Novel Omega-3 Fatty Acid Epoxygenase Metabolite Reduces Kidney Fibrosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
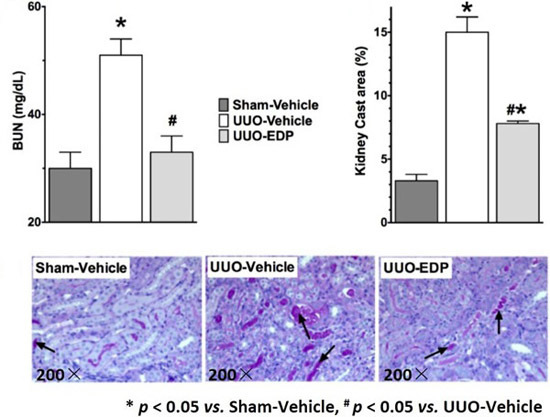
2.1. 19,20-EDP Treatment Attenuates UUO Renal Injury
2.2. Renal Fibrosis Was Reduced in 19,20-EDP Treated UUO Mice
2.3. Renal Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in UUO Mice Was Reduced by 19,20-EDP Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Animal Experiments
4.3. Biochemical Analysis
4.4. Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.5. Western Immunoblotting
4.6. Histopathology
4.7. Immunohistopathological Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jha, V.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Iseki, K.; Li, Z.; Naicker, S.; Plattner, B.; Saran, R.; Wang, A.Y.; Yang, C.W. Chronic kidney disease: Global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 2013, 382, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remuzzi, G.; Bertani, T. Pathophysiology of progressive nephropathies. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. New insights into epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Ng, Y.Y.; Hill, P.A.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Mu, W.; Atkins, R.C.; Lan, H.Y. Transforming growth factor-b regulates tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation in vitro. Kidney Int. 1999, 56, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanez-Mo, M.; Lara-Pezzi, E.; Selgas, R.; Ramirez-Huesca, M.; Dominguez-Jimenez, C.; Jiménez-Heffernan, J.A.; Aguilera, A.; Sánchez-Tomero, J.A.; Bajo, M.A.; Alvarez, V. Peritoneal dialysis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of mesothelial cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, Y. Dissection of key events in tubular epithelial to myofibroblast transition and its implications in renal interstitial fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, F.Y.; Peng, Y.M.; Hou, T.; Duan, S.B.; Li, J.; Luo, J.H.; Sun, L.; Ling, G.H. Norcantharidin attenuates tubulointerstitial fibrosis in rat models with diabetic nephropathy. Ren. Fail. 2011, 33, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisberg, M.; Maeshima, Y.; Mosterman, B.; Kalluri, R. Renal fibrosis|: Extracellular matrix microenvironment regulates migratory behavior of activated tubular epithelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, A.A.; Norris, A.W. Action of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids on cellular function. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeldin, D.C. Epoxygenase pathways of arachidonic acid metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 36059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, C.; Markovic, M.; Blossey, K.; Wallukat, G.; Fischer, R.; Dechend, R.; Konkel, A.; von Schacky, C.; Luft, F.C.; Muller, D.N.; et al. Arachidonic acid-metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes are targets of ω-3 fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 32720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Panigrahy, D.; Mahakian, L.M.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.Y.; Stephen Lee, K.S.; Wettersten, H.I.; Ulu, A.; Hu, X.; Tam, S.; et al. Epoxy metabolites of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) inhibit angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulu, A.; Harris, T.R.; Morisseau, C.; Miyabe, C.; Inoue, H.; Schuster, G.; Dong, H.; Iosif, A.M.; Liu, J.Y.; Weiss, R.H.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors in angiotensin-II-dependent hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 62, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulu, A.; Stephen Lee, K.S.; Miyabe, C.; Yang, J.; Hammock, B.G.; Dong, H.; Hammock, B.D. An omega-3 epoxide of docosahexaenoic acid lowers blood pressure in angiotensin-II-dependent hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 64, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.F.; Chang, S.Y.; Lee, T.C.; Chuang, L.Y.; Guh, J.Y.; Hung, C.Y.; Hung, T.J.; Hung, Y.J.; Chen, P.Y.; Hsieh, P.F.; et al. Dioscorea alata attenuates renal interstitial cellular fibrosis by regulating smad- and epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47482. [Google Scholar]
- Zeisberg, M.; Neilson, E.G. (2010) Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, H.J.; Vielhauer, V.; Schlondorff, D. Chemokines and chemokine receptors are involved in the resolution or progression of renal disease. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohle, A.; Mackensen-Haen, S.; von Gise, H. Significance of tubulointerstitial changes in the renal cortex for the excretory function and concentration ability of the kidney: A morphometric contribution. Am. J. Nephrol. 1987, 7, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, L.; White-Guay, B.; Dorais, M.; Dragomir, A.; Lessard, M.; Perreault, S. Adherence to antihypertensive agents improves risk reduction of end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perico, N.; Codreanu, I.; Schieppati, A.; Remuzzi, G. Prevention of progression and remission/regression strategies for chronic renal diseases: Can we do better now than five years ago? Kidney Int. 2005, 68, S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, R.L.; Forbes, M.S.; Thornhill, B.A. Ureteral obstruction as a model of renal interstitial fibrosis and obstructive nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabry, A.; El-Dahshan, K.; El-Hussieni, A. Prevention of chronic cyclosporine nephrotoxicity in Sprague-Dawley rats: Role of colchicine and omega-3-fatty acids. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2007, 39, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Pestka, J.J. Attenuation of mycotoxin-induced IgA nephropathy by eicosapentaenoic acid in the mouse: Dose response and relation to IL-6 expression. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2006, 17, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garman, J.H.; Mulroney, S.; Manigrasso, M.; Flynn, E.; Maric, C. Omega-3 fatty acid rich diet prevents diabetic renal disease. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2008, 296, F316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, B.A.; Ficociello, L.H.; Ostrander, B.E.; Silva, K.H.; Weinberg, J.; Warram, J.H.; Krolewski, A.S. Microalbuminuria and the risk for early progressive renal function decline in type 1 diabetes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, H.; Ohtani, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Sato, N.; Mori, M.; Shimomura, Y. Long-term effect of eicosapentaenoic acid ethyl (EPA-E) on albuminuria of non-insulin dependent diabetic patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1995, 28, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollsten, A.V.; Dahlquist, G.G.; Stattin, E.L.; Rudberg, S. Higher intakes of fish protein are related to a lower risk of microalbuminuria in young Swedish type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, W.S.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, K.H.; Vaziri, N.D. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation attenuates oxidative stress, inflammation, and tubulointerstitial fibrosis in the remnant kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 297, F895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikawa, M.; Yamazaki, K.; Hamazaki, T.; Wakaki, K.; Koizumi, F.; Yano, S.; Kobayashi, M. Effect of eicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester on albuminuria in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1994, 40, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabry, A.; El-Husseini, A.; Sheashaa, H.; Abdel-Shafy, E.; El-Dahshan, K.; Abdel-Rahim, M.; Abdel-Kaleek, E.; Abo-Zena, H. Colchicine vs. omega-3 fatty acids for prevention of chronic cyclosporine nephrotoxicity in Sprague Dawley rats: An experimental animal model. Arch. Med. Res. 2006, 37, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagamoto, T.; Eguchi, G.; Beebe, D.C. α-smooth muscle actin expression in cultured lens epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 1122. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, J.L.; Glass, W.F. Renal interstitial fibrosis: A critical evaluation of the origin of myofibroblasts. Contrib. Nephrol. 2011, 169, 73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mack, M.; Yanagita, M. Origin of myofibroblasts and cellular events triggering fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriz, W.; Kaissling, B.; Le Hir, M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in kidney fibrosis: Fact or fantasy? J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, M.T.; Lo’pez-Novoa, J.M. Fibroblast activation and myofibroblast generation in obstructive nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2009, 5, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Muragaki, Y.; Saika, S.; Roberts, A.B.; Ooshima, A. Targeted disruption of TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling protects against renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, A.; Pérez-Moreno, M.A.; Rodrigo, I.; Locascio, A.; Blanco, M.J.; del Barrio, M.G.; Portillo, F.; Nieto, M.A. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batlle, E.; Sancho, E.; Francí, C.; Domínguez, D.; Monfar, M.; Baulida, J.; García De Herreros, A. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Lamouille, S.; Derynck, R. TGF-β-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisseau, C.; Inceoglu, B.; Schmelzer, K.; Tsai, H.J.; Jinks, S.L.; Hegedus, C.M.; Hammock, B.D. Naturally occurring monoepoxides of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid are bioactive antihyperalgesic lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Schmelzer, K.; Georgi, K.; Hammock, B.D. Quantitative profiling method for oxylipin metabolome by liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Padanilam, B.J. Loss of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 attenuates renal fibrosis and inflammation during unilateral ureteral obstruction. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2011, 301, F450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, G.K.; Enwemeka, C.S. A simplified method for the analysis of hydroxyprolinein biological tissues. Clin. Biochem. 1996, 29, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hye Khan, M.A.; Fish, B.; Wahl, G.; Sharma, A.; Falck, J.R.; Paudyal, M.P.; Moulder, J.E.; Imig, J.D.; Cohen, E.P. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid analogue mitigates kidney injury in a rat model of radiation nephropathy. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2016, 130, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, A.; Khan, M.A.H.; Levick, S.P.; Lee, K.S.S.; Hammock, B.D.; Imig, J.D. Novel Omega-3 Fatty Acid Epoxygenase Metabolite Reduces Kidney Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050751
Sharma A, Khan MAH, Levick SP, Lee KSS, Hammock BD, Imig JD. Novel Omega-3 Fatty Acid Epoxygenase Metabolite Reduces Kidney Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(5):751. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050751
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Amit, Md. Abdul Hye Khan, Scott P. Levick, Kin Sing Stephen Lee, Bruce D. Hammock, and John D. Imig. 2016. "Novel Omega-3 Fatty Acid Epoxygenase Metabolite Reduces Kidney Fibrosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 5: 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050751