Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Obesity, Insulin Resistance Syndrome, Type 2 Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Review of Human Clinical Trials
Abstract
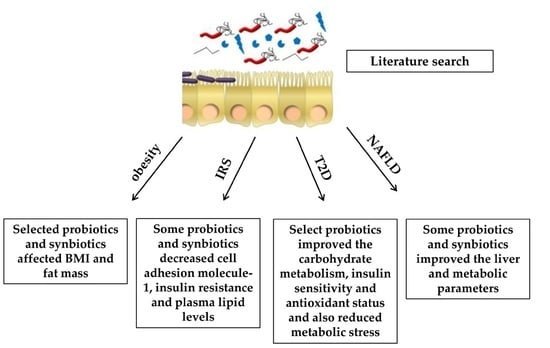
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Obesity
2.1.1. Probiotics
2.1.2. Synbiotics
2.2. Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Insulin Resistance Syndrome
2.2.1. Probiotics
2.2.2. Synbiotics
2.3. Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics in Type 2 Diabetes
2.3.1. Probiotics
2.3.2. Synbiotics
2.4. Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
2.4.1. Probiotics
2.4.2. Synbiotics
3. Methodology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Backhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 2005, 307, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, L.V.; Midtvedt, T.; Gordon, J.I. How host-microbial interactions shape the nutrient environment of the mammalian intestine. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 283–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Díaz, J.; Fernandez-Caballero, J.Á.; Chueca, N.; Garcia, F.; Gómez-Llorente, C.; Sáez-Lara, M.J.; Fontana, L.; Gil, A. Pyrosequencing analysis reveals changes in intestinal microbiota of healthy adults who received a daily dose of immunomodulatory probiotic strains. Nutrients 2015, 7, 3999–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, K.D.; Köller, Y. New developments providing mechanistic insight into the impact of the microbiota on allergic disease. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 159, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, R.; Eneli, I. Severe childhood obesity: An under-recognised and growing health problem. Postgrad. Med. J. 2015, 91, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanthier, N.; Leclercq, I.A. Adipose tissues as endocrine target organs. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 28, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forslund, K.; Hildebrand, F.; Nielsen, T.; Falony, G.; Le Chatelier, E.; Sunagawa, S.; Prifti, E.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Krogh Pedersen, H.; et al. Disentangling type 2 diabetes and metformin treatment signatures in the human gut microbiota. Nature 2015, 7581, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, F.H.; Tremaroli, V.; Nookaew, I.; Bergström, G.; Behre, C.J.; Fagerberg, B.; Nielsen, J.; Bäckhed, F. Gut metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic glucose control. Nature 2013, 498, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.; Darimont, C.; Drapeau, V.; Emady-Azar, S.; Lepage, M.; Rezzonico, E.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Berger, B.; Philippe, L.; Ammon-Zuffrey, C.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus CGMCC1.3724 supplementation on weight loss and maintenance in obese men and women. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.R.; Ha, C.D.; Kong, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Song, M.G.; Kang, H.S. Roles of physical activity and cardiorespiratory fitness on sex difference in insulin resistance in late elementary years. J. Exerc. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 18, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhan-Vague, I.; Morange, P.E.; Alessi, M.C. The insulin resistance syndrome: Implications for thrombosis and cardiovascular disease. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2002, 32, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun-Ling, H.; Hui-Ling, L. Intestinal microbiota and type 2 diabetes: From mechanism insights to therapeutic perspective. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 17737–17745. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, N.; Vogensen, F.K.; van den Berg, F.W.J.; Nielsen, D.S.; Andreasen, A.S.; Pedersen, B.K.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Sørensen, S.J.; Hansen, L.H.; Jakobsen, M. Gut microbiota in human adults with type 2 diabetes differs from non-diabetic adults. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulston, C.J.; Churnside, A.A.; Venables, M.C. Probiotic supplementation prevents high-fat, overfeeding-induced insulin resistance in human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ley, R.E.; Bäckhed, F.; Turnbaugh, P.; Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R.D.; Gordon, J.I. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11070–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization and Food & Agriculture Organization. Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food; Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Working Group on Drafting Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food; FAO/WHO: London, ON, Canada, 2002; Available online: ftp://ftp.fao.org/es/esn/food/wgreport2.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2016).
