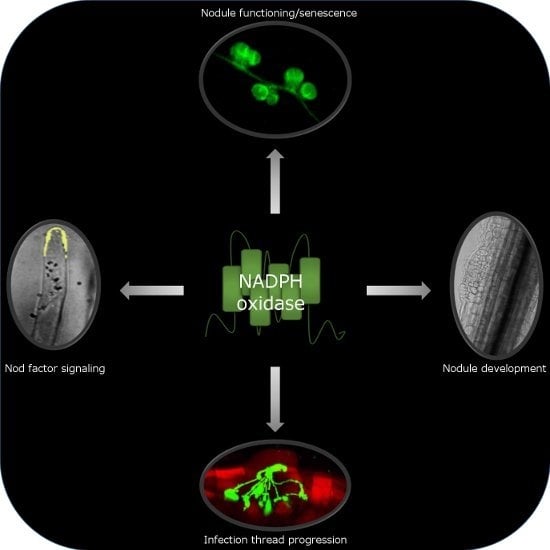
Legume NADPH Oxidases Have Crucial Roles at Different Stages of Nodulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. RBOHs Function Downstream of Nodulation Factor (NF) Perception
3. RBOHs Mediate Infection Thread (IT) Progression and Nodule Organogenesis
4. RBOHs Impact Nodule Function and Senescence
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NOX | NADPH oxidases |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RBOHs | Respiratory burst oxidase homologs |
| NFs | Nodulation factors |
| IT | Infection thread |
| NBT | Nitroblue tetrazolium blue |
References
- Aguirre, J.; Lambeth, J.D. Nox enzymes from fungus to fly to fish and what they tell us about Nox function in mammals. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1342–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, D.; Dunand, C.; Puppo, A.; Pauly, N. A burst of plant NADPH oxidases. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 1360–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, M.A.; Dangl, J.L. Functions of the respiratory burst oxidase in biotic interactions, abiotic stress and development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2005, 8, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glyan’ko, A.K.; Ischenko, A.A. Structural and functional characteristics of plant NADPH oxidase: A review. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2010, 46, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Sharma, A.; Guruprasad, K.; Pati, P.K. Versatile roles of plant NADPH oxidases and emerging concepts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, N.; Miller, G.; Morales, J.; Shulaev, V.; Torres, M.A.; Mittler, R. Respiratory burst oxidases: The engines of ROS signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthikala, M.K.; Sanchez-Lopez, R.; Nava, N.; Santana, O.; Cardenas, L.; Quinto, C. RbohB, a Phaseolus vulgaris NADPH oxidase gene, enhances symbiosome number, bacteroid size, and nitrogen fixation in nodules and impairs mycorrhizal colonization. New Phytol. 2014, 202, 886–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, D.; Andrio, E.; Danchin, E.G.J.; Oger, E.; Gucciardo, S.; Lambert, A.; Puppo, A.; Pauly, N. A Medicago truncatula NADPH oxidase is involved in symbiotic nodule functioning. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montiel, J.; Nava, N.; Cardenas, L.; Sanchez-Lopez, R.; Arthikala, M.K.; Santana, O.; Sanchez, F.; Quinto, C. A Phaseolus vulgaris NADPH Oxidase Gene is Required for Root Infection by Rhizobia. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 1751–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldroyd, G.E. Speak, friend, and enter: Signalling systems that promote beneficial symbiotic associations in plants. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downie, J.A. Legume nodulation. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R184–R190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzaki, T.; Yoro, E.; Kawaguchi, M. Leguminous plants: Inventors of root nodules to accommodate symbiotic bacteria. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 316, 111–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ehrhardt, D.; Wais, R.; Long, S.R. Calcium spiking in plant root hairs responding to Rhizobium nodulation signals. Cell 1996, 85, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, D.W.; Atkinson, E.M.; Long, S.R. Depolarization of Alfalfa Root Hair Membrane-Potential by Rhizobium-Meliloti Nod Factors. Science 1992, 256, 998–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felle, H.H.; Kondorosi, E.; Kondorosi, A.; Schultze, M. Rapid alkalinization in alfalfa root hairs in response to rhizobial lipochitooligosaccharide signals. Plant J. 1996, 10, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felle, H.H.; Kondorosi, E.; Kondorosi, A.; Schultze, M. The role of ion fluxes in Nod factor signalling in Medicago sativa. Plant J. 1998, 13, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, L.; Feijo, J.A.; Kunkel, J.G.; Sanchez, F.; Holdaway-Clarke, T.; Hepler, P.K.; Quinto, C. Rhizobium Nod factors induce increases in intracellular free calcium and extracellular calcium influxes in bean root hairs. Plant J. 1999, 19, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, L.; Holdaway-Clarke, T.L.; Sanchez, F.; Quinto, C.; Feijo, J.A.; Kunkel, J.G.; Hepler, P.K. Ion changes in legume root hairs responding to nod factors. Plant Physiol. 