Polyester-Based (Bio)degradable Polymers as Environmentally Friendly Materials for Sustainable Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Main Routes of Polyesters Degradation
2.1. Alkali-Catalysed Polyester Hydrolysis

2.2. Acid-Catalysed Polyester Hydrolysis

2.3. Enzymatic Degradation of Polyesters

3. Polyhydroxyalkanoates—Polyesters of Microbiological Origin and Their Synthetic Analogues
3.1. Poly(3-hydroxyalkanoate)s from Renewable Resources—Synthesis and Properties

3.2. Synthetic Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)s—Polymers from Fossil Resources
3.3. Copolymers, Blends and Composites Based on Microbial and/or Synthetic Poly(3-hydroxyalkanoate)s
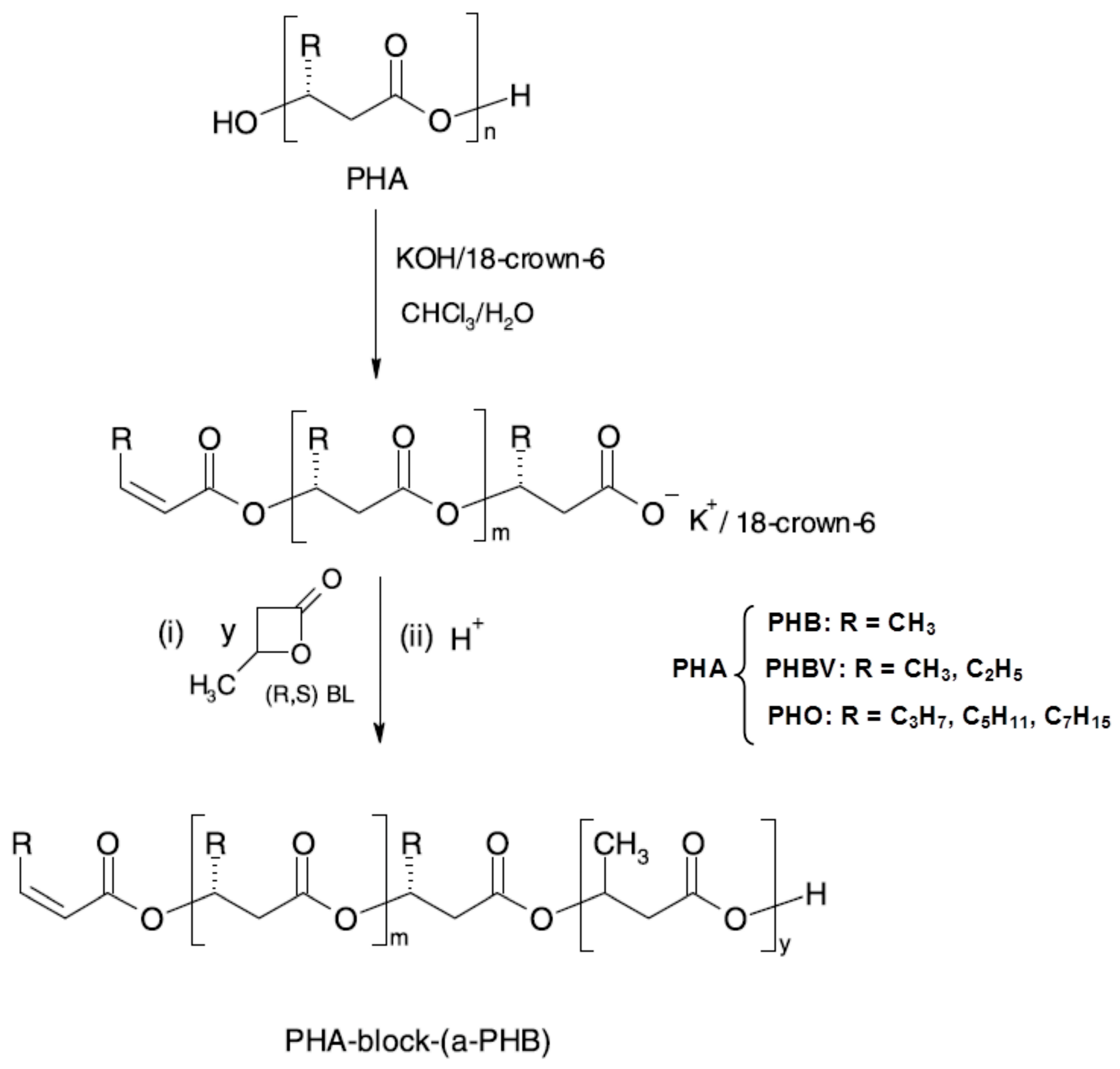
3.4. Utility and (Bio)degradation of Poly(3-hydroxyalkanoate)s

4. Polylactide—Synthetic Polymer from Renewable and Synthetic Monomers
4.1. Synthesis of Polylactide and Polylactide-Based Copolymers, Blends and Composites
| Polylactide * | Catalyst | Solvent | Molar Mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| PDLLA/PLLA | Aluminium isopropoxide | Toluene | Mn = 90,000 |
| PDLLA | Stannous octoate | Alcohols | MW < 350,000 |
| PLLA | Stannous octoate | Alcohols, carboxylic acids | Mn = 250,000 |
| PLLA | Stannous octoate, titanium or zirconium compounds | Toluene | Mn = 40,000–100,000 |
| PDLA/PLLA/PDLLA | Stannous trifluoromethane sulfonate, scandium(III) trifluoromethane sulfonate | Ethanol | – |
| PLLA | alkoxides of Mg, Al, Zn, Ti | Methylene chloride | – |
| PLLA | Yttrium tris(2,6-di-tert butyl phenolate) in toluene | 2-Propanol, butanol, ethanol | Mn < 25,000 |
| PDLLA | Zn lactate | Bulk | Mn = 212,000 |
| PDLLA/PLLA | Butylmagnesium halides (Grignard reagents) | Ethers | Mn < 300,000 |
| PLLA | Potassium naphthalenide | THF, toluene | Mn < 16,000 |
| PLLA | Complexes of iron with acetic, butyric, isobutyric or dichloroacetic acid | Bulk | MW = 150,000 |
4.2. Properties, Utility and (Bio)degradation of Polylactide

5. Aliphatic Polyamides
5.1. Synthetic Pathways and General Properties of Aliphatic Polyamides
| Name and Chemical Structure | Melting Point (°C) | Typical Application | Producer (Trade Name) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon-6 (PA 6) –[NH(CH2)5CO]n– | 219–220 | High-temperature applications; automotive industry; electrical and electronic industry (housings, plug and socket connectors, printed circuit boards); sports equipment. | BASF AG (Ultramid ® B); DSM (Akulon® and Novamid®); Honeywell Resins and Chemicals L.L.C. (Capron®); DuPont (Zytel®); Rhodia (Technyl®). |
| Nylon-66 (PA 66) –[NH(CH2)-NHCO-(CH2)4CO]n– | 260–300 | Industrial yarns and textile; automotive industry (radial tires; intake manifolds, engine covers, gears). | DuPont (Zytel®); BASF AG (Ultramid® A); DSM (Akulon® S); Rhodia (Technyl®); Ascent Performance Materials (Vydyne®). |
| Nylon-610 (PA 610) –[NH(CH2)6-NHCO-(CH2)8CO]n– | 211–236 | Engineering and construction materials; industrial parts, tubings, rods and profiles; sheet applications. | BASF AG (Ultramid ® S); Rhodia (Special Technyl® grades); Toray Resin Company (Amilan®). |
| Nylon-612 (PA 612) –[NH(CH3)6-NHCO-(CH2)10CO]n– | 206–246 | Pipes, bushings, electrical connectors, industrial parts, bristles, tubings, rods. | DuPont (Zytel® 150 series); Evonik (Vestamid® D series). |
5.2. Utility and Biodegradation of Aliphatic Polyamides

6. Conclusions
| Polymer | The Impact on Sustainable Environment | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | Limitations | |
| PHA | Polymer from renewable natural resources; produced by bacteria as storage material; commercial production by living organisms using biochemical processes; biodegradable polymers with lack of toxicity, converted to the same metabolites as in living organisms: water and carbon dioxide; reduction of fossil energy (“old carbon”) usage. | Availability of waste collection systems and recycling methods; compostable plastic waste deposited on a landfill has a negative social environmental impact; approval of new bioplastics by society requires high level of customers’ awareness which depends on capital and education expenditure; too energy-intensive extraction stage. |
| aPHB | Synthetic polymer biodegrade under appropriate conditions (in the presence of PhaZ7 depolymerase from Paucimonas lemoignei) to form of monomer, dimer and trimer. | End-of-life treatment problems; post-synthetic residues (e.g., organic solvents). |
| PLA | Synthesis from renewable monomer; easily hydrolytically degradable polymer; less greenhouse gases emission and less consumption of non-renewable energy than traditional polymers. | Availability of waste collection systems and recycling methods; compostable plastic waste deposited on a landfill has a negative social environmental impact; approval of new bio-based plastics by society requires high level of customers’ awareness which depends on capital and education expenditure. |