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Gomez-Llorente, C.; Abadia-Molina, F.; Saez-Lara, M.J.; Campaña-Martin, L.; Muñoz-Quezada, S.; Romero, F.; Gil, A.; Fontana, L. Effects of Lactobacillus paracasei CNCM I-4034, Bifidobacterium breve CNCM I-4035 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-4036 on hepatic steatosis in Zucker rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98401. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization, Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations. Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria; FAO Nutrition Paper; FAO: Cordoba, Argentina, 2001; Volume 85, pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruis, W.; Fric, P.; Pokrotnieks, J.; Lukás, M.; Fixa, B.; Kascák, M.; Kamm, M.A.; Weismueller, J.; Beglinger, C.; Stolte, M.; et al. Maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis with the probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 is as effective as with standard mesalazine. Gut 2004, 53, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermudez-Brito, M.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Muñoz-Quezada, S.; Gómez-Llorente, C.; Gil, A. Probiotic mechanisms of action. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, L.; Bermudez-Brito, M.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Muñoz-Quezada, S.; Gil, A. Sources, isolation, characterisation and evaluation of probiotics. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 2, S35–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineiro, M.; Asp, N.G.; Reid, G.; Macfarlane, S.; Morelli, L.; Brunser, O.; Tuohy, K. FAO Technical meeting on prebiotics. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 42, S156–S159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, N.; Moudgal, V. Probiotics: A Review. J. Clin. Outcomes Manag. 2012, 19, 76–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.W.; Suda, W.; Kim, S.; Oshima, K.; Fukuda, S.; Ohno, H.; Morita, H.; Hattori, M. Robustness of gut microbiota of healthy adults in response to probiotic intervention revealed by high-throughput pyrosequencing. DNA Res. 2013, 20, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrario, C.; Taverniti, V.; Milani, C.; Fiore, W.; Laureati, M.; de Noni, I.; Stuknyte, M.; Chouaia, B.; Riso, P.; Guglielmetti, S. Modulation of fecal Clostridiales bacteria and butyrate by probiotic intervention with Lactobacillus paracasei DG varies among healthy adults. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Kim, S.S. Probiotics and prebiotics: Present status and future perspectives on metabolic disorders. Nutrients 2016, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, N.; Vogensen, F.K.; Gøbel, R.J.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Forssten, S.D.; Lahtinen, S.J.; Jakobsen, M. Effect of Lactobacillus salivarius Ls-33 on fecal microbiota in obese adolescents. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gøbel, R.J.; Larsen, N.; Jakobsen, M.; Mølgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F. Probiotics to adolescents with obesity: Effects on Inflammation and metabolic syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadooka, Y.; Sato, M.; Imaizumi, K.; Ogawa, A.; Ikuyama, K.; Akai, Y.; Okano, M.; Kagoshima, M.; Tsuchida, T. Regulation of abdominal adiposity by probiotics (Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055) in adults with obese tendencies in a randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadooka, Y.; Sato, M.; Ogawa, A.; Miyoshi, M.; Uenishi, H.; Ogawa, H. Effect of Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055 in fermented milk on abdominal adiposity in adults in a randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1696–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharafedtinov, K.K.; Plotnikova, O.A.; Alexeeva, R.I.; Sentsova, T.B.; Songisepp, E.; Stsepetova, J.; Smidt, I.; Mikelsaar, M. Hypocaloric diet supplemented with probiotic cheese improves body mass index and blood pressure indices of obese hypertensive patients—A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrati, M.; Salehi, E.; Nourijelyani, K.; Mofid, V.; Zadeh, M.J.; Najafi, F.; Ghaflati, Z.; Bidad, K.; Chamari, M.; Karimi, M.; et al. Effects of probiotic yogurt on fat distribution and gene expression of proinflammatory factors in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in overweight and obese people with or without weight-loss diet. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2014, 33, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrati, M.; Shidfar, F.; Nourijelyani, K.; Mofid, V.; Hossein zadeh-Attar, M.J.; Bidad, K.; Najafi, F.; Gheflati, Z.; Chamari, M.; Salehi, E. Lactobacillus acidophilus La5, Bifidobacterium BB12, and Lactobacillus casei DN001 modulate gene expression of subset specific transcription factors and cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of obese and overweight people. Biofactors 2013, 39, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrati, M.; Salehi, E.; Mofid, V.; Hossein Zadeh-Attar, M.J.; Nourijelyani, K.; Bidad, K.; Shidfar, F. Relationship between probiotic consumption and IL-10 and IL-17 secreted by PBMCs in overweight and obese people. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013, 12, 404–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agerholm-Larsen, L.; Raben, A.; Haulrik, N.; Hansen, A.S.; Manders, M.; Astrup, A. Effect of 8 week intake of probiotic milk products on risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 54, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkumar, H.; Mahmood, N.; Kumar, M.; Varikuti, S.R.; Challa, H.R.; Myakala, S.P. Effect of probiotic (VSL#3) and Ω-3 on lipid profile, insulin sensitivity, inflammatory markers, and gut colonization in overweight adults: A randomized, controlled trial. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 348959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahe, L.K.; Le Chatelier, E.; Prifti, E.; Pons, N.; Kennedy, S.; Blædel, T.; Håkansson, J.; Dalsgaard, T.K.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O. Dietary modulation of the gut microbiota—A randomised controlled trial in obese postmenopausal women. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivey, K.L.; Hodgson, J.M.; Kerr, D.A.; Lewis, J.R.; Thompson, P.L.; Prince, R.L. The effects of probiotic bacteria on glycaemic control in overweight men and women: A randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivey, K.L.; Hodgson, J.M.; Kerr, D.A.; Thompson, P.L.; Stojceski, B.; Prince, R.L. The effect of yoghurt and its probiotics on blood pressure and serum lipid profile; a randomised controlled trial. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safavi, M.; Farajian, S.; Kelishadi, R.; Mirlohi, M.; Hashemipour, M. The effects of synbiotic supplementation on some cardio metabolic risk factors in overweight and obese children: A randomized triple-masked controlled trial. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 64, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipar, N.; Aydogdu, S.D.; Yildirim, G.K.; Inal, M.; Gies, I.; Vandenplas, Y.; Dinleyici, E.C. Effects of synbiotic on anthropometry, lipid profile and oxidative stress in obese children. Benef. Microbes 2015, 6, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leber, B.; Tripolt, N.J.; Blattl, D.; Eder, M.; Wascher, T.C.; Pieber, T.R.; Stauber, R.; Sourij, H.; Oettl, K.; Stadlbauer, V. The influence of probiotic supplementation on gut permeability in patients with metabolic syndrome: An open label, randomized pilot study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 66, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripolt, N.J.; Leber, B.; Blattl, D.; Eder, M.; Wonisch, W.; Scharnagl, H.; Stojakovic, T.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B.; Wascher, T.C.; Pieber, T.R.; et al. Effect of supplementation with Lactobacillus casei Shirota on insulin sensitivity, β-cell function, and markers of endothelial function and inflammation in subjects with metabolic syndrome—A pilot study. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, F.M.; Colado Simão, A.N.; Morimoto, H.K.; Batisti Lozovoy, M.A.; Dichi, I.; Helena da Silva Miglioranza, L. Beneficial effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on glycemia and homocysteine levels in postmenopausal women with metabolic syndrome. Nutrition 2014, 30, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslamparast, T.; Zamani, F.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Sharafkhah, M.; Eghtesad, S.; Malekzadeh, R.; Poustchi, H. Effects of synbiotic supplementation on insulin resistance in subjects with the metabolic syndrome: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hariri, M.; Salehi, R.; Feizi, A.; Mirlohi, M.; Ghiasvand, R.; Habibi, N. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial on probiotic soy milk and soy milk: Effects on epigenetics and oxidative stress in patients with type II diabetes. Genes Nutr. 2015, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonucci, L.B.; Olbrich Dos Santos, K.M.; Licursi de Oliveira, L.; Rocha Ribeiro, S.M.; Duarte Martino, H.S. Clinical application of probiotics in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin. Nutr. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamadshahi, M.; Veissi, M.; Haidari, F.; Javid, A.Z.; Mohammadi, F.; Shirbeigi, E. Effects of probiotic yogurt consumption on lipid profile in type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ejtahed, H.S.; Mohtadi-Nia, J.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Niafar, M.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Mofid, V. Probiotic yogurt improves antioxidant status in type 2 diabetic patients. Nutrition 2012, 28, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejtahed, H.S.; Mohtadi-Nia, J.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Niafar, M.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Mofid, V.; Akbarian-Moghari, A. Effect of probiotic yogurt containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium lactis on lipid profile in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 3288–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreasen, A.S.; Larsen, N.; Pedersen-Skovsgaard, T.; Berg, R.M.; Møller, K.; Svendsen, K.D.; Jakobsen, M.; Pedersen, B.K. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM on insulin sensitivity and the systemic inflammatory response in human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asemi, Z.; Zohreh, Z.; Shakeri, H.; Sima-sadat Sabihi, S.S.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Effect of multispecies probiotic supplements on metabolic profiles, hs-CRP, and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajadadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Bahmani, F.; Shakeri, H.; Hadaegh, H.; Hijijafari, M.; Abedi, F.; Asemi, Z. Effects of daily consumption of synbiotic bread on insulin metabolism and serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein among diabetic patients: A double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 65, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeri, H.; Hadaegh, H.; Abedi, F.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Mazroii, N.; Ghandi, Y.; Asemi, Z. Consumption of synbiotic bread decreases triacylglycerol and VLDL levels while increasing HDL levels in serum from patients with type-2 diabetes. Lipids 2014, 49, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroti, C.; Souza Magri, L.F.; Rezende-Costa, M.; Cavallini, D.; Sivieri, K. Effect of the consumption of a new symbiotic shake on glycemia and cholesterol levels in elderly people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aller, R.; De Luis, D.A.; Izaola, O.; Conde, R.; Gonzalez Sagrado, M.; Primo, D.; de la Fuente, B.; Gonzalez, J. Effect of a probiotic on liver aminotransferases in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients: A double blind randomized clinical trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vajro, P.; Mandato, C.; Licenziati, M.R.; Franzese, A.; Vitale, D.F.; Lenta, S.; Caropreso, M.; Vallone, G.; Meli, R. Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG in pediatric obesity-related liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 52, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, S.; Rafraf, M.; Somi, M.H.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M. Effects of probiotic yogurt consumption on metabolic factors in individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 7386–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alisi, A.; Bedogni, G.; Baviera, G.; Giorgio, V.; Porro, E.; Paris, C.; Giammaria, P.; Reali, L.; Anania, F.; Nobili, V. Randomised clinical trial: The beneficial effects of VLS≠3 in obese children with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, D.A.; D’Alessio, D.A. Physiology of proglucagon petides: Role of glucagon and GLP-1 in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 513–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslamparast, T.; Poustchi, H.; Zamani, F.; Sharafkhah, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hetmatdoost, A. Synbiotic supplementation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lirussi, F.; Mastropasqua, E.; Orando, S.; Orlando, R. Probiotics for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and/or steatohepatitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, 1, CD005165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.; Won, G.L.; Chim, A.M.; Chu, W.C.; Yeung, D.K.; Li, K.C.; Chan, L. Treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with probiotics. A proof-of-concept study. Ann. Hepatol. 