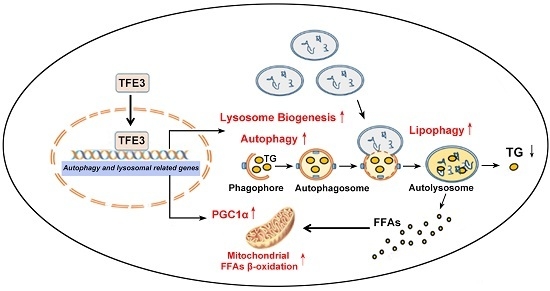
TFE3 Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis through Autophagy-Induced Lipophagy and PGC1α-Mediated Fatty Acid β-Oxidation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Autophagy Flux Is Impaired in Free Fatty Acids (FFAs) Induced Hepatocellular Steatosis and Transcription Factor E3 (TFE3) May Be Involved in Dysfunctional Hepatic Lipid Metabolism
2.2. Overexpression of TFE3 Augments Autophagy Flux, and Knockdown of TFE3 Produces the Opposite Results
2.3. TFE3 Alleviates Hepatocyte Steatosis in an Autophagy-Mediated Lipophagy Dependent Way
2.4. TFE3 Alleviates Hepatocyte Steatosis by Increasing Peroxisome Proliferative Activated Receptor Gamma Coactivator 1α (PGC1α)-Dependent Mitochondrial Fatty Acid β-Oxidation
2.5. TFE3 Regulates PGC1α via Binding to Its Promoter Region
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Antibodies
3.2. Cell Culture and FFA Treatment
3.3. Construction of Inducible TFE3 Expression Cell Lines
3.4. Oil Red O Staining and Lipid Content Measurement
3.5. Measurement of Biochemical Parameters
3.6. Autophagic Flux Analysis
3.7. RNA Purification and Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analysis
3.8. Western Blot Analysis
3.9. RNA Interference
3.10. BODIPY 493/503 Staining and Immunofluorescence Assay
3.11. Seahorse XF-96 Metabolic Flux Analysis
3.12. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (CHIP) Assay
3.13. Luciferase Reporter
3.14. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brunt, E.M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Pros and Cons of Histologic Systems of Evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 17, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.S.; Diehl, A.M. Hepatic triglyceride synthesis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2008, 19, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlanga, A.; Guiu-Jurado, E.; Porras, J.A.; Auguet, T. Molecular pathways in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2014, 7, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martinet, W.; Agostinis, P.; Vanhoecke, B.; Dewaele, M.; de Meyer, G.R. Autophagy in disease: A double-edged sword with therapeutic potential. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 697–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, M.; Czaja, M.J. Autophagy in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 5, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinsztein, D.C.; Codogno, P.; Levine, B. Autophagy modulation as a potential therapeutic target for diverse diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 709–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, A.M.; Ryter, S.W.; Levine, B. Autophagy in human health and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1845–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Kaushik, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Novak, I.; Komatsu, M.; Tanaka, K.; Cuervo, A.M.; Czaja, M.J. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature 2009, 458, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, H.; Kaushik, S.; Cuervo, A.M. Altered lipid content inhibits autophagic vesicular fusion. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 3052–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, P.; Fu, S.; Calay, E.S.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Defective hepatic autophagy in obesity promotes ER stress and causes insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inami, Y.; Yamashina, S.; Izumi, K.; Ueno, T.; Tanida, I.; Ikejima, K.; Watanabe, S. Hepatic steatosis inhibits autophagic proteolysis via impairment of autophagosomal acidification and cathepsin expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, M.; Hanada, S.; Toivola, D.M.; Ghori, N.; Omary, M.B. Autophagy activation by rapamycin eliminates mouse Mallory-Denk bodies and blocks their proteasome inhibitor-mediated formation. Hepatology 2008, 47, 2026–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.W.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Xiong, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Dong, X.C.; Yin, X.M. Pharmacological promotion of autophagy alleviates steatosis and injury in alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver conditions in mice. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Wang, Q.; Song, S.; Liu, F.; He, B.; Gao, X. Protective role of autophagy in methionine-choline deficient diet-induced advanced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 770, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, M.; Nadanaka, S.; Tanakura, S.; Sawaguchi, S.; Midori, S.; Kawai, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Shimada, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Matsumura, Y.; et al. TFE3 is a bHLH-ZIP-type transcription factor that regulates the mammalian Golgi stress response. Cell Struct. Funct. 2015, 40, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martina, J.A.; Diab, H.I.; Lishu, L.; Jeong, A.L.; Patange, S.; Raben, N.; Puertollano, R. The nutrient-responsive transcription factor TFE3 promotes autophagy, lysosomal biogenesis, and clearance of cellular debris. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, ra9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasset, I.; Cuervo, A.M. Role of chaperone-mediated autophagy in metabolism. FEBS J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabeya, Y.; Mizushima, N.; Yamamoto, A.; Oshitani-Okamoto, S.; Ohsumi, Y.; Yoshimori, T. LC3, GABARAP and GATE16 localize to autophagosomal membrane depending on form-II formation. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 2805–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skop, V.; Cahova, M.; Papackova, Z.; Palenickova, E.; Dankova, H.; Baranowski, M.; Zabielski, P.; Zdychova, J.; Zidkova, J.; Kazdova, L. Autophagy-lysosomal pathway is involved in lipid degradation in rat liver. Physiol. Res. 2012, 61, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fukuo, Y.; Yamashina, S.; Sonoue, H.; Arakawa, A.; Nakadera, E.; Aoyama, T.; Uchiyama, A.; Kon, K.; Ikejima, K.; Watanabe, S. Abnormality of autophagic function and cathepsin expression in the liver from patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavallard, V.J.; Gual, P. Autophagy and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 120179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martina, J.A.; Diab, H.I.; Li, H.; Puertollano, R. Novel roles for the MiTF/TFE family of transcription factors in organelle biogenesis, nutrient sensing, and energy homeostasis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 2483–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Lipotoxicity in NASH. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdecantos, M.P.; Prieto-Hontoria, P.L.; Pardo, V.; Modol, T.; Santamaria, B.; Weber, M.; Herrero, L.; Serra, D.; Muntane, J.; Cuadrado, A.; et al. Essential role of Nrf2 in the protective effect of lipoic acid against lipoapoptosis in hepatocytes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 84, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Luo, Y.; Deng, H.; Qin, S.; Tang, W.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, B. Hugan Qingzhi medication ameliorates hepatic steatosis by activating AMPK and PPARα pathways in L02 cells and HepG2 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finck, B.N.; Kelly, D.P. PGC-1 coactivators: Inducible regulators of energy metabolism in health and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolo, A.P.; Teodoro, J.S.; Palmeira, C.M. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura-Clapier, R.; Garnier, A.; Veksler, V. Transcriptional control of mitochondrial biogenesis: The central role of PGC-1α. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 79, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpulla, R.C. Metabolic control of mitochondrial biogenesis through the PGC-1 family regulatory network. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Shimano, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Ide, T.; Tamura, M.; Furusawa, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Inoue, N.; Matsuzaka, T.; Takahashi, A.; et al. TFE3 transcriptionally activates hepatic IRS-2, participates in insulin signaling and ameliorates diabetes. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, H.; Naka, A.; Iida, K.T.; Nakagawa, Y.; Matsuzaka, T.; Ishii, K.A.; Kobayashi, K.; Takahashi, A.; Yatoh, S.; Yahagi, N.; et al. TFE3 regulates muscle metabolic gene expression, increases glycogen stores, and enhances insulin sensitivity in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endoc. Metab. 2012, 302, E896–E902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksan, I.; Goding, C.R. Targeting the microphthalmia basic helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper transcription factor to a subset of E-box elements in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 6930–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.A.; Farah, B.L.; Singh, B.K.; Siddique, M.M.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ilkayeva, O.R.; Gooding, J.; Ching, J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Caffeine stimulates hepatic lipid metabolism by the autophagy-lysosomal pathway in mice. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1366–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| TFE3 | CCGTGTTCGTGCTGTTGGA | GCTCGTAGAAGCTGTCAGGAT |
| VPS11 | CAAGCCTACAAACTACGGGTG | GAGTGCAGAGTGGATTGCCA |
| VPS18 | CACTCGGGGTATGTGAATGCC | TCGGAAGGGGTGAAGTCAATG |
| CTSD | TGCTCAAGAACTACATGGACGC | CGAAGACGACTGTGAAGCACT |
| CTSL | CGTGACGCCAGTGAAGAATCA | CGCTCAGTGAGACAAGTTTCC |
| Atg5 | AAAGATGTGCTTCGAGATGTGT | CACTTTGTCAGTTACCAACGTCA |
| Atg16 | AACGCTGTGCAGTTCAGTCC | AGCTGCTAAGAGGTAAGATCCA |
| LAMP1 | TCTCAGTGAACTACGACACCA | AGTGTATGTCCTCTTCCAAAAGC |
| MCOLN1 | TTCGCCGTCGTCTCAAATACT | CTCTTCCCGGAATGTCACAGC |
| FASN | AAGGACCTGTCTAGGTTTGATGC | TGGCTTCATAGGTGACTTCCA |
| ACC | ATGTCTGGCTTGCACCTAGTA | CCCCAAAGCGAGTAACAAATTCT |
| SCD1 | GCCCCTCTACTTGGAAGACGA | AAGTGATCCCATACAGGGCTC |
| DGAT1 | TATTGCGGCCAATGTCTTTGC | CACTGGAGTGATAGACTCAACCA |
| DGAT2 | ATTGCTGGCTCATCGCTGT | GGGAAAGTAGTCTCGAAAGTAGC |
| PNPLA2 | ATGGTGGCATTTCAGACAACC | CGGACAGATGTCACTCTCGC |
| LIPC | ATCAAGTGCCCTTGGACAAAG | TGACAGCCCTGATTGGTTTCT |
| PPARα | TTCGCAATCCATCGGCGAG | CCACAGGATAAGTCACCGAGG |
| PGC1α | TCTGAGTCTGTATGGAGTGACAT | CCAAGTCGTTCACATCTAGTTCA |
| CPT1α | TCCAGTTGGCTTATCGTGGTG | TCCAGAGTCCGATTGATTTTTGC |
| ACOX1 | ACTCGCAGCCAGCGTTATG | AGGGTCAGCGATGCCAAAC |
| GAPDH | CTGGGCTACACTGAGCACC | AAGTGGTCGTTGAGGGCAATG |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, J.; Wang, K.; He, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, D.; Chen, F. TFE3 Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis through Autophagy-Induced Lipophagy and PGC1α-Mediated Fatty Acid β-Oxidation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030387
Xiong J, Wang K, He J, Zhang G, Zhang D, Chen F. TFE3 Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis through Autophagy-Induced Lipophagy and PGC1α-Mediated Fatty Acid β-Oxidation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(3):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030387
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Jie, Kezhou Wang, Jiangping He, Guangya Zhang, Dandan Zhang, and Fengling Chen. 2016. "TFE3 Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis through Autophagy-Induced Lipophagy and PGC1α-Mediated Fatty Acid β-Oxidation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 3: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030387
APA StyleXiong, J., Wang, K., He, J., Zhang, G., Zhang, D., & Chen, F. (2016). TFE3 Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis through Autophagy-Induced Lipophagy and PGC1α-Mediated Fatty Acid β-Oxidation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(3), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030387