Bone Metastasis from Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Natural History of Bone Metastasis in RCC
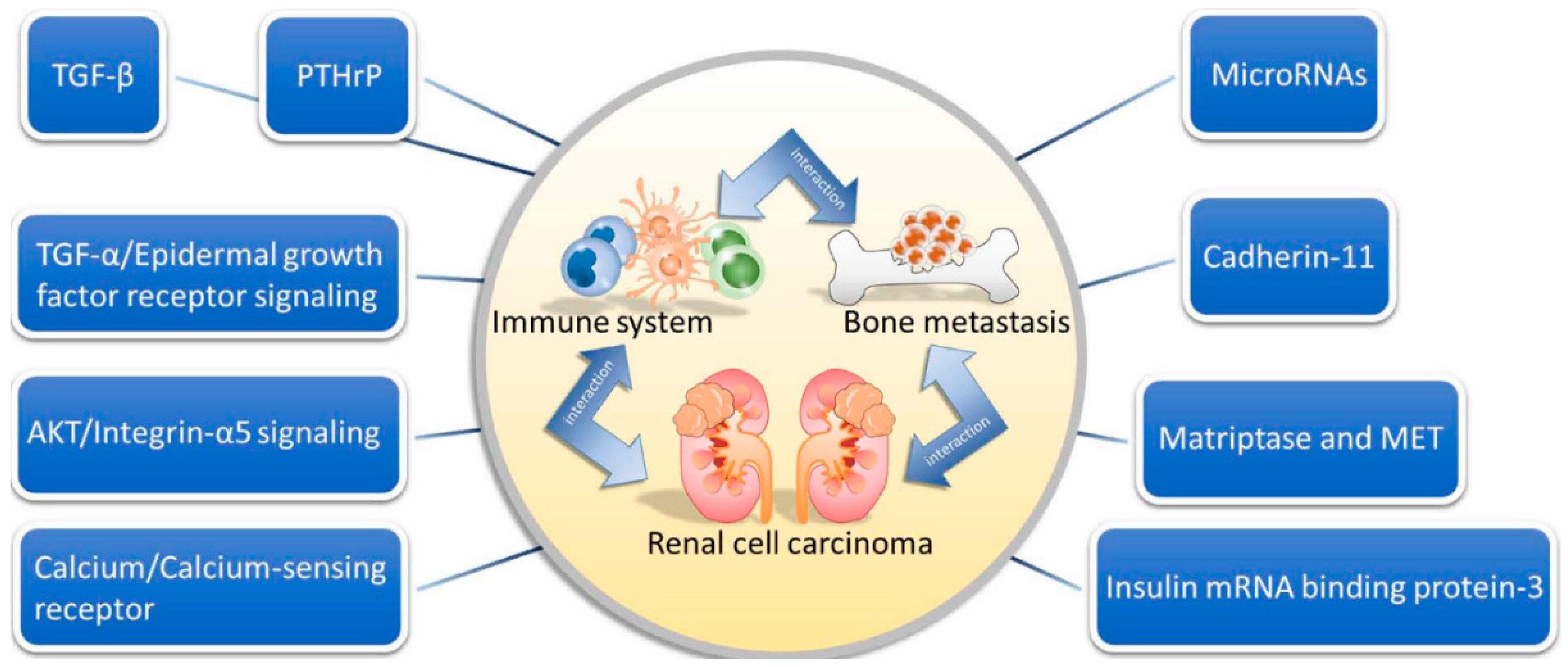
3. Interactions among the Immune System, Bone and Tumor
3.1. Interplay between Bone and the Immune System
3.2. Interplay between Bone and RCC
3.3. Interplay between the Immune System and RCC
4. Molecular Mechanisms of RCC
4.1. The Role of TGF-β in RCC Bone Metastasis
4.2. The Role of TGF-α/Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling
4.3. The Role of Insulin mRNA Binding Protein-3
4.4. The Role of Cadherin-11
4.5. The Role of PTHrP
4.6. The Role of Calcium/Calcium-Sensing Receptor
4.7. The Role of AKT/Integrin-α5 Signaling
4.8. The Role of Matriptase and MET
4.9. The Role of MicroRNAs
4.10. Other Immunogenic Biomarkers
5. Diagnostic Value of Bone Turnover Markers in RCC Bone Metastasis
6. Therapy for RCC Bone Metastasis
6.1. Drug Therapy
6.1.1. Zoledronic Acid
6.1.2. Denosumab
6.1.3. Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Antigen-4 Antibody
6.1.4. Programmed Death-1 Inhibitors
6.2. Non-Drug Therapy
7. Healthcare Burden of SREs in RCC Bone Metastasis
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| mRCC | metastatic RCC |
| VEGF-TKIs | vascular endothelial growth factor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| IFN-α | interferon-α |
| SREs | skeletal-related events |
| TTBM | time from nephrectomy to bone metastasis |
| RANKL | nuclear factor NF-κB ligand |
| RANK | nuclear factor NF-κB |
| OPG | osteoprotegerin |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor-β |
| PTHrP | parathyroid hormone-related peptide |
| EGF-R | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| IMP3 | insulin mRNA binding protein-3 |
| Bo-786-O | bone metastasis-derived 786-O cells |
| PTH | parathyroid hormone |
| VHL | von Hippel–Lindau |
| CaSR | calcium-sensing receptor |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| HGF | hepatocyte growth factor |
| CTLA-4 | cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 |
| CPRs | checkpoint receptors |
| PD-1 | programmed death-1 inhibitors |
References
- Murai, M.; Oya, M. Renal cell carcinoma: Etiology, incidence and epidemiology. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2004, 14, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Rathmell, W.K.; Godley, P. Renal cell carcinoma. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2008, 20, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I. Stabilization of disease in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma using sorafenib. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2006, 3, 602–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Bacik, J.; Mazumdar, M. Prognostic factors for survival of patients with stage iv renal cell carcinoma: Memorial sloan-kettering cancer center experience. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6302S–6303S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.K.; Nelson, R.A.; Vogelzang, N. Disease-specific survival in de novo metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the cytokine and targeted therapy era. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Tomczak, P.; Michaelson, M.D.; Bukowski, R.M.; Oudard, S.; Negrier, S.; Szczylik, C.; Pili, R.; Bjarnason, G.A.; et al. Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon α in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3584–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Bacik, J.; Mariani, T.; Russo, P.; Mazumdar, M.; Reuter, V. Treatment outcome and survival associated with metastatic renal cell carcinoma of non-clear-cell histology. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 2376–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Bacik, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Reuter, V.; Russo, P.; Marion, S.; Mazumdar, M. Prognostic factors for survival in previously treated patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Mazumdar, M.; Bacik, J.; Berg, W.; Amsterdam, A.; Ferrara, J. Survival and prognostic stratification of 670 patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 2530–2540. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, M.; Sun, M.; Jeldres, C.; Shariat, S.F.; Trinh, Q.D.; Briganti, A.; Tian, Z.; Schmitges, J.; Graefen, M.; Perrotte, P.; et al. Distribution of metastatic sites in renal cell carcinoma: A population-based analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, E.; Jagdev, S.; McParland, L.; Clark, K.; Gregory, W.; Newsham, A.; Rogerson, S.; Hayward, K.; Selby, P.; Brown, J. Skeletal complications and survival in renal cancer patients with bone metastases. Bone 2011, 48, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zekri, J.; Ahmed, N.; Coleman, R.E.; Hancock, B.W. The skeletal metastatic complications of renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2001, 19, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnane, N. Burden of bone disease. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2007, 11 (Suppl. 2), S28–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, D.; Procopio, G.; Porta, C.; Ibrahim, T.; Barni, S.; Mazzara, C.; Fontana, A.; Berruti, A.; Berardi, R.; Vincenzi, B.; et al. Natural history of malignant bone disease in renal cancer: Final results of an italian bone metastasis survey. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santoni, M.; Conti, A.; Procopio, G.; Porta, C.; Ibrahim, T.; Barni, S.; Guida, F.M.; Fontana, A.; Berruti, A.; Berardi, R.; et al. Bone metastases in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Are they always associated with poor prognosis? J. Exp. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2015, 34, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McNichols, D.W.; Segura, J.W.; DeWeerd, J.H. Renal cell carcinoma: Long-term survival and late recurrence. J. Urol. 1981, 126, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miyao, N.; Naito, S.; Ozono, S.; Shinohara, N.; Masumori, N.; Igarashi, T.; Nakao, M.; Tsushima, T.; Senga, Y.; Horie, S.; et al. Late recurrence of renal cell carcinoma: Retrospective and collaborative study of the japanese society of renal cancer. Urology 2011, 77, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roodman, G.D. Mechanisms of bone metastasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofbauer, L.C.; Kuhne, C.A.; Viereck, V. The OPG/RANKL/RANK system in metabolic bone diseases. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal. Interact. 2004, 4, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kostenuik, P.J.; Shalhoub, V. Osteoprotegerin: A physiological and pharmacological inhibitor of bone resorption. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2001, 7, 613–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, D.; Perrone, G.; Roato, I.; Godio, L.; Pantano, F.; Grasso, D.; Russo, A.; Vincenzi, B.; Fratto, M.E.; Sabbatini, R.; et al. Expression pattern of receptor activator of NFκB (RANK) in a series of primary solid tumors and related bone metastases. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hofbauer, L.C.; Khosla, S.; Dunstan, C.R.; Lacey, D.L.; Boyle, W.J.; Riggs, B.L. The roles of osteoprotegerin and osteoprotegerin ligand in the paracrine regulation of bone resorption. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2000, 15, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacifici, R. T cells, osteoblasts, and osteocytes: Interacting lineages key for the bone anabolic and catabolic activities of parathyroid hormone. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1364, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikami, S.; Katsube, K.; Oya, M.; Ishida, M.; Kosaka, T.; Mizuno, R.; Mochizuki, S.; Ikeda, T.; Mukai, M.; Okada, Y. Increased rankl expression is related to tumour migration and metastasis of renal cell carcinomas. J. Pathol. 2009, 218, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beuselinck, B.; Jean-Baptiste, J.; Couchy, G.; Job, S.; de Reynies, A.; Wolter, P.; Theodore, C.; Gravis, G.; Rousseau, B.; Albiges, L.; et al. RANK /OPG ratio of expression in primary clear-cell renal cell carcinoma is associated with bone metastasis and prognosis in patients treated with anti-VEGFR-TKIs. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paget, S. The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. 1889. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1989, 8, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Shiozawa, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jung, Y.; Pienta, K.J.; Mehra, R.; Loberg, R.; Taichman, R.S. The role of CXCR7/RDC1 as a chemokine receptor for CXCL12/SDF-1 in prostate cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 4283–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschka, P.V.; Mavrakos, A.E.; Iafrati, M.D.; Doleman, S.E.; Klagsbrun, M. Growth factors in bone matrix. Isolation of multiple types by affinity chromatography on heparin-sepharose. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 12665–12674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Kim, S.; Cremasco, V.; Hirbe, A.C.; Collins, L.; Piwnica-Worms, D.; Novack, D.V.; Weilbaecher, K.; Faccio, R. CD8+ T cells regulate bone tumor burden independent of osteoclast resorption. Cancer. Res. 2011, 71, 4799–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miossec, P.; Korn, T.; Kuchroo, V.K. Interleukin-17 and type 17 helper T cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallas, S.L.; Rosser, J.L.; Mundy, G.R.; Bonewald, L.F. Proteolysis of latent transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β)-binding protein-1 by osteoclasts. A cellular mechanism for release of TGF-β from bone matrix. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 21352–21360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakonen, S.M.; Selander, K.S.; Chirgwin, J.M.; Yin, J.J.; Burns, S.; Rankin, W.A.; Grubbs, B.G.; Dallas, M.; Cui, Y.; Guise, T.A. Transforming growth factor-β stimulates parathyroid hormone-related protein and osteolytic metastases via smad and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 24571–24578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kominsky, S.L.; Doucet, M.; Brady, K.; Weber, K.L. TGF-β promotes the establishment of renal cell carcinoma bone metastasis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumm, G.; Eberwein, S.; Rostock-Wolf, S.; Stein, H.; Pomer, S.; Schlegel, J.; Waldherr, R. Concomitant overexpression of the EGFR and erbB-2 genes in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is correlated with dedifferentiation and metastasis. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 69, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moch, H.; Sauter, G.; Buchholz, N.; Gasser, T.C.; Bubendorf, L.; Waldman, F.M.; Mihatsch, M.J. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression is associated with rapid tumor cell proliferation in renal cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 1997, 28, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.; Doucet, M.; Kominsky, S. Renal cell carcinoma bone metastasis--elucidating the molecular targets. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007, 26, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; MacDonald, B.R.; Hon, J.; Winkler, M.E.; Derynck, R.; Mundy, G.R.; Roodman, G.D. Recombinant human transforming growth factor-α stimulates the formation of osteoclast-like cells in long-term human marrow cultures. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 78, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Chu, P.G.; Woda, B.A.; Liu, Q.; Balaji, K.C.; Rock, K.L.; Wu, C.L. Combination of quantitative IMP3 and tumor stage: A new system to predict metastasis for patients with localized renal cell carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5579–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, Y.M.; Chang, C.C.; Hu, F.C.; Chou, H.Y.; Kao, H.L.; Wang, T.H.; Hsu, H.C. RNA-binding protein insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3 expression promotes tumor invasion and predicts early recurrence and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.L.; Wachter, K.; Muhleck, B.; Pazaitis, N.; Kohn, M.; Lederer, M.; Huttelmaier, S. Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs): Post-transcriptional drivers of cancer progression? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 2657–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.A.; Vickers, M.M.; Heng, D.Y. Clinical and molecular prognostic factors in renal cell carcinoma: What we know so far. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 25, 871–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yao, J.; Yin, G.; Bi, Q.; O’Keefe, R.J.; Schwarz, E.M.; Tyler, W. Increased insulin mRNA binding protein-3 expression correlates with vascular enhancement of renal cell carcinoma by intravenous contrast-CT and is associated with bone metastasis. J. Bone Oncol. 