Overexpression of Glucocorticoid Receptor β Enhances Myogenesis and Reduces Catabolic Gene Expression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. GRβ Responsiveness to Dexamethasone and Insulin
2.2. GR Isoform and Muscle Regulatory Factor mRNA Levels through Differentiation
2.3. Overexpression of GRβ Increases Muscle Regulatory Factor mRNA Levels
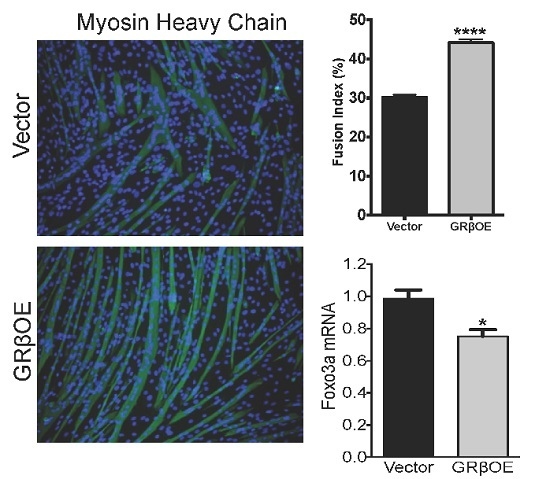
2.4. Overexpression of GRβ Enhances the Myotube Formation
2.5. Overexpression of GRβ Blunts Dex-Induced Catabolic Gene Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Cell Lines
4.3. Proliferation Assays
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Myosin Heavy Chain Immunofluorescence
4.6. Quantification of Fusion and Myotube Formation
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GC | glucocorticoid |
| GRE | glucocorticoid response elements |
| GR | glucocorticoid receptor |
| GRα | glucocorticoid receptor α |
| GRβ | glucocorticoid receptor β |
| GRβOE | glucocorticoid receptor β overexpressing cells |
| MAFbx | muscle atrophy F-box |
| MuRF1 | muscle ring finger 1 |
| FOXO | forkhead box O |
| PTEN | phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 |
| IRS1 and 2 | insulin receptor substrate 1 and 2 |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
References
- Ferrando, A.A.; Wolfe, R.R. Restoration of hormonal action and muscle protein. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, S630–S634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitts, R.H.; Romatowski, J.G.; Peters, J.R.; Paddon-Jones, D.; Wolfe, R.R.; Ferrando, A.A. The deleterious effects of bed rest on human skeletal muscle fibers are exacerbated by hypercortisolemia and ameliorated by dietary supplementation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 293, C313–C320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanaoka, B.Y.; Peterson, C.A.; Horbinski, C.; Crofford, L.J. Implications of glucocorticoid therapy in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.S.; Ignatoski, K.M.; Daignault, S.; Lindland, C.; Gauger, P.G.; Doherty, G.M.; Wang, S.C. A quantitative tool to assess degree of sarcopenia objectively in patients with hypercortisolism. Surgery 2011, 150, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Nathan, J.A.; Goldberg, A.L. Muscle wasting in disease: Molecular mechanisms and promising therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, K.L.; Cidlowski, J.A. Tissue-specific glucocorticoid action: A family affair. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 19, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitzer, M.D.; Wolf, I.M.; Sanchez, E.R.; Witchel, S.F.; DeFranco, D.B. Glucocorticoid receptor physiology. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2007, 8, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schakman, O.; Kalista, S.; Barbe, C.; Loumaye, A.; Thissen, J.P. Glucocorticoid-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2163–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinds, T.D., Jr.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Cash, H.A.; Stechschulte, L.A.; Heinrich, G.; Najjar, S.M.; Sanchez, E.R. Discovery of glucocorticoid receptor-β in mice with a role in metabolism. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, R.H.; Jewell, C.M.; Yudt, M.R.; Bofetiado, D.M.; Cidlowski, J.A. The dominant negative activity of the human glucocorticoid receptor isoform: Specificity and mechanisms of action. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 27857–27866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, R.H.; Sar, M.; Cidlowski, J.A. The human glucocorticoid receptor β isoform—Expression, biochemical properties, and putative function. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 9550–9559. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whorwood, C.B.; Donovan, S.J.; Wood, P.J.; Phillips, D.I. Regulation of glucocorticoid receptor α and β isoforms and type I 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase expression in human skeletal muscle cells: A key role in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 2296–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y.; Hamid, Q.; Vottero, A.; Szefler, S.J.; Surs, W.; Minshall, E.; Chrousos, G.P.; Klemm, D.J. Association of glucocorticoid insensitivity with increased expression of glucocorticoid receptor β. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goleva, E.; Li, L.B.; Eves, P.T.; Strand, M.J.; Martin, R.J.; Leung, D.Y. Increased glucocorticoid receptor β alters steroid response in glucocorticoid-insensitive asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, A.R.; Lane, S.J.; Cidlowski, J.A.; Staynov, D.Z.; Lee, T.H. Glucocorticoid resistance in asthma is associated with elevated in vivo expression of the glucocorticoid receptor β-isoform. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longui, C.A.; Vottero, A.; Adamson, P.C.; Cole, D.E.; Kino, T.; Monte, O.; Chrousos, G.P. Low glucocorticoid receptor α/β ratio in T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. Horm. Metab. Res. 2000, 32, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowska, H.; Jagodzinski, P.P. Glucocorticoid receptor α and β variant expression is associated with ASF/SF2 splicing factor upregulation in HT-29 colon cancer and MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Arch. Med. Res. 2009, 40, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, J.C.; Oakley, R.H.; Jewell, C.M.; Cidlowski, J.A. Proinflammatory cytokines regulate human glucocorticoid receptor gene expression and lead to the accumulation of the dominant negative β isoform: A mechanism for the generation of glucocorticoid resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6865–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kino, T.; Su, Y.A.; Chrousos, G.P. Human glucocorticoid receptor isoform β: Recent understanding of its potential implications in physiology and pathophysiology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3435–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stechschulte, L.A.; Wuescher, L.; Marino, J.S.; Hill, J.W.; Eng, C.; Hinds, T.D., Jr. Glucocorticoid receptor β stimulates Akt1 growth pathway by attenuation of PTEN. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 17885–17894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Deng, L.; Jiao, G.; Zhang, B.; Xie, P.; Mu, H.; Qiao, W.; Zou, J. Glucocorticoid receptor β regulates injury-mediated astrocyte activation and contributes to glioma pathogenesis via modulation of β-catenin/TCF transcriptional activity. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 59, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligr, M.; Li, Y.; Logan, S.K.; Taneja, S.; Melamed, J.; Lepor, H.; Garabedian, M.J.; Lee, P. Mifepristone inhibits GRβ coupled prostate cancer cell proliferation. J. Urol. 2012, 188, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentzinger, C.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Rudnicki, M.A. Building muscle: Molecular regulation of myogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charge, S.B.; Rudnicki, M.A. Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 209–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotwein, P.; Wilson, E.M. Distinct actions of Akt1 and Akt2 in skeletal muscle differentiation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 219, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandl, A.; Sarkes, D.; Carricaburu, V.; Jung, V.; Rameh, L. Serum withdrawal-induced accumulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase lipids in differentiating 3T3-L6 myoblasts: Distinct roles for SHIP2 and PTEN. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 8098–8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Qin, W.; Pan, J.; Qin, Y.; Lee, D.N.; Bauman, W.A.; Cardozo, C. Identification of functional glucocorticoid response elements in the mouse Foxo1 promoter. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Ohkawa, S.; Li, H.; Roberts-Wilson, T.K.; Price, S.R. Foxo3a mediates signaling crosstalk that coordinates ubiquitin and atrogin-1/MAFbx expression during glucocorticoid-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 2660–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddell, D.S.; Baehr, L.M.; van den Brandt, J.; Johnsen, S.A.; Reichardt, H.M.; Furlow, J.D.; Bodine, S.C. The glucocorticoid receptor and Foxo1 synergistically activate the skeletal muscle atrophy-associated MuRF1 gene. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E785–E797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, M.L.; Baehr, L.M.; Reichardt, H.M.; Tuckermann, J.P.; Bodine, S.C.; Furlow, J.D. A cell-autonomous role for the glucocorticoid receptor in skeletal muscle atrophy induced by systemic glucocorticoid exposure. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E1210–E1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menconi, M.; Gonnella, P.; Petkova, V.; Lecker, S.; Hasselgren, P.O. Dexamethasone and corticosterone induce similar, but not identical, muscle wasting responses in cultured l6 and C2C12 myotubes. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 105, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baehr, L.M.; Furlow, J.D.; Bodine, S.C. Muscle sparing in muscle ring finger 1 null mice: Response to synthetic glucocorticoids. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 4759–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seene, T.; Kaasik, P.; Pehme, A.; Alev, K.; Riso, E.M. The effect of glucocorticoids on the myosin heavy chain isoforms’ turnover in skeletal muscle. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 86, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodine, S.C.; Latres, E.; Baumhueter, S.; Lai, V.K.; Nunez, L.; Clarke, B.A.; Poueymirou, W.T.; Panaro, F.J.; Na, E.; Dharmarajan, K.; et al. Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science 2001, 294, 1704–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecker, S.H.; Jagoe, R.T.; Gilbert, A.; Gomes, M.; Baracos, V.; Bailey, J.; Price, S.R.; Mitch, W.E.; Goldberg, A.L. Multiple types of skeletal muscle atrophy involve a common program of changes in gene expression. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillero, E.; Alamdari, N.; Lecker, S.H.; Hasselgren, P.O. Suppression of atrogin-1 and MuRF1 prevents dexamethasone-induced atrophy of cultured myotubes. Metabolism 2013, 62, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipovic, D.; Pirkmajer, S.; Mis, K.; Mars, T.; Grubic, Z. Expression of glucocorticoid receptors in the regenerating human skeletal muscle. Physiol. Res. 2011, 60 (Suppl. S1), S147–S154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.; Williams-Dautovich, J.; Cummins, C.L. Minireview: New molecular mediators of glucocorticoid receptor activity in metabolic tissues. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schacke, H.; Docke, W.D.; Asadullah, K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 96, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, C.; Muzzin, P.; Rohner-Jeanrenaud, F. Role of glucocorticoids in the physiopathology of excessive fat deposition and insulin resistance. Int. J. Obes. 2004, 28 (Suppl. S4), S45–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, T.; Harris, C.A.; Wang, J.C. Metabolic functions of glucocorticoid receptor in skeletal muscle. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 380, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Qin, W.; Pan, J.; Wu, Y.; Bauman, W.A.; Cardozo, C. Dependence of dexamethasone-induced Akt/Foxo1 signaling, upregulation of MAFbx, and protein catabolism upon the glucocorticoid receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 378, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, N.; Yoshikawa, N.; Ito, N.; Maruyama, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Takeda, S.; Nakae, J.; Tagata, Y.; Nishitani, S.; Takehana, K.; et al. Crosstalk between glucocorticoid receptor and nutritional sensor mtor in skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgino, F.; Almahfouz, A.; Goodyear, L.J.; Smith, R.J. Glucocorticoid regulation of insulin receptor and substrate IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation in rat skeletal muscle in vivo. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, H.; Lee, I.H.; Du, J.; Mitch, W.E. Endogenous glucocorticoids and impaired insulin signaling are both required to stimulate muscle wasting under pathophysiological conditions in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3059–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, T.; Lew, M.J.; Mayba, O.; Harris, C.A.; Speed, T.P.; Wang, J.C. Genome-wide analysis of glucocorticoid receptor-binding sites in myotubes identifies gene networks modulating insulin signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11160–11165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.V.; Waddell, D.S.; Siu, R.; Stein, M.; Dewey, S.; Furlow, J.D.; Bodine, S.C. Upregulation of proteasome activity in muscle ring finger 1-null mice following denervation. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 2986–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tintignac, L.A.; Lagirand, J.; Batonnet, S.; Sirri, V.; Leibovitch, M.P.; Leibovitch, S.A. Degradation of myod mediated by the SCF (MAFbx) ubiquitin ligase. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 2847–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jogo, M.; Shiraishi, S.; Tamura, T.A. Identification of MAFbx as a myogenin-engaged F-box protein in SCF ubiquitin ligase. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 2715–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, J.S.; Hinds, T.D., Jr.; Potter, R.A.; Ondrus, E.; Onion, J.L.; Dowling, A.; McLoughlin, T.J.; Sanchez, E.R.; Hill, J.W. Suppression of protein kinase C theta contributes to enhanced myogenesis in vitro via IRS1 and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. BMC Cell Biol. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, B.A.; Drujan, D.; Willis, M.S.; Murphy, L.O.; Corpina, R.A.; Burova, E.; Rakhilin, S.V.; Stitt, T.N.; Patterson, C.; Latres, E.; et al. The E3 ligase MuRF1 degrades myosin heavy chain protein in dexamethasone-treated skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Brault, J.J.; Gygi, S.P.; Glass, D.J.; Valenzuela, D.M.; Gartner, C.; Latres, E.; Goldberg, A.L. During muscle atrophy, thick, but not thin, filament components are degraded by MuRF1-dependent ubiquitylation. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.A.; Eliazer, S.; Ilaria, R.L., Jr.; Richardson, J.A.; Olson, E.N. Regulation of microtubule dynamics and myogenic differentiation by MuRF, a striated muscle ring-finger protein. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, K.; Marino, J.S.; Sanchez, E.R.; Hinds, T.D., Jr. The glucocorticoid receptor: Cause or cure for obesity? Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Gene | Sequence 5’ to 3’ |
|---|---|
| GAPDH | Forward: ATGTTTGTGATGGGTGTGAA |
| Reverse: ATGCCAAAGTTGTCATGGAT | |
| MyoD | Forward: TACCCAAGGTGGAGATCCTG |
| Reverse: GCATCTGAGTCGCCACTGTA | |
| Myogenin | Forward: CGCGATCTCCGCTACAGA |
| Reverse: TGGGACCGAACTCCAGTG | |
| MAFbx | Forward: CCAGGATCCGCAGCCCTCCA |
| Reverse: ATGCGGCGCGTTGGGAAGAT | |
| MuRF1 | Forward: GGGGGTCAGGGGACGAAGACA |
| Reverse: TCTCGCCCACCTGCGTCACA | |
| GRα | Forward: AAAGAGCTAGGAAAAGCCATTGTC |
| Reverse: CTGTCTTTGGGCTTTTGAGATAGG | |
| GRβ | Forward: CAATCATGTTGCAGCAATTCACT |
| Reverse: CCCCATAAAAATCTAGGGCCTCT | |
| Foxo3a | Forward: GAGCTGGAGCTCGAACCTT |
| Reverse: CTTGGGCTCTTGCTCTCTCC |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hinds, T.D., Jr.; Peck, B.; Shek, E.; Stroup, S.; Hinson, J.; Arthur, S.; Marino, J.S. Overexpression of Glucocorticoid Receptor β Enhances Myogenesis and Reduces Catabolic Gene Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020232
Hinds TD Jr., Peck B, Shek E, Stroup S, Hinson J, Arthur S, Marino JS. Overexpression of Glucocorticoid Receptor β Enhances Myogenesis and Reduces Catabolic Gene Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(2):232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020232
Chicago/Turabian StyleHinds, Terry D., Jr., Bailey Peck, Evan Shek, Steven Stroup, Jennifer Hinson, Susan Arthur, and Joseph S. Marino. 2016. "Overexpression of Glucocorticoid Receptor β Enhances Myogenesis and Reduces Catabolic Gene Expression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 2: 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020232
APA StyleHinds, T. D., Jr., Peck, B., Shek, E., Stroup, S., Hinson, J., Arthur, S., & Marino, J. S. (2016). Overexpression of Glucocorticoid Receptor β Enhances Myogenesis and Reduces Catabolic Gene Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(2), 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020232