Domain Motions and Functionally-Key Residues of l-Alanine Dehydrogenase Revealed by an Elastic Network Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Comparison of the Predicted Mean-Square Fluctuations with the Experimental Temperature Factors (B-Factors)

2.2. The Slow Motion Modes




2.3. The Fast Motion Modes

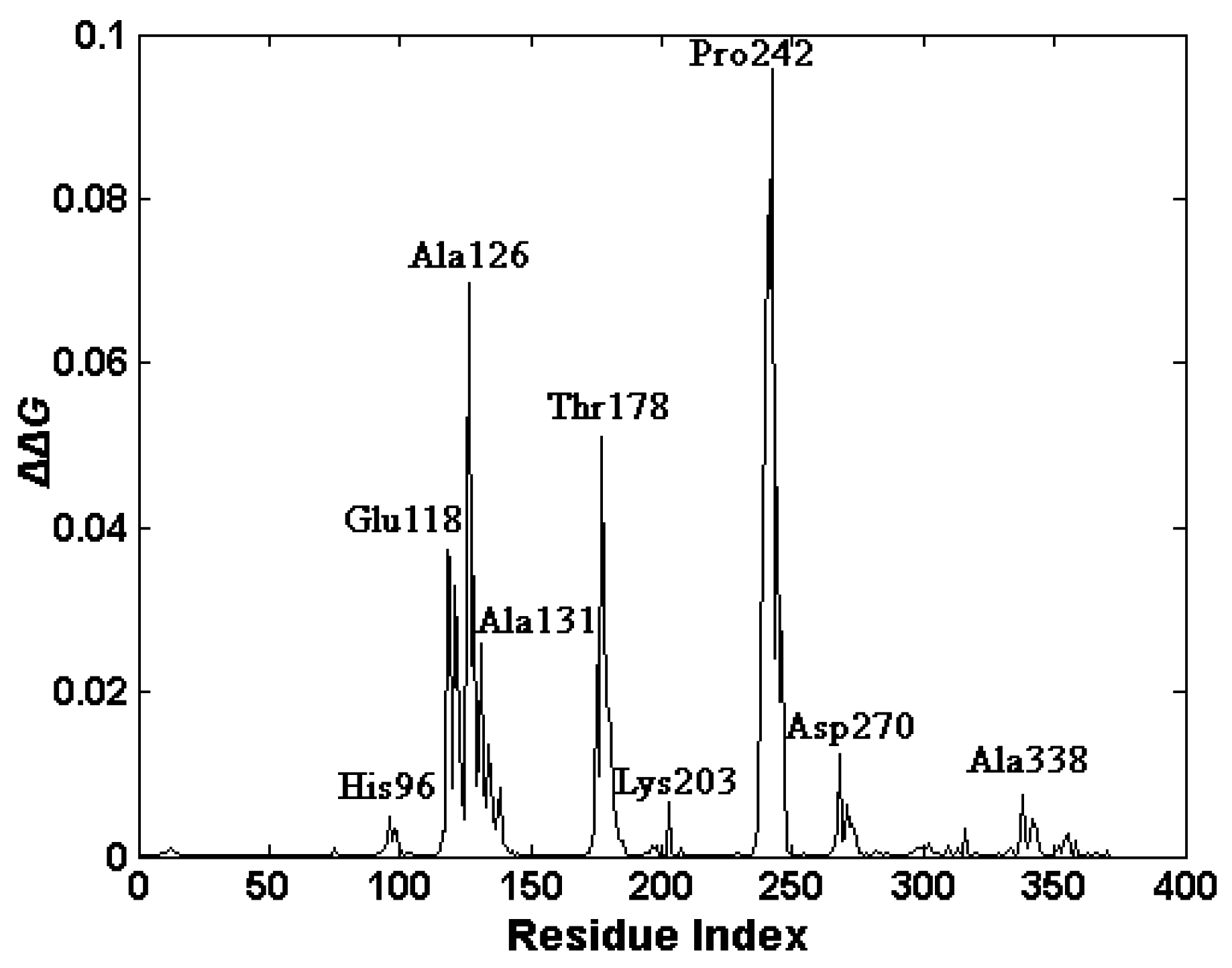
2.4. The Functionally-Important Residues Identified with the Thermodynamic Method
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. The Gaussian Network Model and the Anisotropy Elastic Network Model
3.2. Correlation Coefficient and Overlap
3.3. Thermodynamic Cycle Method
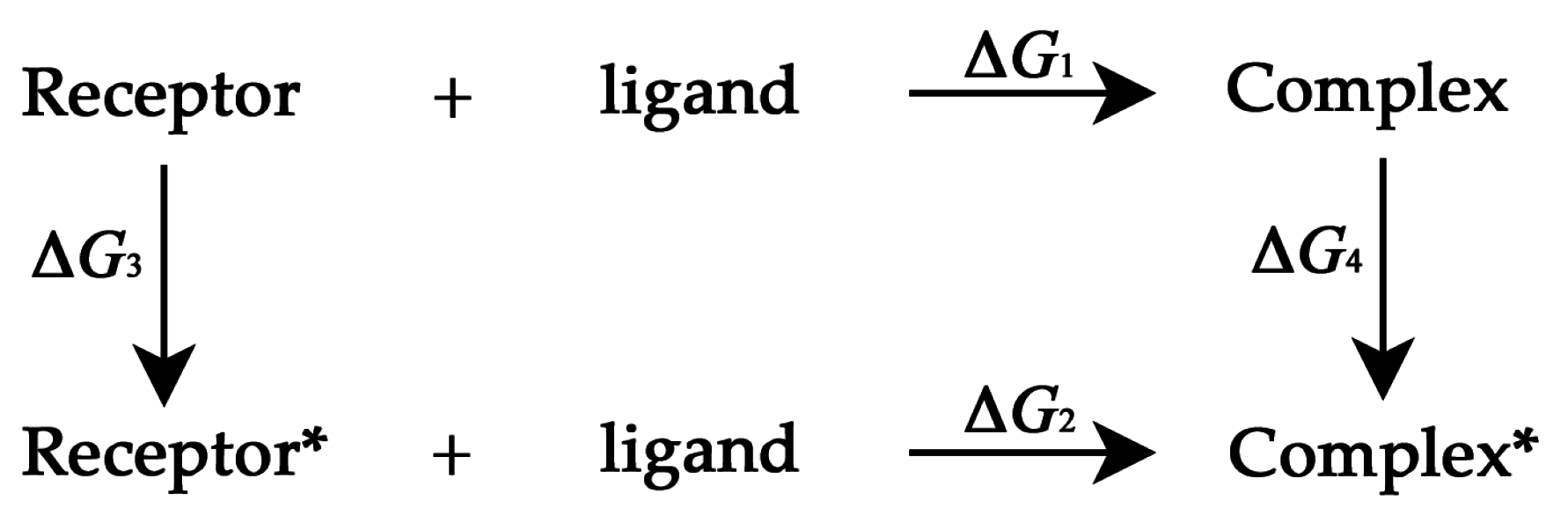
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bloom, B.R.; McKinney, J.D. The death and resurrection of tuberculosis. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Control: Surveillance and Financing; WHO Report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wayne, L.G.; Sramek, H.A. Metronidazole is bactericidal to dormant cells of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 2054–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, R.; Schneider, G. Structural enzymology of sulphur metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 396, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wayne, L.G.; Hayes, L.G. An in vitro model for sequential study of shiftdown of Mycobacterium tuberculosis through two stages of nonreplicating persistence. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 2062–2069. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Usha, V.; Jayaraman, R.; Toro, J.C.; Hoffner, S.E.; Das, K.S. Glycine and alanine dehydrogenase activities are catalyzed by the same protein in Mycobacterium smegmatis: Upregulation of both activities under microaerophilic adaptation. Can. J. Microbiol. 2002, 48, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimshaw, C.E.; Cleland, W.W. Kinetic mechanism of Bacillus subtilis l-alanine dehydrogenase. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 5650–5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, S.M.; Ramachandran, R. Crystal structures of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis secretory antigen alanine dehydrogenase (Rv2780) in apo and ternary complex forms captures “open” and “closed” enzyme conformations. Proteins 2008, 72, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agren, D.; Stehr, M.; Berthold, C.L.; Kapoor, S.; Oehlmann, W.; Singh, M.; Schneider, G. Three-dimensional structures of apo- and holo-l-alanine dehydrogenase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveal conformational changes upon coenzyme binding J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 377, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, B.; Sun, M.; Bi, S.; Jing, Z.; Liu, Y. Molecular dynamics simulations of the coenzyme induced conformational changes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis l-alanine dehydrogenase. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2012, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haliloglu, T.; Bahar, I.; Erman, B. Gaussian dynamics of folded proteins. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 3090–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, I.; Atilgan, A.R.; Erman, B. Direct evaluation of thermal fluctuations in proteins using a single-parameter harmonic potential. Fold. Des. 1997, 2, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atilgan, A.R.; Durell, S.R.; Jernigan, R.L.; Demirel, M.C.; Keskin, O.; Bahar, I. Anisotropy of fluctuation dynamics of proteins with an elastic network model. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Jernigan, R.L. Molecular mechanism of domain swapping in proteins: An analysis of slower motions. Biophys. J. 2004, 86, 3846–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jernigan, R.L.; Demirel, M.C.; Bahar, I. Relating structure to function through the dominant slow modes of motion of DNA topoisomerase II. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1999, 75, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Rader, A.J.; Bahar, I.; Jernigan, R.L. Global ribosome motions revealed with elastic network model. J. Struct. Biol. 2004, 147, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirion, M.M. Large amplitude elastic motions in proteins from a single-parameter, atomic analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 1905–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J. Usefulness and limitations of normal mode analysis in modeling dynamics of biomolecular complexes. Structure 2005, 13, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.K.; Chirikjian, G.S.; Jernigan, R.L. Elastic models of conformational transitions in macromolecules. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2002, 21, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, M.C.; Atilgan, A.R.; Jernigan, R.L.; Erman, B.; Bahar, I. Identification of kinetically hot residues in proteins. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 2522–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haliloglu, T.; Keskin, O.; Ma, B.; Nussinov, R. How similar are protein folding and protein binding nuclei? Examination of vibrational motions of energy hot spots and conserved residues. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.G.; Xu, X.J.; Li, C.H.; Chen, W.Z.; Wang, C.X. Identification of key residues for protein conformational transition using elastic network model. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 174101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.G.; Du, H.J.; Hao, R.; Xu, X.J.; Li, C.H.; Chen, W.Z.; Wang, C.X. Identification of functionally key residues in AMPA receptor with a thermodynamic method. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2013, 117, 8689–8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, S.; Melton, J.S.; Sorensen, D.C.; Phillips, G.N. Dynamics of proteins in crystals: Comparison of experiment with simple models. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, I.; Atilgan, A.R.; Demirel, M.C.; Erman, B. Vibrational dynamics of folded proteins: Significance of slow and fast motions in relation to function and stability. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 2733–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD-visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Xie, F.; Zhang, J.C.; Su, J.G. Study, by use of coarse-grained models, of the functionally crucial residues and allosteric pathway of anesthetic regulation of the Gloeobacter violaceus ligand-gated ion channel. Eur. Biophys. J. 2014, 43, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahar, I.; Rader, A.J. Coarse-grained normal mode analysis in structural biology. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005, 15, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.-Y.; Zhang, J.-C.; Zhu, Y.-Y.; Su, J.-G. Domain Motions and Functionally-Key Residues of l-Alanine Dehydrogenase Revealed by an Elastic Network Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29383-29397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226170
Li X-Y, Zhang J-C, Zhu Y-Y, Su J-G. Domain Motions and Functionally-Key Residues of l-Alanine Dehydrogenase Revealed by an Elastic Network Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(12):29383-29397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226170
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xing-Yuan, Jing-Chao Zhang, Yan-Ying Zhu, and Ji-Guo Su. 2015. "Domain Motions and Functionally-Key Residues of l-Alanine Dehydrogenase Revealed by an Elastic Network Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 12: 29383-29397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226170
APA StyleLi, X.-Y., Zhang, J.-C., Zhu, Y.-Y., & Su, J.-G. (2015). Domain Motions and Functionally-Key Residues of l-Alanine Dehydrogenase Revealed by an Elastic Network Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(12), 29383-29397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226170




