Construction of the High-Density Genetic Linkage Map and Chromosome Map of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
2.1.1. Sequencing and Genotyping
2.1.2. Construction of the Genetic Map
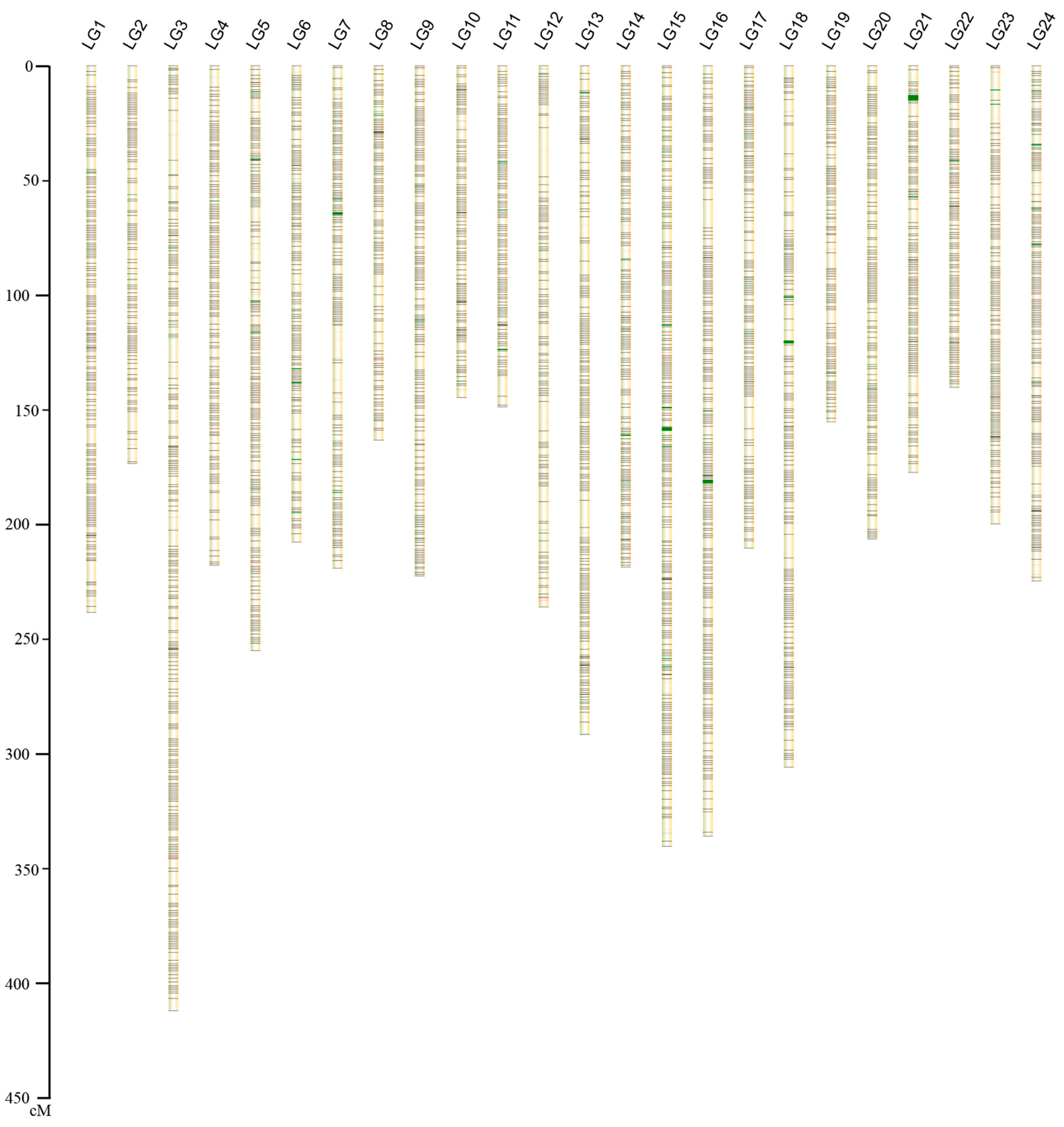
| Linkage Group ID | Markers Used for Genetic Map | Length (cM) | Average Inter-Loci Distance | Markers Used in Anchoring to Chromosome | Numbers of Scaffolds in Chromosome | Length (Mb) | Pseudo-Chromosome ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LG1 | 504 | 238.74 | 0.47 | 115 | 33 | 21.58 | chr1 |
| LG2 | 310 | 173.62 | 0.56 | 67 | 16 | 10.78 | chr2 |
| LG3 | 517 | 412.46 | 0.80 | 122 | 23 | 19.38 | chr3 |
| LG4 | 397 | 218.16 | 0.55 | 78 | 25 | 23.68 | chr4 |
| LG5 | 467 | 255.29 | 0.55 | 138 | 35 | 24.60 | chr5 |
| LG6 | 447 | 207.93 | 0.47 | 90 | 29 | 17.75 | chr6 |
| LG7 | 471 | 219.35 | 0.47 | 101 | 41 | 29.75 | chr7 |
| LG8 | 341 | 163.48 | 0.48 | 99 | 13 | 10.83 | chr8 |
| LG9 | 409 | 222.76 | 0.55 | 189 | 29 | 25.66 | chr9 |
| LG10 | 437 | 144.85 | 0.33 | 56 | 14 | 7.66 | chr10 |
| LG11 | 380 | 148.97 | 0.39 | 59 | 7 | 8.85 | chr11 |
| LG12 | 221 | 236.23 | 1.07 | 142 | 13 | 13.88 | chr12 |
| LG13 | 634 | 291.87 | 0.46 | 114 | 24 | 18.96 | chr13 |
| LG14 | 406 | 218.84 | 0.54 | 52 | 9 | 6.91 | chr14 |
| LG15 | 645 | 340.75 | 0.53 | 173 | 54 | 46.00 | chr15 |
| LG16 | 595 | 336.27 | 0.57 | 99 | 14 | 12.52 | chr16 |
| LG17 | 355 | 210.61 | 0.59 | 159 | 19 | 15.55 | chr17 |
| LG18 | 358 | 306.07 | 0.86 | 117 | 21 | 11.65 | chr18 |
| LG19 | 302 | 155.54 | 0.52 | 247 | 16 | 13.46 | chr19 |
| LG20 | 339 | 206.53 | 0.61 | 105 | 21 | 13.41 | chr20 |
| LG21 | 347 | 177.56 | 0.51 | 139 | 13 | 10.30 | chr21 |
| LG22 | 411 | 140.4 | 0.34 | 167 | 13 | 9.53 | chr22 |
| LG23 | 461 | 199.99 | 0.43 | 99 | 25 | 23.34 | chr23 |
| LG24 | 396 | 225.01 | 0.57 | 162 | 26 | 25.19 | chr24 |
| Average | 423 | 227.14 | 0.54 | 120.375 | 42.64 | 17.55 | |
| Total | 10,150 | 5451.3 | 0.54 | 2889 | 533 | 421.22 |
2.1.3. Chromosomal Assembly and Comparative Genome Analysis
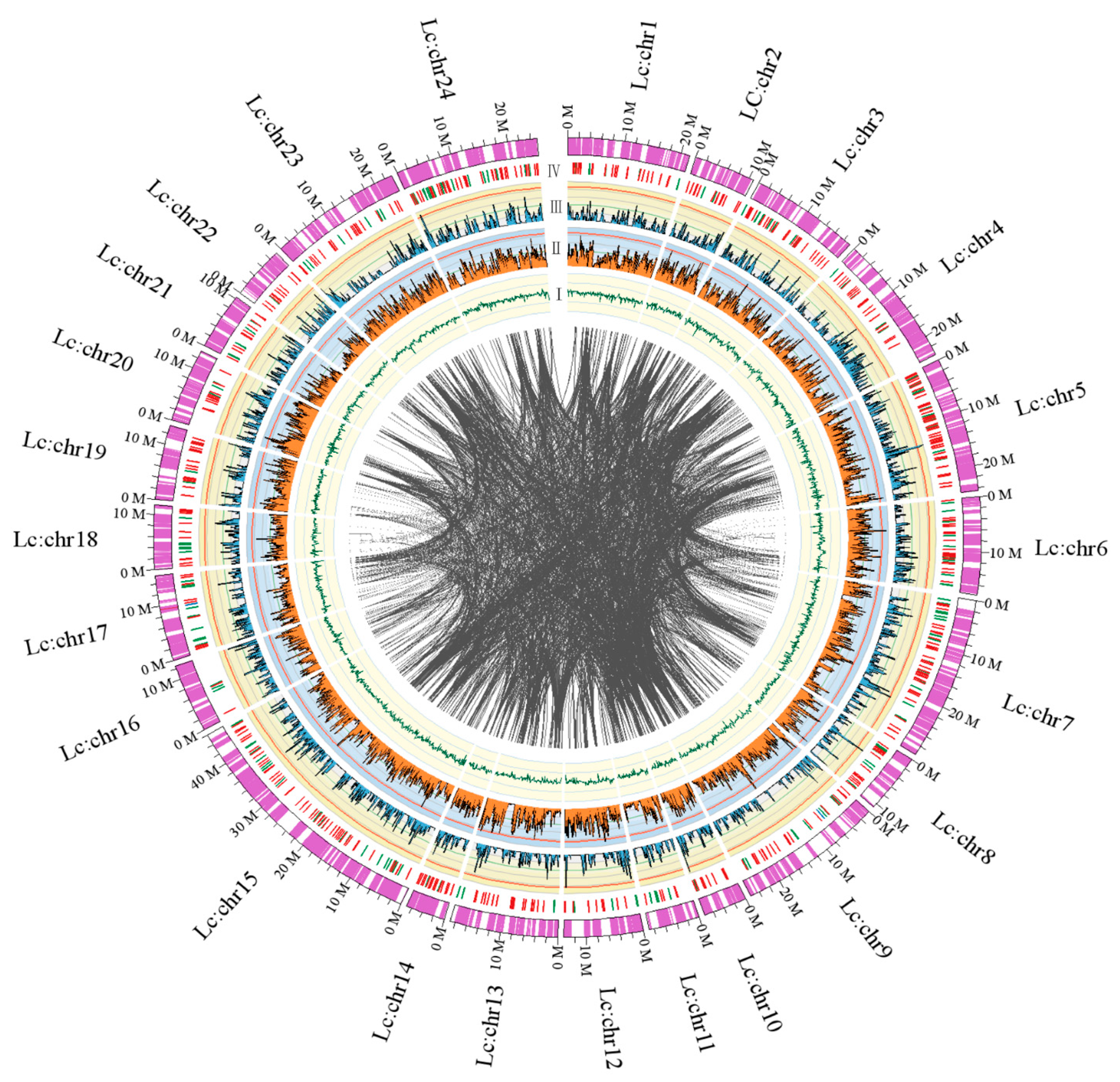

2.1.4. Mapping of Immunity- and Hypoxia-related Genes
2.2. Discussion
2.2.1. The High-resolution Genetic Map of Large Yellow Croaker
2.2.2. Genomic Synteny Based on Chromosomal Assembly Levels
2.2.3. Immunity- and Hypoxia-Related Genes
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Mapping Population and DNA Isolation