| Polyamides | Possible synthesis from renewable monomers. Bio-based polyamide and poly(ester-amide)s thermoplastics of valuable properties. | Biodegradation possible only for polyamides of low molar mass; environmental impact still under evaluation. |
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kowalczuk, M. New Generation of the Polymeric Packaging Materials Susceptible to Organic Recycling. Europe for Sustainable Plastics; eBrochure of Launch conference PLASTiCE: Bologna, Italy, 2011; pp. 29–31. Available online: http://www.plastice.org/pl/publications (accessed on 25 September 2014).
- Sikorska, W.; Dacko, P.; Sobota, M.; Rydz, J.; Musioł, M.; Kowalczuk, M. Degradation study of polymers from renewable resources and their compositions in industrial composting pile. Macromol. Symp. 2008, 272, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musioł, M.T.; Rydz, J.; Sikorska, W.J.; Rychter, P.R.; Kowalczuk, M.M. A preliminary study of the degradation of selected commercial packaging materials in compost and aqueous environments. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2011, 13, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avérous, L. Polylactic acid: Synthesis, properties and applications. In Monomers, Polymers and Composites from Renewable Resources; Belgacem, M.N., Gandini, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 433–450. [Google Scholar]
- Vert, M. Aliphatic polyesters: Great degradable polymers that cannot do everything. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydz, J.; Zawidlak-Węgrzyńska, B.; Christova, D. Degradable polymers. In Encyclopedia of Biomedical Polymers and Polymeric Biomaterials; Mishra, M.K., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ikada, Y.; Tsuji, H. Biodegradable polyesters for medical and ecological applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2000, 21, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, H.S.; Reis, R.L. Understanding the enzymatic degradation of biodegradable polymers and strategies to control their degradation rate. In Biodegradable Systems in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine; Reis, R.L., Roman, J.S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 177–201. [Google Scholar]
- Murthy, N.; Wilson, S.; Sy, J.C. Biodegradation of polymers. In Polymer Science: A Comprehensive Reference; Matyjaszewski, K., Möller, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 547–560. [Google Scholar]
- McIntire, J.E. Polyester fibers. In Handbook of Fiber Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Lewin, M., Pearce, E.M., Eds.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, S.R.; Hakkarainen, M.; Inkinen, S.; Södergård, A.; Albertsson, A.-C. Leads to higher hydrolytic stability but more acidic hydrolysis product pattern. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cam, D.; Suong-Hyu, H.; Ikada, Y. Degradation of high molecular weight poly(l-lactide) in alkaline medium. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, G. Requirements for biodegradable water-soluble polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stable 1998, 59, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, R.-J. Biological degradation of synthetic polyesters—Enzymes as potential catalysts for polyester recycling. Process. Biochem. 2006, 41, 2124–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, T.; Augusta, J.; Muller, R.-J.; Widdecke, H.; Klein, J. Enzymatic degradation of a model polyester by lipase from Rhizopus. delemar. Enzym. Microb. Tecnhnol. 1995, 17, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemani, K.; Scholz, C. Introduction and overview of degradable and renewable polymers and materials. In Degradable Polymers and Materials: Principles and Practice, 2nd ed.; Khemani, K., Scholz, C., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. xi. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, S.; Keshavarz, T.; Roy, I. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Biodegradable polymers with a range of applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2007, 82, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 762–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, J.C.; Tipton, A.J. Synthetic biodegradable polymers as orthopedic devices. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2335–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, A.J.; Dawes, E.A. Occurrence, metabolism, metabolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiol. Rev. 1990, 54, 50–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, J.G.C.; Méndez, B.S.; Nikel, P.I.; Pettinari, M.J.; Prieto, M.A.; Silva, L.F. Making green polymers even greener: Towards sustainable production of polyhydroxyalkanoates from agroindustrial by-products. Advances in Applied Biotechnology; Petre, M., Ed.; InTech Open Access Publisher, 2012. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/31847 (accessed on 16 September 2014).
