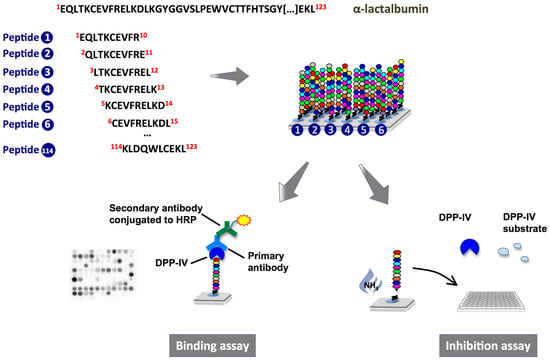
Peptide Array on Cellulose Support—A Screening Tool to Identify Peptides with Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitory Activity within the Sequence of α-Lactalbumin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Binding of Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV (DPP-IV) to Deca-Peptides on the Array


2.2. DPP-IV Inhibitory Activity of SPOT-Synthesized Deca-Peptides
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 11 | 16 | 20 | 20 | 17 | 16 | 18 | 14 | 17 | 14 | 8 |
| B | 11 | 11 | 13 | 13 | 11 | 17 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 9 |
| C | 26 | 14 | 18 | 26 | 16 | 10 | 5 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 14 |
| D | 11 | 9 | 11 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 11 | 15 | 13 | 14 | 11 |
| E | 14 | 14 | 13 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 9 | 13 | 20 | 6 | 21 |
| F | 22 | 17 | 19 | 21 | 29 | 15 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 8 | 15 |
| G | 11 | 9 | 16 | 19 | 25 | 31 | 17 | 19 | 18 | 21 | 22 |
| H | 19 | 18 | 18 | 21 | 14 | 19 | 25 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 15 |
| I | 17 | 19 | 26 | 18 | 17 | 20 | 19 | 16 | 22 | 22 | 20 |
| J | 25 | 18 | 15 | 20 | 16 | 27 | 21 | 20 | 24 | 21 | 25 |
| K | 22 | 19 | 24 | 19 | 16 | 23 | 25 | 15 | 24 | 19 | 31 |

2.3. Validation of the DPP-IV Inhibitory Activity of the Deca-Peptides

| Category a | Position | Sequence | pI | % DPP-IV Inhibition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPOT-Synthesized b | Traditionally-Synthesized c,d | ||||
| High inhibitory activity, strong binding | C1 | LPEWVCTTFH | 5.24 | 26 | 26 |
| J6 | LAHKALCSEK | 8.21 | 27 | 31 | |
| K6 | LKPTPEGDLE | 4.14 | 23 | 24 | |
| High inhibitory activity, moderate/no binding | F5 | WCKDDQNPHS | 5.21 | 29 | 51 |
| J11 | LCSEKLDQWL | 4.37 | 25 | 25 | |
| K7 | IPAVFKIDAL | 5.84 | 25 | 48 | |
| K11 | YPSKPDNPGE | 4.37 | 31 | 25 | |
| Low inhibitory activity, strong binding | A1 | EQLTKCEVFR | 6.23 | 11 | 10 |
| A8 | VFRELKDLKG | 8.58 | 14 | 3 | |
| B6 | GYGGVSLPEW | 4.00 | 17 | 8 | |
| C9 | FHTSGYDTQA | 5.08 | 12 | 2 | |
| Low inhibitory activity, moderate/no binding | C11 | TSGYDTQAIV | 3.80 | 14 | −1 |
| D4 | DTQAIVQNND | 3.56 | 14 | 2 | |
| F6 | CKDDQNPHSS | 5.21 | 15 | −3 | |
| F10 | QNPHSSNICN | 6.73 | 8 | 2 | |
2.4. Modes of Inhibition of Deca-Peptides
| Sequence | Ki (µM) a | Mode of Inhibition |
|---|---|---|
| LPEWVCTTFH | 300 ± 16 | Competitive |
| LAHKALCSEK | 217 ± 9 | Competitive |
| LKPTPEGDLE | 729 ± 128 | Mixed |
| WCKDDQNPHS | 76 ± 5 | Un-competitive |
| LCSEKLDQWL | 217 ± 15 | Mixed |
| IPAVFKIDAL | 156 ± 11 | Competitive |
| YPSKPDNPGE | 262 ± 17 | Competitive |

