The Expression Profile of Complement Components in Podocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
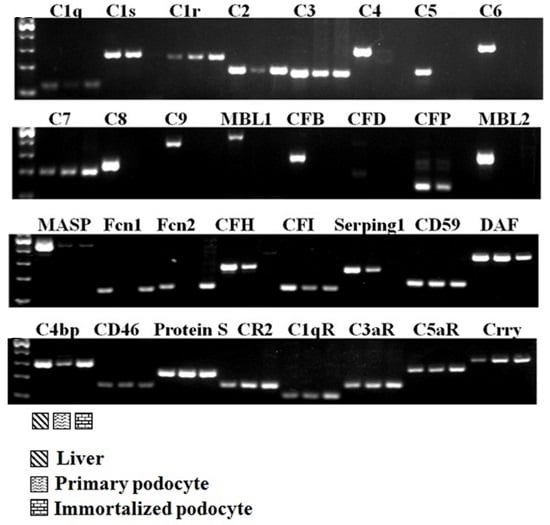
2.1. Complement Gene Expression in Podocytes
2.2. Complement Protein Expression in Podocytes Determined Using Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry/Mass Spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) Analysis
2.3. The Effect of Multiple Stimulating Factors on Complement Gene Expression
2.4. The Effect of Puromycin Aminonucleoside (PAN) on Complement Protein Expression as Determined Using iTRAQ LC–MS/MS Analysis
2.5. Multiple Complement Factor Expression and Distribution in PAN-Induced Rat Nephropathy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. RNA Isolation and Reverse Transcription
4.4. Conventional Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.5. Treatment of Podocytes with Various Factors
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.7. Protein Extraction, Digestion, and Labeling with iTRAQ Reagents, LC–MS/MS, and Database Searches
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Fluorescence Confocal Microscopy
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walport, M.J. Complement. First of two parts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sacks, S.; Zhou, W. New boundaries for complement in renal disease. JASN 2008, 19, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, B.P.; Gasque, P. Extrahepatic complement biosynthesis where, when and why? Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1997, 107, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Marsh, J.E.; Sacks, S.H. Intrarenal synthesis of complement. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragon-Durey, M.A.; Loirat, C.; Cloarec, S.; Macher, M.A.; Blouin, J.; Nivet, H.; Weiss, L.; Fridman, W.H.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V. Anti-Factor H autoantibodies associated with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. JASN 2005, 16, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Koji, T.; Furusu, A.; Shioshita, K.; Tsukasaki, S.; Ozono, Y.; Harada, T.; Sakai, H.; Kohno, S. Intraglomerular synthesis of complement C3 and its activation products in IgA nephropathy. Nephron 2001, 87, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, A.; Rastaldi, M.P.; Calvaresi, N.; Oortwijn, B.D.; Schlagwein, N.; van Gijlswijk-Janssen, D.J.; Stahl, G.L.; Matsushita, M.; Fujita, T.; van Kooten, C.; et al. Glomerular activation of the lectin pathway of complement in IgA nephropathy is associated with more severe renal disease. JASN 2006, 17, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, B.G.; Tryggvason, K.; Sundaramoorthy, M.; Neilson, E.G. Alport’s syndrome, Goodpasture’s syndrome, and type IV collagen. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2543–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheerin, N.S.; Springall, T.; Abe, K.; Sacks, S.H. Protection and injury: The differing roles of complement in the development of glomerular injury. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Li, K.; Smyth, L.A.; Xing, G.; Wang, N.; Meader, L.; Lu, B.; Sacks, S.H.; Zhou, W. C3a and C5a promote renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. JASN 2012, 23, 1474–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbate, M.; Zoja, C.; Corna, D.; Rottoli, D.; Zanchi, C.; Azzollini, N.; Tomasoni, S.; Berlingeri, S.; Noris, M.; Morigi, M.; et al. Complement-mediated dysfunction of glomerular filtration barrier accelerates progressive renal injury. JASN 2008, 19, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Zhou, W.; Sheerin, N.S.; Vaughan, R.W.; Sacks, S.H. Contribution of renal secreted complement C3 to the circulating pool in humans. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 4336–4341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sacks, S.H.; Zhou, W.; Andrews, P.A.; Hartley, B. Endogenous complement C3 synthesis in immune complex nephritis. Lancet 1993, 342, 1273–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montinaro, V.; Lopez, A.; Monno, R.; Cappiello, V.; Manno, C.; Gesualdo, L.; Schena, F.P. Renal C3 synthesis in idiopathic membranous nephropathy: Correlation to urinary C5b-9 excretion. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosolits, S.; Magyarlaki, T.; Nagy, J. Membrane attack complex and membrane cofactor protein are related to tubulointerstitial inflammation in various human glomerulopathies. Nephron 1997, 75, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, A.; Morita, Y.; Maruyama, S.; Hotta, N.; Nadai, M.; Wang, L.; Hasegawa, T.; Matsuo, S. Role of complement in acute tubulointerstitial injury of rats with aminonucleoside nephrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nangaku, M.; Pippin, J.; Couser, W.G. C6 mediates chronic progression of tubulointerstitial damage in rats with remnant kidneys. JASN 2002, 13, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sheerin, N.S.; Risley, P.; Abe, K.; Tang, Z.; Wong, W.; Lin, T.; Sacks, S.H. Synthesis of complement protein C3 in the kidney is an important mediator of local tissue injury. FASEB 2008, 22, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, E.; Navis, G.; Tiebosch, A.T.; de Jong, P.E.; de Zeeuw, D. Systemic factors are involved in the pathogenesis of proteinuria-induced glomerulosclerosis in adriamycin nephrotic rats. JASN 1999, 10, 2359–2366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pavenstadt, H.; Kriz, W.; Kretzler, M. Cell biology of the glomerular podocyte. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 253–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Fan, Q.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Guan, N.; Guan, Y.; Ding, J. Newly identified cytoskeletal components are associated with dynamic changes of podocyte foot processes. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appay, M.D.; Kazatchkine, M.D.; Levi-Strauss, M.; Hinglais, N.; Bariety, J. Expression of CR1 (CD35) mRNA in podocytes from adult and fetal human kidneys. Kidney Int. 1990, 38, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigg, R.J.; Galishoff, M.L.; Sneed, A.E., 3rd; Kim, D. Isolation and characterization of complement receptor type 1 from rat glomerular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 1993, 43, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, S.H.; Zhou, W.; Pani, A.; Campbell, R.D.; Martin, J. Complement C3 gene expression and regulation in human glomerular epithelial cells. Immunology 1993, 79, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Campbell, R.D.; Martin, J.; Sacks, S.H. Interferon-gamma regulation of C4 gene expression in cultured human glomerular epithelial cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 2477–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Chang, A.; Jacob, A.; Minto, A.W.; Karmegam, M.; Haas, M.; Quigg, R.J. Mouse podocyte complement factor H: The functional analog to human complement receptor 1. JASN 2007, 18, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Spiller, O.B.; St John, P.L.; Haas, M.; Hack, B.K.; Ren, G.; Cunningham, P.N.; Doshi, M.; Abrahamson, D.R.; Morgan, B.P.; et al. Decay-accelerating factor expression in the rat kidney is restricted to the apical surface of podocytes. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 2010–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheerin, N.S.; Sacks, S.H. The local production of complement in the pathogenesis of renal inflammation. Nephrologie 1999, 20, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vieyra, M.B.; Heeger, P.S. Novel aspects of complement in kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooimans, R.A.; Stegmann, A.P.; van Dorp, W.T.; van der Ark, A.A.; van der Woude, F.J.; van Es, L.A.; Daha, M.R. Interleukin 2 mediates stimulation of complement C3 biosynthesis in human proximal tubular epithelial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Chen, M.; Xu, H. Complement gene expression and regulation in mouse retina and retinal pigment epithelium/choroid. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; McClure, R.A.; Kelleher, N.L. Screening for expressed nonribosomal peptide synthetases and polyketide synthases using LC–MS/MS-based proteomics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1401, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Furuta, M.; Weil, R.J.; Vortmeyer, A.O.; Huang, S.; Lei, J.; Huang, T.N.; Lee, Y.S.; Bhowmick, D.A.; Lubensky, A.; Oldfield, E.H.; et al. Protein patterns and proteins that identify subtypes of glioblastoma multiforme. Oncogene 2004, 23, 6806–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Such-Sanmartin, G.; Bache, N.; Callesen, A.K.; Rogowska-Wrzesinska, A.; Jensen, O.N. Targeted mass spectrometry analysis of the proteins IGF1, IGF2, IBP2, IBP3 and A2GL by blood protein precipitation. J. Proteom. 2015, 113, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millioni, R.; Tolin, S.; Puricelli, L.; Sbrignadello, S.; Fadini, G.P.; Tessari, P.; Arrigoni, G. High abundance proteins depletion vs. low abundance proteins enrichment: Comparison of methods to reduce theplasma proteome complexity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa Abreu, R.; Penalva, L.O.; Marcotte, E.M.; Vogel, C. Global signatures of protein and mRNA expression levels. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 5, 1512–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montinaro, V.; di Cillo, M.; Perissutti, S.; Serra, L.; Tedesco, F.; Rifai, A.; Schena, F.P. Modulation of renal production of C3 by proinflammatory cytokines. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1993, 39, S37–S40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andrews, P.A.; Finn, J.E.; Lloyd, C.M.; Zhou, W.; Mathieson, P.W.; Sacks, S.H. Expression and tissue localization of donor-specific complement C3 synthesized in human renal allografts. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ault, B.H.; Colten, H.R. Cellular specificity of murine renal C3 expression in two models of inflammation. Immunology 1994, 81, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robson, M.G.; Cook, H.T.; Botto, M.; Taylor, P.R.; Busso, N.; Salvi, R.; Pusey, C.D.; Walport, M.J.; Davies, K.A. Accelerated nephrotoxic nephritis is exacerbated in C1q-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 6820–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanafusa, N.; Sogabe, H.; Yamada, K.; Wada, T.; Fujita, T.; Nangaku, M. Contribution of genetically engineered animals to the analyses of complement in the pathogenesis of nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002, 17, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Wang, Y.; Chang, A.; Minto, A.W.; Zhou, J.; Kang, H.; Haas, M.; Quigg, R.J. Unrestricted C3 activation occurs in Crry-deficient kidneys and rapidly leads