- Steinbüchel, A.; Valentin, H.E.; Schonebaum, A.J. Application of recombinant gene technology for production of polyhydroxyalkanoic acids: Biosynthesis of poly(4-hydroxybutyric acid) homopolyester. J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 1994, 2, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, Y.; Somerville, C.; Schechtman, L.A.; Satkowski, M.M.; Noda, I. Synthesis of high-molecular-weight poly([R]-3-hydroxybutyrate) in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plant cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1995, 17, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verlinden, R.A.J.; Hill, D.J.; Kenward, M.A.; Williams, C.D.; Radecka, I. Bacterial synthesis of biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, Y. Microbial Polyesters; VCH Publishers: Weinheim, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Lenz, R.W.; Marchessault, R.H. Bacterial polyesters: Biosynthesis, biodegradable plastics and biotechnology. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reusch, R.N.; Bryant, M.E.; Henry, D.N. Increased poly-(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate concentrations in streptozotocin (STZ) diabetic rats. Acta Diabetol. 2003, 40, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedkova, E.N.; Blatter, L.A. Role of β-hydroxybutyrate, its polymer poly-β-hydroxybutyrate and inorganic polyphosphate in mammalian health and disease. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Chen, J.-C.; Wu, Q.; Chen, G.-Q. Polyhydroxyalkanoates as a source of chemicals, polymers, and biofuels. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunasundari, B.; Sudesh, K. Isolation and recovery of microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Express Polym. Lett. 2011, 5, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; Koelling, K.; Vodovotz, Y. Assessment of PHB with varying hydroxyvalerate content for potential packaging applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.Y.; Gross, R.A.; Rutherford, D.R. Microbial Polyester Synthesis: Effects of poly(ethylene glycol) on product composition, repeat unit sequence, and end group structure. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.Y.; Ashby, R.; Gross, R.A. Use of poly(ethylene glycol)s to regulate poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) molecular weight during Alcaligenes. eutrophus cultivations. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 7753–7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedliński, Z.; Kowalczuk, M.; Kurcok, P.; Adamus, G.; Matuszowicz, A.; Sikorska, W.; Gross, R.A.; Xu, J.; Lenz, R.W. Stereochemical control in the anionic-polymerization of beta-butyrolactone initiated with alkali-metal alkoxides. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 3773–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedliński, Z.; Kurcok, P.; Lenz, R.W. First facile synthesis of biomimetic poly-(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate via regioselective anionic polymerization of (S)-β-butyrolactone. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 6718–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydz, J.; Wolna-Stypka, K.; Adamus, G.; Janeczek, H.; Musioł, M.; Sobota, M.; Marcinkowski, A.; Krzan, A.; Kowalczuk, M. Forensic engineering of advanced polymeric materials. Part 1—Degradation studies of polylactide blends with atactic poly[(R,S)-3-hydroxybutyrate] in paraffin. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2015. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Jedliński, Z.; Kowalczuk, M.; Głowkowski, W.; Grobelny, J.; Szwarc, M. Novel polymerization of β-butyrolactone initiated by potassium naphthalenide in the presence of a crown ether or a cryptand. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurcok, P.; Kowalczuk, M.; Hennek, K.; Jedliński, Z. Anionic polymerization of beta-lactones initiated with alkali-metal alkoxides: Reinvestigation of the polymerization mechanism. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 2017–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurcok, P.; Śmiga, M.; Jedliński, Z. β-Butyrolactone polymerization initiated with tetrabutylammonium carboxylates: A novel approach to biomimetic polyester synthesis. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2002, 40, 2184–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juzwa, M.; Jedliński, Z. Novel synthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). Macromolecules 2006, 39, 4627–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalec, M.; Sobota, M.; Scandola, M.; Kowalczuk, M.; Kurcok, P. A convenient route to PHB macromonomers via anionically controlled moderate-temperature degradation of PHB. J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2010, 48, 5490–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassie, N.; Murray, E.J.; Holmes, P.A. The thermal degradation of poly(-(D)-β-hydroxybutyric acid): Part 1-Identification and quantitative analysis of products. Polym. Degrad. Stable 1984, 6, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopinke, F.D.; Remmler, M.; Mackenzie, K. Thermal decomposition of biodegradable polyesters I: Poly(β-hydroxybutyric acid). Polym. Degrad. Stable 1996, 52, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.; Yu, G.; Marchessault, R.H. Thermal degradation of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates): Preparation of well-defined oligomers. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Doi, Y.; Abe, H. Effects of residual metal compounds and chain-end structure on thermal degradation of poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid). Polym. Degrad. Stable 2006, 91, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedliński, Z.; Kurcok, P.; Kowalczuk, M. Method of the Synthesis of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate). Polish Patent 199104, 16 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kurcok, P.; Kowalczuk, M.; Kawalec, M.; Sobota, M.; Michalak, M. Method of Puryfying β-Butyrolactone, in Particular for the Synthesis of poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) and Its Copolymers. Polish Patent Application P-393751, 27 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kawalec, M.; Adamus, G.; Kurcok, P.; Kowalczuk, M.; Foltran, I.; Focarete, M.L.; Scandola, M. Carboxylate induced degradation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)s. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkin, Z.G.; Rydz, J.; Adamus, G.; Kowalczuk, M. Watersoluble l-alanine and related oligopeptide conjugates with poly[(R,S)-3-hydroxybutanoic acid. Oligomers] Synthesis and structural studies by means of electrospray ionization multistage mass spectrometry. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2001, 12, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczuk, M.; Adamus, G.; Jedliński, Z. Synthesis of new graft polymers via anionic grafting of β-butyrolactone on poly(methyl methacrylate). Macromolecules 1994, 27, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, D.; Rydz, J.; Goebel, I.; Dacko, P.; Kowalczuk, M. Synthesis of graft copolymers containing biodegradable poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) chains. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 1767–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseva, N.S.; Novakov, Ch.P.; Rydz, J.; Kurcok, P.; Kowalczuk, M. Synthesis of aPHB-PEG brush co-polymers through ATRP in a macroinitiator–macromonomer feed system and their characterization. Des. Monomers Polym. 2010, 13, 579–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalec, M.; Adamus, G.; Kurcok, P.; Kowalczuk, M. Synthesis of Poly[(R,S)-3-hydroxybutyrate-block-ethylene glycol-block-(R,S)-3-hydroxybutyrate. Macromol. Symp. 2007, 253, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.L.; Goh, S.H.; Li, J. Controlled synthesis and characterizations of amphiphilic poly[(R,S)-3-hydroxybutyrate]-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly[(R,S)-3-hydroxybutyrate] triblock copolymers. Polymer 2008, 49, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazer, B. Macromonomeric initiators. In Polymeric Materials Encyclopedia; Salamone, J.C., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 1996; pp. 3911–3918. [Google Scholar]
- Jedliński, Z.; Kowalczuk, M.; Adamus, G.; Sikorska, W.; Rydz, J. Novel synthesis of functionalized poly(3-hydroxybutanoic acid) and its copolymers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 25, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamus, G.; Sikorska, W.; Montaudo, M.; Scandola, M.; Kowalczuk, M. Sequence distribution and fragmentation studies of bacterial copolyester macromolecules: Characterization of PHBV macroinitiator by electrospray ion-trap multistage mass spectrometry. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 5797–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamus, G.; Sikorska, W.; Kowalczuk, M.; Noda, I.; Satkowski, M.M. Electrospray ion-trap multistage mass spectrometry for characterisation of co-monomer compositional distribution of bacterial poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) at the molecular level. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 2260–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamus, G. Aliphatic polyesters for advanced technologies structural characterization of biopolyesters with the aid of mass spectrometry. Macromol. Symp. 2006, 239, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagar, E.; Krzan, A.; Adamus, G.; Kowalczuk, M. Sequence Distribution in Microbial Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Co-polyesters determined by NMR and MS. Biomacromolecules. 2006, 7, 2210–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamus, G.; Sikorska, W.; Janeczek, H.; Kwiecien, M.; Sobota, M.; Kowalczuk, M. Novel block copolymers of atactic PHB with natural PHA for cardiovascular engineering: Synthesis and characterization. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurcok, P.; Dubois, Ph.; Sikorska, W.; Jedliński, Z.; Jerome, R. Macromolecular engineering of lactones and lactides. 24. Controlled synthesis of (R,S)-β-butyrolactone-b-ε-caprolactone block copolymers by anionic and coordination polymerization. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 5591–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandola, M.; Focarte, L.; Gazzano, M.; Matuszowicz, A.; Sikorska, W.; Adamus, G.; Kurcok, P.; Kowalczuk, M.; Jedliński, Z. Crystallinity-induced biodegradation of novel [(R,S)-β-butyrolactone]-b-pivalolactone copolymers. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 7743–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, P.A. Applications of PHB—A microbially produced biodegradable thermoplastic. Phys. Technol. 1985, 14, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker Chemie, A.G. (Ed.) VINNEX®—Enabling the Next Generation of Bioplastics; Wacker Chemie AG: München, Germany. Available online: http://www.wacker.com/cms/media/publications/downloads/7002_EN.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2014).
- Metabolix, Inc. Metabolix. to Highlight High Performance Biopolymers for Packaging Applications at Interpack 2014. Available online: http://ir.metabolix.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=845609 (accessed on 25 September 2014).
- Metabolix, Inc. Reinvent Your Brand with Eco-Friendly Products. Available online: http://www.metabolix.com/brand-owner (accessed on 25 September 2014).
- Website of Biomer: Krailling, Germany. Available online: http://www.biomer.de (accessed on 24 July 2014).
- Chanprateep, S. Current trends in biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 110, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G-Q. A microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) based bio- and materials industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2434–2446. [Google Scholar]
- Marketsandmarkets.com. Polyhydroxyalkanoate. (PHA) Market, by Application (Packaging, Food Services, Bio-Medical, Agriculture) & Raw Material—Global Trends & Forecasts to 2018. Available online: http://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/pha-market-395.html (accessed on 14 March 2014).