3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Peptide Array Synthesis
4.2.2. Probing of the Membrane-Bound Peptide Arrays
4.2.3. DPP-IV Inhibition Assay on SPOT-Synthesized Peptides
4.2.4. DPP-IV Inhibition Assay on Traditionally-Synthesized Peptides
4.2.5. Determination of the Mode of Inhibition and the Inhibition Constant (Ki)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jahan-Mihan, A.; Luhovyy, B.L.; Khoury, D.E.; Anderson, G.H. Dietary proteins as determinants of metabolic and physiologic functions of the gastrointestinal tract. Nutrients 2011, 3, 574–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Zhong, Y. Bioactive peptides. J. AOAC Int. 2008, 91, 914–931. [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen, H. Milk-derived bioactive peptides: From science to applications. J. Funct. Foods 2009, 1, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, R.; Meisel, H. Food-derived peptides with biological activity: From research to food applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregi, P. Bioactive peptides from food proteins: New opportunities and challenges. Food Sci. Tech. Bull. Funct. Foods 2008, 5, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamau, S.M.; Lu, R.-R.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.-M.; Tian, F.-W.; Shen, Y.; Gao, T. Functional significance of bioactive peptides derived from milk proteins. Food Rev. Int. 2010, 26, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziuba, M.; Dziuba, B.; Iwaniak, A. Milk proteins as precursors of bioactive peptides. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2009, 8, 71–90. [Google Scholar]
- Tulipano, G.; Sibilia, V.; Caroli, A.M.; Cocchi, D. Whey proteins as sources of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (dipeptidyl peptidase-4) inhibitors. Peptides 2011, 32, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, M.; Ohshida, Y.; Mogami, O. Novel dipeptidyl peptidase-4–inhibiting peptide derived from β-lactoglobulin. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 117, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uenishi, H.; Kabuki, T.; Seto, Y.; Serizawa, A.; Nakajima, H. Isolation and identification of casein-derived dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP-4)-inhibitory peptide LPQNIPPL from gouda-type cheese and its effect on plasma glucose in rats. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 22, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory and antioxidative properties of milk protein-derived peptides and hydrolysates. Peptides 2013, 39, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, I.M.E.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Evaluation of the potential of dietary proteins as precursors of dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-IV inhibitors by an in silico approach. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 403–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, I.M.E.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activity of dairy protein hydrolysates. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 25, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, I.M.E.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-IV and α-glucosidase activities by pepsin-treated whey proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7500–7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, I.M.E.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Isolation and characterization of peptides with dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activity from pepsin-treated bovine whey proteins. Peptides 2014, 54, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.E.; Brubaker, P. Glucagon-like peptide 1 secretion by the L-cell. The view from within. Diabetes 2006, 55, S70–S77. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, L.K.; Prins, J.B. Update on incretin hormones. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1243, E55–E77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, C.F. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A comparative review. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udenigwe, C.C. Bioinformatics approaches, prospects and challenges of food bioactive peptide research. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 36, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaldi, N. Bioinformatics approaches for identifying new therapeutic bioactive peptides in food. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2012, 2, 325–338. [Google Scholar]
- Li-Chan, E.C.Y.; Hunag, S.-L.; Jao, C.-L.; Ho, K.-P.; Hsu, K.-C. Peptides derived from Atlantic salmon skin gelatin as dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-L.; Joa, C.-L.; Ho, K.-P.; Hsu, K.-C. Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitory activity of peptides derived from tuna cooking juice hydrolysates. Peptides 2012, 35, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatanaka, T.; Inoue, Y.; Arima, J.; Kumagai, Y.; Usuki, H.; Kawakami, K.; Kimura, M.; Mukaihara, T. Production of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides from defatted rice bran. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilpert, K.; Winkler, D.F.H.; Hancock, R.E.W. Peptide arrays on cellulose support: SPOT synthesis, a time and cost effective method for synthesis of large numbers of peptides in a parallel and addressable fashion. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1333–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmer, R.; Tapia, V.; Landgraf, C. Synthetic peptide arrays for investigating protein interaction domains. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2780–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.-H.; Mrksich, M. Peptide arrays: Towards routine implementation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2004, 8, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn-Wache, K.; Bär, J.; Hoffmann, T.; Wolf, R.; Rahfeld, J.-U.; Demuth, H.-U. Selective inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 by targeting a substrate-specific secondary binding site. Biol. Chem. 2011, 392, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, V.T.T.; Ito, K.; Ito, S.; Kawarasaki, Y. Trp-Arg-Xaa tripeptides act as uncompetitive-type inhibitors of human dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Peptides 2014, 54, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, C.; Levy-Beladev, L.; Rotem-Bamberger, S.; Rito, T.; Rüdiger, S.G.D.; Friedler, A. Studying protein–protein interactions using peptide arrays. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2131–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Rao, X.; Rajagopalan, S. An emerging role of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) beyond glucose control: Potential implications in cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2013, 226, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lacroix, I.M.E.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Peptide Array on Cellulose Support—A Screening Tool to Identify Peptides with Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitory Activity within the Sequence of α-Lactalbumin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20846-20858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120846
Lacroix IME, Li-Chan ECY. Peptide Array on Cellulose Support—A Screening Tool to Identify Peptides with Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitory Activity within the Sequence of α-Lactalbumin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(11):20846-20858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120846
Chicago/Turabian StyleLacroix, Isabelle M. E., and Eunice C. Y. Li-Chan. 2014. "Peptide Array on Cellulose Support—A Screening Tool to Identify Peptides with Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitory Activity within the Sequence of α-Lactalbumin" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 11: 20846-20858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120846
APA StyleLacroix, I. M. E., & Li-Chan, E. C. Y. (2014). Peptide Array on Cellulose Support—A Screening Tool to Identify Peptides with Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitory Activity within the Sequence of α-Lactalbumin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(11), 20846-20858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120846