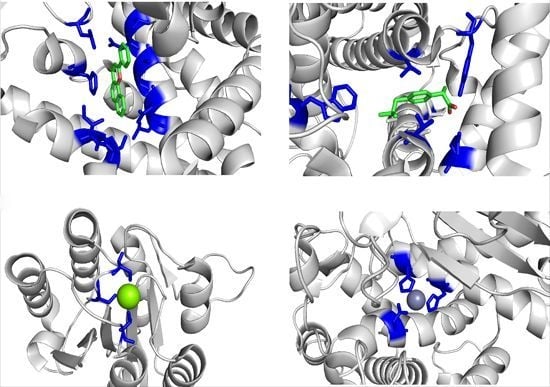
Proteins and Their Interacting Partners: An Introduction to Protein–Ligand Binding Site Prediction Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. In Silico Methods for the Prediction of Protein–Ligand Binding Sites and Their Associated Binding Site Residues
2.1. Sequence-Based Methods
2.2. Structure-Based Methods
2.2.1. Considerations When Employing Structure-Based Methods
2.2.2. Geometric Methods
2.2.3. Energetic Methods
2.2.4. Miscellaneous Methods
3. Methods for the Evaluation of Protein–Ligand Binding Site Residue Predictions
4. Prediction of Enzyme Commission Numbers (EC) and Gene Ontology Terms (GO)
5. CASP, CAFA, and CAMEO—Their Role in Development and Assessment of Protein–Ligand Binding Site Prediction Algorithms
6. The Application of in Silico Protein–Ligand Binding Site Prediction Methods: Impact on in Vitro Studies
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roche, D.B.; Buenavista, M.T.; McGuffin, L.J. FunFOLDQA: A quality assessment tool for protein–ligand binding site residue predictions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, D.B.; Buenavista, M.T.; McGuffin, L.J. Predicting protein structures and structural annotation of proteomes. In Encyclopedia of Biophysics; Roberts, G.C.K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Roche, D.B.; Buenavista, M.T.; McGuffin, L.J. The FunFOLD2 server for the prediction of protein–ligand interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, D.B.; Tetchner, S.J.; McGuffin, L.J. FunFOLD: An improved automated method for the prediction of ligand binding residues using 3D models of proteins. BMC Bioinforma. 2011, 12, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rang, H.P.; Ritter, J.M.; Flower, R.J.; Henderson, G. Rang and dale's pharmacology, 8th ed.; Elsevier Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, A.A.; Szklarz, G.D.; Scott, E.E. Human cytochrome P450 1A1 structure and utility in understanding drug and xenobiotic metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12932–12943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, M.G. Effects of CYP inducers and inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of intravenous theophylline in rats: Involvement of CYP1A1/2 in the formation of 1,3-DMU. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, G.; Ezkurdia, I.; Tress, M.L. Assessment of ligand binding residue predictions in CASP8. Proteins 2009, 77, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, C.; Karypis, G. Ligand-binding residue prediction. In Introduction to protein structure prediction: Methods and algorithms; Rangwala, H., Karypis, G., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yuriev, E.; Holien, J.; Ramsland, P.A. Improvements, trends, and new ideas in molecular docking: 2012–2013 in review. J. Mol. Recognit. 2015, 28, 581–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, K.; Feenstra, K.A.; Heringa, J.; Ijzerman, A.P.; Marchiori, E. Multi-relief: A method to recognize specificity determining residues from multiple sequence alignments using a machine-learning approach for feature weighting. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.-J.; Hu, J.; Yang, J.; Shen, H.-B.; Tang, J.; Yang, J.-Y. Designing template-free predictor for targeting protein–ligand binding sites with classifier ensemble and spatial clustering. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2013, 10, 994–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Huang, J.H.Z.; Gao, X. Ligandrfs: Random forest ensemble to identify ligand-binding residues from sequence information alone. BMC Bioinforma. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.J.; Hu, J.; Li, Q.M.; Tang, Z.M.; Yang, J.Y.; Shen, H.B. Constructing query-driven dynamic machine learning model with application to protein–ligand binding sites prediction. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2015, 14, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Sankararaman, S.; Kolaczkowski, B.; Sjolander, K. Intrepid: A web server for prediction of functionally important residues by evolutionary analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankararaman, S.; Sha, F.; Kirsch, J.F.; Jordan, M.I.; Sjolander, K. Active site prediction using evolutionary and structural information. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashkenazy, H.; Erez, E.; Martz, E.; Pupko, T.; Ben-Tal, N. Consurf 2010: Calculating evolutionary conservation in sequence and structure of proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J. Confunc—functional annotation in the twilight zone. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierschin, T.; Wang, K.; Welter, M.; Waack, S.; Stanke, M. Combining features in a graphical model to predict protein binding sites. Proteins 2015, 83, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kononenko, I. Estimating attributes: Analysis and extensions of relief. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Machine Learning; Springer-Verlag New York, Inc.: Catania, Italy, 1994; pp. 171–182. [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima, S.; Pokarowski, P.; Pokarowska, M.; Kolinski, A.; Katayama, T.; Kanehisa, M. AAindex: Amino acid index database, progress report 2008. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt, C. UniProt: A hub for protein information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 204–212. [Google Scholar]
