invasion and Motility Is Phospho-Ezrin Thr567 Dependent

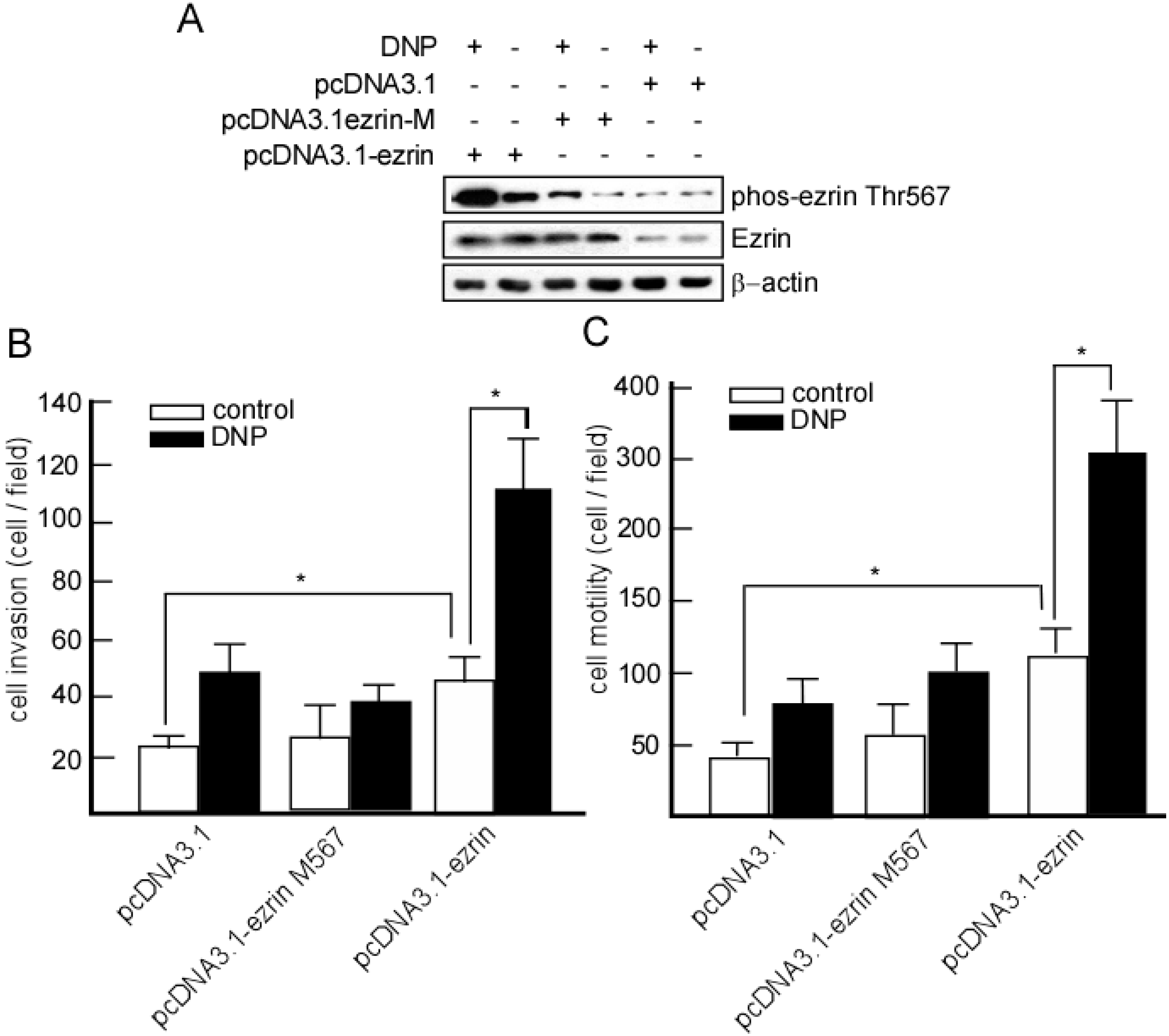
2.6. Expression of Phospho-Ezrin Thr567 in Metastatic NPC

3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. LDH Activity Assay
4.3. Cell Motility and Invasion Assay
4.4. Cell Culture and DNP Treatment
4.5. Immunoprecipitation
4.6. Proteomics Analysis
4.7. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS)
4.8. Spectrometer
4.9. Database Analysis
4.10. Western-Blotting Analysis
4.11. Construction of Expression Vectors and Gene Transfection
4.12. Immunohistochemistry
5. Conclusions
Abbreviations
| DNP | N,N'-dinitrosopiperazine |
| NPC | nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| DTT | dl-dithiothreitol |
| PMSF | phenylmethane-sulfonyl-fluoride |
| phospho | phosphorylation |
| Thr | threonine |
| Ser | Serine |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium |
| EDTA | ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| PKC | protein kinase C |
| EGFR | epithelial growth factor receptor |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| IPG | immobilized pH gradient |
| IEF | isoelectric focusing |
| PMF | peptide mass fingerprint |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| EMT | epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, I.-C.; Chen, L.-C.; Chung, A.-K.; Chao, M.; Huang, H.-Y.; Hsueh, C.; Tsang, N.-M.; Chang, K.-P.; Liang, Y.; Li, H.-P. Matrix metalloproteinase 12 is induced by heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K and promotes migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 348. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, T.W.; Tung, S.Y.; Sze, W.K.; Wong, F.C.; Yuen, K.K.; Lui, C.M.; Lo, S.H.; Ng, T.Y.; Sai-Ki, O. Treatment results of 1070 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An analysis of survival and failure patterns. Head Neck 2005, 27, 555–565. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.W.; Lin, J.C.; Ng, W.T. Current management of nasopharyngeal cancer. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 22, 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.C.; Lui, L.T.; Lynn, T.C. Nasopharyngeal cancer: Study III. A review of 1206 patients treated with combined modalities. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1985, 11, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, D.T.; Sham, J.S.; Kwong, D.L.; Wei, W.I.; Au, G.K.; Choy, D. Locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Treatment results for patients with computed tomography assessment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1998, 41, 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sarraf, M.; LeBlanc, M.; Giri, P.G.; Fu, K.K.; Cooper, J.; Vuong, T.; Forastiere, A.A.; Adams, G.; Sakr, W.A.; Schuller, D.E.; et al. Chemoradiotherapy vs. radiotherapy in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal cancer: Phase III randomized Intergroup study 0099. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, S.; Hu, X. LMP1 expression is positively associated with metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Evidence from a meta-analysis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 65, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Deng, X.; Tang, M.; Li, L.; Xiao, L.; Yang, L.; Zhong, J.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z.; Tao, Y.; et al. Tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase-1 and tyrosine sulfation of chemokine receptor 4 are induced by Epstein–Barr virus encoded latent membrane protein 1 and associated with the metastatic potential of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One 2013, 8, e56114. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.C.; Liu, H.P.; Chao, M.; Liang, Y.; Tsang, N.M.; Huang, H.Y.; Wu, C.C.; Chang, Y.S. NF-kappaB-mediated transcriptional upregulation of TNFAIP2 by the Epstein–Barr virus oncoprotein, LMP1, promotes cell motility in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3648–3659. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Deng, X.; Wu, M.; Zhang, G.; Huang, J. Down-regulation of miRNA-204 by LMP-1 enhances CDC42 activity and facilitates invasion of EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Wan, X.; Jiang, R.; Deng, L.; Gao, Y.; Tang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yan, X.; Yao, K.; et al. EBV-encoded LMP2A promotes EMT in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via MTA1 and mTOR signaling induction. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11872–11885. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Y.Y.; Hsiao, J.R.; Chang, K.C.; Chang, J.S.; Chen, C.W.; Lai, H.C.; Wu, S.Y.; Yeh, T.H.; Chang, F.H.; Lin, W.H.; et al. Epstein–Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A promotes invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through ERK/Fra-1-mediated induction of matrix metalloproteinase 9. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6656–6667. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Tian, W.D.; Xu, X.; Nie, B.; Lu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Dong, Q.; Sunwoo, J.B.; Li, G.; et al. Epstein–Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) protein induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer 2014, 120, 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, W.L.; Chung, P.J.; Tsai, M.H.; Chang, C.L.; Liang, C.L. A role for Epstein–Barr viral BALF1 in facilitating tumor formation and metastasis potential. Virus Res. 2012, 163, 617–627. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Yi, Y.H.; Chang, K.P.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, S.J.; Chen, H.C. The Epstein–Barr virus-encoded microRNA MiR-BART9 promotes tumor metastasis by targeting E-cadherin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003974. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.Q.; Duan, C.J.; Huang, D.M.; Wang, W.W.; Xie, C.L.; Meng, J.J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, H.Y.; Feng, D.Y.; Wu, S.H.; et al. HSP70 and mucin 5B: Novel protein targets of N,N'-dinitrosopiperazine-induced nasopharyngeal tumorigenesis. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 216–224. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.C.; Pan, S.C.; Yao, K.T. Chemical transformation of human embryonic nasopharyngeal epithelial cells in vitro. IARC Sci. Publ. 1991, 105, 434–438. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Zou, F.; Peng, Z.; Huang, D.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Duan, C.; Cao, Y.; Mei, W.; Tang, X.; et al. N,N'-dinitrosopiperazine-mediated ezrin protein phosphorylation via activation of Rho kinase and protein kinase C is involved in metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma 6-10B cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 36956–36967. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, N.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, Z.; Duan, C.; Tang, X.; Tan, G.; Yan, G.; Mei, W.; et al. Proteomic analysis on N,N'-dinitrosopiperazine-mediated metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma 6-10B cells. BMC Biochem. 2012, 13, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Cans, C.; Mangano, R.; Barila, D.; Neubauer, G.; Superti-Furga, G. Nuclear tyrosine phosphorylation: The beginning of a map. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Xie, Z.; Zhu, H.; Qian, J. Understanding protein phosphorylation on a systems level. Brief. Funct. Genomics 2010, 9, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, M.A.; Kutuk, O.; Basaga, H. Protein kinases as drug targets in cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2006, 6, 623–634. [Google Scholar]
- Druker, B.J.; Tamura, S.; Buchdunger, E.; Ohno, S.; Segal, G.M.; Fanning, S.; Zimmermann, J.; Lydon, N.B. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Abl positive cells. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 561–566. [Google Scholar]