2015, 4, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.L.; Lecanda, F.; Davidson, M.K.; Warlow, P.M.; Zhang, S.F.; Zhang, L.; Suzuki, S.; St John, T.; Civitelli, R. Human osteoblasts express a repertoire of cadherins, which are critical for BMP-2-induced osteogenic differentiation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1998, 13, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, M.; Takeshita, S.; Kawai, S.; Kikuno, R.; Tsujimura, A.; Kudo, A.; Amann, E. Molecular cloning and characterization of OB-cadherin, a new member of cadherin family expressed in osteoblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 12092–12098. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.F.; Lira, C.; Chu, K.; Bilen, M.A.; Lee, Y.C.; Ye, X.; Kim, S.M.; Ortiz, A.; Wu, F.L.; Logothetis, C.J.; et al. Cadherin-11 increases migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells and enhances their interaction with osteoblasts. Cancer. Res. 2010, 70, 4580–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, D.; Hiraga, T.; Myoui, A.; Yoshikawa, H.; Yoneda, T. Cadherin-11-mediated interactions with bone marrow stromal/osteoblastic cells support selective colonization of breast cancer cells in bone. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 33, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satcher, R.L.; Pan, T.; Cheng, C.J.; Lee, Y.C.; Lin, S.C.; Yu, G.; Li, X.; Hoang, A.G.; Tamboli, P.; Jonasch, E.; et al. Cadherin-11 in renal cell carcinoma bone metastasis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philbrick, W.M.; Wysolmerski, J.J.; Galbraith, S.; Holt, E.; Orloff, J.J.; Yang, K.H.; Vasavada, R.C.; Weir, E.C.; Broadus, A.E.; Stewart, A.F. Defining the roles of parathyroid hormone-related protein in normal physiology. Physiol. Rev. 1996, 76, 127–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, T.J.; Moseley, J.M.; Williams, E.D. Parathyroid hormone-related protein: Hormone and cytokine. J. Endocrinol. 1997, 154, S23–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, P.B.; Moniz, C.; Knight, D.E. Parathyroid hormone related peptide can function as an autocrine growth factor in human renal cell carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 167, 1134–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massfelder, T.; Lang, H.; Schordan, E.; Lindner, V.; Rothhut, S.; Welsch, S.; Simon-Assmann, P.; Barthelmebs, M.; Jacqmin, D.; Helwig, J.J. Parathyroid hormone-related protein is an essential growth factor for human clear cell renal carcinoma and a target for the von hippel-lindau tumor suppressor gene. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choyke, P.L.; Glenn, G.M.; Walther, M.M.; Zbar, B.; Weiss, G.H.; Alexander, R.B.; Hayes, W.S.; Long, J.P.; Thakore, K.N.; Linehan, W.M. The natural history of renal lesions in von hippel-lindau disease: A serial ct study in 28 patients. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1992, 159, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talon, I.; Lindner, V.; Sourbier, C.; Schordan, E.; Rothhut, S.; Barthelmebs, M.; Lang, H.; Helwig, J.J.; Massfelder, T. Antitumor effect of parathyroid hormone-related protein neutralizing antibody in human renal cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, E.M.; Gamba, G.; Riccardi, D.; Lombardi, M.; Butters, R.; Kifor, O.; Sun, A.; Hediger, M.A.; Lytton, J.; Hebert, S.C. Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid. Nature 1993, 366, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez-Fraile, A.; Lammens, T.; Benoit, Y.; D’Herde, K.G. The calcium-sensing receptor as a regulator of cellular fate in normal and pathological conditions. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, D.T.; Riccardi, D. New concepts in calcium-sensing receptor pharmacology and signalling. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, S.C.; Conigrave, A.D. Regulation of cellular signal transduction pathways by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2009, 10, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihai, R.; Stevens, J.; McKinney, C.; Ibrahim, N.B. Expression of the calcium receptor in human breast cancer—A potential new marker predicting the risk of bone metastases. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 32, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joeckel, E.; Haber, T.; Prawitt, D.; Junker, K.; Hampel, C.; Thuroff, J.W.; Roos, F.C.; Brenner, W. High calcium concentration in bones promotes bone metastasis in renal cell carcinomas expressing calcium-sensing receptor. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pylayeva, Y.; Gillen, K.M.; Gerald, W.; Beggs, H.E.; Reichardt, L.F.; Giancotti, F.G. Ras- and PI3K-dependent breast tumorigenesis in mice and humans requires focal adhesion kinase signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haber, T.; Jockel, E.; Roos, F.C.; Junker, K.; Prawitt, D.; Hampel, C.; Thuroff, J.W.; Brenner, W. Bone metastasis in renal cell carcinoma is preprogrammed in the primary tumor and caused by akt and integrin alpha5 signaling. J. Urol. 2015, 194, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Veine, D.M.; Zeng, Z.Z.; Fay, K.S.; Staszewski, E.D.; Livant, D.L. Increased potency of the PHSCN dendrimer as an inhibitor of human prostate cancer cell invasion, extravasation, and lung colony formation. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2010, 27, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell-McGuinn, K.M.; Matthews, C.M.; Ho, S.N.; Barve, M.; Gilbert, L.; Penson, R.T.; Lengyel, E.; Palaparthy, R.; Gilder, K.; Vassos, A.; et al. A phase ii, single-arm study of the anti-α5β integrin antibody volociximab as monotherapy in patients with platinum-resistant advanced epithelial ovarian or primary peritoneal cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 121, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, H.; Miyata, S.; Uchinokura, S.; Itoh, H. Roles of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) activator and HGF activator inhibitor in the pericellular activation of HGF/scatter factor. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giubellino, A.; Linehan, W.M.; Bottaro, D.P. Targeting the Met signaling pathway in renal cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2009, 9, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, Y.; Kanetake, H.; Kanda, S. Presence of phosphorylated hepatocyte growth factor receptor/C-Met is associated with tumor progression and survival in patients with conventional renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2006, 12, 4876–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, K.L.; Pathak, S.; Multani, A.S.; Price, J.E. Characterization of a renal cell carcinoma cell line derived from a human bone metastasis and establishment of an experimental nude mouse model. J. Urol. 2002, 168, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previdi, S.; Maroni, P.; Matteucci, E.; Broggini, M.; Bendinelli, P.; Desiderio, M.A. Interaction between human-breast cancer metastasis and bone microenvironment through activated hepatocyte growth factor/met and β-catenin/Wnt pathways. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 1679–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karar, J.; Maity, A. PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in angiogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroni, P.; Bendinelli, P.; Matteucci, E.; Locatelli, A.; Nakamura, T.; Scita, G.; Desiderio, M.A. Osteolytic bone metastasis is hampered by impinging on the interplay among autophagy, anoikis and ossification. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- List, K.; Bugge, T.H.; Szabo, R. Matriptase: Potent proteolysis on the cell surface. Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgy, S.R.; Pagel, C.N.; Ghasem-Zadeh, A.; Zebaze, R.M.; Pike, R.N.; Sims, N.A.; Mackie, E.J. Proteinase-activated receptor-2 is required for normal osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation during skeletal growth and repair. Bone 2012, 50, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najy, A.J.; Won, J.J.; Movilla, L.S.; Kim, H.R. Differential tumorigenic potential and matriptase activation between PDGF B versus PDGF D in prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, S.; Yorita, K.; Kawagoe, Y.; Katayama, Y.; Nakahara, K.; Kamibeppu, T.; Sugie, S.; Tukino, H.; Kamoto, T.; Kataoka, H. Matriptase and met are prominently expressed at the site of bone metastasis in renal cell carcinoma: Immunohistochemical analysis. Hum. Cell. 2015, 28, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, Y.M.; White, N.M.; Grigull, J.; Krizova, A.; Samy, C.; Mejia-Guerrero, S.; Evans, A.; Yousef, G.M. Accurate molecular classification of kidney cancer subtypes using microrna signature. Eur. Urol. 2011, 59, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottardo, F.; Liu, C.G.; Ferracin, M.; Calin, G.A.; Fassan, M.; Bassi, P.; Sevignani, C.; Byrne, D.; Negrini, M.; Pagano, F.; et al. Micro-RNA profiling in kidney and bladder cancers. Urol. Oncol. 