- McGuffin, L.J.; Bryson, K.; Jones, D.T. The PSIPRED protein structure prediction server. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brylinski, M.; Skolnick, J. A threading-based method (FINDSITE) for ligand-binding site prediction and functional annotation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, J.C.; Martinez, M.; Henrich, S.; Stank, A.; Richter, S.; Wade, R.C. Ligdig: A web server for querying ligand-protein interactions. Bioinformatics 2015, 13, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.R.; Liu, C.K.; Hsiao, F.C.; Yao, A.; Hwang, M.J. LISE: A server using ligand-interacting and site-enriched protein triangles for prediction of ligand-binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Xiong, Y.; Kihara, D. Large-scale binding ligand prediction by improved patch-based method patch-surfer2.0. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitzer, R.; Cleves, A.E.; Jain, A.N. Surface-based protein binding pocket similarity. Proteins 2011, 79, 2746–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdin, S.; Ward, R.M.; Venner, E.; Lichtarge, O. Evolutionary trace annotation of protein function in the structural proteome. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 396, 1451–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivak, R.; Hoksza, D. Improving protein–ligand binding site prediction accuracy by classification of inner pocket points using local features. J. Cheminform. 2015, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kokubo, H.; Tanaka, T.; Okamoto, Y. Two-dimensional replica-exchange method for predicting protein–ligand binding structures. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2601–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Ishikawa, T.; Kuwata, K.; Takada, S. Protein-specific force field derived from the fragment molecular orbital method can improve protein–ligand binding interactions. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada, T.; Zhang, B.; Cicotti, P.; Armen, R.S.; Taufer, M. A scalable and accurate method for classifying protein–ligand binding geometries using a mapreduce approach. Comput. Biol. Med. 2012, 42, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desaphy, J.; Raimbaud, E.; Ducrot, P.; Rognan, D. Encoding protein–ligand interaction patterns in fingerprints and graphs. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.C.A.; Nassif, H.; Page, D.; Muggleton, S.H.; Sternberg, M.J.E. Automated identification of protein–ligand interaction features using inductive logic programming: A hexose binding case study. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, L.; Vert, J.P. Protein-ligand interaction prediction: An improved chemogenomics approach. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, M.H.; Schmitt, F.; Herz, T.; Kramer, B. Propose: A docking engine based on a fully configurable protein–ligand interaction model. J. Mol. Model. 2004, 10, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Sillitoe, I.; Lee, D.; Lees, J.G.; Dawson, N.L.; Ward, J.; Orengo, C.A. Cath funfhmmer web server: Protein functional annotations using functional family assignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Liang, Z.; Teng, M.; Niu, L. Mfasd: A structure-based algorithm for discriminating different types of metal-binding sites. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1938–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konc, J.; Janezic, D. Probis-2012: Web server and web services for detection of structurally similar binding sites in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konc, J.; Janezic, D. Probis algorithm for detection of structurally similar protein binding sites by local structural alignment. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krotzky, T.; Fober, T.; Hullermeier, E.; Klebe, G. Extended graph-based models for enhanced similarity search in cavbase. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2014, 11, 878–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, S.; Kuhn, D.; Klebe, G. A new method to detect related function among proteins independent of sequence and fold homology. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 323, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, M.; Ghersi, D.; Sanchez, R. Sitehound-web: A server for ligand binding site identification in protein structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amari, S.; Aizawa, M.; Zhang, J.; Fukuzawa, K.; Mochizuki, Y.; Iwasawa, Y.; Nakata, K.; Chuman, H.; Nakano, T. Viscana: Visualized cluster analysis of protein–ligand interaction based on the ab initio fragment molecular orbital method for virtual ligand screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2006, 46, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Yoo, S.; Sanchez, R. Sitecomp: A server for ligand binding site analysis in protein structures. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1172–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozakov, D.; Grove, L.E.; Hall, D.R.; Bohnuud, T.; Mottarella, S.E.; Luo, L.; Xia, B.; Beglov, D.; Vajda, S. The FTMap family of web servers for determining and characterizing ligand-binding hot spots of proteins. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 733–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Roy, A.; Zhang, Y. Protein-ligand binding site recognition using complementary binding-specific substructure comparison and sequence profile alignment. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2588–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Cofactor: An accurate comparative algorithm for structure-based protein function annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, L.; Shin, W.H.; Lee, M.S.; Seok, C. GalaxySite: Ligand-binding-site prediction by using molecular docking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izidoro, S.C.; de Melo-Minardi, R.C.; Pappa, G.L. GASS: Identifying enzyme active sites with genetic algorithms. Bioinformatics 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Li, B.; Cheng, L.T.; Zhou, S.; McCammon, J.A.; Che, J. Identification of protein–ligand binding sites by the level-set variational implicit-solvent approach. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salentin, S.; Schreiber, S.; Haupt, V.J.; Adasme, M.F.; Schroeder, M. Plip: Fully automated protein–ligand interaction profiler. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Schroeder, M. Ligsitecsc: Predicting ligand binding sites using the connolly surface and degree of conservation. BMC Struct. Biol. 2006, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, C.D.; Chen, B.Y.; Linusson, A. Mapping of ligand-binding cavities in proteins. Proteins 2010, 78, 1408–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, D.B.; McGuffin, L.J. In silico identification and characterization of protein–ligand binding sites, methods in molecular biology. In Structure based and computational design of ligand binding proteins; Stoddard, B., Baker, D., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hastings, J.; de Matos, P.; Dekker, A.; Ennis, M.; Harsha, B.; Kale, N.; Muthukrishnan, V.; Owen, G.; Turner, S.; Williams, M.; et al. The ChEBi reference database and ontology for biologically relevant chemistry: Enhancements for 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, S.; Yamada, T.; Hamajima, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Bork, P.; Goto, S.; Kanehisa, M. KEGG Atlas mapping for global analysis of metabolic pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.R.; Hwang, M.J. An interaction-motif-based scoring function for protein–ligand docking. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrey, D.; Chen, T.S.; Deng, L.; Garzon, J.I.; Hwang, H.; Lasso, G.; Lee, H.; Silkov, A.; Honig, B. Template-based prediction of protein function. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 32, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, D.B.; Buenavista, M.T.; Tetchner, S.J.; McGuffin, L.J. The intfold server: An integrated web resource for protein fold recognition, 3D model quality assessment, intrinsic disorder prediction, domain prediction and ligand binding site prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuffin, L.J.; Atkins, J.D.; Salehe, B.R.; Shuid, A.N.; Roche, D.B. IntFOLD: An integrated server for modelling protein structures and functions from amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, J.; Roth, S.; Arnold, K.; Kiefer, F.; Schmidt, T.; Bordoli, L.; Schwede, T. The protein model portal—A comprehensive resource for protein structure and model information. Database 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Skolnick, J. Tm-align: A protein structure alignment algorithm based on the TM-score. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2302–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Roy, A.; Zhang, Y. Biolip: A semi-manually curated database for biologically relevant ligand-protein interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, D.B.; Tetchner, S.J.; McGuffin, L.J. The binding-site distance test score: A robust method for the assessment of predicted protein binding sites. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2920–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, B.W. Comparison of the predicted and observed secondary structure of T4 phage lysozyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1975, 405, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gene Ontology Consortium. Gene ontology consortium: Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Capra, J.A.; Laskowski, R.A.; Thornton, J.M.; Singh, M.; Funkhouser, T.A. Predicting protein ligand binding sites by combining evolutionary sequence conservation and 3D structure. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furnham, N.; Holliday, G.L.; de Beer, T.A.; Jacobsen, J.O.; Pearson, W.R.; Thornton, J.M. The catalytic site atlas 2.0: Cataloging catalytic sites and residues identified in enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talavera, D.; Laskowski, R.A.; Thornton, J.M. Wssas: A web service for the annotation of functional residues through structural homologues. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1192–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.; Haas, J.; Gallo Cassarino, T.; Schwede, T. Assessment of ligand-binding residue predictions in casp9. Proteins 2011, 79, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo Cassarino, T.; Bordoli, L.; Schwede, T. Assessment of ligand binding site predictions in CASP10. Proteins 2014, 82, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, A.G.; Tipton, K.F. Fifty-five years of enzyme classification: Advances and difficulties. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piovesan, D.; Giollo, M.; Leonardi, E.; Ferrari, C.; Tosatto, S.C. Inga: Protein function prediction combining interaction networks, domain assignments and sequence similarity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlt, J.A.; Bouvier, J.T.; Davidson, D.B.; Imker, H.J.; Sadkhin, B.; Slater, D.R.; Whalen, K.L. Enzyme function initiative-enzyme similarity tool (EFI-EST): A web tool for generating protein sequence similarity networks. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1854, 1019–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahraeian, S.M.; Luo, K.R.; Brenner, S.E. Sifter search: A web server for accurate phylogeny-based protein function prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundersen, G.W.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Kou, Y.; Monteiro, C.D.; Feldmann, A.S.; Hu, K.S.; Ma’ayan, A. Geo2enrichr: Browser extension and server app to extract gene sets from geo and analyze them for biological functions. Bioinformatics 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskinen, P.; Toronen, P.; Nokso-Koivisto, J.; Holm, L. Pannzer: High-throughput functional annotation of uncharacterized proteins in an error-prone environment. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Zhu, H.; Domeniconi, C. Predicting protein functions using incomplete hierarchical labels. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Mori, H.; Zhang, C.; Kurokawa, K.; Xing, X.H.; Yamada, T. Domsign: A top-down annotation pipeline to enlarge enzyme space in the protein universe. BMC Bioinforma. 2015, 16, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radivojac, P.; Clark, W.T.; Oron, T.R.; Schnoes, A.M.; Wittkop, T.; Sokolov, A.; Graim, K.; Funk, C.; Verspoor, K.; Ben-Hur, A.; et al. A large-scale evaluation of computational protein function prediction. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.; Joo, K.; Lee, J. Protein-binding site prediction based on three-dimensional protein modeling. Proteins 2009, 77, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wass, M.N.; Kelley, L.A.; Sternberg, M.J. 3DLigandsite: Predicting ligand-binding sites using similar structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xue, S.; Yang, J.J. Calciomics: Integrative studies of Ca2+-binding proteins and their interactomes in biological systems. Metallomics 2013, 5, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Don, C.G.; Riniker, S. Scents and sense: In silico perspectives on olfactory receptors. J. Comput. Chem. 2014, 35, 2279–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arredondo, J.; Lara, M.; Ng, F.; Gochez, D.A.; Lee, D.C.; Logia, S.P.; Nguyen, J.; Maselli, R.A. Cooh-terminal collagen Q (COLQ) mutants causing human deficiency of endplate acetylcholinesterase impair the interaction of ColQ with proteins of the basal lamina. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Q.; Menon, R.; Omenn, G.S.; Zhang, Y. Structural bioinformatics inspection of nextprot PE5 proteins in the human proteome. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 3750–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindschedler, L.V.; McGuffin, L.J.; Burgis, T.A.; Spanu, P.D.; Cramer, R. Proteogenomics and in silico structural and functional annotation of the barley powdery mildew blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei. Methods 2011, 54, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, C.; Ver Loren van Themaat, E.; McGuffin, L.J.; Abbott, J.C.; Burgis, T.A.; Barton, G.; Bindschedler, L.V.; Lu, X.; Maekawa, T.; Wessling, R.; et al. Structure and evolution of barley powdery mildew effector candidates. BMC Genomics 2012, 13, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlidi, N.; Tseliou, V.; Riga, M.; Nauen, R.; Van Leeuwen, T.; Labrou, N.E.; Vontas, J. Functional characterization of glutathione S-transferases associated with insecticide resistance in Tetranychus urticae. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 121, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, T.B.; Mulley, G.; Dills, A.H.; Alsohim, A.S.; McGuffin, L.J.; Studholme, D.J.; Silby, M.W.; Brockhurst, M.A.; Johnson, L.J.; Jackson, R.W. Evolutionary resurrection of flagellar motility via rewiring of the nitrogen regulation system. Science 2015, 347, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roche, D.B.; Brackenridge, D.A.; McGuffin, L.J. Proteins and Their Interacting Partners: An Introduction to Protein–Ligand Binding Site Prediction Methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29829-29842. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226202
Roche DB, Brackenridge DA, McGuffin LJ. Proteins and Their Interacting Partners: An Introduction to Protein–Ligand Binding Site Prediction Methods. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(12):29829-29842. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226202
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoche, Daniel Barry, Danielle Allison Brackenridge, and Liam James McGuffin. 2015. "Proteins and Their Interacting Partners: An Introduction to Protein–Ligand Binding Site Prediction Methods" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 12: 29829-29842. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226202
APA StyleRoche, D. B., Brackenridge, D. A., & McGuffin, L. J. (2015). Proteins and Their Interacting Partners: An Introduction to Protein–Ligand Binding Site Prediction Methods. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(12), 29829-29842. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226202