3.2. RAD Library Preparation and Sequencing
3.3. SNP Discovery and Genotyping
3.4. Genetic Map Construction
3.5. Pseudo-Chromosomes Assembly and Genome Alignment
3.6. Distributions of Genes Involving in Immunity and Hypoxia Adaptation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, Z.; Cao, Q. Ichthyology, 1st ed.; Agricultural Press House: Beijing, China, 1979; pp. 154–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Liu, G.; Ao, J.; Chen, X. Expression analysis of immune-relevant genes in the spleen of large yellow croaker (pseudosciaena crocea) stimulated with poly I:C. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 21, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cai, M.; Wang, Z.; Guo, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Ning, Y. Microsatellite-centromere mapping in large yellow croaker (pseudosciaena crocea) using gynogenetic diploid families. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Xie, F. A genetic map of large yellow croaker pseudosciaena crocea. Aquaculture 2007, 264, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y. Breeding and Farming of Pseudosciaena Crocea, 1st ed.; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Xu, Z. Effect of hypoxia on the blood of large yellow croaker (pseudosciaena crocea). Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2011, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Niu, Y.; Rastas, P.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Tai, S.; Tian, Y.; et al. Genome-wide SNP identification for the construction of a high-resolution genetic map of japanese flounder (paralichthys olivaceus): Applications to QTL mapping of vibrio anguillarum disease resistance and comparative genomic analysis. DNA Res. 2015, 22, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Genetic mapping and QTL analysis of growth traits in the large yellow croaker larimichthys crocea. Mar. Biotechnol. 2014, 16, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, J.; Mu, Y.; Xiang, L.X.; Fan, D.; Feng, M.; Zhang, S.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, L.Y.; Li, T.; Ding, Y.; et al. Genome sequencing of the perciform fish larimichthys crocea provides insights into molecular and genetic mechanisms of stress adaptation. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, N.A.; Etter, P.D.; Atwood, T.S.; Currey, M.C.; Shiver, A.L.; Lewis, Z.A.; Selker, E.U.; Cresko, W.A.; Johnson, E.A. Rapid SNP discovery and genetic mapping using sequenced RAD markers. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amish, S.J.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Painter, S.; Leary, R.F.; Muhlfeld, C.; Allendorf, F.W.; Luikart, G. RAD sequencing yields a high success rate for westslope cutthroat and rainbow trout species-diagnostic SNP assays. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchi, L.; Lanteri, S.; Portis, E.; Vale, G.; Volante, A.; Pulcini, L.; Ciriaci, T.; Acciarri, N.; Barbierato, V.; Toppino, L.; et al. A RAD tag derived marker based eggplant linkage map and the location of QTLs determining anthocyanin pigmentation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chutimanitsakun, Y.; Nipper, R.W.; Cuesta-Marcos, A.; Cistue, L.; Corey, A.; Filichkina, T.; Johnson, E.A.; Hayes, P.M. Construction and application for QTL analysis of a restriction site associated DNA (RAD) linkage map in barley. BMC Genom. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, R.; Azam, S.; Jeena, G.; Khan, A.W.; Choudhary, S.; Jain, M.; Yadav, G.; Tyagi, A.K.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Bhatia, S. High-throughput snp discovery and genotyping for constructing a saturated linkage map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). DNA Res. 2012, 19, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willing, E.M.; Hoffmann, M.; Klein, J.D.; Weigel, D.; Dreyer, C. Paired-end RAD-seq for de novo assembly and marker design without available reference. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2187–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.; Shu, L.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Luo, J.; Lu, J.; Mu, Q.; Bai, J.; Xia, Q.; Chen, Q.; et al. Construction of high-density genetic linkage maps for orange-spotted grouper Epinephelus coioides using multiplexed shotgun genotyping. BMC Genet. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastas, P.; Paulin, L.; Hanski, I.; Lehtonen, R.; Auvinen, P. Lep-map: Fast and accurate linkage map construction for large SNP datasets. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 3128–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, C.; Wang, J.; Ding, S.; Su, Y.; Yao, J. The karyotypes of pseudosciaena crocea (richardson). J. Xiamen Univ. Nat. Sci. 2000, 39, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Saurabh, S.; Sahoo, P. Lysozyme: An important defence molecule of fish innate immune system. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierst, J.L. Using linkage maps to correct and scaffold de novo genome assemblies: Methods, challenges, and computational tools. Front. Genet. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, W.; Nomura, K.; Fujiwara, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Yasuike, M.; Ojima, N.; Masaoka, T.; Ozaki, A.; Kazeto, Y.; Gen, K.; et al. A ddRAD-based genetic map and its integration with the genome assembly of japanese eel (Anguilla japonica) provides insights into genome evolution after the teleost-specific genome duplication. BMC Genom. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, S.; Brenna-Hansen, S.; Moen, T.; Roseth, A.; Davidson, W.S.; Omholt, S.W.; Lien, S. BAC-based upgrading and physical integration of a genetic SNP map in Atlantic salmon. Anim. Genet. 2010, 41, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninwichian, P.; Peatman, E.; Liu, H.; Kucuktas, H.; Somridhivej, B.; Liu, S.; Li, P.; Jiang, Y.; Sha, Z.; Kaltenboeck, L.; et al. Second-generation genetic linkage map of catfish and its integration with the BAC-based physical map. G3: Genes Genomes Genet. 2012, 2, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buermans, H.P.; den Dunnen, J.T. Next generation sequencing technology: Advances and applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1932–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.L.; Chen, C.M.; Pai, T.W.; Leong, H.W.; Chong, K.F. Homologous synteny block detection based on suffix tree algorithms. J. Bioinform. Comput. Biol. 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diopere, E.; Maes, G.E.; Komen, H.; Volckaert, F.A.; Groenen, M.A. A genetic linkage map of sole (Solea solea): A tool for evolutionary and comparative analyses of exploited (flat)fishes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palti, Y. Toll-like receptors in bony fish: From genomics to function. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanier, C.; Zemirli, N.; Portier, A.; Garcin, D.; Bidere, N.; Vazquez, A.; Arnoult, D. MAVS ubiquitination by the E3 ligase TRIM25 and degradation by the proteasome is involved in type I interferon production after activation of the antiviral RIG-I-like receptors. BMC Biol. 