- Matavulj, M.; Sad, N.; Molitoris, H.P. Biodegradation of Polyhydroxyalkanoate-Based Plastic (BIOPOL) Under Different Environmental Conditions; Hoppea, Denkschr. Regensb. Bot. Ges. Bresinsky-Festschrift: Regensburg, Germany, 2000; pp. 735–749. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji, H.; Suzuyoshi, K. Environmental degradation of biodegradable polyesters. 2. Poly(ε-caprolactone), poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] and poly(l-lactide) films in natural dynamic seawater. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2002, 75, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volova, T.G.; Boyandin, A.N.; Vasiliev, A.D.; Karpov, V.A. Biodegradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) in tropical coastal waters and identification of PHA-degrading bacteria. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2010, 95, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akmal, D.; Azizan, M.N.; Majid, M.I.A. Biodegradation of microbial polyesters P(3HB) and P(3HB-co-3HV) under the tropical climate environment. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2003, 80, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OʼBrine, T.; Thompson, R.C. Degradation of plastic carrier bags in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 2279–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilck, A.; Grossmann, M.; Yamashita, F. Biodegradable mulch films for strawberry production. Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Krasowska, K.; Heimowska, A.; Kowalczuk, M. Degradation of the blends of natural and synthetic copolysters in different natural environment. Macromol. Symp. 2003, 197, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohee, R.; Unmar, G.D.; Mudhoo, A.; Khadoo, P. Biodegradability of biodegradable/degradable plastic materials under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freier, T.; Kunze, C.; Nischan, C.; Kramer, S.; Sternberg, K.; Sass, M.; Hopt, U.T.; Schmitz, K.-P. In vitro and in vivo degradation studies for development of a biodegradable patch based on poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2649–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scandola, M.; Focarete, L.; Adamus, G.; Sikorska, W.; Kowalczuk, M.; Jedliński, Z.; Baranowska, I.; Świerczek, S.; Gnatowski, M. Polymer blends of natural poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and synthetic atactic poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). Characterization and biodegradation studies. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 2568–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Matsubara, I.; Doi, Y. Physical properties and enzymic degradability of polymer blends of bacterial poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] and poly[(R,S)-3-hydroxybutyrate] stereoisomers. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focarete, M.L.; Ceccorulli, G.; Scandola, M.; Kowalczuk, M. Further Evidence of crystallinity-induced biodegradation of synthetic atactic poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) by PHB-depolymerase A from Pseudomonas lemoignei. Blends of atactic Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) with crystalline polyesters. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 8485–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Dean, K.; Li, L. Polymer blends and composites from renewable resources. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 576–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avella, M.; Martuscelli, E.; Raimo, M. Review: Properties of blends and composites based on poly(3-hydroxy)butyrate (PHB) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) copolymers. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 523–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zini, E.; Focarete, M.L.; Noda, I.; Scandola, M. Bio-composite of bacterial poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) reinforced with vegatable fibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avella, M.; La Rota, G.; Martuscelli, E.; Raimo, M. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and wheat straw fibre composites: Thermal, mechanical properties and biodegradation behaviour. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Krasowska, K.; Heimowska, A.; Adamus, G.; Sobota, M.; Musioł, M.; Janeczek, H.; Sikorska, W.; Krzan, A.; Žagar, E.; et al. Environmental degradation of blends of atactic poly[(R,S)-3-hydroxybutyrate] with natural PHBV in Baltic Sea water and compost with activated sludge. J. Polym. Environ. 2008, 16, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychter, P.; Biczak, R.; Herman, B.; Smyłła, A.; Kurcok, P.; Adamus, G.; Kowalczuk, M. Environmental degradation of polyester blends containing atactic poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). Biodegradation in soil and ecotoxicological impact. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3125–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumel, A.M.; Annuar, M.S.M.; Chisti, Y. Recent advances in the production, recovery and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoates. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 580–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piddubnyak, V.; Kurcok, P.; Matuszowicz, A.; G1owala, M.; Fiszer-Kierzkowska, A.; Jedliński, Z.; Juzwa, M.; Krawczyk, Z. Oligo-3-hydroxybutyrates as potential carriers for drug delivery. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5271–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juzwa, M.; Rusin, A.; Zawidlak-Węgrzyńska, B.; Krawczyk, Z.; Obara, I.; Jedliński, Z. Oligo(3-hydroxybutanoate) conjugates with acetylsalicylic acid and their antitumour activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 1785–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawidlak-Węgrzyńska, B.; Kawalec, M.; Bosek, I.; Łuczyk-Juzwa, M.; Adamus, G.; Rusin, A.; Filipczak, P.; Głowala-Kosińska, M.; Wolańska, K.; Krawczyk, Z.; et al. Synthesis and antiproliferative properties of ibuprofen-oligo(3-hydroxybutyrate) conjugates. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Y. Medical applications of biopolyesters polyhydroxyalkanoates. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 31, 719–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.; Kleerebezem, R.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Influence of ammonium on the accumulation of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) in aerobic open mixed cultures. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 147, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.J.; Luo, R.C.; Wang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Chen, G.Q. Application of (R)-3-hydroxyalkanoate methyl esters derived from microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates as novel biofuels. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, P.; O’Brien, M. Polylactides “NatureworksTM PLA”. In Biopolymers: Polyesters III—Applications and Commercial Products; Steinbüchel, A., Doi, Y., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2002; Volume 4, pp. 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- Avérous, L.; Pollet, E. Biodegradable polymers. In Environmental Silicate Nano-Biocomposites; Avérous, L., Pollet, E., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.P.; Jin, B.; Lant, P.; Zhou, J. Biotechnological production of lactic acid integrated with potato wastewater treatment by Rhizopus. arrhizus. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2003, 78, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Tang, C. Controlled polymerization of next-generation renewable monomers and beyond. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 1689–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, E.T.H.; Rábago, K.R.; Glassner, D.A.; Gruber, P.R. Applications of life cycle assessment to NatureWorks polylactide (PLA) production. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2003, 80, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nampoothiri, K.M.; Nair, N.R.; John, R.P. An overview of the recent developments in polylactide (PLA) research. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8493–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, M. Chemical syntheses of biodegradable polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 87–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsson, A-C.; Varma, I.K. Aliphatic polyesters: Synthesis, properties and applications. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2002, 157, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczuk, M.; Adamus, G.; Sikorska, W.; Rydz, J. Structural studies of biorelated polymers derived from natural PHA and their synthetic analogues with the aid of electrospray multistage mass spectrometry. Polym. Prepr. Am. Chem. Soc. Div. Polym. Chem. 2000, 41, 1626–1627. [Google Scholar]
