Phosphosite Mapping of HIP-55 Protein in Mammalian Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
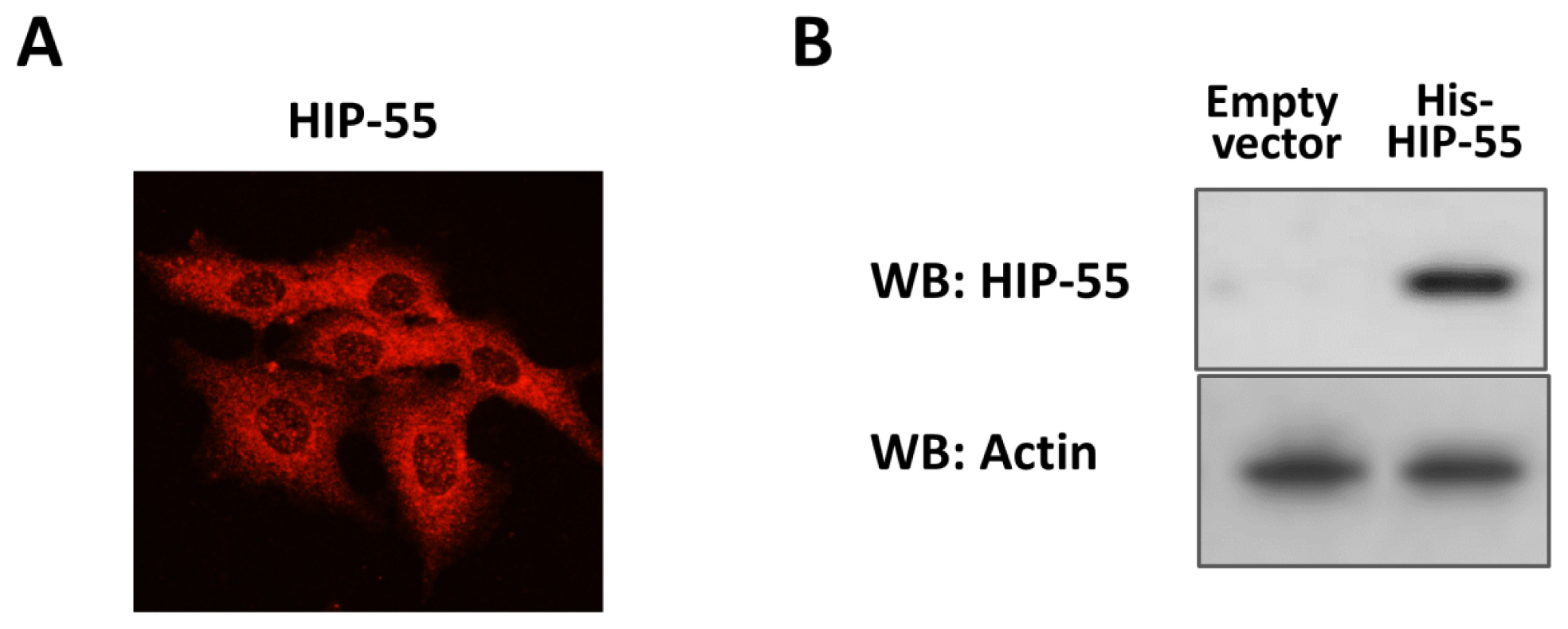
2.1. Expression and Purification of His-Tagged HIP-55 Protein
2.2. Identification of HIP-55 Protein by MS
2.3. MS Analysis of Phosphorylation Sites of HIP-55 Protein
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Expression and Purification of HIP-55 Protein
3.3. Tryptic Digestion
3.4. Mass Spectrometry
3.5. Peptide and Protein Identification
3.6. Motif Analysis of Phosphosites
3.7. SDS-PAGE and Immunoblotting
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fischer, E.H. Cellular regulation by protein phosphorylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2013, 430, 865–867. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, P. The regulation of protein function by multisite phosphorylation—A 25 year update. Trends Biochem. Sci 2000, 25, 596–601. [Google Scholar]
- Via, A.; Diella, F.; Gibson, T.J.; Helmer-Citterich, M. From sequence to structural analysis in protein phosphorylation motifs. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2011, 16, 1261–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Ensenat, D.; Yao, Z.; Wang, X.S.; Kori, R.; Zhou, G.; Lee, S.C.; Tan, T.H. A novel src homology 3 domain-containing adaptor protein HIP-55 that interacts with hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1. J. Biol. Chem 1999, 274, 33945–33950. [Google Scholar]
- Kessels, M.M.; Engqvist-Goldstein, A.E.; Drubin, D.G.; Qualmann, B. Mammalian Abp1 a signal-responsive F-actin-binding protein links the actin cytoskeleton to endocytosis via the GTPase dynamin. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 351–366. [Google Scholar]
- Fenster, S.D.; Kessels, M.M.; Qualmann, B.; Chung, W.J.; Nash, J.; Gundelfinger, E.D.; Garner, C.C. Interactions between Piccolo and the actin/dynamin-binding protein Abp1 link vesicle endocytosis to presynaptic active zones. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 20268–20277. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Kori, R.; Shui, J.W.; Chen, U.R.; Yao, Z.; Tan, T.H. The SH3 domain-containing adaptor HIP-55 mediates c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation in T cell receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 52195–52202. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Shui, J.W.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, B.; Han, S.; Tan, T.H. HIP-55 is important for T-cell proliferation cytokine production and immune responses. Mol. Cell. Biol 2005, 25, 6869–6878. [Google Scholar]
- Onabajo, O.O.; Seeley, M.K.; Kale, A.; Qualmann, B.; Kessels, M.; Han, J.; Tan, T.H.; Song, W. Actin-binding protein 1 regulates B cell receptor-mediated antigen processing and presentation in response to B cell receptor activation. J. Immunol 2008, 180, 6685–6695. [Google Scholar]