2000, 123, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, L.; Martinez, A.; Sanchez, F.; Quinto, C. Fast, transient and specific intracellular ROS changes in living root hair cells responding to Nod factors (NFs). Plant J. 2008, 56, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, L.; Vidali, L.; Dominguez, J.; Perez, H.; Sanchez, F.; Hepler, P.K.; Quinto, C. Rearrangement of actin microfilaments in plant root hairs responding to Rhizobium etli nodulation signals. Plant Physiol. 1998, 116, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruijter, N.C.A.; Bisseling, T.; Emons, A.M.C. Rhizobium Nod factors induce an increase in sub-apical fine bundles of actin filaments in Vicia sativa root hairs within minutes. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1999, 12, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morieri, G.; Martinez, E.A.; Jarynowski, A.; Driguez, H.; Morris, R.; Oldroyd, G.E.; Downie, J.A. Host-specific Nod-factors associated with Medicago truncatula nodule infection differentially induce calcium influx and calcium spiking in root hairs. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S.; Gapper, C.; Kaya, H.; Bell, E.; Kuchitsu, K.; Dolan, L. Local positive feedback regulation determines cell shape in root hair cells. Science 2008, 319, 1241–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, Y.; Kaya, H.; Hiraoka, G.; Yumoto, F.; Kimura, S.; Kadota, Y.; Hishinuma, H.; Senzaki, E.; Yamagoe, S.; Nagata, K.; et al. Synergistic activation of the Arabidopsis NADPH oxidase AtrbohD by Ca2+ and phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 8885–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, T.; Hashimoto, H.; Kuwabara, N.; Akashi, S.; Hayashi, K.; Kojima, C.; Wong, H.L.; Kawasaki, T.; Shimamoto, K.; Sato, M.; et al. Structure of the N-terminal regulatory domain of a plant NADPH oxidase and its functional implications. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potocky, M.; Jones, M.A.; Bezvoda, R.; Smirnoff, N.; Zarsky, V. Reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidase are involved in pollen tube growth. New Phytol. 2007, 174, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Kimura, S.; Kaya, H.; Iizuka, A.; Wong, H.L.; Shimamoto, K.; Kuchitsu, K. Reactive oxygen species production and activation mechanism of the rice NADPH oxidase OsRbohB. J. Biochem. 2012, 152, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foreman, J.; Demidchik, V.; Bothwell, J.H.; Mylona, P.; Miedema, H.; Torres, M.A.; Linstead, P.; Costa, S.; Brownlee, C.; Jones, J.D.; et al. Reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidase regulate plant cell growth. Nature 2003, 422, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glyan’ko, A.K.; Ischenko, A.A. Influence of Rhizobial (Rhizobium leguminosarum) Inoculation and calcium ions on the NADPH oxidase activity in roots of etiolated pea (Pisum sativum L.) seedlings. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2013, 49, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, I.; Pauly, N.; Puppo, A.; Brouquisse, R.; Boscari, A. Reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide control early steps of the legume-rhizobium symbiotic interaction. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, B.W.; Feechan, A.; Yin, M.; Saidi, N.B.; Le Bihan, T.; Yu, M.; Moore, J.W.; Kang, J.G.; Kwon, E.; Spoel, S.H.; et al. S-nitrosylation of NADPH oxidase regulates cell death in plant immunity. Nature 2011, 478, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belmondo, S.; Calcagno, C.; Genre, A.; Puppo, A.; Pauly, N.; Lanfranco, L. The Medicago truncatula MtRbohE gene is activated in arbusculated cells and is involved in root cortex colonization. Planta 2016, 243, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedito, V.A.; Torres-Jerez, I.; Murray, J.D.; Andriankaja, A.; Allen, S.; Kakar, K.; Wandrey, M.; Verdier, J.; Zuber, H.; Ott, T.; et al. A gene expression atlas of the model