- Geyer, C.E.; Forster, J.; Lindquist, D.; Chan, S.; Romieu, C.G.; Pienkowski, T.; Jagiello-Gruszfeld, A.; Crown, J.; Chan, A.; Kaufman, B.; et al. Lapatinib plus capecitabine for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, P. The role of protein phosphorylation in human health and disease. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 5001–5010. [Google Scholar]
- MATRIX SCIENCE. Available online: http://www.matrixscience.com (accessed on 20 October 1999).
- Yu, Y.; Khan, J.; Khanna, C.; Helman, L.; Meltzer, P.S.; Merlino, G. Expression profiling identifies the cytoskeletal organizer ezrin and the developmental homeoprotein Six-1 as key metastatic regulators. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 175–81. [Google Scholar]
- Ivaska, J.; Pallari, H.M.; Nevo, J.; Eriksson, J.E. Novel functions of vimentin in cell adhesion, migration, and signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar]
- Minin, A.A.; Moldaver, M.V. Intermediate vimentin filaments and their role in intracellular organelle distribution. Biochem. Biokhimiia 2008, 73, 1453–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Satelli, A.; Li, S. Vimentin in cancer and its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 3033–3046. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Tannehill-Gregg, S.H.; Nadella, M.V.; He, G.; Levine, A.; Cao, Y.; Rosol, T.J. Parathyroid hormone-related protein and ezrin are up-regulated in human lung cancer bone metastases. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2007, 24, 107–119. [Google Scholar]
- Chuan, Y.C.; Pang, S.T.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Norstedt, G.; Pousette, A.; Flores-Morales, A. Androgen induction of prostate cancer cell invasion is mediated by ezrin. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 29938–29948. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.Y.; Wu, W.Z.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhou, K.; Zha, X.L.; Liu, K.D. The membrane-cytoskeleton organizer ezrin is necessary for hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth and invasiveness. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 132, 685–697. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.Y.; Ren, C.P.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Jiang, C.J.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhao, M.; Yao, K.T. Identification of differentially expressed genes in metastatic and non-metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by suppression subtractive hybridization. Cell. Oncol. 2005, 27, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, C.; Wan, X.; Bose, S.; Cassaday, R.; Olomu, O.; Mendoza, A.; Yeung, C.; Gorlick, R.; Hewitt, S.M.; Helman, L.J. The membrane-cytoskeleton linker ezrin is necessary for osteosarcoma metastasis. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Saotome, I.; Curto, M.; McClatchey, A.I. Ezrin is essential for epithelial organization and villus morphogenesis in the developing intestine. Dev. Cell 2004, 6, 855–864. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, S.; Salazar-Fontana, L.I.; Semichon, M.; Tybulewicz, V.L.; Bismuth, G.; Trautmann, A.; Germain, R.N.; Delon, J. ERM proteins regulate cytoskeleton relaxation promoting T cell-APC conjugation. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 272–279. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Zhou, R.; Mettler, S.; Wu, T.; Abbas, A.; Delaney, J.; Forte, J.G. High turnover of ezrin T567 phosphorylation: Conformation, activity, and cellular function. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 293, C874–C884. [Google Scholar]
