Withaferin-A—A Natural Anticancer Agent with Pleitropic Mechanisms of Action
Abstract
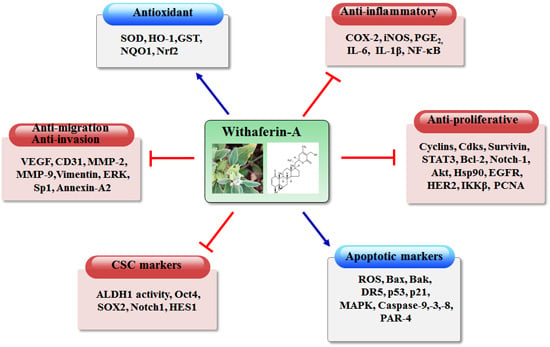
:1. Introduction
2. Effects of Withaferin-A on Multiorgan Carcinogenesis—Evidence from Animal Model Studies
2.1. Sarcoma and Ascites Tumor
2.2. Prostate Cancer
2.3. Gynecological Cancer
2.4. Melanoma
2.5. Thyroid Cancer
2.6. Gastrointestinal Cancer
2.7. Other Cancers
3. Biochemical Basis of Anticancer Effects of Withaferin-A
3.1. Effects of Withaferin-A on Cytoprotective Enzymes
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Withaferin-A
3.3. Antiproliferative Effects of Withaferin-A
3.4. Induction of Tumor Cell Apoptosis by Withaferin-A
3.4.1. Involvement of ROS in Withaferin-A-Induced Apoptosis
3.4.2. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Mechanisms of Apoptosis Induction by Withaferin-A
3.4.3. Withaferin-A Alters the Expression of pro- and Anti-Apoptotic Proteins
3.4.4. Withaferin-A-Induces Apoptosis through Activation of p53 Family Members
3.4.5. Endoplasmic (ER) Stress-Mediated Induction of Apoptosis by Withaferin-A
3.4.6. Withaferin-A-Induced Apoptosis Is Mediated through Activation of Par-4
3.4.7. Other Mechanisms of Apoptosis Induction by Withaferin-A
3.5. Autophagy Induction by Withaferin-A and Its Implication in Cancer
3.6. Withaferin-A as an Inhibitor of Tumor Angiogenesis
3.7. Anti-Migratory, Anti-Invasive and Anti-Metastatic Effects of Withaferin-A
3.8. Chemosensitizing and/or Synergistic Effect of Withaferin-A with Chemotherapeutic Agents
3.9. Targeting Cancer Stem Cells with Withaferin-A
3.10. Withaferin-A as a Cancer Immunotherapy
4. Withaferin-A as a Cysteine Thiol Modifier
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mann, J.R.; Backlund, M.G.; DuBois, R.N. Mechanisms of disease: Inflammatory mediators and cancer prevention. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 2, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; Orlikova, B.; Diederich, M. Non-edible plants as an attractive source of compounds with chemopreventive potential. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surh, Y.J. Cancer chemoprevention with dietary phytochemicals. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, A.R.; Singh, S.V. Molecular targets and mechanisms of cancer prevention and treatment by withaferin-A, a naturally occurring steroidal lactone. AAPS J. 2014, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurup, P.A. The antibacterial principle of Withania somnifera. I. Isoation and antibacterial activity. Antibiot. Chemother. 1958, 8, 511–515. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, P.U.; Sharada, A.C.; Solomon, F.E.; Kamath, M.S. In vivo growth inhibitory effect of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) on a transplantable mouse tumor, Sarcoma 180. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 1992, 30, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davis, L.; Kuttan, G. Effect of Withania somnifera on 20-methylcholanthrene induced fibrosarcoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 19, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prakash, J.; Gupta, S.K.; Kochupillai, V.; Singh, N.; Gupta, Y.K.; Joshi, S. Chemopreventive activity of Withania somnifera in experimentally induced fibrosarcoma tumours in Swiss albino mice. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, L.; Kuttan, G. Effect of Withania somnifera on DMBA induced carcinogenesis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 75, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazal, K.F.; Samuel, T.; Hill, D.L.; Grubbs, C.J. Effect of an extract of Withania somnifera root on estrogen receptor-positive mammary carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 1519–1523. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panjamurthy, K.; Manoharan, S.; Menon, V.P.; Nirmal, M.R.; Senthil, N. Protective role of withaferin-A on 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced genotoxicity in bone marrow of Syrian golden hamsters. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2008, 22, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shohat, B.; Gitter, S.; Abraham, A.; Lavie, D. Antitumor activity of withaferin-A (NSC-101088). Cancer Chemother. Rep. 1967, 51, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shohat, B.; Shaltiel, A.; Ben-Bassat, M.; Joshua, H. The effect of withaferin-A, a natural steroidal lactone, on the fine structure of S-180 tumor cells. Cancer Lett. 1976, 2, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.U.; Sharada, A.C.; Solomon, F.E. In vivo growth inhibitory and radiosensitizing effects of withaferin-A on mouse Ehrlich ascites carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 1995, 95, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma Devi, P.; Kamath, R. Radiosensitizing effect of withaferin-A combined with hyperthermia on mouse fibrosarcoma and melanoma. J. Radiat. Res. 2003, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahat, G.; Zhu, Q.S.; Huang, K.L.; Wang, S.; Bolshakov, S.; Liu, J.; Torres, K.; Langley, R.R.; Lazar, A.J.; Hung, M.C.; et al. Vimentin is a novel anti-cancer therapeutic target; insights from in vitro and in vivo mice xenograft studies. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widodo, N.; Kaur, K.; Shrestha, B.G.; Takagi, Y.; Ishii, T.; Wadhwa, R.; Kaul, S.C. Selective killing of cancer cells by leaf extract of Ashwagandha: Identification of a tumor-inhibitory factor and the first molecular insights to its effect. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2298–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Shi, G.; Dou, Q.P. The tumor proteasome is a primary target for the natural anticancer compound Withaferin-A isolated from “Indian winter cherry”. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stan, S.D.; Hahm, E.R.; Warin, R.; Singh, S.V. Withaferin-A causes FOXO3a- and Bim-dependent apoptosis and inhibits growth of human breast cancer cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7661–7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaiparambil, J.T.; Bender, L.; Ganesh, T.; Kline, E.; Patel, P.; Liu, Y.; Tighiouart, M.; Vertino, P.M.; Harvey, R.D.; Garcia, A.; et al. Withaferin-A inhibits breast cancer invasion and metastasis at sub-cytotoxic doses by inducing vimentin disassembly and serine 56 phosphorylation. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2744–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahm, E.R.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.H.; Sehrawat, A.; Arlotti, J.A.; Shiva, S.S.; Bhargava, R.; Singh, S.V. Metabolic alterations in mammary cancer prevention by withaferin-A in a clinically relevant mouse model. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munagala, R.; Kausar, H.; Munjal, C.; Gupta, R.C. Withaferin-A induces p53-dependent apoptosis by repression of HPV oncogenes and upregulation of tumor suppressor proteins in human cervical cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakar, S.S.; Ratajczak, M.Z.; Powell, K.S.; Moghadamfalahi, M.; Miller, D.M.; Batra, S.K.; Singh, S.K. Withaferin-A alone and in combination with cisplatin suppresses growth and metastasis of ovarian cancer by targeting putative cancer stem cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, P.U.; Kamath, R.; Rao, B.S. Radiosensitization of a mouse melanoma by withaferin A: In vivo studies. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2000, 38, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samadi, A.K.; Cohen, S.M.; Mukerji, R.; Chaguturu, V.; Zhang, X.; Timmermann, B.N.; Cohen, M.S.; Person, E.A. Natural withanolide withaferin-A induces apoptosis in uveal melanoma cells by suppression of Akt and c-MET activation. Tumour Biol. 2012, 33, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Du, H.; Huang, V.; Sun, B.; Harris, J.P.; Richardson, Q.; Shen, X.; Jin, R.; Li, G.; et al. Withaferin-A suppresses the up-regulation of acetyl-coA carboxylase 1 and skin tumor formation in a skin carcinogenesis mouse model. Mol. Carcinog. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadi, A.K.; Mukerji, R.; Shah, A.; Timmermann, B.N.; Cohen, M.S. A novel RET inhibitor with potent efficacy against medullary thyroid cancer in vivo. Surgery 2010, 148, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheryan, V.T.; Wu, W.; Cui, C.Q.; Polin, L.A.; Pass, H.I.; Dou, Q.P.; Rishi, A.K.; Wali, A. Withaferin-A inhibits the proteasome activity in mesothelioma in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoharan, S.; Panjamurthy, K.; Balakrishnan, S.; Vasudevan, K.; Vellaichamy, L. Circadian time-dependent chemopreventive potential of withaferin-A in 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced oral carcinogenesis. Pharmacol. Rep. 2009, 61, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, S.; Panjamurthy, K.; Menon, V.P.; Balakrishnan, S.; Alias, L.M. Protective effect of Withaferin-A on tumour formation in 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene induced oral carcinogenesis in hamsters. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 47, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panjamurthy, K.; Manoharan, S.; Nirmal, M.R.; Vellaichamy, L. Protective role of Withaferin-A on immunoexpression of p53 and bcl-2 in 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene -in duced experimental oral carcinogenesis. Investig. New Drugs 2009, 27, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Hamza, A.; Zhang, T.; Gu, M.; Zou, P.; Newman, B.; Li, Y.; Gunatilaka, A.A.; Zhan, C.G.; Sun, D. Withaferin-A targets heat shock protein 90 in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.Y.; Kim, B.W. Withaferin-A inhibits colon cancer cell growth by blocking STAT3 transcriptional activity. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 20, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.; Pohling, C.; Natarajan, A.; Witney, T.H.; Kaur, J.; Xu, L.; Gowrishankar, G.; L D’Souza, A.; Murty, S.; Schick, S.; et al. AshwaMAX and Withaferin-A inhibits gliomas in cellular and murine orthotopic models. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 126, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, J.K.; Surh, Y.J. Emerging avenues linking inflammation and cancer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 2013–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Kim, T.H.; Ku, S.K.; Min, K.J.; Lee, H.S.; Kwon, T.K.; Bae, J.S. Barrier protective effects of withaferin-A in HMGB1-induced inflammatory responses in both cellular and animal models. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 262, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.J.; Choi, K.; Kwon, T.K. Withaferin-A down-regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression and PGE2 production through the inhibition of STAT1/3 activation in microglial cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SoRelle, J.A.; Itoh, T.; Peng, H.; Kanak, M.A.; Sugimoto, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Levy, M.F.; Lawrence, M.C.; Naziruddin, B. Withaferin-A inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine-induced damage to islets in culture and following transplantation. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surh, Y.J.; Kundu, J.K.; Na, H.K. Nrf2 as a master redox switch in turning on the cellular signaling involved in the induction of cytoprotective genes by some chemopreventive phytochemicals. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 1526–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.K.; Satyan, K.S.; Ghosal, S. Antioxidant activity of glycowithanolides from Withania somnifera. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 1997, 35, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jadeja, R.N.; Urrunaga, N.H.; Dash, S.; Khurana, S.; Saxena, N.K. Withaferin-A reduces acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 97, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, H.K.; Surh, Y.J. Oncogenic potential of Nrf2 and its principal target protein heme oxygenase-1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 67, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panjamurthy, K.; Manoharan, S.; Balakrishnan, S.; Suresh, K.; Nirmal, M.R.; Senthil, N.; Alias, L.M. Protective effect of Withaferin-A on micronucleus frequency and detoxication agents during experimental oral carcinogenesis. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2008, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, A.; Shandilya, A.; Punetha, A.; Bisaria, V.S.; Sundar, D. Inhibition of the NEMO/IKKβ association complex formation, a novel mechanism associated with the NF-κB activation suppression by Withania somnifera's key metabolite withaferin A. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyninck, K.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Van der Veken, P.; Haegeman, G.; Vanden Berghe, W. Withaferin-A inhibits NF-κB activation by targeting cysteine 179 in IKKβ. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 91, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.P.; Harris, C.C. Inflammation and cancer: An ancient link with novel potentials. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, J.K.; Surh, Y.J. Breaking the relay in deregulated cellular signal transduction as a rationale for chemoprevention with anti-inflammatory phytochemicals. Mutat. Res. 2005, 591, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, J.K.; Surh, Y.J. Inflammation: Gearing the journey to cancer. Mutat. Res. 2008, 659, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.H.; Lee, T.J.; Park, J.W.; Kwon, T.K. Withaferin-A inhibits iNOS expression and nitric oxide production by Akt inactivation and down-regulating LPS-induced activity of NF-κB in RAW 264.7 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 599, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.J.; Park, E.J.; Min, K.J.; Park, J.W.; Kwon, T.K. Endoplasmic reticulum stress mediates withaferin-A-induced apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2011, 25, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martorana, F.; Guidotti, G.; Brambilla, L.; Rossi, D. Withaferin-A inhibits nuclear factor-κB-dependent pro-inflammatory and stress response pathways in the astrocytes. Neural Plast. 2015, 2015, 381964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Kim, T.H.; Kang, M.J.; Choi, J.A.; Pack, D.Y.; Lee, I.R.; Kim, M.G.; Han, S.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Oh, S.M.; et al. Inhibitory effect of withaferin-A on Helicobacter pyloriinduced IL8 production and NFκB activation in gastric epithelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ku, S.K.; Han, M.S.; Bae, J.S. Withaferin-A is an inhibitor of endothelial protein C receptor shedding in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Roy, K.S.; Chakrabarti, T.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Roychoudhury, S. Withaferin-A modulates the Spindle assembly checkpoint by degradation of Mad2-Cdc20 complex in colorectal cancer cell lines. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 91, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grogan, P.T.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Timmermann, B.N.; Cohen, M.S. Oxidative cytotoxic agent withaferin-A resensitizes temozolomide-resistant glioblastomas via MGMT depletion and induces apoptosis through Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitory modulation. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 32, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, T.Z.; Wang, G.S. Antiproliferation potential of withaferin A on human osteosarcoma cells via the inhibition of G2/M checkpoint proteins. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 10, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.V.; Suman, S.; Das, T.P.; Luevano, J.E.; Damodaran, C. Withaferin-A, a steroidal lactone from Withania somnifera, induces mitotic catastrophe and growth arrest in prostate cancer cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1909–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Timmermann, B.; Samadi, A.K.; Cohen, M.S. Withaferin-A induces proteasome-dependent degradation of breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 and heat shock factor 1 proteins in breast cancer cells. ISRN Biochem. 2012, 2012, 707586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Samadi, A.K.; Roby, K.F.; Timmermann, B.; Cohen, M.S. Inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptosis in ovarian carcinoma cell lines CaOV3 and SKOV3 by natural withanolide Withaferin-A. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 124, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koduru, S.; Kumar, R.; Srinivasan, S.; Evers, M.B.; Damodaran, C. Notch-1 inhibition by Withaferin-A: A therapeutic target against colon carcinogenesis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Sheng, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.; Bai, C. Effect of Withaferin-A on A549 cellular proliferation and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 1711–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, M.K.; Gachuki, B.W.; Alhakeem, S.S.; Oben, K.N.; Rangnekar, V.M.; Gupta, R.C.; Bondada, S. Anti-cancer activity of withaferin-A in B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, M.L.; Lee, J.; Hahm, E.R.; Kim, S.H.; Marcus, A.I.; Kumari, V.; Ji, X.; Yang, Z.; Vowell, C.L.; Wipf, P.; et al. Growth arrest by the antitumor steroidal lactone withaferin-A in human breast cancer cells is associated with down-regulation and covalent binding at cysteine 303 of β-tubulin. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1852–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Okuzaki, D.; Fukushima, K.; Mukai, S.; Ohno, S.; Ozaki, Y.; Yabuta, N.; Nojima, H. Withaferin A induces cell death selectively in androgen-independent prostate cancer cells but not in normal fibroblast cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Ranga, R.S.; Burikhanov, R.; Han, S.S.; Chendil, D. Par-4-dependent apoptosis by the dietary compound withaferin A in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 246–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.E.; Shin, J.A.; Jeong, J.H.; Jeon, J.G.; Lee, M.H.; Cho, S.D. Anticancer activity of Ashwagandha against human head and neck cancer cell lines. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.J.; Um, H.J.; Min do, S.; Park, J.W.; Choi, K.S.; Kwon, T.K. Withaferin-A sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-mediated up-regulation of death receptor 5 and down-regulation of c-FLIP. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, F.; Kumar, A.; Bhushan, S.; Khan, S.; Bhatia, A.; Suri, K.A.; Qazi, G.N.; Singh, J. Reactive oxygen species generation and mitochondrial dysfunction in the apoptotic cell death of human myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells by a dietary compound withaferin-A with concomitant protection by N-acetyl cysteine. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 2115–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayola, E.; Gallerne, C.; Esposti, D.D.; Martel, C.; Pervaiz, S.; Larue, L.; Debuire, B.; Lemoine, A.; Brenner, C.; Lemaire, C. Withaferin A induces apoptosis in human melanoma cells through generation of reactive oxygen species and down-regulation of Bcl-2. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 1014–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.G.; Piao, J.L.; Rehman, M.U.; Ogawa, R.; Li, P.; Zhao, Q.L.; Kondo, T.; Inadera, H. Molecular mechanisms of hyperthermia-induced apoptosis enhanced by withaferin A. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 723, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahm, E.R.; Singh, S.V. Withaferin-A-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells is associated with suppression of inhibitor of apoptosis family protein expression. Cancer Lett. 2013, 334, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahm, E.R.; Lee, J.; Huang, Y.; Singh, S.V. Withaferin-A suppresses estrogen receptor-α expression in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2011, 50, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Mukerji, R.; Samadi, A.K.; Cohen, M.S. Down-regulation of estrogen receptor-α and rearranged during transfection tyrosine kinase is associated with withaferin a-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahm, E.R.; Moura, M.B.; Kelley, E.E.; Van Houten, B.; Shiva, S.; Singh, S.V. Withaferin A-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells is mediated by reactive oxygen species. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gamerdinger, M.; Kaya, A.M.; Wolfrum, U.; Clement, A.M.; Behl, C. BAG3 mediates chaperone-based aggresome-targeting and selective autophagy of misfolded proteins. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, C.; Dutta, A.; Mallick, A.; Chandra, S.; Misra, L.; Sangwan, R.S. Withaferin A induces apoptosis by activating p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascade in leukemic cells of lymphoid and myeloid origin through mitochondrial death cascade. Apoptosis 2008, 13, 1450–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagalingam, A.; Kuppusamy, P.; Singh, S.V.; Sharma, D.; Saxena, N.K. Mechanistic elucidation of the antitumor properties of withaferin a in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2617–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkers, P.F.; Medema, R.H.; Lammers, J.W.; Koenderman, L.; Coffer, P.J. Expression of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member Bim is regulated by the forkhead transcription factor FKHR-L1. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnavi, K.; Saxena, N.; Shah, N.; Singh, R.; Manjunath, K.; Uthayakumar, M.; Kanaujia, S.P.; Kaul, S.C.; Sekar, K.; Wadhwa, R. Differential activities of the two closely related withanolides, Withaferin-A and Withanone: Bioinformatics and experimental evidences. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, M.; Qiu, S.G.; Vasudevan, K.M.; Rangnekar, V.M. Par-4 drives trafficking and activation of Fas and Fasl to induce prostate cancer cell apoptosis and tumor regression. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 7255–7263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sells, S.F.; Han, S.S.; Muthukkumar, S.; Maddiwar, N.; Johnstone, R.; Boghaert, E.; Gillis, D.; Liu, G.; Nair, P.; Monnig, S.; et al. Expression and function of the leucine zipper protein Par-4 in apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 3823–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchitto, A.; Torrice, A.; Semeraro, R.; Napoli, C.; Nuzzo, G.; Giuliante, F.; Alpini, G.; Carpino, G.; Berloco, P.B.; Izzo, L.; et al. Prostate apoptosis response-4 is expressed in normal cholangiocytes, is down-regulated in human cholangiocarcinoma, and promotes apoptosis of neoplastic cholangiocytes when induced pharmacologically. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindqvist, L.M.; Simon, A.K.; Baehrecke, E.H. Current questions and possible controversies in autophagy. Cell Death Discov. 2015, 1, 15036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.; Mei, Y.; Sinha, S. Role of the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in cancer. J. Oncol. 2013, 2013, 102735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahm, E.R.; Singh, S.V. Autophagy fails to alter withaferin-A-mediated lethality in human breast cancer cells. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 640–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, M.Y.; Jin, S.; Rane, M.; Singh, R.K.; Gupta, R.; Kakar, S.S. Withaferin-A synergizes the therapeutic effect of doxorubicin through ROS-mediated autophagy in ovarian cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanna, K.S.; Shilpa, P.; BP, S. Withaferin A suppresses the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells via Sp1 transcription factor. Curr. Trends Biotechnol. Pharm. 2009, 3, 138–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.P.; Thippeswamy, G.; Salimath, B.P. WITHDRAWN: Anti-tumor and proapoptotic effect of withaferin-A is mediated by up-regulation of Bax and inhibition NF-κB in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Islam, M.K.; Shilpi, J.A.; Hasan, S. Inhibition of VEGF: A novel mechanism to control angiogenesis by Withania somnifera's key metabolite Withaferin A. In Silico Pharmacol. 2013, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Shah, N.; Lee, J.S.; Katiyar, S.P.; Li, L.; Oh, E.; Sundar, D.; Yun, C.O.; Wadhwa, R.; Kaul, S.C. Withanone-rich combination of Ashwagandha withanolides restricts metastasis and angiogenesis through hnRNP-K. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 2930–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Hahm, E.R.; Marcus, A.I.; Singh, S.V. Withaferin-A inhibits experimental epithelial-mesenchymal transition in MCF-10A cells and suppresses vimentin protein level in vivo in breast tumors. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Lim, I.H.; Sung, E.G.; Kim, J.Y.; Song, I.H.; Park, Y.K.; Lee, T.J. Withaferin-A inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity by suppressing the Akt signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szarc vel Szic, K.; Op de Beeck, K.; Ratman, D.; Wouters, A.; Beck, I.M.; Declerck, K.; Heyninck, K.; Fransen, E.; Bracke, M.; De Bosscher, K.; et al. Pharmacological levels of Withaferin-A (Withania somnifera) trigger clinically relevant anticancer effects specific to triple negative breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87850. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Sehrawat, A.; Singh, S.V. Withaferin-A causes activation of Notch2 and Notch4 in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suttana, W.; Mankhetkorn, S.; Poompimon, W.; Palagani, A.; Zhokhov, S.; Gerlo, S.; Haegeman, G.; Berghe, W.V. Differential chemosensitization of P-glycoprotein overexpressing K562/Adr cells by withaferin-A and Siamois polyphenols. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kakar, S.S.; Jala, V.R.; Fong, M.Y. Synergistic cytotoxic action of cisplatin and withaferin-A on ovarian cancer cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 423, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.T.; Weng, C.C.; Hsiao, P.J.; Chen, L.H.; Kuo, T.L.; Chen, Y.W.; Kuo, K.K.; Cheng, K.H. Stem cell marker nestin is critical for TGF-β1-mediated tumor progression in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Singh, S.V. Mammary cancer chemoprevention by withaferin-A is accompanied by in vivo suppression of self-renewal of cancer stem cells. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, M.; Eastman, B.M.; Webb, D.L.; Stoletov, K.; Klemke, R.; Gonias, S.L. Cell signaling by urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor induces stem cell-like properties in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8948–8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Dontu, G.; Mantle, I.D.; Patel, S.; Ahn, N.S.; Jackson, K.W.; Suri, P.; Wicha, M.S. Hedgehog signaling and Bmi-1 regulate self-renewal of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6063–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, P.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cell function is reduced by Withaferin-A, a potent and abundant component of Withania somnifera root extract. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambhir, L.; Checker, R.; Sharma, D.; Thoh, M.; Patil, A.; Degani, M.; Gota, V.; Sandur, S.K. Thiol dependent NF-κB suppression and inhibition of T-cell mediated adaptive immune responses by a naturally occurring steroidal lactone Withaferin A. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 289, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaileh, M.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Heyerick, A.; Horion, J.; Piette, J.; Libert, C.; De Keukeleire, D.; Essawi, T.; Haegeman, G. Withaferin-A strongly elicits IκB kinase β hyperphosphorylation concomitant with potent inhibition of its kinase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 4253–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.S.; Oberley, C.; Hooper, C.P.; Grindle, K.; Wuerzberger-Davis, S.; Wolff, J.; McCool, K.; Rui, L.; Miyamoto, S. Withaferin-A disrupts ubiquitin-based NEMO reorganization induced by canonical NF-κB signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 331, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.H.; Pan, W.; Kang, L.H.; Feng, H.; Song, Y.Q. Association of annexin A2 with cancer development. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Falsey, R.R.; Marron, M.T.; Gunaherath, G.M.; Shirahatti, N.; Mahadevan, D.; Gunatilaka, A.A.; Whitesell, L. Actin microfilament aggregation induced by withaferin-A is mediated by annexin II. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozorowski, G.; Ryan, C.M.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Luecke, H. Withaferin-A binds covalently to the N-terminal domain of annexin A2. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grin, B.; Mahammad, S.; Wedig, T.; Cleland, M.M.; Tsai, L.; Herrmann, H.; Goldman, R.D. Withaferin-A alters intermediate filament organization, cell shape and behavior. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Experimental Models | Molecular Targets | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Prostate cancer cells | Induced G2/M phase arrest. ↑ phosphorylation of Wee-1, p21, Aurora B and histone H3 ↓ expression of cyclin-A2, -B1 and -E2 ↓ phosphorylation of Cdc2, (tyrosine-15), Chk1 (serine-345) and Chk2 (threonine-68) | [58] |
