A Jacalin-Related Lectin Regulated the Formation of Aerial Mycelium and Fruiting Body in Flammulina velutipes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Structure of the Fv-JRL1 Gene and Phylogenetic Analysis of the Fv-JRL1 Protein
2.2. Expression Patterns Revealed the Potential Function of Fv-JRL1 Protein in the Formation of the Fruiting Body
2.3. Confirmation of the Ratio between Plasmid DNA and Liposomes
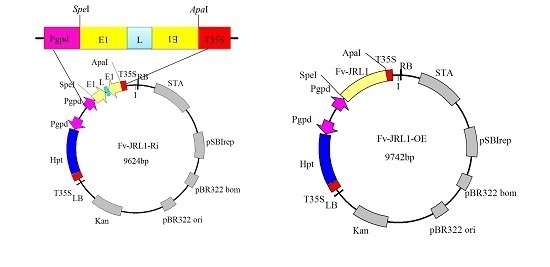
2.4. Generation of Mutants and Fv-JRL1 Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Phenotypic Characterization of Mutants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains, Vector, and Culture Conditions
4.2. Identification of Fv-JRL1 from F. velutipes
4.3. Transcription Pattern Analysis of Fv-JRL1 Gene
4.4. Construction of Gene Expression Plasmids
4.5. Eletrophoretic Mobility of Plasmids DNA: Liposomes Complexes at Different Ratios
4.6. Fungal Transformation and Screening of Transgenic F. velutipes with PCR
4.7. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
4.8. Phenotype of Mutants
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldstein, I.J.; Hayes, C.E. The lectins: Carbohydrate-binding proteins of plants and animals. Adv. Carbohydr. Chen. Biol. 1978, 35, 127–340. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.A.A.; Rouf, R.; Tiralongo, E.; May, T.W.; Tiralongo, J. Mushroom lectins: Specificity, structure and bioactivity relevant to human disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7802–7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirelman, D.; Galun, E.; Sharon, N.; Lotan, R. Inhibition of fungal growth by wheat germ agglutinin. Nature 1975, 256, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janzen, D.H.; Juster, H.B.; Liener, I.E. Insecticidal action of the phytohemagglutinin in black beans on a bruchid beetle. Science 1976, 192, 795–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatehouse, A.M.R.; Powell, K.S.; Peumans, W.J.; van Damme, E.J.; Gatehouse, J.A. Insecticidal properties of plant lectins: Their potential in plant protection. In Lectins Biomedical Perspectives; Taylor & Francis e-library: Bristol, PA, USA, 1995; pp. 35–57. [Google Scholar]
- Peumans, W.J.; van Damme, E.J. Lectins as plant defense proteins. Plant Physiol. 1995, 109, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, T.; Madigan, M.; Martinko, J.; Parker, J. Biology of Microorganisms, 7th ed.; Prentice-HallInternational, Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Sharon, N. Lectin receptors as lymphocyte surface markers. Adv. Immunol. 1983, 34, 213–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raz, A.; Lotan, R. Endogenous galactoside-binding lectins: A new class of functional tumor cell surface molecules related to metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1987, 6, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotan, R.; Raz, A. Lectins in cancer cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1988, 551, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junqueira, L.C.; Carneiro, J.; Kelley, R.O. Basic Histology, 8th ed.; Appleton and Lange: Connecticut, Norwalk, CT, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.T.; Miles, P.G. Mushroom biology—A new disciplines. Mycologist 1992, 6, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.S.; Wang, H.; Chan, Y.S.; Pan, W.; Dan, X.; Yin, C.M.; Akkouh, O.; Ng, T.B. Lectins from edible mushrooms. Molecules 2014, 20, 446–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.T.; Buswell, J.A. Mushroom nutriceuticals. World J. Microb. Biotechnol. 1996, 12, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulshreshtha, S.; Mathur, N.; Bhatnagar, P. Mushroom as a product and their role in mycoremediation. AMB Express 2014, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillamón, E.; García-Lafuente, A.; Lozano, M.; D’Arrigo, M.; Rostagno, M.A.; Villares, A.; Martínez, J.A. Edible mushrooms: Role in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasser, S.P. Medicinal mushroom science: History, current status, future trends, and unsolved problems. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2010, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yan, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. Bioactive proteins from mushrooms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasser, S.P. Medicinal mushroom science: Current perspectives, advances, evidences, and challenges. Biomed. J. 2014, 37, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ng, T.B.; Ooi, V.E.C. Lectins from mushrooms. Mycol. Res. 1998, 102, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, J.; Ng, T.B. A new lectin with highly potent antihepatoma and antisarcoma activities from the oyster mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Liang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, D.C. Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic studies of an antitumour lectin from the edible mushroom Agrocybe aegerita. Protein Pept. Lett. 2005, 12, 705–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatohgo, T.; Nakata, M.; Tsumuraya, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Yamamoto, S. Purification and properties of a lectin from the fruitbodies of Flammulina velutipes. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1988, 52, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguri, S.; Ando, A.; Nagata, Y. A novel developmental stage-specific lectin of the basidiomycete Pleurotus cornucopiae. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 5692–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woffelman, C. DNAMAN for Windows; Version 5.2.10; Lynon Biosoft, Institute of Molecular Plant Sciences, Leiden University: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.E.