The Effect of Minimally Invasive Hematoma Aspiration on the JNK Signal Transduction Pathway after Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Neurological Evaluation
2.2. Brain Water Content (BWC)
2.3. Effects on Histopathology
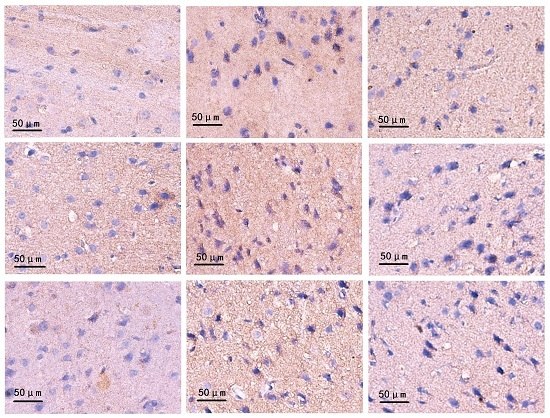
2.4. Changes on Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Western Blotting
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Experiment Groups
4.3. Induction of ICH and Treatment Methods
4.4. Neurological Evaluation
4.5. Brain Water Content (BWC)
4.6. Preparation of Paraffin Section
4.7. Hematoxylin–Eosin (HE) Staining
4.8. Immunohistochemistry Staining (IHC)
4.9. Preparation of Protein Samples
4.10. Western Blotting (WB)
4.11. Statistical Method
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qureshi, A.I.; Mendelow, A.D.; Hanley, D.F. Intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet 2009, 373, 1632–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Asch, C.J.; Luitse, M.J.; Rinkel, G.J.; van der Tweel, I.; Algra, A.; Klijn, C.J. Incidence, case fatality, and functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemphill, J.C., 3rd; Greenberg, S.M.; Anderson, C.S.; Becker, K.; Bendok, B.R.; Cushman, M.; Fung, G.L.; Goldstein, J.N.; Macdonald, R.L.; Mitchell, P.H.; et al. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2015, 46, 2032–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proust, F.; Leveque, S.; Derrey, S.; Tollard, E.; Vandhuick, O.; Clavier, E.; Langlois, O.; Fréger, P. Spontaneous supratentorial cerebral hemorrhage: Role of surgical treatment. Neurochirurgie 2007, 53 Pt 1, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, M.; Stadnik, A.; Awad, I.A. Spontaneous intracerebral and intraventricular hemorrhage: Advances in minimally invasive surgery and thrombolytic evacuation, and lessons learned in recent trials. Neurosurgery 2014, 74, S142–S150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibi, M.; Lin, A.; Smeal, T.; Minden, A.; Karin, M. Identification of an oncoprotein and UV-responsive protein kinase that binds and potentiats the c-Jun activation domain. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 2135–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, C.R.; Davis, R.J. The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffey, E.T. Nuclear and cytosolic JNK signalling in neurons. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel-Monigadon, D.; Bonny, C.; Hirt, L. c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway inhibition in intracerebral hemorrhage. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2010, 29, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Y.H.; Liang, Y.X.; Liu, L.G.; Ellis-Behnke, R.G.; Wu, W.T.; So, K.F.; Cheung, R.T. Rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage permitting hematoma aspiration plus intralesional injection. Exp. Anim. 2013, 62, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, C. The intracereral hemorrhage model in rats. Guide China Med. 2012, 34, 88–89. [Google Scholar]
- Tournier, C.; Dong, C.; Turner, T.K.; Jones, S.N.; Flavell, R.A.; Davis, R.J. MKK7 is an essential component of the JNK signal transduction pathway activated by proinflammatory cytokines. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Spigolon, G.; Bonny, C.; Culman, J.; Vercelli, A.; Herdegen, T. The JNK inhibitor D-JNKI-1 blocks apoptotic JNK signaling in brain mitochondria. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2012, 49, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zu, J.; Zan, K.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, L.; Bao, L.; He, Q.; Zhou, S.; Cui, G. The JNK inhibitor XG-102 protects against intracerebral hemorrhage. Acta Acad. Med. Xuzhou 2014, 34, 384–387. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.; Hoff, J.T.; Keep, R.F. Acute inflammatory reaction following experimental intracerebral hemorrhage in rat. Brain Res. 2000, 871, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminska, B.; Gozdz, A.; Zawadzka, M.; Ellert-Miklaszewska, A.; Lipko, M. MAPK signal transduction underlying brain inflammation and gliosis as therapeutic target. Anat. Rec. 2009, 292, 1902–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benakis, C.; Bonny, C.; Hirt, L. JNK inhibition and inflammation after cerebral ischemia. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, P.; McColl, B.W.; Cooper, L.; Rothwell, N.J.; Allan, S.M. Interleukin-1 drives cerebrovascular inflammation via MAP kinase-independent pathways. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2010, 7, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronowski, J.; Zhao, X. Molecular pathophysiology of cerebral hemorrhage: Secondary brain injury. Stroke 2011, 42, 1781–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodmer, D.; Vaughan, K.A.; Zacharia, B.E.; Hickman, Z.L.; Connolly, E.S. The Molecular Mechanisms that Promote Edema after Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Transl. Stroke Res. 2012, 3, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuki, H. Exploring neuroprotective drug therapies for intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 114, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, B.Y.; Appelboom, G.; Ayer, A.; Kellner, C.P.; Kotchetkov, I.S.; Gigante, P.R.; Haque, R.; Kellner, M.; Connolly, E.S. Advances in neuroprotective strategies: Potential therapies for intracerebral hemorrhage. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2011, 31, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keep, R.F.; Zhou, N.; Xiang, J.; Andjelkovic, A.V.; Hua, Y.; Xi, G. Vascular disruption and blood-brain barrier dysfunction in intracerebral hemorrhage. Fluids Barriers CNS 2014, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, R.; Bagley, J.H.; Di, C.; Friedman, A.H.; Adamson, C. Thrombin and hemin as central factors in the mechanisms of intracerebral hemorrhage-induced secondary brain injury and as potential targets for intervention. Neurosurg. Focus 2012, 32, E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cui, G.; Meng, W.; Kong, L.; Bao, L.; He, Q.; Zhou, S.; Zu, J.; Liu, Y. Changes of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in rat models of intracerebral hemorrhage and effect of argathoban on it. Chin. J. Neuromed. 2014, 13, 778–782. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.P.; Xi, G.; Keep, R.F.; Hua, Y.; Nemoianu, A.; Hoff, J.T. Brain edema after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage: Role of hemoglobin degradation products. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 96, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Zhan, R.; Zheng, S.; Hua, Y.; Xi, G. Activation of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage: The role of iron. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 63, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Gould, T.W.; Newbern, J.; Milligan, C.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Oppenheim, R.W. Phosphorylation of c-Jun in avian and mammalian motoneurons in vivo during programmed cell death: An early reversible event in the apoptotic cascade. Neuroscience 2005, 25, 5595–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.C.; Fang, F.; Zhu, Y.G.; Chen, L.M.; Zhou, Y.C.; Chen, Y. Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on MPP+-induced apoptosis in SHSY5Y cells. J. Neural Transm. 2003, 110, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, B.; Pu, H.; Cao, Q.; Jing, H.; Liu, X. Activation of caspase-3 and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase signaling pathways involving heroin-induced neuronal apoptosis. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 502, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Bao, L.; Zimering, J.; Zan, K.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, H.; Zu, J.; Yang, X.; Hua, F.; Ye, X.; et al. The protective role of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in thrombin-induced neuronal cell apoptosis and JNK-MAPK activation. Neuroreport 2015, 26, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Tang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Yan, C.; Cui, Y. Effects of intracerebral hemorrhage and subsequent minimally invasive hematoma aspiration on expression of apoptosis related genes in rats. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 5371–5378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.Y.; Betz, A.L.; Chenevert, T.L.; Brunberg, J.A.; Hoff, J.T. Experimental intracerebral hemorrhage: Relationship between brain edema, blood flow, and blood-brain barrier permeability in rats. J. Neurosurg. 1994, 81, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bederson, J.B.; Pitts, L.H.; Tsuji, M.; Nishimura, M.C.; Davis, R.L.; Bartkowski, H. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: Evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 1986, 17, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Groups | n | 6 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | 120 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham-operated group | 6 | 0.5 ± 0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.5 | 0.2 ± 0.4 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Intracereral hemorrhage (ICH) group | 6 | 1.8 ± 0.8 * | 2.2 ± 0.8 * | 2.3 ± 0.5 * | 2.5 ± 0.5 * | 1.8 ± 0.8 * | 1.7 ± 0.5 * |
| Minimally invasive hematoma aspiration (MIHA) group | 6 | 2.0 ± 0.9 * | 2.0 ± 0.6 * | 1.5 ± 0.5 *,# | 1.2 ± 0.8 *,# | 0.8 ± 0.4 *,# | 0.7 ± 0.5 *,# |
| χ2 | 8.70 | 11.13 | 13.56 | 13.95 | 13.65 | 13.01 | |
| P | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Groups | n | 24 h | 72 h | 120 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham-operated group | 6 | 72.205 ± 0.676 | 72.613 ± 0.990 | 72.328 ± 0.802 |
| ICH group | 6 | 80.418 ± 0.787 * | 84.369 ± 1.009 * | 82.198 ± 0.896 * |
| MIHA group | 6 | 77.624 ± 1.003 *,# | 80.266 ± 0.928 *,# | 79.664 ± 1.113 *,# |
| F | 150.70 | 223.90 | 176.20 | |
| P | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Groups | n | 72 h denatured cell index (DCI) |
|---|---|---|
| Sham-operated group | 6 | 0.160 ± 0.052 |
| ICH group | 6 | 0.481 ± 0.093 * |
| MIHA group | 6 | 0.285 ± 0.068 *,# |
| F | 29.41 | |
| P | 0.00 |
| Groups | n | 24 h | 72 h | 120 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham-operated group | 6 | 0.099 ± 0.030 | 0.110 ± 0.027 | 0.104 ± 0.026 |
| ICH group | 6 | 0.268 ± 0.024 * | 0.320 ± 0.022 * | 0.248 ± 0.031 * |
| MIHA group | 6 | 0.198 ± 0.035 *,# | 0.215 ± 0.028 *,# | 0.182 ± 0.026 *,# |
| F | 48.79 | 98.73 | 40.85 | |
| P | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Groups | n | pJNK | JNK | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 72 h | 120 h | 24 h | 72 h | 120 h | ||
| Sham-operated group | 6 | 0.390 ± 0.077 | 0.378 ± 0.083 | 0.383 ± 0.063 | 1.058 ± 0.082 | 1.125 ± 0.079 | 1.107 ± 0.088 |
| ICH group | 6 | 0.670 ± 0.084 * | 0.779 ± 0.083 * | 0.661 ± 0.070 * | 1.062 ± 0.105 | 1.135 ± 0.090 | 1.099 ± 0.103 |
| MIHA group | 6 | 0.529 ± 0.079 *,# | 0.606 ± 0.119 *,# | 0.505 ± 0.076 *,# | 1.078 ± 0.084 | 1.140 ± 0.088 | 1.106 ± 0.076 |
| F | 18.44 | 26.05 | 23.72 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.02 | |
| P | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.98 | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pei, H.; Jiang, T.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Luo, K.; An, J.; Li, G.; Guo, Y. The Effect of Minimally Invasive Hematoma Aspiration on the JNK Signal Transduction Pathway after Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050710
Pei H, Jiang T, Liu G, Li Z, Luo K, An J, Li G, Guo Y. The Effect of Minimally Invasive Hematoma Aspiration on the JNK Signal Transduction Pathway after Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(5):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050710
Chicago/Turabian StylePei, Haitao, Tao Jiang, Guofang Liu, Zhaoxing Li, Kai Luo, Jingjiao An, Guangcheng Li, and Yunliang Guo. 2016. "The Effect of Minimally Invasive Hematoma Aspiration on the JNK Signal Transduction Pathway after Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 5: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050710
APA StylePei, H., Jiang, T., Liu, G., Li, Z., Luo, K., An, J., Li, G., & Guo, Y. (2016). The Effect of Minimally Invasive Hematoma Aspiration on the JNK Signal Transduction Pathway after Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(5), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050710