legume Medicago truncatula. Plant J. 2008, 55, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, B.; Rodde, N.; Jardinaud, M.F.; Timmers, T.; Sauviac, L.; Cottret, L.; Carrere, S.; Sallet, E.; Courcelle, E.; Moreau, S.; et al. An integrated analysis of plant and bacterial gene expression in symbiotic root nodules using laser-capture microdissection coupled to RNA sequencing. Plant J. 2014, 77, 817–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, A.J.; Iniguez, L.P.; Fu, F.; Bucciarelli, B.; Miller, S.S.; Jackson, S.A.; McClean, P.E.; Li, J.; Dai, X.; Zhao, P.X.; et al. An RNA-Seq based gene expression atlas of the common bean. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthikala, M.K.; Montiel, J.; Sánchez-López, R.; Nava, N.; Pérez, A.L.; Alvarado-Affantranger, X.; Quinto, C. PvRbohA controls rhizobial infection and nodule development in Phaseolus vulgaris. In Proceedings of the XVI Congress of the International Society of Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, Rhodes Island, Greece, 6–10 July 2014; p. 682.
- Lohar, D.P.; Haridas, S.; Gantt, J.S.; VandenBosch, K.A. A transient decrease in reactive oxygen species in roots leads to root hair deformation in the legume-rhizobia symbiosis. New Phytol. 2007, 173, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, S.L.; Long, S.R. Nod factor inhibition of reactive oxygen efflux in a host legume. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 2196–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiirika, L.M.; Bergmann, H.F.; Schikowsky, C.; Wimmer, D.; Korte, J.; Schmitz, U.; Niehaus, K.; Colditz, F. Silencing of the Rac1 GTPase MtROP9 in Medicago truncatula stimulates early mycorrhizal and oomycete root colonizations but negatively affects rhizobial infection. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.D. Invasion by invitation: Rhizobial infection in legumes. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunand, C.; Crevecoeur, M.; Penel, C. Distribution of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide in Arabidopsis root and their influence on root development: Possible interaction with peroxidases. New Phytol. 2007, 174, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.; Herouart, D.; Sigaud, S.; Touati, D.; Puppo, A. Oxidative burst in alfalfa-Sinorhizobium meliloti symbiotic interaction. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2001, 14, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrio, E.; Marino, D.; Marmeys, A.; de Segonzac, M.D.; Damiani, I.; Genre, A.; Huguet, S.; Frendo, P.; Puppo, A.; Pauly, N. Hydrogen peroxide-regulated genes in the Medicago truncatula-Sinorhizobium meliloti symbiosis. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleg-Grossman, S.; Volpin, H.; Levine, A. Root hair curling and Rhizobium infection in Medicago truncatula are mediated by phosphatidylinositide-regulated endocytosis and reactive oxygen species. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 1637–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, K.; Fukai, E.; Madsen, L.H.; Jurkiewicz, A.; Rueda, P.; Radutoiu, S.; Held, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Szczyglowski, K.; Morieri, G.; et al. Rearrangement of actin cytoskeleton mediates invasion of Lotus japonicus roots by Mesorhizobium loti. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.S.; Liao, J.Q.; James, E.K.; Sato, S.; Tabata, S.; Jurkiewicz, A.; Madsen, L.H.; Stougaard, J.; Ross, L.; Szczyglowski, K. Lotus japonicus ARPC1 is required for rhizobial infection. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.P.; Lin, J.S.; Xu, J.; Sato, S.; Parniske, M.; Wang, T.L.; Downie, J.A.; Xie, F. SCARN a novel class of SCAR protein that is required for root-hair infection during legume nodulation. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zepeda, I.; Sánchez-López, R.; Kunkel, J.G.; Bañuelos, L.A.; Hernández-Barrera, A.; Sánchez, F.; Quinto, C.; Cárdenas, L. Visualization of highly dynamic F-actin plus ends in growing Phaseolus vulgaris root hair cells and their response to Rhizobium etli Nod Factors. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas, L.; Instituto de Biotecnología, UNAM, Cuernavaca, México. Unpublished work. 2016.