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Quevillon, E.; Silventoinen, V.; Pillai, S.; Harte, N.; Mulder, N.; Apweiler, R.; Lopez, R. InterProScan: protein domains identifier. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W116–W120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The clustal_x windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using MAXIMUM likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Yan, J.; Xie, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, S.; Li, D.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, X.; Deng, Y.; et al. Genes encoding FAD-binding proteins in Volvariella volvacea exhibit differential expression in homokaryons and heterokaryons. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Szoka, F.C. Mechanism of DNA release from cationic liposome/DNA complexes used in cell transfection. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 5616–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Christopher, M.E.; Nagata, L.P.; Zabielski, M.A.; Li, H.; Wong, J.P.; Samuel, J. Intranasal immunization with liposome-encapsulated plasmid DNA encoding influenza virus hemagglutinin elicits mucosal, cellular and humoral immune responses. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 31, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lis, H.; Sharon, N. Lectins: Carbohydrate-specific proteins that mediate cellular recognition. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 637–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, M.; Chandra, N. Lectins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1999, 9, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stillmark, H. Ueber Ricin ein giftiges Ferment aus den Samen von Ricinus communis L. und einigen anderen Euphorbiaceen. Inaugural-Dissertation, Dorpat, Schnakenburg, Tartu, Estonia, 1888. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.S.; Bhari, R.; Kaur, H.P. Mushroom lectins: Current status and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2010, 30, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhao, C.G.; Tong, X.; Qi, Y.P. A lectin with mycelia differentiation and antiphytovirus activities from the edible mushroom Agrocybe aegerita. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 36, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.J.; Baek, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, C.; Rhee, H.; Kim, H.; Seo, J.S.; Park, H.R.; Yoon, D.E.; Nam, J.Y.; et al. Whole genome and global gene expression analyses of the model mushroom Flammulina velutipes reveal a high capacity for lignocellulose degradation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.Z.; Xie, B.G. Homocitrate synthase expression and lysine content in fruiting body of different developmental stages in Flammulina velutipes. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 70, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porebski, S.; Bailey, L.G.; Baum, B.R. Modification of a CTAB DNA extraction protocol for plants containing high polysaccharide and polyphenol components. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 1997, 15, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, F.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, G.; Guo, L.; Chen, R.; Chen, B.; Lu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Xie, B. The multigene family of fungal laccases and their expression in the white rot basidiomycete Flammulina velutipes. Gene 2015, 563, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Ma, B. ZOOM Lite: Next-Generation sequencing data mapping and visualization software. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W743–W748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.M.; Yan, J.J.; Yang, Z.Y.; Zhang, T.J.; Xie, B.G. Analysis on structure and differential expression of a laccase gene fv-lac4 that possible involves in development of fruit body of Flammulina velutipes. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2014, 33, 1254–1260. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.L.; van Peer, A.F.; Guo, L.X.; Chen, R.L.; Wang, W.; Yan, J.J.; Deng, Y.J.; Xie, B.G. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of an endogenous HMG-box transcription factor fvhom1 in Flammulina velutipes. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2014, 33, 1268–1274. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.-P.; Chen, R.-L.; Long, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.-J.; Xie, B.-G. A Jacalin-Related Lectin Regulated the Formation of Aerial Mycelium and Fruiting Body in Flammulina velutipes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17121884
Lu Y-P, Chen R-L, Long Y, Li X, Jiang Y-J, Xie B-G. A Jacalin-Related Lectin Regulated the Formation of Aerial Mycelium and Fruiting Body in Flammulina velutipes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(12):1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17121884
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yuan-Ping, Ren-Liang Chen, Ying Long, Xiao Li, Yu-Ji Jiang, and Bao-Gui Xie. 2016. "A Jacalin-Related Lectin Regulated the Formation of Aerial Mycelium and Fruiting Body in Flammulina velutipes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 12: 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17121884
APA StyleLu, Y.-P., Chen, R.-L., Long, Y., Li, X., Jiang, Y.-J., & Xie, B.-G. (2016). A Jacalin-Related Lectin Regulated the Formation of Aerial Mycelium and Fruiting Body in Flammulina velutipes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(12), 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17121884