Improved Fibroblast Functionalities by Microporous Pattern Fabricated by Microelectromechanical Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Surface Characterization

2.2. Fibroblast Adhesion

2.3. Fibroblast Proliferation

2.4. Fibroblast Morphology and Cytoskeletal Actin Organization

2.5. Fibronectin Secretion

3. Discussion
4. Experimental
4.1. Precisely Designed Microporous Structure Manufactured by MEMS
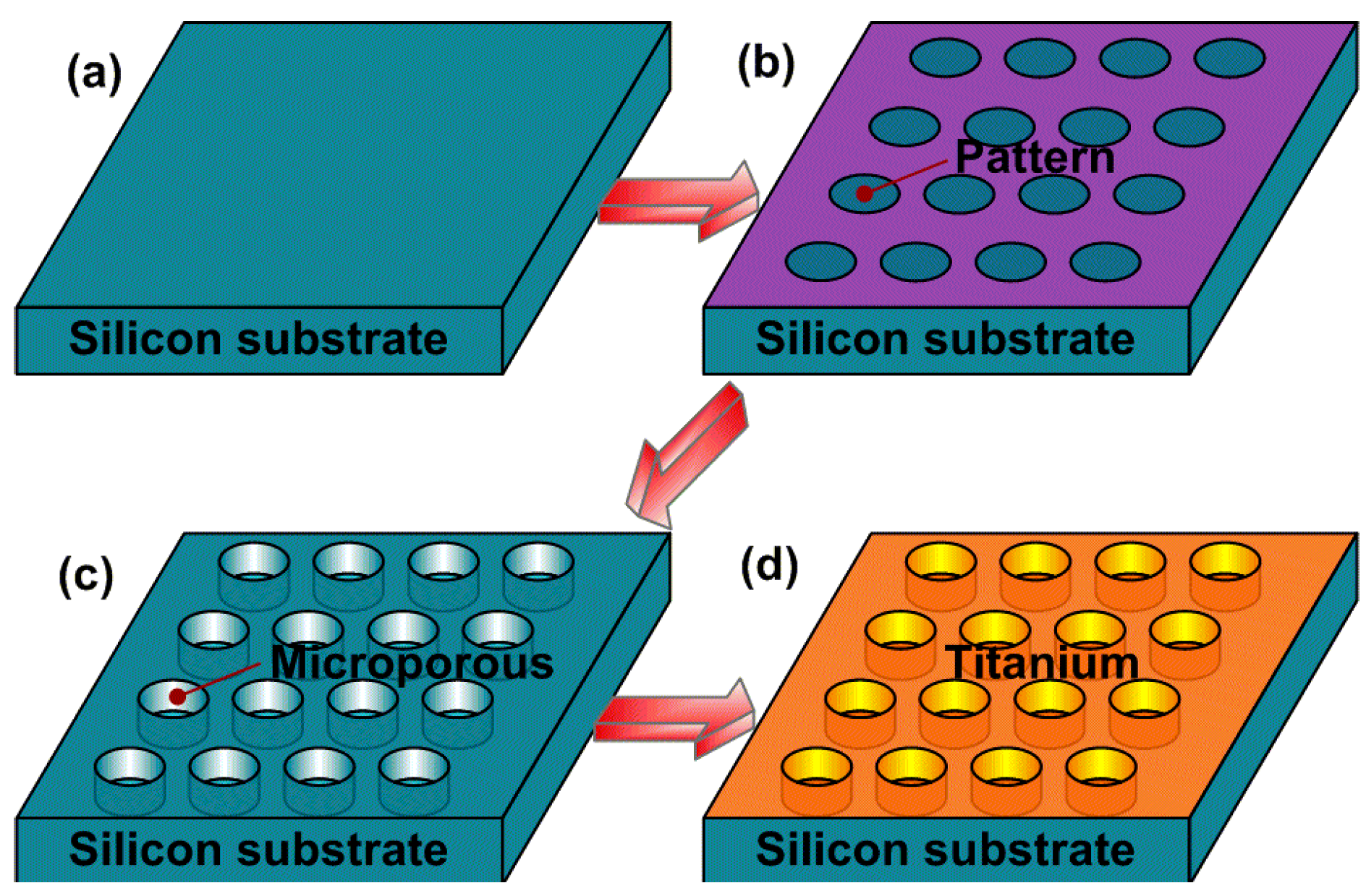
4.2. Fibroblast Culture
4.3. Cell Adhesion Assay
4.4. Fibroblast Proliferation Assay
4.5. Fluorescent Staining of Cytoskeletal Actin
4.6. Fibronectin Secretion Assay
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Von Recum, A.F. Applications and failure modes of percutaneous devices: A review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1984, 18, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitto, C.A.; Plata, W.G.; Schaaf, N.G. Evaluation of the peri-implant epithelial tissue of percutaneous implant abutments supporting maxillofacial prostheses. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1994, 9, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, J.A.; Paquay, Y.G.; van der Waerden, J.P. Tissue reaction to soft-tissue anchored percutaneous implants in rabbits. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1994, 28, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, M.; Blanco, L.; Khraisat, A.; Tresguerres, I.F. Influence of titanium surface charge on fibroblast adhesion. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2006, 8, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinari, M.; Matsuzaka, K.; Inoue, T.; Oda, Y.; Shimono, M. Effects of multigrooved surfaces on fibroblast behavior. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2003, 65, 359–368. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.W.; Kikkawa, D.O.; Aboy, A.; Glasgow, B.J. Chronic exposure of hydroxyapatite orbital implants: Cilia implantation and epithelial downgrowth. Ophthal. Plast. Recons. 2000, 16, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knabe, C.; Grosse-Siestrup, C.; Gross, U. Histologic evaluation of a natural permanent percutaneous structure and clinical percutaneous devices. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasse, K.A. Infection of percutaneous devices: prevention, monitoring, and treatment. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1984, 18, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, V.; Schwartz, S.A.; Roth, A.M.; Gorniowsky, M.J. Percutaneous implant devices. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1977, 5, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangjee, T.; Colaizzo, R.; von Recum, A.F. Species-related differences in percutaneous wound healing. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1985, 13, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehroudi, B.; Brunette, D.M. Subcutaneous microfabricated surfaces inhibit epithelial recession and promote long-term survival of percutaneous implants. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Abraham, D.J.; Shi-Wen, X.; Pearson, J.D.; Black, C.M.; Lyons, K.M.; Leask, A. CCN2 (connective tissue growth factor) promotes fibroblast adhesion to fibronectin. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 5635–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielty, C.M.; Shuttleworth, C.A. Microfibrillar elements of the dermal matrix. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1997, 38, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könönen, M.; Hormia, M.; Kivilahti, J.; Hautaniemi, J.; Thesleff, I. Effect of surface processing on the attachment, orientation, and proliferation of human gingival fibroblasts on titanium. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Murakami, H.; Chehroudi, B.; Textor, M.; Brunette, D.M. Effects of surface topography on the connective tissue attachment to subcutaneous implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2006, 21, 354–365. [Google Scholar]
