The Folding of de Novo Designed Protein DS119 via Molecular Dynamics Simulations
Abstract
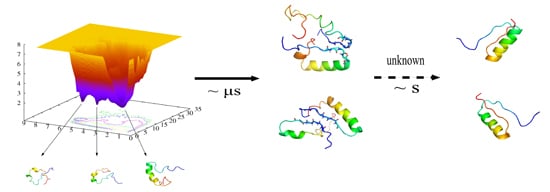
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Folding Free Energy Landscapes of DS119
2.2. Structure Features of Intermediate States
2.3. Common Contact Pattern of Initial Dimeric Aggregates
2.4. DS119 in Initial Dimeric Aggregates Stabilized in the Intermediate States
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Replica Exchange Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4.2. Conventional Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4.3. Structural Details in the Simulations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobson, C.M.; Sali, A.; Karplus, M. Protein folding—A perspective from theory and experiment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Eng. 1998, 37, 868–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, F.U.; Bracher, A.; Hayer-Hartl, M. Molecular chaperones in protein folding and proteostasis. Nature 2011, 475, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, F.U.; Hayer-Hartl, M. Molecular chaperones in the cytosol: From nascent chain to folded protein. Science 2002, 295, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, C.M. Protein folding and misfolding. Nature 2003, 426, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.E. How do small single-domain proteins fold? Fold. Des. 1998, 3, R81–R91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrick, D. What have we learned from the studies of two-state folders, and what are the unanswered questions about two-state protein folding? Phys. Biol. 2009, 6, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, C.M. Protein misfolding, evolution and disease. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999, 24, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalley-Kim, M.; Baker, D. Characterization of the folding energy landscapes of computer generated proteins suggests high folding free-energy barriers and cooperativity may be consequences of natural selection. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 338, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Piana, S.; Dror, R.O.; Shaw, D.E. How Fast-Folding Proteins Fold. Science 2011, 334, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, D.E.; Maragakis, P.; Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Piana, S.; Dror, R.O.; Eastwood, M.P.; Bank, J.A.; Jumper, J.M.; Salmon, J.K.; Shan, Y.B.; et al. Atomic-level characterization of the structural dynamics of proteins. Science 2010, 330, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiyat, B.I.; Mayo, S.L. De novo protein design: Fully automated sequence selection. Science 1997, 278, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.S.; Feldmeier, K.; Parmeggiani, F.; Fernandez Velasco, D.A.; Höcker, B.; Baker, D. De novo design of a four-fold symmetric TIM-barrel protein with atomic-level accuracy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunette, T.J.; Parmeggiani, F.; Huang, P.S.; Bhabha, G.; Ekiert, D.C.; Tsutakawa, S.E.; Hura, G.L.; Tainer, J.A.; Baker, D. Exploring the repeat protein universe through computational protein design. Nature 2015, 528, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlman, B.; Dantas, G.; Ireton, G.C.; Varani, G.; Stoddard, B.L.; Baker, D. Design of a novel globular protein fold with atomic-level accuracy. Science 2003, 302, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, Y.; Huang, P.S.; Hsu, F.C.; Huang, S.J.; Mayo, S.L. Computational design and experimental verification of a summetric protein homodimer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10714–10719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfoss, G.L.; Kuhlman, B. Computer-based design of novel protein structures. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2006, 35, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadqi, M.; de Alba, E.; Perez-Jimenez, R.; Sanchez-Ruiz, J.M.; Munoz, V. A designed protein as experimental model of primordial folding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4127–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Shea, J.E. On the origins of the weak folding cooperativity of a designed ββα ultrafast protein FSD-1. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1000998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Alonso, D.O.V.; Maki, K.; Huang, C.Y.; Lahr, S.J.; Daggett, V.; Roder, H.; DeGrado, W.F.; Gai, F. Ultrafast folding of α3D: A de novo designed three-helix bundle protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15486–15491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, R.B.; Hummer, G.; Eaton, W.A. Native contacts determine protein folding mechanisms in atomistic simulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17874–17879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watters, A.L.; Deka, P.; Corrent, C.; Callender, D.; Varani, G.; Sosnick, T.; Baker, D. The highly cooperative folding of small naturally occurring proteins is likely the result of natural selection. Cell 2007, 128, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Chan, H.S. Native topology of the designed protein top7 is not conducive to cooperative folding. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, L25–L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Chan, H.S. Competition between native topology and nonnative interactions in simple and complex folding kinetics of natural and designed proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2920–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.H.; Chen, H.; Fan, K.Q.; Wei, P.; Guo, X.R.; Jin, C.W.; Zeng, C.; Tang, C.; Lai, L.H. De novo design of a βαβ motif. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3301–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.F.; Huang, Y.Q.; Liang, H.H.; Liu, Z.R.; Lai, L.H. Folding simulations of a de novo designed protein with a βαβ fold. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Dai, Z.W.; Liang, H.H.; Zhang, T.; Gai, F.; Lai, L.H. Slow and bimolecular folding of a de novo designed monomeric protein DS119. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, I.C.; Lee, M.S.; Olson, M.A. Calculation of protein heat capacity from replica-exchange molecular dynamics simulations with different implicit solvent models. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 15064–15073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.H.; Tarus, B.; Derreumaux, P. Familial Alzheimer A2 V mutation reduces the intrinsic disorder and completely changes the free-energy landscape of the Aβ1–28 monomer. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarus, B.; Tran, T.T.; Nasica-Labouze, J.; Stepone, F.; Nguyen, P.H.; Derreumaux, P. Structures of the Alzheimer’s wild-type Aβ1–40 dimer from atomistic simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 10478–10487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.X.; Wu, C.; Liu, H.G.; Duan, Y. Folding free-energy landscape of villin headpiece subdomain from molecular dynamics simulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4925–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.; Yu, C.; Lai, L.H.; Liu, Z.R. Ligand clouds around protein clouds: A scenario of ligand binding with intrinsically disordered proteins. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.Y.; Jiang, F.; Wu, Y.D. Folding thermodynamics and mechanism of five TRP-cage variants from replica-exchange MD simulations with RSFF2 force field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 5473–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Vanderspoel, D.; Vandrunen, R. Gromacs: A message-passing parallel molecular-dynamics implementation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 91, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W.; Sander, C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure-pattern-recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers 1983, 22, 2577–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonneau, R.; Baker, D. Ab initio protein structure prediction: Progress and prospects. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2001, 30, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, Y.M.; Pande, V.S. Multiplexed-replica exchange molecular dynamics method for protein folding simulation. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranges, P.B.; Machius, M.; Miley, M.J.; Tripathy, A.; Kuhlman, B. Computational design of a symmetric homodimer using β-trand assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20562–20567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, D.A.; Darden, T.A.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Simmerling, C.L.; Wang, J.; Duke, R.E.; Luo, R.; Walker, R.C.; Zhang, W.; Merz, K.M.; et al. AMBER2015; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hornak, V.; Abel, R.; Okur, A.; Strockbine, B.; Roitberg, A.; Simmerling, C. Comparison of multiple amber force fields and development of improved protein backbone parameters. Proteins 2006, 65, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onufriev, A.; Bashford, D.; Case, D.A. Exploring protein native states and large-scale conformational changes with a modified generalized born model. Proteins 2004, 55, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, B.; Simonson, T. Implicit solvent models. Biophys. Chem. 1999, 78, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckaert, J.-P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H.J.C. Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald—An N log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; Vangunsteren, W.F.; Dinola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular-dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The PyMOL Molecular graphics system. Available online: http://www.citeulike.org/group/340/article/240061 (accessed on 25 March 2014).






© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Z. The Folding of de Novo Designed Protein DS119 via Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050612
Wang M, Hu J, Zhang Z. The Folding of de Novo Designed Protein DS119 via Molecular Dynamics Simulations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(5):612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050612
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Moye, Jie Hu, and Zhuqing Zhang. 2016. "The Folding of de Novo Designed Protein DS119 via Molecular Dynamics Simulations" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 5: 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050612
APA StyleWang, M., Hu, J., & Zhang, Z. (2016). The Folding of de Novo Designed Protein DS119 via Molecular Dynamics Simulations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(5), 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050612