2013, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Reference | Subjects | Strain/Dose | Time | Main Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probiotics | ||||
| Larsen et al., 2013 [31] | 50 obese adolescents | L. salivarius Ls-33 | 12 wk | Increase in the ratios of Bacteroides, Prevotellae and Porphyromonas. |
| Gobel et al., 2012 [32] | 50 adolescents with obesity | L. salivarius Ls-33, 1010 CFU | 12 wk | No effect. |
| Kadooka et al., 2010 [33] | 87 subjects with high BMI | L. gasseri SBT2055, 5 × 1010 CFU | 12 wk | Reduction in BMI, abdominal VFA. Increase in adiponectin levels. |
| Kadooka et al., 2013 [34] | 210 adults with large VFA | L. gasseri SBT2055, 108 CFU | 12 wk | Reduction in BMI, waist, abdominal VFA and hip circumference. |
| Sharafedtinov et al., 2013 [35] | 40 adults with obesity | L. plantarum 1.5 × 1011 CFU/g | 3 wk | Reduction in BMI and arterial BP values. |
| Zarrati et al., 2013a, 2013b, 2014 [36,37,38] | 75 subjects with high BMI | L. acidophilus La5, B. lactis Bb12, and L. casei DN001, 108 CFU/g | 8 wk | Changes in gene expression in PBMCs as well as BMI, fat percentage and leptin levels. |
| Agerholm-Larsen et al., 2000 [39] | 70 overweight and obese subjects | E. faecium and two strains of S. thermophilus | 8 wk | Reduction in body weight, systolic BP, LDL-C, and increase on fibrinogen levels. |
| Rajkumar et al., 2013 [40] | 60 overweight subjects | Bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, and S. thermophilus | 6 wk | Improvement in lipid profile, insulin sensitivity, and decrease in CRP. |
| Brahe et al., 2015 [41] | 58 obese PM women | L. paracasei N19, 9.4× 1010 CFU | 6 wk | No effect. |
| Ivey et al., 2014, 2015 [42,43] | 156 overweight adults | L. acidophilus La5 and B. animalis subsp. lactis Bb12 | 6 wk | Reduction in fasting glucose concentration and increase in HOMA-IR. |
| Synbiotics | ||||
| Sánchez et al., 2014 [12] | 153 obese men and women | L. rhamnosus CGMCC1.3724, 6 × 108 CFU, and inulin | 36 wk | Weight loss and reduction in leptin. Increase in Lachnospiraceae. |
| Safavi et al., 2013 [44] | 70 children and adolescents with high BMI | L. casei, L. rhamnosus, S. thermophilus, B. breve, L. acidophilus, B. longum, L. bulgaricus, and FOS | 8 wk | Decrease in BMI z-score and waist circumference. |
| Ipar et al., 2015 [45] | 77 obese children | L. acidophilus, L. rhamnosus, B. bifidum, B. longum, E. faecium, and FOS | 4 wk | Changes in anthropometric measurements. Decrease in TC, LDL-C and total oxidative stress serum levels. |
| Reference | Subjects | Strain/Dose | Time | Main Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probiotics | ||||
| Leber et al., 2013 [46] | 28 patients with IRS | L. casei Shirota, 3 × 6.5 × 109 CFU | 12 wk | No effects. |
| Tripolt et al., 2012 [47] | 30 patients with IRS | L. casei Shirota | 12 wk | Significant reduction in thesVCAM-1 level. |
| Barreto et al., 2014 [48] | 24 PM women with IRS | L. plantarum | 12 wk | Glucose and homocysteine levels were significantly reduced. |
| Synbiotics | ||||
| Eslamparast et al., 2014 [49] | 38 subjects with IRS | L. casei, L. rhamnosus, S. thermophilus, B. breve, L. acidophilus, B. longum, L. bulgaricus, and FOS | 28 wk | The levels of fasting blood sugar and insulin resistance improved significantly. |
| Reference | Subjects | Strain/Dose | Time | Main Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probiotics | ||||
| Hariri et al., 2015 [50] | 40 patients with T2D | L. plantarum A7 | 8 wk | Decreased methylation process, SOD and 8-OHDG. |
| Tonucci et al., 2015 [51] | 45 patients with T2D | L. acidophilus La-5 and B. animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 | 6 wk | Significant difference between groups concerning mean changes of HbA1c, TC and LDL-C. |
