Neutralization of Bacterial YoeBSpn Toxicity and Enhanced Plant Growth in Arabidopsis thaliana via Co-Expression of the Toxin-Antitoxin Genes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Production of yefMSpn Antitoxin in Transgenic A. thaliana
2.2. Transgenic A. thaliana Showed Normal Morphology after 17-β-Estradiol Induction for the Expression of yefMSpn Antitoxin
2.3. Crosses of T1 Transgenic yoeBSpn-GFP Plants with T1 Transgenic yefMSpn Plants Produced yefMSpn × yoeBSpn-GFP Hybrid Lines
2.4. Hybrids of Transgenic Plants Expressed Both yefMSpn and yoeBSpn-GFP after Induction with 17-β-Estradiol
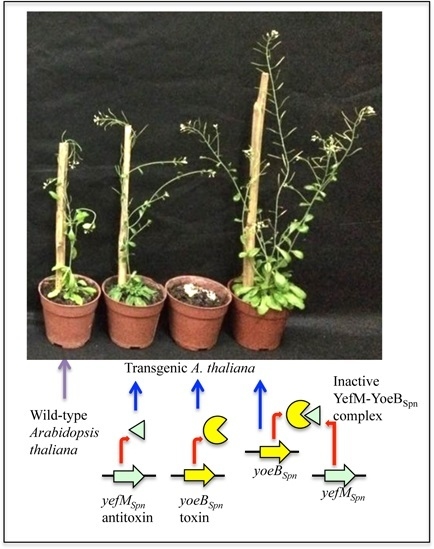
2.5. Induced Expression of yefMSpn and yoeBSpn-GFP Enhanced Growth in Hybrid A. thaliana
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Construction of Plasmids
4.2. Plant Material and Growth Condition
4.3. Plant Transformation and Selection
4.4. PCR Analysis
4.5. Morphology of Transgenic A. thaliana
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Cross-Pollination and Selection of Hybrid T2 Seeds
4.8. Southern Blot Analysis
4.9. qRT-PCR Analyses of yefMSpn and yoeBSpn-GFP Expression in Transgenic Hybrid Plants
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CTAB | Cetyl trimethylammonium bromide |
| GFP | Green fluorescent protein |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase PCR |
| TA | toxin-antitoxin |
References
- Gerdes, K.; Christensen, S.K.; Løbner-Olesen, A. Prokaryotic toxin antitoxin stress response loci. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, F.; Kędzierska, B. Regulating toxin-antitoxin expression: Controlled detonation of intracellular molecular timebombs. Toxins 2014, 6, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, F.; Van Melderen, L. Toxins-antitoxins: Diversity, evolution and function. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 46, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, H.; Tan, Q.; Awano, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Inouye, M. A novel membrane-bound toxin for cell division, CptA (YgfX), inhibits polymerization of cytoskeleton proteins, FtsZ and MreB, in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 328, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lord, D.M.; Cheng, H.Y.; Osbourne, D.O.; Hong, S.H.; Sanchez-Torres, V.; Quiroga, C.; Zheng, K.; Herrmann, T.; Peti, W.; et al. A new type V toxin–antitoxin system where mRNA for toxin GhoT is cleaved by antitoxin GhoS. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, C.F.; Bertram, R. Toxin–antitoxin systems are ubiquitous and versatile modulators of prokaryotic cell fate. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 340, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Park, J.H.; Inouye, M. Toxin-antitoxin systems in bacteria and archaea. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2011, 45, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutschler, H.; Gebhardt, M.; Shoeman, R.L.; Meinhart, A. A novel mechanism of programmed cell death in bacteria by toxin-antitoxin systems corrupts peptidoglycan synthesis. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristoffersen, P.; Jensen, G.B.; Gerdes, K.; Piskur, J. Bacterial toxin-antitoxin gene system as containment control in yeast cells. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 5524–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.M.; Gerdes, K.; Tunnacliffe, A. Bacterial toxin RelE induces apoptosis in human cells. FEBS Lett. 2002, 519, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.L.; Wolfson, L.J.; Watt, J.P.; Henkle, E.; Deloria-Knoll, M.; McCall, N.; Cherian, T. Burden of disease caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in children younger than 5 years: Global estimates. Lancet 2009, 374, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.T.; Moreno-Córdoba, I.; Yeo, C.C.; Espinosa, M. Toxin-antitoxin genes of the Gram-positive pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae: So few and yet so many. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.T.; Moreno-Córdoba, I.; Yeo, C.C.; Espinosa, M. Toxin-antitoxin loci in Streptococcus pneumoniae. In Prokaryotic Toxin-Antitoxins; Gerdes, K., Ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany; Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 315–339. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, W.T.; Yeo, C.C.; Sadowy, E.; Espinosa, M. Functional validation of putative toxin-antitoxin genes from the Gram-positive pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae: Phd-doc is the fourth bona-fide operon. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, C.; Cherny, I.; Khoo, S.K.; de Lacoba, M.G.; Chan, W.T.; Yeo, C.C.; Espinosa, M. The yefM-yoeB toxin-antitoxin systems of Escherichia coli and Streptococcus pneumoniae: Functional and structural correlation. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Bakar, F.; Yeo, C.C.; Harikrishna, J.A. Expression of the Streptococcus pneumoniae yoeB Chromosomal toxin gene causes cell death in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Biotechnol. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, L.; Horler, M.; Nuesch, E.; Vassalli, S.; Barrell, P.; Yang, W.; Jefferson, R.A.; Grossniklaus, U.; Curtis, M.D. A versatile and reliable two-component system for tissue-specific gene induction in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.T.; Neito, C.; Harikrishna, J.A.; Khoo, S.K.; Othman, R.Y.; Espinosa, M.; Yeo, C.C. Genetic regulation of the yefM-yoeBspn toxin-antitoxin locus of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 4612–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Arabidopsis thaliana Genome. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/?term=arabidopsis+thaliana (accessed on 15 September 2015).
- Li, S.; Blanchoin, L.; Yang, Z.; Lord, E.M. The putative Arabidopsis Arp2/3 complex controls leaf cell morphogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 2034–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, M.; Sharma, D.; Singh, M.; Tripathi, R.D.; Trivedi, P.K. Expression of OsMATE1 and OsMATE2 alters development, stress responses and pathogen susceptibility in Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Brattain, M.G. The maximal size of protein to diffuse through the nuclear pore is larger than 60 kDa. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 3164–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holsters, M.; de Waele, D.; Depicker, A.; Messens, E.; van Montagu, M.; Schell, J. Transfection and transformation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1978, 163, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.M.; Hall, A.; Millar, A.J.; Darrah, C.; Davis, S.J. Protocol: Streamlined sub-protocols for floral-dip transformation and selection of transformants in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Methods 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, S.O.; Bendich, A.J. Extraction of total cellular DNA from plants, algae and fungi. In Plant Molecular Biology Manual; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1994; pp. 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu Bakar, F.; Yeo, C.C.; Harikrishna, J.A. Neutralization of Bacterial YoeBSpn Toxicity and Enhanced Plant Growth in Arabidopsis thaliana via Co-Expression of the Toxin-Antitoxin Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040321
Abu Bakar F, Yeo CC, Harikrishna JA. Neutralization of Bacterial YoeBSpn Toxicity and Enhanced Plant Growth in Arabidopsis thaliana via Co-Expression of the Toxin-Antitoxin Genes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(4):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040321
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu Bakar, Fauziah, Chew Chieng Yeo, and Jennifer Ann Harikrishna. 2016. "Neutralization of Bacterial YoeBSpn Toxicity and Enhanced Plant Growth in Arabidopsis thaliana via Co-Expression of the Toxin-Antitoxin Genes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 4: 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040321
APA StyleAbu Bakar, F., Yeo, C. C., & Harikrishna, J. A. (2016). Neutralization of Bacterial YoeBSpn Toxicity and Enhanced Plant Growth in Arabidopsis thaliana via Co-Expression of the Toxin-Antitoxin Genes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(4), 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040321