Ischemia, Immunosuppression and Infection—Tackling the Predicaments of Post-Stroke Complications
Abstract
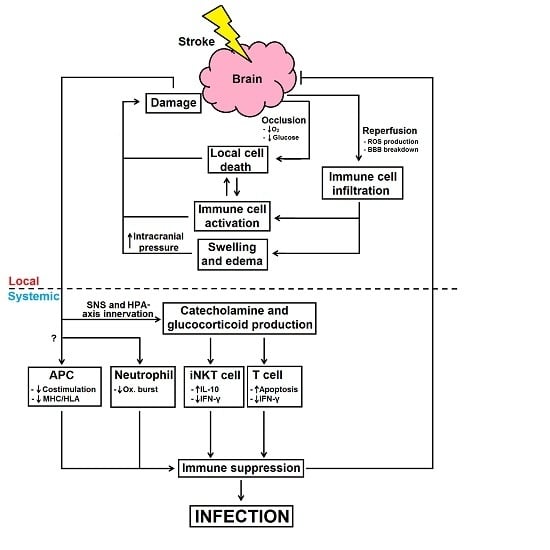
:1. Introduction
2. Local Immune Responses and Impairment after Stroke
3. Infections after Stroke
4. Stroke-Induced Immune Suppression

5. Other Causes of Infection after Stroke
6. Treatments for Stroke-Associated Infections
6.1. Antibiotics
6.2. Immune Modulation
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Mensah, G.A.; Connor, M.; Bennett, D.A.; Moran, A.E.; Sacco, R.L.; Anderson, L.; Truelsen, T.; et al. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990–2010: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease study 2010. Lancet 2014, 383, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, J.; Mensah, G.A. The atlas of heart disease and stroke. In The Atlas of Heart Disease and Stroke; Ann, H., Ed.; World Heath Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Chapter 16; pp. 52–53. [Google Scholar]
- Strong, K.; Mathers, C.; Bonita, R. Preventing stroke: Saving lives around the world. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadilhac, D.A.; Carter, R.; Thrift, A.G.; Dewey, H.M. Estimating the long-term costs of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke for australia: New evidence derived from the north east melbourne stroke incidence study (NEMESIS). Stroke 2009, 40, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; de Ferranti, S.; Despres, J.P.; Fullerton, H.J.; Howard, V.J.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2015 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 131, e29–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, T.W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.T. Excitotoxicity and stroke: Identifying novel targets for neuroprotection. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 115, 157–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.; Lee, S.T.; Sinn, D.I.; Ko, S.Y.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, S.J.; Park, D.K.; Jung, K.H.; Song, E.C.; et al. Pharmacological induction of ischemic tolerance by glutamate transporter-1 (EAAT2) upregulation. Stroke 2007, 38, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, N.R.; Muyderman, H. Mitochondria, oxidative metabolism and cell death in stroke. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2010, 1802, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohacek, I.; Cordeau, P.; Lalancette-Hebert, M.; Gorup, D.; Weng, Y.-C.; Gajovic, S.; Kriz, J. Toll-like receptor 2 deficiency leads to delayed exacerbation of ischemic injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesz, A.; Dalpke, A.; Mracsko, E.; Antoine, D.J.; Roth, S.; Zhou, W.; Yang, H.; Na, S.Y.; Akhisaroglu, M.; Fleming, T.; et al. DAMP signaling is a key pathway inducing immune modulation after brain injury. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansing, L.H.; Harris, T.H.; Welsh, F.A.; Kasner, S.E.; Hunter, C.A.; Kariko, K. Toll-like receptor 4 contributes to poor outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, G.; Granger, D.N. Leukocyte recruitment and ischemic brain injury. Neuromol. Med. 2010, 12, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gertz, K.; Kronenberg, G.; Kälin, R.E.; Baldinger, T.; Werner, C.; Balkaya, M.; Eom, G.D.; Hellmann–Regen, J.; Kröber, J.; Miller, K.R.; et al. Essential role of interleukin-6 in post-stroke angiogenesis. Brain 2012, 135, 1964–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradillo, J.M.; Denes, A.; Greenhalgh, A.D.; Boutin, H.; Drake, C.; McColl, B.W.; Barton, E.; Proctor, S.D.; Russell, J.C.; Rothwell, N.J.; et al. Delayed administration of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist reduces ischemic brain damage and inflammation in comorbid rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, C.D.; Lopez-Castejon, G.; Denes, A.; Brough, D. NLRP3–inflammasome activating DAMPs stimulate an inflammatory response in glia in the absence of priming which contributes to brain inflammation after injury. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenglet, S.; Montecucco, F.; Denes, A.; Coutts, G.; Pinteaux, E.; Mach, F.; Schaller, K.; Gasche, Y.; Copin, J.C. Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator enhances microglial cell recruitment after stroke in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscher, K.; Kuric, E.; Liu, Y.; Walter, H.L.; Issazadeh-Navikas, S.; Englund, E.; Wieloch, T. Inhibition of CXCL12 signaling attenuates the postischemic immune response and improves functional recovery after stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesz, A.; Zhou, W.; Mracskó, É.; Karcher, S.; Bauer, H.; Schwarting, S.; Sun, L.; Bruder, D.; Stegemann, S.; Cerwenka, A.; et al. Inhibition of lymphocyte trafficking shields the brain against deleterious neuroinflammation after stroke. Brain 2011, 134, 704–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramov, A.Y.; Scorziello, A.; Duchen, M.R. Three distinct mechanisms generate oxygen free radicals in neurons and contribute to cell death during anoxia and reoxygenation. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuschmann, P.U.; Kolominsky-Rabas, P.L.; Misselwitz, B.; Hermanek, P.; Leffmann, C.; Janzen, R.; Rother, J.; Buecker-Nott, H.-J.; Berger, K.; et al. Predictors of in-hospital mortality and attributable risks of death after ischemic stroke: The German Stroke Registers Study Group. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahedi, K.; Hofmeijer, J.; Juettler, E.; Vicaut, E.; George, B.; Algra, A.; Amelink, G.J.; Schmiedeck, P.; Schwab, S.; Rothwell, P.M.; et al. Early decompressive surgery in malignant infarction of the middle cerebral artery: A pooled analysis of three randomised controlled trials. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelderblom, M.; Leypoldt, F.; Steinbach, K.; Behrens, D.; Choe, C.U.; Siler, D.A.; Arumugam, T.V.; Orthey, E.; Gerloff, C.; Tolosa, E.; et al. Temporal and spatial dynamics of cerebral immune cell accumulation in stroke. Stroke 2009, 40, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliem, M.; Mausberg, A.K.; Lee, J.I.; Simiantonakis, I.; van Rooijen, N.; Hartung, H.P.; Jander, S. Macrophages prevent hemorrhagic infarct transformation in murine stroke models. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinschnitz, C.; Bendszus, M.; Frank, M.; Solymosi, L.; Toyka, K.V.; Stoll, G. In vivo monitoring of macrophage infiltration in experimental ischemic brain lesions by magnetic resonance imaging. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2003, 23, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clausen, B.H.; Lambertsen, K.L.; Babcock, A.A.; Holm, T.H.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Finsen, B. Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha are expressed by different subsets of microglia and macrophages after ischemic stroke in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2008, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gregersen, R.; Lambertsen, K.; Finsen, B. Microglia and macrophages are the major source of tumor necrosis factor in permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2000, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Li, P.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Leak, R.K.; Chen, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J. Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics reveal novel mechanism of injury expansion after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2012, 43, 3063–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, B.H.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Saver, J.L.; Bang, O.Y.; Yun, S.W.; Starkman, S.; Ali, L.K.; Kim, D.; Villablanca, J.P.; Salamon, N.; et al. Early neutrophilia is associated with volume of ischemic tissue in acute stroke. Stroke 2008, 39, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Qu, Y.Z.; Zhao, Z.W.; Wu, S.X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wei, X.Y.; Gao, L.; Gao, G.D. Astragaloside IV protects against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury correlating to suppression of neutrophils adhesion-related molecules. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, H.; McKee, D.; Ritter, L. Systemic neutrophil activation in a mouse model of ischemic stroke and reperfusion. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2011, 13, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.; Menon, D.; Peters, A.; Ballinger, J.; Barber, R.; Balan, K.; Lynch, A.; Xuereb, J.; Fryer, T.; Guadagno, J.; et al. Cerebral neutrophil recruitment, histology, and outcome in acute ischemic stroke: An imaging-based study. Stroke 2004, 35, 1659–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.K.; Ergul, A.; Kozak, A.; Machado, L.S.; Johnson, M.H.; Fagan, S.C. Effect of neutrophil depletion on gelatinase expression, edema formation and hemorrhagic transformation after focal ischemic stroke. BMC Neurosci. 2005, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cuartero, M.I.; Ballesteros, I.; Moraga, A.; Nombela, F.; Vivancos, J.; Hamilton, J.A.; Corbí, Á.L.; Lizasoain, I.; Moro, M.A. N2 neutrophils, novel players in brain inflammation after stroke modulation by the PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone. Stroke 2013, 44, 3498–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurn, P.D.; Subramanian, S.; Parker, S.M.; Afentoulis, M.E.; Kaler, L.J.; Vandenbark, A.A.; Offner, H. T-and B-cell-deficient mice with experimental stroke have reduced lesion size and inflammation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 27, 1798–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinschnitz, C.; Schwab, N.; Kraft, P.; Hagedorn, I.; Dreykluft, A.; Schwarz, T.; Austinat, M.; Nieswandt, B.; Wiendl, H.; Stoll, G. Early detrimental T-cell effects in experimental cerebral ischemia are neither related to adaptive immunity nor thrombus formation. Blood 2010, 115, 3835–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, G.; Arumugam, T.V.; Stokes, K.Y.; Granger, D.N. Role of T lymphocytes and interferon-γ in ischemic stroke. Circulation 2006, 113, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offner, H.; Hurn, P.D. A novel hypothesis: Regulatory B lymphocytes shape outcome from experimental stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2012, 3, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Akiyoshi, K.; Dziennis, S.; Vandenbark, A.A.; Herson, P.S.; Hurn, P.D.; Offner, H. Regulatory B cells limit CNS inflammation and neurologic deficits in murine experimental stroke. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 8556–8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Yang, G.; Li, G. Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: Role of inflammatory cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesz, A.; Suri-Payer, E.; Veltkamp, C.; Doerr, H.; Sommer, C.; Rivest, S.; Giese, T.; Veltkamp, R. Regulatory T cells are key cerebroprotective immunomodulators in acute experimental stroke. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinschnitz, C.; Kraft, P.; Dreykluft, A.; Hagedorn, I.; Göbel, K.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Langhauser, F.; Helluy, X.; Schwarz, T.; Bittner, S.; et al. Regulatory T cells are strong promoters of acute ischemic stroke in mice by inducing dysfunction of the cerebral microvasculature. Blood 2013, 121, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, E.H. A new penumbra: Transitioning from injury into repair after stroke. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Anrather, J.; Shi, F.D. Immune interventions in stroke. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langhauser, F.; Kraft, P.; Göb, E.; Leinweber, J.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Lorenz, K.; Gelderblom, M.; Bittner, S.; Meuth, S.G.; Wiendl, H.; et al. Blocking of α4 integrin does not protect from acute ischemic stroke in mice. Stroke 2014, 45, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäbitz, W.R.; Dirnagl, U. Are we ready to translate T-cell transmigration in stroke? Stroke 2014, 45, 1610–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, S.R.; Pereira, J.P.; Matloubian, M.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cyster, J.G. Lymphocyte sequestration through S1P lyase inhibition and disruption of S1P gradients. Science 2005, 309, 1735–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Yemisci, M.; Kim, H.H.; Yung, L.M.; Shin, H.K.; Hwang, S.K.; Guo, S.; Qin, T.; Alsharif, N.; Brinkmann, V.; et al. Fingolimod provides long-term protection in rodent models of cerebral ischemia. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, F.; Qin, T.; Castillo, J.; Seo, J.H.; Arai, K.; Lo, E.H.; Waeber, C. Fingolimod reduces hemorrhagic transformation associated with delayed tissue plasminogen activator treatment in a mouse thromboembolic model. Stroke 2013, 44, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Ren, L.; Yan, Y.; Sun, N.; Li, Y.J.; Han, W.; Xue, R.; Liu, Q.; Hao, J.; et al. Impact of an immune modulator fingolimod on acute ischemic stroke. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18315–18320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, R.; McKinney, A.M.; Swenson, B.; Janardhan, V. Blood–brain barrier, reperfusion injury, and hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Neurology 2012, 79, S52–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jin, X.; Liu, K.J.; Liu, W. Matrix metalloproteinase-2-mediated occludin degradation and caveolin-1-mediated claudin-5 redistribution contribute to blood–brain barrier damage in early ischemic stroke stage. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 3044–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renú, A.; Amaro, S.; Laredo, C.; San Román, L.; Llull, L.; Lopez, A.; Urra, X.; Blasco, J.; Oleaga, L.; Chamorro, Á. Relevance of blood–brain barrier disruption after endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke dual-energy computed tomographic study. Stroke 2015, 46, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.J.; Kalil, A.J.; Tanzi, P.; Zierath, D.K.; Savos, A.V.; Gee, J.M.; Hadwin, J.; Carter, K.T.; Shibata, D.; Cain, K.C. Autoimmune responses to the brain after stroke are associated with worse outcome. Stroke 2011, 42, 2763–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wu, W.; Yin, J.X.; Bai, X.F.; Shen, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; La Cava, A.; Poursine-Laurent, J.; et al. Ischemic neurons recruit natural killer cells that accelerate brain infarction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2704–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, A.M.; Gómez-Choco, M.; Urra, X.; Gorina, R.; Caballero, M.; Chamorro, Á. Brain-derived antigens in lymphoid tissue of patients with acute stroke. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 2156–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langhorne, P.; Stott, D.; Robertson, L.; MacDonald, J.; Jones, L.; McAlpine, C.; Dick, F.; Taylor, G.; Murray, G. Medical complications after stroke a multicenter study. Stroke 2000, 31, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernino, S.; Brown, R.D.; Sejvar, J.J.; Sicks, J.D.; Petty, G.W.; O’Fallon, W.M. Cause-specific mortality after first cerebral infarction a population-based study. Stroke 2003, 34, 1828–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrado, E.; Rizzo, M.; Tantillo, R.; Muratori, I.; Bonura, F.; Vitale, G.; Novo, S. Markers of inflammation and infection influence the outcome of patients with baseline asymptomatic carotid lesions: A 5-year follow-up study. Stroke 2006, 37, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Minematsu, K.; Kazui, S.; Yamaguchi, T. Mortality and cause of death after hospital discharge in 10,981 patients with ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2005, 19, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulm, L.; Harms, H.; Ohlraun, S.; Reimnitz, P.; Meisel, A. Impact of infections on long-term outcome after severe middle cerebral artery infarction. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 319, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.D. Mortality and cost of pneumonia after stroke for different risk groups. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2012, 21, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.J.; Emsley, H.C.; Gavin, C.M.; Georgiou, R.F.; Vail, A.; Barberan, E.M.; del Zoppo, G.J.; Hallenbeck, J.M.; Rothwell, N.J.; Hopkins, S.J.; et al. Peak plasma interleukin-6 and other peripheral markers of inflammation in the first week of ischaemic stroke correlate with brain infarct volume, stroke severity and long-term outcome. BMC Neurol. 