to chronic renal failure. JASN 2007, 18, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Lu, B.; Hatch, E.; Sacks, S.H.; Sheerin, N.S. C3a mediates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in proteinuric nephropathy. JASN 2009, 20, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Fukuda, N.; Matsuda, H.; Endo, M.; Wang, X.; Saito, K.; Ueno, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Soma, M.; et al. Complement 3 activates the renal renin-angiotensin system by induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of the nephrotubulus in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2013, 305, F957–F967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelfelder, S.; Mokosch, B.; Lingnau, M.1.; Grahammer, F.; Huber, T.B.; Häffner, K. Expression and Functional Characterization of Complement Factor H (CFH) and Factor H Related Proteins (CFHRs) on Human Podocytes (Abstract). In Proceedings of the 10th International Podocyte Conference, Freiburg, Germany, 4–6 June 2014; Nephron Clinical Practice: Basel, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Boor, P.; Konieczny, A.; Villa, L.; Schult, A.L.; Bucher, E.; Rong, S.; Kunter, U.; van Roeyen, C.R.; Polakowski, T.; Hawlisch, H.; et al. Complement C5 mediates experimental tubulointerstitial fibrosis. JASN 2007, 18, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangan, G.K.; Pippin, J.W.; Coombes, J.D.; Couser, W.G. C5b-9 does not mediate chronic tubulointerstitial disease in the absence of proteinuria. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.K.; Shi, H.; Koraishy, F.; Marlier, A.; Ding, Z.; Shan, A.; Cantley, L.G. The Terminator mouse is a diphtheria toxin-receptor knock-in mouse strain for rapid and efficient enrichment of desired cell lineages. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zheng, C.; Fan, Y.; Zeng, C.; Chen, Z.; Qin, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; et al. Downregulation of microRNA-30 facilitates podocyte injury and is prevented by glucocorticoids. JASN 2014, 25, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Ding, F.; Ding, J. The role of survivin in podocyte injury induced by puromycin aminonucleoside. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6657–6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneveld, R.; van der Vlag, J.; Baltissen, M.P.; Verkaart, S.A.; Wetzels, J.F.; Berden, J.H.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Nijenhuis, T. Glucose specifically regulates TRPC6 expression in the podocyte in an AngII-dependent manner. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Accession Number Protein Name Protein Score | Protein Molecular Weight (MW) | Protein Isoelectric Point (PI) |
|---|---|---|
| P01027 complement C3 43.17 | 186.4 | 6.73 |
| Q64735 complement component 36.46 receptor 1-like protein | 53.7 | 6.65 |
| O35658 complement component 1 Q 171.45 subcomponent-binding protein | 31 | 4.92 |
| Accession Number | Protein Name | Fold Change in Expression | Protein MW | Protein PI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P01027 | Complement C3 | 1.278 | 186.4 | 6.7 |
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Product (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| C1qb | Forward ACGGGGCTACACAGAAAGTC | 123 |
| NM_009777.2 | Reverse TGCGTGGCTCATAGTTCTCG | |
| C1s | Forward TGGACAGTGGAGCAACTCCGGT | 256 |
| NM_144938.2 | Reverse GGTGGGTACTCCACAGGCTGGAA | |
| C1r | Forward GCCATGCCCAGGTGCAAGATCAA | 313 |
| NM_023143.3 | Reverse TGGCTGGCTGCCCTCTGATG | |
| C2 | Forward CTCATCCGCGTTTACTCCAT | 178 |
| NM_013484.2 | Reverse TGTTCTGTTCGATGCTCAGG | |