- Savagner, P. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) phenomenon. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, vii89–vii92. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Sun, Y.L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.S.; Zhao, X.H. Expression and phosphorylation of stathmin correlate with cell migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Pardoll, D.; Jove, R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 798–809. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Harikumar, K.B.; Gupta, S.R.; Tharakan, S.T.; Koca, C.; Dey, S.; Sung, B. Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and cancer: How intimate is the relationship? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1171, 59–76. [Google Scholar]
- Attiga, F.A.; Fernandez, P.M.; Weeraratna, A.T.; Manyak, M.J.; Patierno, S.R. Inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis inhibit human prostate tumor cell invasiveness and reduce the release of matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 4629–4637. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, G.; Luo, W.; Lu, Z.; Luo, X.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Tang, M.; Dong, Z.; Cao, Y. Epstein–Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 mediates phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of annexin A2 by activating PKC pathway. Cell. Signal. 2007, 19, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Wang, D.; Duan, C.; Huang, D.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Xie, C.; Meng, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Berberine inhibits metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma 5-8F cells by targeting Rho kinase-mediated ezrin phosphorylation at threonine 567. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27456–27466. [Google Scholar]
- Corbett, J.M.; Dunn, M.J.; Posch, A.; Gorg, A. Positional reproducibility of protein spots in two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis using immobilised pH gradient isoelectric focusing in the first dimension: An interlaboratory comparison. Electrophoresis 1994, 15, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Seow, T.K.; Ong, S.E.; Liang, R.C.; Ren, E.C.; Chan, L.; Ou, K.; Chung, M.C. Two-dimensional electrophoresis map of the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, HCC-M, and identification of the separated proteins by mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 1787–813. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, G.; Tang, X.; Huang, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, N.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, C.; Lu, J.; Yan, G.; et al. RETRACTED: Dinitrosopiperazine-Mediated Phosphorylated-Proteins Are Involved in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20054-20071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120054
Tan G, Tang X, Huang D, Li Y, Liu N, Peng Z, Zhang Z, Duan C, Lu J, Yan G, et al. RETRACTED: Dinitrosopiperazine-Mediated Phosphorylated-Proteins Are Involved in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Metastasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(11):20054-20071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120054
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Gongjun, Xiaowei Tang, Damao Huang, Yuejin Li, Na Liu, Zhengke Peng, Zhenlin Zhang, Chaojun Duan, Jinping Lu, Guangrong Yan, and et al. 2014. "RETRACTED: Dinitrosopiperazine-Mediated Phosphorylated-Proteins Are Involved in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Metastasis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 11: 20054-20071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120054
APA StyleTan, G., Tang, X., Huang, D., Li, Y., Liu, N., Peng, Z., Zhang, Z., Duan, C., Lu, J., Yan, G., & Tang, F. (2014). RETRACTED: Dinitrosopiperazine-Mediated Phosphorylated-Proteins Are Involved in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Metastasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(11), 20054-20071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120054