- Liszkay, A.; Kenk, B.; Schopfer, P. Evidence for the involvement of cell wall peroxidase in the generation of hydroxyl radicals mediating extension growth. Planta 2003, 217, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Murray, J.D.; Kim, J.; Heckmann, A.B.; Edwards, A.; Oldroyd, G.E.; Downie, J.A. Legume pectate lyase required for root infection by rhizobia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinto, C.; Sánchez-López, R.; Cárdenas, L.; Montiel, J.; Arthikala, M.K.; Nava, N.; Santana, O. The simbiosis between Phaseolus vulgaris and rhizobia. Legum. Perspect. 2014, 2, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukagoshi, H.; Busch, W.; Benfey, P.N. Transcriptional regulation of ROS controls transition from proliferation to differentiation in the root. Cell 2010, 143, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, M.C.; James, E.K.; Clemente, M.R.; Bucciarelli, B.; Fedorova, M.; Vance, C.P.; Becana, M. Localization of superoxide dismutases and hydrogen peroxide in legume root nodules. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2004, 17, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesandrini, F.; Mathis, R.; van de Sype, G.; Herouart, D.; Puppo, A. Possible roles for a cysteine protease and hydrogen peroxide in soybean nodule development and senescence. New Phytol. 2003, 158, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.W.; Alloing, G.; Mandon, K.; Frendo, P. Redox regulation of differentiation in symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matamoros, M.A.; Dalton, D.A.; Ramos, J.; Clemente, M.R.; Rubio, M.C.; Becana, M. Biochemistry and molecular biology of antioxidants in the rhizobia-legume symbiosis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puppo, A.; Groten, K.; Bastian, F.; Carzaniga, R.; Soussi, M.; Lucas, M.M.; de Felipe, M.R.; Harrison, J.; Vanacker, H.; Foyer, C.H. Legume nodule senescence: Roles for redox and hormone signalling in the orchestration of the natural aging process. New Phytol. 2005, 165, 683–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PvGEA. Available online: http://plantgrn.noble.org/PvGEA/index.jsp (accessed on 2 March 2016).




© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montiel, J.; Arthikala, M.-K.; Cárdenas, L.; Quinto, C. Legume NADPH Oxidases Have Crucial Roles at Different Stages of Nodulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050680
Montiel J, Arthikala M-K, Cárdenas L, Quinto C. Legume NADPH Oxidases Have Crucial Roles at Different Stages of Nodulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(5):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050680
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontiel, Jesús, Manoj-Kumar Arthikala, Luis Cárdenas, and Carmen Quinto. 2016. "Legume NADPH Oxidases Have Crucial Roles at Different Stages of Nodulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 5: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050680
APA StyleMontiel, J., Arthikala, M.-K., Cárdenas, L., & Quinto, C. (2016). Legume NADPH Oxidases Have Crucial Roles at Different Stages of Nodulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(5), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050680