- Shuai, X.; Jedliński, Z.; Kowalczuk, M.; Rydz, J.; Tan, H. Enzymatic synthesis of polyesters from hydroxyl acids. Eur. Polym. J. 1999, 35, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Deng, S.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Polylactic acid (PLA) synthesis and modifications: A review. Front. Chem. China 2009, 4, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzynski, P. Initiation of L-lactide polymerization carried out with zirconium (IV) acetylacetonate. J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2004, 42, 1886–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasprilla, A.J.R.; Martinez, G.A.R.; Lunelli, B.H.; Jardini, A.L.; Filho, R.M. Poly-lactic acid synthesis for application in biomedical devices—A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrzynski, P.; Li, S.; Kasperczyk, J.; Bero, M.; Gasc, F.; Vert, M. Structure-property relationships of copolymers obtained by ring-opening polymerization of glycolide and ε-caprolactone. Part 1. Synthesis and characterization. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezas, L.I.; Mazarro, R.; Gracia, I.; de Lucas, A.; Rodríguez, J.F. Optimizing the bulk copolymerization of d,l-lactide and glycolide by response surface methodology. Express Polym. Lett. 2013, 7, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrzynski, P.; Kasperczyk, J.; Janeczek, H. Synthesis of biodegradable copolymers with the use of low toxic zirconium compounds. 1. Copolymerization of glycolide with l-Lactide initiated by Zr(Acac)4. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 5090–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamula, E.; Dobrzynski, P.; Bero, M.; Paluszkiewicz, C. Hydrolytic degradation of porous scaffolds for tissue engineering from terpolymer of l-lactide, ε-caprolactone and glycolide. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 744–747, 557–562. [Google Scholar]
- Kasperczyk, J.; Li, S.; Jaworska, J.; Dobrzynski, P.; Vert, M. Degradation of copolymers obtained by ring-opening polymerization of glycolide and ε-caprolactone: A high resolution NMR and ESI-MS study. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2008, 93, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Avila, C.; Erbetta, C.; Alves, R.J.; Resende, J.M.; de Souza Freitas, R.F.; de Sousa, R.G. Synthesis and characterization of poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) copolymer. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2012, 3, 208–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; He, Y.; Wei, J.; Fan, Z.; Dobrzynski, P.; Kasperczyk, J.; Bero, M.; Li, S. Hydrolytic degradation of glycolide/l-lactide/ε-caprolactone terpolymers initiated by zirconium (IV) acetylacetonate. J. Appl. Pol. Sci. 2007, 103, 2451–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chłopek, J.; Morawska-Chochol, A.; Paluszkiewicz, C.; Jaworska, J.; Kasperczyk, J.; Dobrzynski, P. FTIR and NMR study of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and hydroxyapatite implant degradation under in vivo conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2009, 94, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska-Chochol, A.; Jaworska, J.; Chlopek, J.; Kasperczyk, J.; Dobrzynski, P.; Paluszkiewicz, C.; Bajor, G. Degradation of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and its composites with carbon fibres and hydroxyapatite in rabbit femoral bone. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2011, 96, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamula, E.; Blazewicz, M.; Paluszkiewicz, C.; Dobrzynski, P. FTIR study of degradation products of aliphatic polyesters-carbon fibres composites. J. Mol. Struct. 2001, 596, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentano, I.; Dottori, M.; Fortunati, E.; Mattioli, S.; Kenny, J.M. Biodegradable polymer matrix nanocomposites for tissue engineering: A review. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2010, 95, 2126–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magon, A.; Pyda, M. Study of crystalline and amorphous phases of biodegradable poly(lactic acid) by advanced thermal analysis. Polymer 2009, 50, 3967–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calafel, M.I.; Remiro, P.M.; Cortázar, M.M.; Calahorra, M.E. Cold crystallization and multiple melting behavior of poly(l-lactide) in homogeneous and in multiphasic epoxy blends. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2010, 288, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, G.; Auras, R.; Singh, S.P. Degradation of commercial biodegradable packages under real composting and ambient exposure conditions. J. Polym. Environ. 2006, 14, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeret, A. Environmental-friendly biodegradable polymers and composites. Integrated waste management; Kumar, S., Ed.; InTech Open Access Publisher, 2011; Volume I. Available online: http://www.intechopen.com/books/integrated-waste-management-volume-i/environmental-friendly-biodegradable-polymers-and-composites (accessed on 17 September 2013).
- Zhang, X.; Espiritu, M.; Bilyk, A.; Kurniawan, L. Morphological behaviour of poly(lactic acid) during hydrolytic degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2008, 93, 1964–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auras, R.A.; Harte, B.; Selke, S.; Hernandez, R.J. Mechanical, physical, and barrier properties of poly(lactide) films. J. Plastic Film Sheet. 2003, 19, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J. Processing of PLA. In Biodegradable Poly(Lactic Acid): Synthesis, Modification, Processing and Applications; Ren, J., Ed.; Springer-Verlag: London, UK, 2011; pp. 142–207. [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar, D.H.S.; Bhattacharya, M. Steady shear and dynamic properties of biodegradable polyesters. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1998, 38, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastioli, C. Biodegradable materials-present situation and future perspectives. Macromol. Symp. 1998, 135, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglund, A.; Odelius, K.; Albertsson, A-C. Crucial differences in the hydrolytic degradation between industrial polylactide and laboratory-scale poly(l-lactide). Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 23, 2788–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairncross, R.A.; Becker, J.G.; Ramaswamy, S.; O’Connor, R. Moisture sorption, transport, and hydrolytic degradation in polylactide. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2006, 131, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasowska, K.; Brzeska, J.; Rutkowska, M.; Dacko, P.; Sobota, M.; Kowalczuk, M. The effect of poly(d,l-lactide) modification with poli[(R,S)-3-hydroxybutyrate] on the course of its degradation in natural environments. Polimery 2008, 53, 730–736. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, A.; Li, S.; Roussos, S.; Vert, M. Poly(lactic acid) degradation in soil or under ncontrolled conditions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 62, 2295–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartiser, S.; Wallrabenstein, M.; Stiene, G. Assessment of several test methods for the determination of the anaerobic biodegradability of polymers. J. Environ. Polymer Degrad. 1998, 6, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, G.; Auras, R.; Singh, S.P.; Narayan, R. Biodegradability of polylactide bottles in real and simulated composting conditions. Polym. Test. 2007, 26, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolstad, J.J.; Vink, E.T.H.; de Wilde, B.; Debeer, L. Assessment of anaerobic degradation of Ingeo polylactides under accelerated landfill conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2012, 97, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Girard, A.; Garreau, H.; Vert, M. Enzymatic degradation of polylactide stereocopolymers with predominant D-lactyl contents. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2001, 71, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkarainen, M.; Karlsson, S.; Albertsson, A-C. Rapid (bio)degradation of polylactide by mixed culture of compost microorganisms-low molecular weight products and matrix changes. Polymer 2000, 41, 2331–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorska, W.; Richert, J.; Rydz, J.; Musioł, M.; Adamus, G.; Janeczek, H.; Kowalczuk, M. Degradability studies of poly(l-lactide) after multi-reprocessing experiments in extruder. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2012, 97, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydz, J.; Adamus, G.; Wolna-Stypka, K.; Marcinkowski, A.; Misiurska-Marczak, M.; Kowalczuk, M.M. Degradation of polylactide in paraffin and selected protic media. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2013, 98, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydz, J.; Wolna-Stypka, K.; Musioł, M.; Szeluga, U.; Janeczek, H.; Kowalczuk, M. Further evidence of polylactide degradation in paraffin and in selected protic media. A thermal analysis of eroded polylactide films. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2013, 98, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkarainen, M.; Albertsson, A.C.; Karlsson, S. Weight losses and molecular weight changes correlated with the evolution of hydroxyacids in simulated in vivo degradation of homo- and copolymers of PLA and PGA. Polym. Degrad. Stable 1996, 52, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siparsky, G.L.; Voorhees, K.J.; Miao, F. Hydrolysis of polylactic acid (PLA) and polycaprolactone (PCL) in aqueous acetonitrile solutions: Autocatalysis. J. Polym. Environ. 1988, 6, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; Tan, H.T.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Ooi, C.P. Synthesis and characterisation of PLLA by melt polycondensation using binary catalyst system. SIMTech Tech. Rep. 2005, 6, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Grizzi, I.; Garreau, H.; Li, S.; Vert, M. Hydrolytic degradation of devices based on poly(d,l-lactic acid) size-dependence. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworska, J.; Kasperczyk, J.; Dobrzynski, P. Degradation process of bioresorbable copolyesters. Microstructure investigation by NMR and ESI-MS. Macromol. Symp. 2007, 253, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkarainen, M.; Finne-Wistrand, A. Polylactide. In Handbook of Engineering and Specialty Thermoplastics: Polyethers and Polyesters; Thomas, S., Visakh, P.M., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 349–376. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, P.R. Commodity polymers from renewable resources: Polylactic acid. In Carbon Management: Implications for R & D in the Chemical Sciences and Technology; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; pp. 166–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J. Application in the field of commodity and industry product. In Biodegradable Poly(Lactic Acid): Synthesis, Modification, Processing and Applications; Ren, J., Ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, China and Germany, 2010; pp. 208–239. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, D.; Dharmalingam, S.; Wadsworth, L.C.; Leonas, K.K.; Miles, C.; Inglis, D.A. Biodegradable agricultural mulches derived from biopolymers. In Degradable Polymers and Materials: Principles and Practice, 2nd ed.; Khemani, K., Scholz, C., Eds.; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 1114, pp. 201–223. [Google Scholar]
- Rudnik, E.; Briassoulis, D. Degradation behaviour of poly(lactic acid) films and fibres in soil under Mediterranean field conditions and laboratory simulations testing. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2011, 33, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smock, D. Bioplastics. Producers Ramp up Supply. 2012. Available online: http://www.mypurchasingcenter.com/commodities/commodities-articles/bioplastics-manufacturers-ramp-up-production (accessed on 04 November 2014).
- Bioplastics Magazine. New Market Research Projects Strong Growth for Lactic Acid. Available online: http://www.bioplasticsmagazine.com/en/news/meldungen/new-market-study-lactic-acid.php (accessed on 25 September 2014).
- Lactic Acid Market Worth $3,577.5 Million and Polylactic Acid Market Worth $4,840.1 Million by 2019. Available online: http://www.marketsandmarkets.com/PressReleases/polylacticacid.asp (accessed on 25 September 2014).
- Palmer, R.J. Polyamides, Plastics. In Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology, 3rd ed.; Mark, H., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 618–642. [Google Scholar]
- Page, I.B. Polyamides as Engineering Thermoplastic Materials; Rapra Review Reports (Report 121); Smithers Rapra Technology: Shropshire, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Estes, L.L.; Schweizer, M. Fibers, Polyamide fibers. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 14, p. 451. [Google Scholar]
- Rulkens, R.; Koning, C. Chemistry and Technology of Polyamides. In Polymer Science: A Comprehensive Reference; Matyjaszewski, K., Möller, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 431–467. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, K. Ring-opening polymerization of lactams. Living anionic polymerization and its applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000, 25, 1411–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Sudo, E.; Sugimura, T.; Inagaki, Y. Synthesis of novel block copolymers containing polyamide4 segments and control of their biodegradability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 3492–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, N.; Nakayama, A.; Yamano, N.; Takeda, S.; Kawata, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Aiba, S. Synthesis, thermal and mechanical properties and biodegradation of branched polyamides 4. Polymer 2005, 46, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, L.; Lefebvre, H.; Fradet, A. Polyamide-polyester multiblock copolymers by chain-coupling reactions of carboxy-terminated polymers with phenylene and pyridylene bisoxazolines. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyulavska, M.; Bryaskova, R.; Bozukova, D.; Mateva, R. Synthesis, structure and behavior of new polycaprolactam copolymers based on poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide)-poly(ethylene oxide) macroactivators derived from Pluronic block copolymers. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.S.; Hussain, S.A.; Pandurangadu, V.; PalaniKumar, K. Modeling and Analysis of Spur Gear for Sugarcane Juice Machine under Static Load Condition by Using FEA. Int. J. Mod. Eng. Res. 2012, 2, 2862–2866. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, C. High.-Performance Films; CRC Press: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 1996; p. 336. [Google Scholar]
- McCoy, M. Slowly changing how nylon is made. Chem. Eng. News 2000, 78, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelderich, W.F.; Dahlhoff, G. Developing Technolgy: The “greening” of nylon. The precursor to nylon 6, ε-caprolactam, is manufactured with toxic and corrosive chemicals and produces tons of byproducts. Academic research suggests another approach based on heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Inn. 2001, 31, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Nylon 66 Market—Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth, Trends and Forecast, 2013–2019. Available online: http://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/nylon-66-market.html (accessed on 5 November 2014).
- Advantages of Welded Nylon for Powertrain Applications: Linear Vibration, Orbital Vibration and Hot Plate Welding Technologies. BASF Corporation. Available online: http://www2.basf.us//PLASTICSWEB/displayanyfile?id=0901a5e18000487b (accessed on 5 November 2014).