2004, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whiteley, W.; Jackson, C.; Lewis, S.; Lowe, G.; Rumley, A.; Sandercock, P.; Wardlaw, J.; Dennis, M.; Sudlow, C. Inflammatory markers and poor outcome after stroke: A prospective cohort study and systematic review of interleukin-6. PLoS Med. 2009, 8, e1000145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.A.; Davis, J.P.; Schluter, P.J.; Henderson, R.D.; O’Sullivan, J.D.; Read, S.J. The time course and determinants of temperature within the first 48 h after ischaemic stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2007, 24, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Kulendran, A. Infections after stroke. In Management of Post-Stroke Complications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Esayag, Y.; Nikitin, I.; Bar-Ziv, J.; Cytter, R.; Hadas-Halpern, I.; Zalut, T.; Yinnon, A.M. Diagnostic value of chest radiographs in bedridden patients suspected of having pneumonia. Am. J. Med. 2010, 123, 88. e1–88. e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetze, S.; Engel, O.; Römer, C.; Mueller, S.; Dirnagl, U.; Meisel, C.; Meisel, A. Superiority of preventive antibiotic treatment compared with standard treatment of poststroke pneumonia in experimental stroke: A bed to bench approach. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, U.; Knoblich, R.; Steinhagen, V.; Donat, M.; Benecke, R.; Kloth, A. Predictors of pneumonia in acute stroke patients admitted to a neurological intensive care unit. J. Neurol. 2007, 254, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, H.; Grittner, U.; Dröge, H.; Meisel, A. Predicting post-stroke pneumonia: The pantheris score. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2013, 128, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeusler, K.G.; Schmidt, W.U.; Föhring, F.; Meisel, C.; Helms, T.; Jungehulsing, G.J.; Nolte, C.H.; Schmolke, K.; Wegner, B.; Meisel, A.; et al. Cellular immunodepression preceding infectious complications after acute ischemic stroke in humans. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2008, 25, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisel, A.; Meisel, C.; Harms, H.; Hartmann, O.; Ulm, L. Predicting post-stroke infections and outcome with blood-based immune and stress markers. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2012, 33, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelgesang, A.; Grunwald, U.; Langner, S.; Jack, R.; Bröker, B.M.; Kessler, C.; Dressel, A. Analysis of lymphocyte subsets in patients with stroke and their influence on infection after stroke. Stroke 2008, 39, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, K.Z.; Dale, V.Q.; Dénes, Á.; Bennett, G.; Rothwell, N.J.; Allan, S.M.; McColl, B.W. A rapid and transient peripheral inflammatory response precedes brain inflammation after experimental stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 1764–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Römer, C.; Engel, O.; Winek, K.; Hochmeister, S.; Zhang, T.; Royl, G.; Klehmet, J.; Dirnagl, U.; Meisel, C.; Meisel, A. Blocking stroke-induced immunodeficiency increases CNS antigen-specific autoreactivity but does not worsen functional outcome after experimental stroke. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 7777–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Cassatella, M.A.; Costantini, C.; Jaillon, S. Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, Y.; Sahara, Y.; Itoh, E.; Kawamura, T. Suppressed neutrophil respiratory burst in patients with haemorrhagic stroke. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 17, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhnau, J.; Schulze, K.; Gaida, B.; Langner, S.; Kessler, C.; Bröker, B.; Dressel, A.; Vogelgesang, A. Stroke alters respiratory burst in neutrophils and monocytes. Stroke 2014, 45, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sica, A.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: In vivo veritas. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offner, H.; Subramanian, S.; Parker, S.M.; Afentoulis, M.E.; Vandenbark, A.A.; Hurn, P.D. Experimental stroke induces massive, rapid activation of the peripheral immune system. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2006, 26, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, A.; Medzhitov, R. Control of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Recognition of microorganisms and activation of the immune response. Nature 2007, 449, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelgesang, A.; Becker, K.; Dressel, A. Immunological consequences of ischemic stroke. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2014, 129, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeusler, K.G.; Schmidt, W.U.; Foehring, F.; Meisel, C.; Guenther, C.; Brunecker, P.; Kunze, C.; Helms, T.; Dirnagl, U.; Volk, H.D.; et al. Immune responses after acute ischemic stroke or myocardial infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 155, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hug, A.; Liesz, A.; Muerle, B.; Zhou, W.; Ehrenheim, J.; Lorenz, A.; Dalpke, A.; Veltkamp, R. Reduced efficacy of circulating costimulatory cells after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2011, 42, 3580–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prass, K.; Meisel, C.; Höflich, C.; Braun, J.; Halle, E.; Wolf, T.; Ruscher, K.; Victorov, I.V.; Priller, J.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. Stroke-induced immunodeficiency promotes spontaneous bacterial infections and is mediated by sympathetic activation reversal by poststroke T helper cell type 1–like immunostimulation. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offner, H.; Subramanian, S.; Parker, S.M.; Wang, C.; Afentoulis, M.E.; Lewis, A.; Vandenbark, A.A.; Hurn, P.D. Splenic atrophy in experimental stroke is accompanied by increased regulatory T cells and circulating macrophages. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 6523–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorou, G.; Marousi, S.; Ellul, J.; Mougiou, A.; Theodori, E.; Mouzaki, A.; Karakantza, M. T helper 1 (Th1)/Th2 cytokine expression shift of peripheral blood CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in patients at the post-acute phase of stroke. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 152, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamorro, A.; Horcajada, J.; Obach, V.; Vargas, M.; Revilla, M.; Torres, F.; Cervera, A.; Planas, A.; Mensa, J. The early systemic prophylaxis of infection after stroke study a randomized clinical trial. Stroke 2005, 36, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelbertsen, D.; Andersson, L.; Ljungcrantz, I.; Wigren, M.; Hedblad, B.; Nilsson, J.; Björkbacka, H. T-helper 2 immunity is associated with reduced risk of myocardial infarction and stroke. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klehmet, J.; Harms, H.; Richter, M.; Prass, K.; Volk, H.; Dirnagl, U.; Meisel, A.; Meisel, C. Stroke-induced immunodepression and post-stroke infections: Lessons from the preventive antibacterial therapy in stroke trial. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamorro, A.; Amaro, S.; Vargas, M.; Obach, V.; Cervera, Á.; Torres, F.; Planas, A.M. Interleukin 10, monocytes and increased risk of early infection in ischaemic stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 77, 1279–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, H.C.A.; Smith, C.J.; Gavin, C.M.; Georgiou, R.F.; Vail, A.; Barberan, E.M.; Hallenbeck, J.M.; del Zoppo, G.J.; Rothwell, N.J.; Tyrrell, P.J.; et al. An early and sustained peripheral inflammatory response in acute ischaemic stroke: Relationships with infection and atherosclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2003, 139, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, J.J.; Saadé, N.E.; Safieh-Garabedian, B. Cytokines and neuro–immune–endocrine interactions: A role for the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal revolving axis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 133, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anne, M.; Juha, K.; Makikallio, T.; Mikko, T.; Olli, V.; Kyosti, S.; Heikki, H.; Vilho, M. Neurohormonal activation in ischemic stroke: Effects of acute phase disturbances on long-term mortality. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2007, 4, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, R.; Couch, Y.; Lambertsen, K.L. The effect of stroke on immune function. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 53, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelgesang, A.; May, V.E.; Grunwald, U.; Bakkeboe, M.; Langner, S.; Wallaschofski, H.; Kessler, C.; Bröker, B.M.; Dressel, A. Functional status of peripheral blood T-cells in ischemic stroke patients. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.H.; Jenne, C.N.; Lee, W.Y.; Léger, C.; Kubes, P. Functional innervation of hepatic iNKT cells is immunosuppressive following stroke. Science 2011, 334, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mracsko, E.; Liesz, A.; Karcher, S.; Zorn, M.; Bari, F.; Veltkamp, R. Differential effects of sympathetic nervous system and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis on systemic immune cells after severe experimental stroke. Brain, Behav. Immun. 