- Demetrescu, I.; Pirvu, C.; Mitran, V. Effect of nano-topographical features of Ti/TiO(2) electrode surface on cell response and electrochemical stability in artificial saliva. Bioelectrochemistry. 2010, 79, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauser, R.; Schüpbach, P.; Gottlow, J.; Hämmerle, C.H. Periimplant soft tissue barrier at experimental one-piece mini-implants with different surface topography in humans: A light-microscopic overview and histometric analysis. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2005, 7, s44–s51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unadkat, H.V.; Hulsman, M.; Cornelissen, K.; Papenburg, B.J.; Truckenmüller, R.K.; Carpenter, A.E.; Wessling, M.; Post, G.F.; Uetz, M.; Reinders, M.J. An algorithm-based topographical biomaterials library to instruct cell fate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.USA 2011, 108, 16565–16570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeForest, C.A.; Anseth, K.S. Advances in bioactive hydrogels to probe and direct cell fate. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2012, 3, 421–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, T.; Mannoor, M.S.; Ivanov, D.V. BioMEMS—Advancing the frontiers of Medicine. Sensors 2008, 8, 6077–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawgo, R.S.; Richards Grayson, A.C.; Li, Y.; Cima, M.J. BioMEMS for drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2002, 6, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, A.C.R.; Shawgo, R.S.; Johnson, A.M.; Flynn, N.T.; Li, Y.; Cima, M.J.; Langer, R. A BioMEMS review: MEMS technology for physiologically integrated devices. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, R. BioMEMS: State-of-the-art in detection, opportunities and prospects. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1565–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puckett, S.D.; Lee, P.P.; Ciombor, D.M.; Aaron, R.K.; Webster, T.J. Nanotextured titanium surfaces for enhancing skin growth on transcutaneous osseointegrated devices. Acta. Biomater. 2010, 6, 2352–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Huo, K.; Cui, L.; Zhang, W.; Ni, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chu, P.K. Antibacterial nano-structured titania coating incorporated with silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5706–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, K.C.; Eltgroth, M.; Latempa, T.J.; Grimes, C.A.; Desai, T.A. Decreased Staphylococcus epidermis adhesion and increased osteoblast functionality on antibiotic-loaded titania nanotubes. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4880–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linask, K.K.; Lash, J.W. A role for fibronectin in the migration of avian precardiac cells: I. dose-dependent effects of fibronectin antibody. Dev. Biol. 1988, 129, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.; Bassik, N.; Cho, J.; Randall, C.L.; Gracias, D.H. Directed growth of fibroblasts into three dimensional micropatterned geometries via self-assembling scaffolds. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, S.; Agrawal, Y.K. Advances in microfluidics: Lab-on-a-chip to point of care diagnostic devices. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2013, 5, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolewe, M.E.; Park, H.; Gray, C.; Ye, X.; Langer, R.; Freed, L.E. 3D structural patterns in scalable, elastomeric scaffolds guide engineered tissue architecture. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4459–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Ylinen, S.; Kainlauri, M.; Kapulainen, M. Smooth silicon sidewall etching for waveguide structures using a modified Bosch process. J. Micro. Nanolithogr. MEMS MOEMS 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghalbzouri, A.; van den Bogaerdt, A.J.; Kempenaar, J.; Ponec, M. Human adipose tissue-derived cells delay re-epithelialization in comparison with skin fibroblasts in organotypic skin culture. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 150, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, H.; Zhao, L.; Chen, B.; Bai, S.; Zhao, Y. Improved Fibroblast Functionalities by Microporous Pattern Fabricated by Microelectromechanical Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12998-13009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150712998
Wei H, Zhao L, Chen B, Bai S, Zhao Y. Improved Fibroblast Functionalities by Microporous Pattern Fabricated by Microelectromechanical Systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(7):12998-13009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150712998
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Hongbo, Lingzhou Zhao, Bangdao Chen, Shizhu Bai, and Yimin Zhao. 2014. "Improved Fibroblast Functionalities by Microporous Pattern Fabricated by Microelectromechanical Systems" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 7: 12998-13009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150712998
APA StyleWei, H., Zhao, L., Chen, B., Bai, S., & Zhao, Y. (2014). Improved Fibroblast Functionalities by Microporous Pattern Fabricated by Microelectromechanical Systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(7), 12998-13009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150712998