| C3 | Forward AGCAGGTCATCAAGTCAGGC | 167 |
| NM_009778.2 | Reverse GATGTAGCTGGTGTTGGGCT | |
| C4 | Forward TCGCAGACATCACCCTCCTA | 274 |
| NM_009780.2 | Reverse CTCTTGGTGGGTGCAGCATA | |
| CFB | Forward CTCCTCTGGAGGTGTGAGCG | 264 |
| NM_001142706.1 | Reverse GGTCGTGGGCAGCGTATTG | |
| CFD | Forward TCAATCATGAACCGGACAAC | 180 |
| NM_013459.3 | Reverse ATTGCCACAGACGCGAGAGC | |
| CFP | Forward GAGAGGCCCAGCAATCACAG | 141 |
| NM_008823.3 | Reverse AGCGGCTTCGTGTCTCCTTA | |
| MBL1 | Forward AGGGAGAACCAGGTCAAGGGCT | 414 |
| NM_010775.2 | Reverse ACTGCCCTTCAGTCGCCTCGT | |
| MBL2 | Forward CCCTGCCTGCAGTGACACCA | 443 |
| NM_010776.1 | Reverse AGCACCCAGTTTCTCAGGGCT | |
| Fcn1 | Forward AGGAGAAAAAGCTGAGCCGT | 126 |
| NM_007995.3 | Reverse CCACTGCATTGCTCTGGGTA | |
| Fcn | Forward AGTGCCACACTTCCAACCTG | 137 |
| NM_010190.1 | Reverse CTAGATGAGCCGCACCTTCA | |
| MASP | Forward GGCCTGAACCTGTATTCGG | 497 |
| NM_001003893.2 | Reverse CTGGCCTGAACAAAGGGCT | |
| C5 | Forward AGGGTACTTTGCCTGCTGAA | 173 |
| NM_010406.2 | Reverse TGTGAAGGTGCTCTTGGATG | |
| C6 | Forward GCGCTTCAAGAGTATGCAGC | 285 |
| NM_016704.2 | Reverse CTTGCCACCACAGCTTTGTC | |
| C7 | Forward AGAGGGCAGAGCATCTCCAT | 196 |
| NM_001243837.1 | Reverse ATCCATTGCCCATTAGCTTC | |
| C8b | Forward TGTGACCAGAACCAAACGCT | 229 |
| BC096382.1 | Reverse GTAGATGCCCCCAAGTACGG | |
| C9 | Forward CACCTTAGCCCTTGCCATCT | 354 |
| NM_013485.1 | Reverse TCTCCACAGTCGTTGTCACC | |
| CFH | Forward CGTGAATGTGGTGCAGATGGG | 248 |
| NM_009888.3 | Reverse AGAATTTCCACACATCGTGGCT | |
| CFI | Forward TTCCACTGGGTGTTCGTGAC | 126 |
| NM_007686.2 | Reverse TAAAGGCACACTCCGCCAAA | |
| DAF | Forward ACGGTACGTCATCCAACGAG | 315 |
| NM_010016.2 | Reverse AGCCAACGAAGAGTTACGAAGA | |
| CD46 | Forward CCAGGGCCAGATAAGTTTTC | 153 |
| NM_010778.3 | Reverse TATTTCGCCAGCTCCTGATA | |
| CD59 | Forward TAAGTGAGTTCCTGGCAACC | 152 |
| NM_007652.5 | Reverse AGGGCCTGTGAAGATTATGA | |
| C4bp | Forward GCCAGCAAGTGACGTGAATC | 292 |
| NM_007576.3 | Reverse TTTGCCTCGGACCTCACAAG | |
| Serping 1 | Forward TCTGCGACTGTCTGCTCAGT | 216 |
| NM_009776.3 | Reverse AGCTCTCTCTGCTTTTCGCT | |
| Crry | Forward CCAAACAATGTGGGGATAGCAG | 306 |
| L19874.1 | Reverse TGTCTGCCAAAGTGGGCTTA | |
| CR2 | Forward CCTGCTCCTCTCTGTAAACT | 162 |
| NM_007758.2 | Reverse GATCTGACTGCTTCCACTCA | |
| C3aR | Forward AGAGGTGACTCATGGAAAGGC | 167 |
| AF053757.1 | Reverse ACTGATGATCTGCGAGCCAC | |
| C5aR | Forward TATCAGGTGACCGGGGTGAT | 248 |
| NM_007577.4 | Reverse GTCGTGGACGGAGTGAAAGT | |
| C1qR | Forward AGCAAGCCGACACATGAAGA | 114 |
| NM_010740.3 | Reverse CAGCACCAGCAAGAGTGAGA | |
| Protein S | Forward GTGAGGGTATCCCAGTGTGC | 225 |
| NM_011173.2 | Reverse CATCACGAAGCGCAATCAGG |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Ding, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Ding, J. The Expression Profile of Complement Components in Podocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040471
Li X, Ding F, Zhang X, Li B, Ding J. The Expression Profile of Complement Components in Podocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(4):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040471
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuejuan, Fangrui Ding, Xiaoyan Zhang, Baihong Li, and Jie Ding. 2016. "The Expression Profile of Complement Components in Podocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 4: 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040471
APA StyleLi, X., Ding, F., Zhang, X., Li, B., & Ding, J. (2016). The Expression Profile of Complement Components in Podocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(4), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040471