2014, 41, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, S.J.; Huang, K.Y.; Wang, T.G.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, C.H.; Tang, S.C.; Tsai, L.K.; Yip, P.K.; Jeng, J.S. Dysphagia screening decreases pneumonia in acute stroke patients admitted to the stroke intensive care unit. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 306, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersoz, M.; Ulusoy, H.; Oktar, M.A.; Akyuz, M. Urinary tract infection and bacteriurua in stroke patients: Frequencies, pathogen microorganisms, and risk factors. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 86, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, S. Novel preventive and therapeutic strategy for post-stroke pneumonia. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2009, 9, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, T.; Yoshimi, N.; Fujiwara, H.; Sekizawa, K. Serum substance P concentrations and silent aspiration in elderly patients with stroke. Neurology 2003, 61, 1625–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smithard, D.; O’neill, P.; Park, C.; Morris, J.; Wyatt, R.; England, R.; Martin, D.F. Complications and outcome after acute stroke does dysphagia matter? Stroke 1996, 27, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Selim, M.H.; Caplan, L.R. Medical complications after stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prass, K.; Braun, J.S.; Dirnagl, U.; Meisel, C.; Meisel, A. Stroke propagates bacterial aspiration to pneumonia in a model of cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2006, 37, 2607–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziewas, R.; Ritter, M.; Schilling, M.; Konrad, C.; Oelenberg, S.; Nabavi, D.; Stögbauer, F.; Ringelstein, E.; Lüdemann, P. Pneumonia in acute stroke patients fed by nasogastric tube. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, M.; Horcajada, J.P.; Obach, V.; Revilla, M.; Cervera, Á.; Torres, F.; Planas, A.M.; Mensa, J.; Chamorro, Á. Clinical consequences of infection in patients with acute stroke is it prime time for further antibiotic trials? Stroke 2006, 37, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, H.; Prass, K.; Meisel, C.; Klehmet, J.; Rogge, W.; Drenckhahn, C.; Göhler, J.; Bereswill, S.; Göbel, U.; Wernecke, K.D.; et al. Preventive antibacterial therapy in acute ischemic stroke: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Qing, Y.; Xingyi, J.; Hongbo, Q. Etiologic diagnosis and clinical treatment of multiple drug-resistant bacteria infection in elderly patients with stroke-associated pneumonia after neurosurgery. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 71, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.N. Microbial etiologies of hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51 (Suppl. 1), S81–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laban, K.G.; Rinkel, G.J.; Vergouwen, M.D.I. Nosocomial infections after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: Time course and causative pathogens. Int. J. Stroke 2015, 10, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westendorp, W.F.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Vermeij, J.D.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; van de Beek, D. Post-stroke infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2011, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urra, X.; Miró, F.; Chamorro, A.; Planas, A.M. Antigen-specific immune reactions to ischemic stroke. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K. Autoimmune responses to brain following stroke. Transl.Stroke Res. 2012, 3, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.J.; Kindrick, D.L.; Lester, M.P.; Shea, C.; Ye, Z.C. Sensitization to brain antigens after stroke is augmented by lipopolysaccharide. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2005, 25, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dénes, Á.; Ferenczi, S.; Kovács, K.J. Systemic inflammatory challenges compromise survival after experimental stroke via augmenting brain inflammation, blood-brain barrier damage and brain oedema independently of infarct size. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslanyan, S.; Weir, C.; Diener, H.C.; Kaste, M.; Lees, K.R. Pneumonia and urinary tract infection after acute ischaemic stroke: A tertiary analysis of the GAIN international trial. Eur. J. Neurol. 2004, 11, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisel, C.; Prass, K.; Braun, J.; Victorov, I.; Wolf, T.; Megow, D.; Halle, E.; Volk, H.D.; Dirnagl, U.; Meisel, A. Preventive antibacterial treatment improves the general medical and neurological outcome in a mouse model of stroke. Stroke 2004, 35, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri-Nikpour, M.R.; Nazarbaghi, S.; Hamdi-Holasou, M.; Rezaei, Y. An open-label evaluator-blinded clinical study of minocycline neuroprotection in ischemic stroke: Gender-dependent effect. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2015, 131, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, S.; Al-Shajlawi, F.; Sick, C.; Meairs, S.; Hennerici, M.G. Effects of prophylactic antibiotic therapy with mezlocillin plus sulbactam on the incidence and height of fever after severe acute ischemic stroke: The Mannheim infection in stroke study (MISS). Stroke 2008, 39, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westendorp, W.F.; Vermeij, J. D.; Zock, E.; Hooijenga, I.J.; Kruyt, N.D.; Bosboom, H.J.; Kwa, V.I.; Weisfelt, M.; Remmers, M.J.; ten Houten, R.; et al. The preventive antibiotics in stroke study (PASS): A pragmatic randomised open-label masked endpoint clinical trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Patel, S.; Regan, M.R.; Haenggeli, C.; Huang, Y.H.; Bergles, D.E.; Jin, L.; Hoberg, M.D.; Vidensky, S.; Chung, D.S.; et al. β-Lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nature 2005, 433, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; He, W.-B.; Chen, N.H. Causes of death among persons who survive an acute ischemic stroke. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2014, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Beek, D.; Wijdicks, E.F.; Vermeij, F.H.; de Haan, R.J.; Prins, J.M.; Spanjaard, L.; Dippel, D.W.; Nederkoorn, P.J. Preventive antibiotics for infections in acute stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, L.; Irshad, S.; Hodsoll, J.; Simpson, M.; Gulliford, M.; Smithard, D.; Patel, A.; Rebollo-Mesa, I.; Investigators, S.-I. Prophylactic antibiotics after acute stroke for reducing pneumonia in patients with dysphagia (STROKE-INF): A prospective, cluster-randomised, open-label, masked endpoint, controlled clinical trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziedzic, T.; Slowik, A.; Pera, J.; Szczudlik, A. Beta-blockers reduce the risk of early death in ischemic stroke. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 252, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykora, M.; Siarnik, P.; Diedler, J.; Lees, K.; Alexandrov, A.; Bath, P.; Bluhmki, E.; Bornstein, N.; Claesson, L.; Davis, S.; et al. β-blockers, pneumonia, and outcome after ischemic stroke evidence from virtual international stroke trials archive. Stroke 2015, 46, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, I.L.; Karch, A.; Mikolajczyk, R.; Bähr, M.; Liman, J. Effect of Beta-blocker therapy on the risk of infections and death after acute stroke-a historical cohort study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shim, R.; Wong, C.H.Y. Ischemia, Immunosuppression and Infection—Tackling the Predicaments of Post-Stroke Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010064
Shim R, Wong CHY. Ischemia, Immunosuppression and Infection—Tackling the Predicaments of Post-Stroke Complications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(1):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010064
Chicago/Turabian StyleShim, Raymond, and Connie H. Y. Wong. 2016. "Ischemia, Immunosuppression and Infection—Tackling the Predicaments of Post-Stroke Complications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 1: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010064
APA StyleShim, R., & Wong, C. H. Y. (2016). Ischemia, Immunosuppression and Infection—Tackling the Predicaments of Post-Stroke Complications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(1), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010064