Therapeutic Strategies and New Intervention Points in Chronic Hepatitis Delta Virus Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. HDV Biology
2.1. HDV Structure
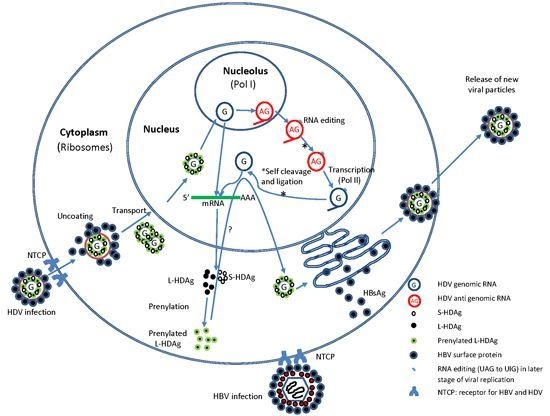
2.2. HDV Life Cycle

2.3. HDV Pathogenesis
2.4. Therapeutic Strategies in CHD
2.4.1. Immunomodulatory Drugs
2.4.2. HBV Polymerase Inhibition as Standalone Therapy
2.4.3. Prenylation Inhibitors
| Compound(s) Tested/Class | Class | Phase of Trial (n) | Sponsor | Status as of this Writing | Publication/Observations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) EBP921 | prenylation inhibitor | Phase 1 (8) | Eiger | Unknown | NA |
| (1) Lonafarnib | (1) farnesyl transferase inhibitor | Phase 2 (40) | Eiger | Recruiting | NA |
| (2) Ritonavir | (2) inhibitor of HIV protease and CYP3A4 | ||||
| (1) Lonafarnib | (1) see above | Phase 2 (21) | Eiger | Recruitiung | Ritonavir + lonafarnib: 3.2 log10 decline in viral load was observed at week 8 of treatment |
| (2) Ritonavir | (2) see above | ||||
| (3) Peginterferon | (3) immunomod | ||||
| (1) Peginterferon alpha2A | (1) immunomod | Phase 2 (13) | NIDDK | Completed (results published) | Heller, Rotman et al. (2014) [44] |
| (1) REP 2139-Ca | (1) NAP:blocks HBV subviral particle formation | Phase 2 (12) | REPLIcor | Ongoing (not recruiting) mid 2016 estimated completion | ~6 log10 decline HDV RNA, standalone REP2139-Ca |
| (2) Pegasys® | (2) immunomod | ||||
| (1) Ribavirin | (1) nucleoside inhibitor | Phase 4 (20) | National Taiwan Univer. Hospital | Unknown | NA |
| (2) Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2B | (2) immunomod | ||||
| (1) Peginterferon alpha2A | (1) immunomod | Observational | Hoffman LaRoche | Ongoing, not recruiting | NA |
| (1) Peginterferon alpha2A | (1) immunomod | Phase 2 (70) | HepNet Study house; Hoffman La-Roche; Gilead | Ongoing, not recruiting | NA |
| (2) Tenofovir | (2) nucleotide analog | ||||
| (1) Lonafarnib | (1) farnesyl transferase inhibitor | Phase 2 (14) | NIDDK | Completed | NA |
| (1) Peginterferon alpha2A | (1) immunomod | Phase 3 (50) | Hoffman-La Roche | Ongoing, not recruiting | NA |
| (2) Tenofovir | (2) nucleotide analog | ||||
| (1) Myrcludex B | (1) hepatocyte entry | Phase 2a (24) | Hepatera | Completed | Myr standalone: >1Log10 HDV RNA decline and ALT normalization in 4 subjects at week 24 |
| 2) PEG-IFNa | (2) immunomod |
2.4.4. RNA Interference
2.4.5. Nucleic Acid Polymers
2.4.6. Therapeutic Vaccines
2.4.7. Blocking Viral Entry
2.4.8. Other Points of Intervention
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, E.; Yoneda, M.; Schiff, E.R. Viral Hepatitis: Past and Future of HBV and HDV. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021245 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandri, M.; Lütgehetmann, M. Mouse models of hepatitis B and delta virus infection. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 410, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattovich, G.; Giustina, G.; Christensen, E.; Pantalena, M.; Zagni, I.; Realdi, G.; Schalm, S.W. Influence of hepatitis delta virus infection on morbidity and mortality in compensated cirrhosis type B. Gut 2000, 46, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cross, T.J.S.; Rizzi, P.; Horner, M.; Jolly, A.; Hussain, M.J.; Smith, H.M.; Vergani, D.; Harrison, P.M. The Increasing Prevalence of Hepatitis Delta Virus (HDV) Infection in South London. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 282, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascarella, S.; Negro, F. Hepatitis D Virus: An update. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.-C.; Wu, S.-M.; Lin, P.-H.; Sheng, W.-H.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Tsai, M.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Huang, M.S.; Chang, S.F.; et al. Increasing incidence of recent hepatitis D virus infection in HIV-infected patients in an area hyperendemic for hepatitis B virus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucirka, L.M.; Farzadegan, H.; Feld, J.J.; Mehta, H.; Winters, M.; Glenn, S.J.; Kirk, G.D.; Segev, D.L.; Nelson, K.E.; Marks, M.; et al. Prevalence, Correlates, and Viral Dynamics of Hepatitis Delta Among Injection Drug Users. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurdaydin, C. Treatment of Chronic Delta Hepatitis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidrich, B.