- Haag, N.; Schwintzer, L.; Ahuja, R.; Koch, N.; Grimm, J.; Heuer, H.; Qualmann, B.; Kessels, M.M. The actin nucleator Cobl is crucial for Purkinje cell development and works in close conjunction with the F-actin binding protein Abp1. J. Neurosci 2012, 32, 17842–17856. [Google Scholar]
- Lock, P.; Abram, C.L.; Gibson, T.; Courtneidge, S.A. A new method for isolating tyrosine kinase substrates used to identify fish an SH3 and PX domain-containing protein and Src substrate. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 4346–4357. [Google Scholar]
- Larbolette, O.; Wollscheid, B.; Schweikert, J.; Nielsen, P.J.; Wienands, J. SH3P7 is a cytoskeleton adapter protein and is coupled to signal transduction from lymphocyte antigen receptors. Mol. Cell. Biol 1999, 19, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.; Suzuki, H.; Miyamoto, T.; Takamatsu, N.; Tatsuguchi, A.; Ueda, K.; Kijima, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Matsuo, Y. Development of an orally-administrative MELK-targeting inhibitor that suppresses the growth of various types of human cancer. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Boateng, L.R.; Cortesio, C.L.; Huttenlocher, A. Src-mediated phosphorylation of mammalian Abp1 (DBNL) regulates podosome rosette formation in transformed fibroblasts. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar]
- St-Denis, N.; Gingras, A.C. Mass spectrometric tools for systematic analysis of protein phosphorylation. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2012, 106, 3–32. [Google Scholar]
- Dephoure, N.; Gould, K.L.; Gygi, S.P.; Kellogg, D.R. Mapping and analysis of phosphorylation sites: A quick guide for cell biologists. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, M.; Ong, S.E.; Grønborg, M.; Steen, H.; Jensen, O.N.; Pandey, A. Analysis of protein phosphorylation using mass spectrometry: deciphering the phosphoproteome. Trends Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Matthias, M.; Ole, N.J. Proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Maaty, W.S.; Lord, C.I.; Gripentrog, J.M.; Riesselman, M.; Keren-Aviram, G.; Liu, T.; Dratz, E.A.; Bothner, B.; Jesaitis, A.J. Identification of C-terminal phosphorylation sites of N-formyl peptide receptor-1 (FPR1) in human blood neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 27042–27058. [Google Scholar]