| Mohamadshahi et al., 2014 [52] | 44 patients with T2D | L. acidophilus La-5 and B. animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 | 8 wk | Increased HDL-C levels and decreased LDL-C/HDL-C ratio. |
| Ejtahed et al., 2012 [53] | 64 patients with T2D | L. acidophilus La5 and B. lactis Bb12 | 6 wk | Reduced fasting blood glucose and antioxidant status. |
| Ejtahed et al., 2011 [54] | 60 patients with T2D | L. acidophilus La5 and B. lactis Bb12 | 6 wk | TC and LDL-C improvement. |
| Andreasen et al., 2010 [55] | 45 males with T2D | L. acidophilus NCFM | 4 wk | No effect. |
| Synbiotics | ||||
| Asemi et al., 2013 [56] | 54 patients with T2D (35–70 years) | L. acidophilus, L. casei, L. rhamnosus, L. bulgaricus, B. breve, B. longum, S. thermophilus, 109 CFU, and 100 mg FOS | 8 wk | Increased HOMA-IR and TGL plasma level; reduced CRP in serum. |
| Tajadadi-Ebrahimi et al., 2014 [57] | 81 patients with T2D | L. sporogenes, 1×108 CFU and 0.07 g inulin per 1 g | 8 wk | Significant reduction in serum insulin levels, HOMA-IR, and homeostatic model assessment-β-cell function. |
| Shakeri et al., 2014 [58] | 78 patients with T2D | L. sporogenes, 1×108 CFU and 0.07 g inulin per 1 g | 8 wk | Decrease in serum lipid profile (TAG, TC/HDL-C) and a significant increase in serum HDL-C levels. |
| Moroti et al., 2012 [59] | 20 patients with T2D | L. acidophilus 108 CFU/mL, B. bifidum 108 CFU/mL and 2 g oligofructose | 2 wk | Increased HDL-C and reduced fasting glycemia. |
| Reference | Subjects | Strain/Dose | Time | Main Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probiotics | ||||
| Vajro P et al., 2011 [61] | 20 obese children with NAFLD | L. rhamnosus GG, 1.2 × 109 CFU/day | 8 wk | Decreased ALT and PG-PS IgAg antibodies. |
| Aller R et al., 2011 [60] | 28 adult individuals with NAFLD | L. bulgaris and S. thermophilus, 5.0 × 1011 CFU/day | 12 wk | Decreased ALT and γ-GTP levels. |
| Nabavi et al., 2014 [62] | 72 patients with NAFLD | L. acidophilus La5 and B. breve subsp. lactis Bb12 | 8 wk | Reduced serum levels of ALT, ASP, TC, and LDL-C. |
| Alisi A et al., 2014 [63] | 44 obese children with NAFLD | Bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, and S. thermophilus | 16 wk | Improved fatty liver severity, decreased BMI and increased GLP1/aGLP1. |
| Synbiotics | ||||
| Wong VW et al., 2013 [67] | 20 individuals with NASH | L. plantarum, L. delbrueckii spp. bulgaricus, L. acidophilus, L. rhamnosus, B. bifidum and inulin | 26 wk | Decreased IHTG content. |
| Eslamparast T et al., 2014 [65] | 52 adult individuals with NAFLD | L. casei, L. rhamnosus, S. thermophilus, B. breve, L. acidophilus, B. longum, L. bulgaricus, and FOS | 30 wk | Inhibition of NF-κB and reduction of TNF-α. |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sáez-Lara, M.J.; Robles-Sanchez, C.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Gil, A. Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Obesity, Insulin Resistance Syndrome, Type 2 Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Review of Human Clinical Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060928
Sáez-Lara MJ, Robles-Sanchez C, Ruiz-Ojeda FJ, Plaza-Diaz J, Gil A. Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Obesity, Insulin Resistance Syndrome, Type 2 Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Review of Human Clinical Trials. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(6):928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060928
Chicago/Turabian StyleSáez-Lara, Maria Jose, Candido Robles-Sanchez, Francisco Javier Ruiz-Ojeda, Julio Plaza-Diaz, and Angel Gil. 2016. "Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Obesity, Insulin Resistance Syndrome, Type 2 Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Review of Human Clinical Trials" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 6: 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060928
APA StyleSáez-Lara, M. J., Robles-Sanchez, C., Ruiz-Ojeda, F. J., Plaza-Diaz, J., & Gil, A. (2016). Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Obesity, Insulin Resistance Syndrome, Type 2 Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Review of Human Clinical Trials. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(6), 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060928