- Brehmer, B. Polyamides from biomass derived monomers. In Bio-Based Plastics: Materials and Applications; Kabasci, S., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2013; pp. 275–293. [Google Scholar]
- Kuciel, S.; Kuzniar, P.; Liber-Knec, A. Polyamides from renewable sources as matricies of short fiber reinforced biocomposites. Polimery 2012, 57, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielen, M. Basics of bio-polyamaides. Bioplastics Mag. 2010, 5, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, A.C.; Gil, M.H.; Simoes, P.N. Biodegradable poly(ester amide)s—A remarkable opportunity for the biomedical area: Review on the synthesis, characterization and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1291–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Galan, A.; Franco, L.; Puiggali, J. Degradable poly(esteramide)s for biomedical applications. Polymers 2010, 3, 65–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herzog, B.; Kohan, M.I.; Mestemacher, S.A.; Pagilagan, R.U.; Redmond, K. Polyamides. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2013; Volume 28, p. 537. [Google Scholar]
- Albertsson, A.-C.; Karlsson, S. Biodegradable polymers. In Comprehensive Polymer Science; Allen, G., Bevington, J.C., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1992; pp. 285–297. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.F. Polymer degradation in biological environments. In Comprehensive Polymer Science; Allen, G., Bevington, J.C., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1989; Volume 6, pp. 607–719. [Google Scholar]
- Negoro, S. Biodegradation of nylon and other synthetic polyamides. In Biopolymers Online; Matsumura, S., Steinbüchel, A., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; Volume 9, pp. 395–415. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, M. Biodegradation and Bioremediation; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1999; pp. 393–407. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Gámez, L.; Soto, D.; Franco, L.; Puiggalí, J. Brill transition and melt crystallization of nylon 56: An odd-even polyamide with two hydrogen-bonding directions. Polymer 2010, 51, 5788–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negoro, S. Biodegradation of nylon oligomers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 54, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguchi, T.; Kakezawa, M.; Nishida, T. Nylon biodegradation by lignin degrading fungi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimao, M. Biodegradation of plastics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2001, 12, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, J.; Zalar, P.; Mohorcic, M.; Klun, U.; Krzan, A. Ability of fungi to degrade synthetic polymer nylon-6. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 2089–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreoni, V.; Baggi, G.; Manfrin, P. Bacterial degradation of 6-aminocaproic acid polyamides (nylon 6) of low molecular weight. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 1993, 31, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, N.; Nakayama, A.; Kawasaki, N.; Yamamoto, N.; Aiba, S. Mechanism and characterization of polyamides 4 degradation by Pseudomonas sp. J. Polym. Environ. 2008, 16, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, N.; Kawasaki, N.; Oshima, M.; Nakayama, A. Polyamide 4 with long-chain fatty acid groups—Suppressing the biodegradability of biodegradable polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2014, 108, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Hamano, T.; Okada, M. Degradation of several polyamides in soils. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 54, 1579–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Sudo, E.; Ohta, K.; Sugimura, T.; Yamada, H.; Aoki, T. Biodegradation of nylon4 and its blends with nylon6. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 2307–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Yoshikawa, M.; Okawa, H. Isolation and characterization of microorganisms degrading nylon 4 in the composted soil. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2010, 95, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, K.; Urano, Y.; Numata, K. Biodegradability of nylon 4 film in a marine environment. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2013, 98, 1847–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, C.; Burton, H. Origins and biological accumulation of small plastic particles in fur seals from Macquarie Island. Ambio 2003, 32, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deguchi, T.; Kitaoka, Y.; Kakezawa, M.; Nishida, T. Purification and characterization of a nylon-degrading enzyme. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1366–1371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomita, K.; Ikeda, N.; Uedo, A. Isolation and characterization of a thermophilic bacterium, Geobacillus thermocatenulatus, degrading nylon 12 and nylon 66. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 1743–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, K.; Hayashi, N.; Ikeda, N.; Kikuchi, Y. Isolation of a thermophilic bacterium degrading some nylons. Polym. Degrad. Stable 2003, 81, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppermann, F.B.; Pickartz, S.; Steinbüchel, A. Biodegradation of polyamides. Polym. Degrad. Stable 1998, 59, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Hinrichsen, G. Biofibres, biodegradable polymers and biocomposites: An overview. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2000, 276–277, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lips, P.; Dijkstra, P.J. Biodegradable Polyesteramides. In Biodegradable Polymers for Industrial Applications; Smith, R., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 107–135. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, M.; Yamada, M.; Yokoe, M.; Aoi, K. Biodegradable polymers based on renewable resources. V. Synthesis and biodegradation behavior of poly(ester amide)s composed of 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-d-glucitol, α-amino acid, and aliphatic dicarboxylic acid units. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 81, 2721–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, S.; Glassner, D.; Vink, E.; Gerngross, T. Evaluating the environmental impact of biopolymers. In Biopolymers Online; Doi, Y., Steinbüchel, A., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; Volume 10, pp. 473–492. [Google Scholar]
- Papageorgiou, A.C.; Hermawan, S.; Singh, C.B.; Jendrossek, D. Structural basis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) hydrolysis by PhaZ7 depolymerase from Paucimonas. lemoignei. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 382, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, J.; Link, U.; Braun, R. Environmental impacts of biobased/biodegradable packaging. Starch 2001, 53, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eubeler, J.P.; Bernhard, M.; Zok, S.; Knepper, T.P. Environmental biodegradation of synthetic polymers I. Test methodologies and procedures. Trend. Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rydz, J.; Sikorska, W.; Kyulavska, M.; Christova, D. Polyester-Based (Bio)degradable Polymers as Environmentally Friendly Materials for Sustainable Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 564-596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16010564
Rydz J, Sikorska W, Kyulavska M, Christova D. Polyester-Based (Bio)degradable Polymers as Environmentally Friendly Materials for Sustainable Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(1):564-596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16010564
Chicago/Turabian StyleRydz, Joanna, Wanda Sikorska, Mariya Kyulavska, and Darinka Christova. 2015. "Polyester-Based (Bio)degradable Polymers as Environmentally Friendly Materials for Sustainable Development" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 1: 564-596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16010564
APA StyleRydz, J., Sikorska, W., Kyulavska, M., & Christova, D. (2015). Polyester-Based (Bio)degradable Polymers as Environmentally Friendly Materials for Sustainable Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(1), 564-596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16010564