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Mo, J.; Swanson, K.V.; Wen, H.; Petrucelli, A.; Gregory, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Schneider, M.; Jiang, Y.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. NLRC3, a member of the NLR family of proteins, is a negative regulator of innate immune signaling induced by the DNA sensor STING. Immunity 2014, 40, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayan, F.; Roux, D.; Brahimi-Horn, M.C.; Pouyssegur, J.; Mazure, N.M. The oxygen sensor factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1 controls expression of distinct genes through the bifunctional transcriptional character of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3688–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, S.C.; Bensaddek, D.; Ortmann, B.; Maure, J.F.; Mudie, S.; Blow, J.J.; Lamond, A.I.; Swedlow, J.R.; Rocha, S. PHD1 links cell-cycle progression to oxygen sensing through hydroxylation of the centrosomal protein cep192. Dev. Cell 2013, 26, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambrook, J.F.; Maniatis, E.T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 463–471. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz, S.; Phillippy, A.; Delcher, A.L.; Smoot, M.; Shumway, M.; Antonescu, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol. 2004, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ao, J.; Li, J.; You, X.; Mu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Mao, K.; Bian, C.; Mu, P.; Shi, Q.; Chen, X. Construction of the High-Density Genetic Linkage Map and Chromosome Map of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26237-26248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125951
Ao J, Li J, You X, Mu Y, Ding Y, Mao K, Bian C, Mu P, Shi Q, Chen X. Construction of the High-Density Genetic Linkage Map and Chromosome Map of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(11):26237-26248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125951
Chicago/Turabian StyleAo, Jingqun, Jia Li, Xinxin You, Yinnan Mu, Yang Ding, Kaiqiong Mao, Chao Bian, Pengfei Mu, Qiong Shi, and Xinhua Chen. 2015. "Construction of the High-Density Genetic Linkage Map and Chromosome Map of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 11: 26237-26248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125951