| ↑ generation of ROS ↑ mRNA and protein expression of c-Fos ↓ expression of c-FLIP; Disruption of vimentin subcellular localization | [65] | |
| ↑ Par-4 expression ↓ NF-κB activity ↓ Bcl-2 expression | [66] | |
| Osteosarcoma cells (MG63 and U20S) | Induced G2/M phase arrest. ↑ phosphorylation of Chk1 (ser345) and Chk2 (Thr68) ↓ phosphorylation of Cdc2 (tyrosine-15) ↓ expression of cyclin-A and -B1, and Cdk2 | [57] |
| Ovarian cancer cells (CaOV3 and SKOV3) | Induced G2/M phase arrest. ↓ expression of Notch-3 and Bcl-2 ↓ phosphorylation of Akt ↑ activation of caspase-3 and cleavage of PARP | [60] |
| Colorectal cells (HCT116 and SW480) | Induced G2/M phase arrest. ↑ proteasomal degradation of Mad2 and Cdc20; interference with spindle assembly and delayed mitosis | [55] |
| Lung cancer cells (A549) | Induced G0/G1 phase arrest. ↓ expression of Bcl-2 ↓ phosphorylation of Akt ↑ activation of caspase-3 and cleavage of PARP | [62] |
| Head and neck carcinoma cells (MC3 and HN22) | ↑ expression of Bim, t-Bid, c-caspase-8, DR-5, c-PARP | [67] |
| Human renal carcinoma cells (Caki) | ↑ ROS generation ↑ expression of CHOP and DR-5 ↓ activation of NF-κB and expression of c-FLIP | [68] |
| Glioblastoma multiforme cells | ↑ expression of cyclin B1 and induction of G2/M phase arrest ↓ phosphorylation of Akt, mTOR, p70 S6K ↓ expression of c-Met, EGFR and Her2 ↑ activation of caspase-8,-9, -7 and -3 ↑expression of HSP70 and HSP32 ↓ expression of HSF-1 | [56] |
| Human leukemia cells (HL60) | ↑ generation of ROS ↑ activation of caspase-9 and -3 ↑ mitochondrial localization of Bax and release of cytochrome c ↑ cleavage of PARP ↑ caspase-8 cleavage ↓ expression of Bid ↓ activation of NF-κB | [69] |
| Melanoma cells | ↑ generation of ROS ↑ activation of caspase-9 and -3 ↓ Bcl-2/Bax and Bcl-2/Bim ratios | [70] |
| Cervical cancer cells (Caski) | Induces G2/M phase arrest. ↓ expression of E6/E7 ↑ accumulation of p53,and expression of p21 and Bax ↓ expression of cyclin B1, Cdc2, Bcl-2 and PCNA ↓ phosphorylation of STAT3 | [22] |
| ↓ GSH/GSSG ratio ↑ caspase-3 activation ↑ tBid and Noxa expression ↓ Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 expression | [71] | |
| Breast cancer cells | ↑ expression of Bim-S and Bim-EL ↑ cleavage of PARP ↓ expression of Bcl-2 | [19] |
| ↓ expression of XIAP; cIAP2 and survivin | [72] | |
| ↓ expression of ERα and pS2 ↑ expression of p53 and p21 ↑ phosphorylation of serine-315 of p53 | [73,74] | |
| Binding to cysteine-303 of β-tubulin and ↓ Hsp90 activity | [64] | |
| ↑ generation of ROS ↑ activation of Bax and Bak | [75] | |
| ↑ autophagy ↑ expression of LC3 and BAG3 | [76] | |
| Pancreatic cancer cells | ↓ Hsp90 activity ↓ expression of Akt, Cdk4 and glucocorticoid receptor | [32] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, I.-C.; Choi, B.Y. Withaferin-A—A Natural Anticancer Agent with Pleitropic Mechanisms of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030290
Lee I-C, Choi BY. Withaferin-A—A Natural Anticancer Agent with Pleitropic Mechanisms of Action. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(3):290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030290
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, In-Chul, and Bu Young Choi. 2016. "Withaferin-A—A Natural Anticancer Agent with Pleitropic Mechanisms of Action" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 3: 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030290
APA StyleLee, I. -C., & Choi, B. Y. (2016). Withaferin-A—A Natural Anticancer Agent with Pleitropic Mechanisms of Action. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(3), 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030290