- Rudashevskaya, E.L.; Ye, J.; Jensen, O.N.; Fuglsang, A.T.; Palmgren, M.G. Phosphosite mapping of P-type plasma membrane H+-ATPase in homologous and heterologous environments. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4904–4913. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, J.H.; Cerda, O.; Trimmer, J.S. Mass spectrometry-based phosphoproteomics reveals multisite phosphorylation on mammalian brain voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, J.A.; Bottrill, A.R.; Mistry, S.; Evans, R.J. Mass spectrometry analysis of human P2X1 receptors; insight into phosphorylation modelling and conformational changes. J. Neurochem. 2012, 123, 725–735. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, D.C. Adaptor proteins. Oncogene 2001, 20, 6270–6272. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.; Tinti, M.; Wood, N.T.; Campbell, D.G.; Toth, R.; Dubois, F.; Geraghty, K.M.; Wong, B.H.; Brown, L.J.; Tyler, J.; et al. Visualization and biochemical analyses of the emerging mammalian 14-3-3-phosphoproteome. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2011, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Phosphopeptides | Experimental m/z (mono) | Theoretical m/z (mono) | Charge | XCorr | Position in protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GACAS *HVSTMASFLK | 795.353 | 795.346 | 2 | 1.98 | 95–109 |
| GACAS *HVSTM *ASFLK | 803.351 | 803.344 | 2 | 1.94 | 95–109 |
| GAHVT *INAR | 509.744 | 509.745 | 2 | 2.37 | 110–118 |
| ASGANY *SFHKES *GR | 835.828 | 835.822 | 2 | 2.21 | 135–148 |
| TNAVS *EIK | 471.224 | 471.221 | 2 | 3.06 | 165–172 |
| VGKDS *FWAK | 559.253 | 559.258 | 2 | 2.57 | 174–182 |
| REQRY *QEQGGEAS *PQR | 1039.924 | 1039.926 | 2 | 1.94 | 220–235 |
| AMS *TTSISSPQPGK | 736.333 | 736.329 | 2 | 3.63 | 267–280 |
| AMS *TT *SISSPQPGK | 776.318 | 776.312 | 2 | 2.56 | 267–280 |
| AM *S *TTSISSPQPGK | 744.324 | 744.326 | 2 | 3.23 | 267–280 |
| LRS *PFLQK | 534.785 | 534.784 | 2 | 2.41 | 281–288 |
| QLT *QPETHFGR | 697.321 | 697.317 | 2 | 2.01 | 289–299 |
| QLT *QPET *HFGR | 737.304 | 737.300 | 2 | 1.98 | 289–299 |
| EPAAAIS *RPR | 574.289 | 574.285 | 2 | 2.49 | 300–309 |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, N.; Sun, N.; Gao, X.; Li, Z. Phosphosite Mapping of HIP-55 Protein in Mammalian Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 4903-4914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15034903
Liu N, Sun N, Gao X, Li Z. Phosphosite Mapping of HIP-55 Protein in Mammalian Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(3):4903-4914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15034903
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ning, Ningning Sun, Xiang Gao, and Zijian Li. 2014. "Phosphosite Mapping of HIP-55 Protein in Mammalian Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 3: 4903-4914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15034903
APA StyleLiu, N., Sun, N., Gao, X., & Li, Z. (2014). Phosphosite Mapping of HIP-55 Protein in Mammalian Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(3), 4903-4914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15034903