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H. Treatment options for hepatitis delta virus infection. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2013, 15, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noureddin, M.; Gish, R. Hepatitis Delta: Epidemiology, Diagnosis and Management 36 Years after Discovery. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2013, 16, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.M. Virology of hepatitis D virus. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, A.M.Y.J.; Choo, Q.; Wang, K.; Govindarajan, S.; Allan, G.; Gerin, J.L.; Houghton, M. A Single Antigenomic Open Reading Frame of the Hepatitis Delta Virus Encodes the Epitope (s) of Both Hepatitis Delta Antigen Polypeptides p248 and p278. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zuccola, H.J.; Rozzelle, J.E.; Lemon, S.M.; Erickson, B.W.; Hogle, J.M. Structural basis of the oligomerization of hepatitis delta antigen. Structure 1998, 6, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, W.; Bayer, M.; Taylor, J. Assembly of Hepatitis Delta Virus Particles. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 2310–2315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gudima, S.; He, Y.; Meier, A.; Chang, J.; Chen, R.; Jarnik, M.; Nicolas, E.; Bruss, V.; Taylor, J. Assembly of hepatitis delta virus: Particle characterization, including the ability to infect primary human hepatocytes. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3608–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, S.; Bartenschlager, R.; Kubitz, R.; Zoulim, F. Strategies to inhibit entry of HBV and HDV into hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, A.; Gripon, P.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B virus infection initiates with a large surface protein-dependent binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Mehrle, S.; Nkongolo, S.; Kaufman, C.; Fälth, M.; Stindt, J.; Königer, C.; Nassal, M.; Kubitz, R.; et al. Hepatitis B and D viruses exploit sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide for species-specific entry into hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Ren, B.; Mao, F.; Jing, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Peng, B.; Yan, H.; Qi, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Hepatitis D Virus infection of mice expressing human sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-J.; Macnaughton, T.; Gao, L.; Lai, M.M.C. RNA-templated replication of hepatitis delta virus: Genomic and antigenomic RNAs associate with different nuclear bodies. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6478–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco-Stewart, V.S.; Schissel, E.; Pelchat, M. The hepatitis delta virus RNA genome interacts with the human RNA polymerases I and III. Virology 2009, 386, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, D.; Schütte, C.; Warnecke, J.; Dorn, I.; Hennig, H.; Kirchner, H.; Schlenke, P. The large form of ADAR1 is responsible for enhanced hepatitis delta virus RNA editing in interferon-alpha-stimulated host cells. J. Viral Hepat. 2006, 13, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Alves, C.; Gudima, S.; Taylor, J. Intracellular localization of hepatitis delta virus proteins in the presence and absence of viral RNA accumulation. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6457–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maydanovych, O.; Beal, P.A. Breaking the central dogma by RNA editing. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 3397–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.L.; Chen, P.J.; Tu, S.-J.; Wang, C.-J.; Chen, D.-S. The large form of hepatitis delta antigen is crucial for assembly of hepatitis delta virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 8490–8494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.B.; Lai, M.M. Isoprenylation masks a conformational epitope and enhances trans-dominant inhibitory function of the large hepatitis delta antigen. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 2958–2964. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.-H.; Cheng, T.-S.; Shu, C.-Y.; Jeng, K.-S.; Lai, M.M.C. Modification of small hepatitis delta virus antigen by SUMO protein. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.M. Hepatitis delta virus. Virology 2006, 344, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, Z.; Afzal, R. Life cycle and pathogenesis of hepatitis D virus: A review. World J. Hepatol. 2013, 5, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.; Davidson, A.; Hibbert, L.; Gruenwald, P.; Schlaak, J.; Ball, S.; Foster, G.R.; Jacobs, M. Dengue Virus inhibits alpha interferon signaling by reducing STAT2 expression. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5414–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randall, R.E.; Goodbourn, S. Interferons and viruses: An interplay between induction, signalling, antiviral responses and virus countermeasures. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugnale, P.; Pazienza, V.; Guilloux, K.; Negro, F. Hepatitis delta virus inhibits alpha interferon signaling. Hepatology 2009, 49, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, S.P.; Chin, D.J.; Cheng, D.T.; Ravindran, P.; Bitter, H.; Gruenbaum, L.; Cote, P.J.; Ma, H.; Klumpp, K.; Menne, S. Identification of an intrahepatic transcriptional signature associated with self-limiting infection in the woodchuck model of hepatitis B. Hepatology 2013, 57, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, V.; Brichler, S.; Khan, E.; Chami, M.; Dény, P.; Kremsdorf, D.; Gordien, E. Large hepatitis delta antigen activates STAT-3 and NF-κB via oxidative stress. J. Viral Hepat. 2012, 19, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, F.-T.; Lee, Y.-J.; Ko, J.-L.; Tsai, C.-C.; Tseng, C.-J.; Sheu, G.T. Hepatitis delta virus epigenetically enhances clusterin expression via histone acetylation in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.K.; Hong, S.W.; Lee, H.; Kim, W.H. Overexpression of clusterin in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2004, 35, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, M.; Pérez-Hernandez, D.; Vázquez, J.; Coelho, A.V.; Cunha, C. Proteomic changes in HEK-293 cells induced by hepatitis delta virus replication. J. Proteomics 2013, 89, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, T.H.; Kemmler, C.B.; Guo, Z.; Mann, D.; Lu, Y.; Coeshott, C.; Gehring, A.J.; Bertoletti, A.; Ho, Z.Z.; Delaney, W.; et al. A whole recombinant yeast-based therapeutic vaccine elicits HBV X, S and Core specific T cells in mice and activates human T cells recognizing epitopes linked to viral clearance. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurdaydin, C.; Bozkaya, H.; Önder, F.O.; Şentürk, H.; Karaaslan, H.; Akdoǧan, M.; Cetinkaya, H.; Erden, E.; Erkan-Esin, O.; Yalçin, K.; et al. Treatment of chronic delta hepatitis with lamivudine vs lamivudine + interferon vs interferon. J. Viral Hepat. 2008, 15, 314–321. [Google Scholar]
- Kabacam, G.; Dalekos, G.N.; Cakaloglu, K.; Kalliopi; Zachou, K.; Bock, T.; Erhardt, A.; Zeuzem, S.; Tabak, F.; Yalçin, K.; et al. Pegylated interferon-based treatment in patients with advanced liver disease due to chronic delta hepatitis. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 23, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castelnau, C.; le Gal, F.; Ripault, M.-P.; Gordien, E.; Martinot-Peignoux, M.; Boyer, N.; Pham, B.N.; Maylin, S.; Bedossa, P.; Dény, P.; et al. Efficacy of peginterferon alpha-2b in chronic hepatitis delta: Relevance of quantitative RT-PCR for follow-up. Hepatology 2006, 44, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niro, G.A.; Ciancio, A.; Gaeta, G.B.; Smedile, A.; Marrone, A.; Olivero, A.; Stanzione, M.; David, E.; Brancaccio, G.; Fontana, R.; et al. Pegylated interferon alpha-2b as monotherapy or in combination with ribavirin in chronic hepatitis delta. Hepatology 2006, 44, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahcecioglu, I.H.; Ispiroglu, M.; Demirel, U.; Yalniz, M. Pegylated Interferon α Therapy in Chronic Delta Hepatitis: A One-Center Experience. Hepat. Mon. 2015, 15, e24366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, T.; Rotman, Y.; Koh, C.; Clark, S.; Haynes-Williams, V.; Chang, R.; McBurney, R.; Schmid, P.; Albrecht, J.; Kleiner, D.E.; et al. Long-term therapy of chronic delta hepatitis with peginterferon alfa. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, W.; Ducancelle, A.; le Gal, F.; le Guillou-Guillemette, H.; Abgueguen, P.; Pivert, A.; Calès, P.; Gordien, E.; Lunel, F. Resolution of chronic hepatitis Delta after 1 year of combined therapy with pegylated interferon, tenofovir and emtricitabine. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 47, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pollicino, T.; Raffa, G.; Santantonio, T.; Gaeta, G.B.; Iannello, G.; Alibrandi, A.; Squadrito, G.; Cacciola, I.; Calvi, C.; Colucci, G.; et al. Replicative and transcriptional activities of hepatitis B virus in patients coinfected with hepatitis B and hepatitis delta viruses. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boffito, M. From Concept to Care: Pharmacokinetic Boosting of Protease Inhibitors. PRN Notebook 2004, 9, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, C.; Canini, L.; Dahari, H.; Zhao, X.; Uprichard, S.L.; Haynes-Williams, V.; Winters, M.A.; Subramanya, G.; Cooper, S.L.; Pinto, P.; et al. Oral prenylation inhibition with lonafarnib in chronic hepatitis D infection: A proof-of-concept randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2A trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordier, B.B.; Ohkanda, J.; Liu, P.; Lee, S.; Salazar, F.H.; Marion, P.L.; Ohashi, K.; Meuse, L.; Kay, M.A.; Casey, J.L.; et al. In vivo antiviral efficacy of prenylation inhibitors against hepatitis delta virus. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravoet, C.; Mineur, P.; Robin, V.; Debusscher, L.; Bosly, A.; André, M.; el Housni, H.; Soree, A.; Bron, D.; Martiat, P. Farnesyl transferase inhibitor (lonafarnib) in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or secondary acute myeloid leukaemia: A phase II study. Ann. Hematol. 2008, 87, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerklaan, B.M.; Diéras, V.; le Tourneau, C.; Mergui-Roelvink, M.; Huitema, A.D.; Rosing, H.; Beijnen, J.H.; Marreaud, S.; Govaerts, A.S.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.J.; et al. Phase 1 study of lonafarnib (SCH66336) in combination with trastuzumab plus paclitaxel in Her2/neu overexpressing breast cancer: EORTC study 16023. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, A.; Barros, S.; Ivanciu, L.; Cooley, B.; Qin, J.; Racie, T.; Hettinger, J.; Carioto, M.; Jiang, Y.; Brodsky, J.; et al. An RNAi therapeutic targeting antithrombin to rebalance the coagulation system and promote hemostasis in hemophilia. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geary, R.S.; Norris, D.; Yu, R.; Bennett, C.F. Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and cell uptake of antisense oligonucleotides. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 87, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, T.; Adams, D.; Silva, A.; Lozeron, P.; Hawkins, P.N.; Mant, T.; Perez, J.; Chiesa, J.; Warrington, S.; Tranter, E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of RNAi therapy for transthyretin amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooke, S.T.; Geary, R.S. Clinical pharmacological properties of mipomersen (Kynamro), a second generation antisense inhibitor of apolipoprotein B. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 76, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooddell, C.I.; Rozema, D.B.; Hossbach, M.; John, M.; Hamilton, H.L.; Chu, Q.; Hegge, J.O.; Klein, J.J.; Wakefield, D.H.; Oropeza, C.E.; et al. Hepatocyte-targeted RNAi therapeutics for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Nischal, A.; Khattri, S.; Nath, R.; Pant, K.K.; Seth, P.K. Design of potential siRNA molecules for hepatitis delta virus gene silencing. Bioinformation 2012, 8, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noordeen, F.; Vaillant, A.; Jilbert, A.R. Nucleic acid polymers prevent the establishment of duck hepatitis B virus infection in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5299–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosinska, A.D.; Zhang, E.; Johrden, L.; Liu, J.; Seiz, P.L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Kemper, T.; Fiedler, M.; Glebe, D.; et al. Combination of DNA prime-adenovirus boost immunization with entecavir elicits sustained control of chronic hepatitis B in the woodchuck model. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggar, A.; Coeshott, C.; Apelian, D.; Rodell, T.; Armstrong, B.R.; Shen, G.; Subramanian, G.M.; McHutchison, J.G. Safety, tolerability and immunogenicity of GS-4774, a hepatitis B virus-specific therapeutic vaccine, in healthy subjects: A randomized study. Vaccine 2014, 32, 4925–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiedler, M.; Kosinska, A.; Schumann, A.; Brovko, O.; Walker, A.; Lu, M.; Johrden, L.; Mayer, A.; Wildner, O.; Roggendorf, M. Prime/boost immunization with DNA and adenoviral vectors protects from hepatitis D virus (HDV) infection after simultaneous infection with HDV and woodchuck hepatitis virus. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7708–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Hsu, S.; Syu, W. Varied immunity generated in mice by DNA vaccines with large and small Hepatitis Delta Antigens. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 12980–12985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauch, C.; Grimm, C.; Meckel, S.; Wands, J.R.; Blum, H.E.; Roggendorf, M.; Geissler, M. Induction of cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses against hepatitis delta virus antigens which protect against tumor formation in mice. Vaccine 2002, 20, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-C.; Kao, J.-H. Viral hepatitis. HBV cure-can we pin our hopes on immunotherapy? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giersch, K.; Allweiss, L.; Volz, T.; Helbig, M.; Bierwolf, J.; Lohse, A.W.; Pollok, J.M.; Petersen, J.; Dandri, M.; Lütgehetmann, M. Hepatitis Delta co-infection in humanized mice leads to pronounced induction of innate immune responses in comparison to HBV mono-infection. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchmann, P.; Dembek, C.; Kuklick, L.; Jäger, C.; Tedjokusumo, R.; von Freyend, M.J.; Drebber, U.; Janowicz, Z.; Melber, K.; Protzer, U. A novel therapeutic hepatitis B vaccine induces cellular and humoral immune responses and breaks tolerance in hepatitis B virus (HBV) transgenic mice. Vaccine 2013, 31, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhl, P.; Fricker, G.; Haberkorn, U.; Mier, W. Current status in the therapy of liver diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 7500–7512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliseev, A. Maxwell Biotech Portfolio Company Hepatera Announces Proof-of-Concept Clinical Results with Myrcludex B, a Novel Entry Inhibitor for Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B and Delta. 2014. Available online: http://webcitation.org/6aVvi8aT5 (accessed on 3 August 2015).
- Hartner, J.C.; Schmittwolf, C.; Kispert, A.; Müller, A.M.; Higuchi, M.; Seeburg, P.H. Liver Disintegration in the Mouse Embryo Caused by Deficiency in the RNA-editing Enzyme ADAR1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4894–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, I.; Been, M.D. Catalytic strategies of the hepatitis delta virus ribozymes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 887–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokowa-Sołtys, K.; Gaggelli, N.; Nagaj, J.; Szczepanik, W.; Ciesiołka, J.; Wrzesiński, J.; Górska, A.; Gaggelli, E.; Valensin, G.; Jeżowska-Bojczuk, M. High affinity of copper(II) towards amoxicillin, apramycin and ristomycin. Effect of these complexes on the catalytic activity of HDV ribozyme. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2013, 124, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Chen, P.-J. Phosphorylation of serine 177 of the small hepatitis delta antigen regulates viral antigenomic RNA replication by interacting with the processive RNA polymerase II. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; King, T. Therapeutic Strategies and New Intervention Points in Chronic Hepatitis Delta Virus Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 19537-19552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160819537
Guo Z, King T. Therapeutic Strategies and New Intervention Points in Chronic Hepatitis Delta Virus Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(8):19537-19552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160819537
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zhimin, and Thomas King. 2015. "Therapeutic Strategies and New Intervention Points in Chronic Hepatitis Delta Virus Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 8: 19537-19552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160819537
APA StyleGuo, Z., & King, T. (2015). Therapeutic Strategies and New Intervention Points in Chronic Hepatitis Delta Virus Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(8), 19537-19552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160819537