2007, 25, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wotschofsky, Z.; Liep, J.; Meyer, H.A.; Jung, M.; Wagner, I.; Disch, A.C.; Schaser, K.D.; Melcher, I.; Kilic, E.; Busch, J.; et al. Identification of metastamirs as metastasis-associated micrornas in clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzelmann, J.; Unrein, A.; Wickmann, U.; Baumgart, S.; Stapf, M.; Szendroi, A.; Grimm, M.O.; Gajda, M.R.; Wunderlich, H.; Junker, K. Micrornas with prognostic potential for metastasis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: A comparison of primary tumors and distant metastases. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paule, B.; Deslandes, E.; le Mouel, S.P.; Bastien, L.; Podgorniak, M.P.; Allory, Y.; de la Taille, A.; Menashi, S.; Calvo, F.; Mourah, S. Identification of a novel biomarker signature associated with risk for bone metastasis in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Markers. 2010, 25, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Guo, X.; Cheng, H.; Ye, Y.; Qi, J.; Yang, C.; You, H. Alterations in enhancer of zeste homolog 2, matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 expression are associated with ex vivo and in vitro bone metastasis in renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 3585–3592. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demers, L.M.; Costa, L.; Chinchilli, V.M.; Gaydos, L.; Curley, E.; Lipton, A. Biochemical markers of bone turnover in patients with metastatic bone disease. Clin. Chem. 1995, 41, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seibel, M.J. Clinical use of markers of bone turnover in metastatic bone disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 2, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramankulov, A.; Lein, M.; Kristiansen, G.; Meyer, H.A.; Loening, S.A.; Jung, K. Elevated plasma osteopontin as marker for distant metastases and poor survival in patients with renal cell carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 133, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.; Lein, M.; Ringsdorf, M.; Roigas, J.; Schnorr, D.; Loening, S.A.; Staack, A. Diagnostic and prognostic validity of serum bone turnover markers in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2006, 176, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klepzig, M.; Sauer-Eppel, H.; Jonas, D.; Oremek, G.M. Value of procollagen type 1 amino-terminal propeptide in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 2443–2446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alcaraz, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, R.; Morote, J.; de la Piedra, C.; Meseguer, C.; Esteban, E.; Climent, M.; Gonzalez-Gragera, B.; Alvarez-Ossorio, J.L.; Chirivella, I.; et al. Biochemical markers of bone turnover and clinical outcome in patients with renal cell and bladder carcinoma with bone metastases following treatment with zoledronic acid: The tugamo study. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, S.; Lyseng-Williamson, K.A. Zoledronic acid: A review of its use in the management of bone metastases of malignancy. Drugs 2008, 68, 507–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, LS.; Gordon, D.; Kaminski, M.; Howell, A.; Belch, A.; Mackey, J.; Apffelstaedt, J.; Hussein, M.; Coleman, R.E.; Reitsma, D.J.; et al. Zoledronic acid versus pamidronate in the treatment of skeletal metastases in patients with breast cancer or osteolytic lesions of multiple myeloma: A phase III, double-blind, comparative trial. Cancer J. 2001, 7, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosen, L.S.; Gordon, D.; Tchekmedyian, S.; Yanagihara, R.; Hirsh, V.; Krzakowski, M.; Pawlicki, M.; de Souza, P.; Zheng, M.; Urbanowitz, G.; et al. Zoledronic acid versus placebo in the treatment of skeletal metastases in patients with lung cancer and other solid tumors: A phase iii, double-blind, randomized trial--the zoledronic acid lung cancer and other solid tumors study group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 3150–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, F.; Gleason, D.M.; Murray, R.; Tchekmedyian, S.; Venner, P.; Lacombe, L.; Chin, J.L.; Vinholes, J.J.; Goas, J.A.; Chen, B. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of zoledronic acid in patients with hormone-refractory metastatic prostate carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1458–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, A.; Zheng, M.; Seaman, J. Zoledronic acid delays the onset of skeletal-related events and progression of skeletal disease in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 2003, 98, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijima, T.; Fujii, Y.; Suyama, T.; Okubo, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Masuda, H.; Yonese, J.; Fukui, I. Radiotherapy to bone metastases from renal cell carcinoma with or without zoledronate. BJU Int. 2009, 103, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassiliou, V.; Kardamakis, D. The management of metastatic bone disease with the combination of bisphosphonates and radiotherapy: From theory to clinical practice. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijima, T.; Koga, F.; Fujii, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Tatokoro, M.; Kihara, K. Zoledronic acid sensitizes renal cell carcinoma cells to radiation by downregulating stat1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broom, R.J.; Hinder, V.; Sharples, K.; Proctor, J.; Duffey, S.; Pollard, S.; Fong, P.C.; Forgeson, G.; Harris, D.L.; Jameson, M.B.; et al. Everolimus and zoledronic acid in patients with renal cell carcinoma with bone metastases: A randomized first-line phase ii trial. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2015, 13, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, C.F.; Rajab, M.H.; Hong, J.; Briody, J.; Hogler, W.; McQuade, M.; Little, D.G.; Cowell, C.T. Acute phase response and mineral status following low dose intravenous zoledronic acid in children. Bone 2007, 41, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayllon, J.; Launay-Vacher, V.; Medioni, J.; Cros, C.; Spano, J.P.; Oudard, S. Osteonecrosis of the jaw under bisphosphonate and antiangiogenic therapies: Cumulative toxicity profile? Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 600–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, G.K.; Bone, H.G.; Chlebowski, R.; Paul, D.; Spadafora, S.; Smith, J.; Fan, M.; Jun, S. Randomized trial of denosumab in patients receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitors for nonmetastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4875–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fizazi, K.; Lipton, A.; Mariette, X.; Body, J.J.; Rahim, Y.; Gralow, J.R.; Gao, G.; Wu, L.; Sohn, W.; Jun, S. Randomized phase II trial of denosumab in patients with bone metastases from prostate cancer, breast cancer, or other neoplasms after intravenous bisphosphonates. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.R.; Egerdie, B.; Hernandez Toriz, N.; Feldman, R.; Tammela, T.L.; Saad, F.; Heracek, J.; Szwedowski, M.; Ke, C.; Kupic, A.; et al. Denosumab in men receiving androgen-deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, A.; Fizazi, K.; Stopeck, A.T.; Henry, D.H.; Brown, J.E.; Yardley, D.A.; Richardson, G.E.; Siena, S.; Maroto, P.; Clemens, M.; et al. Superiority of denosumab to zoledronic acid for prevention of skeletal-related events: A combined analysis of 3 pivotal, randomised, phase 3 trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 3082–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fizazi, K.; Carducci, M.; Smith, M.; Damiao, R.; Brown, J.; Karsh, L.; Milecki, P.; Shore, N.; Rader, M.; Wang, H.; et al. Denosumab versus zoledronic acid for treatment of bone metastases in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer: A randomised, double-blind study. Lancet 2011, 377, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, D.H.; Costa, L.; Goldwasser, F.; Hirsh, V.; Hungria, V.; Prausova, J.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Sleeboom, H.; Spencer, A.; Vadhan-Raj, S.; et al. Randomized, double-blind study of denosumab versus zoledronic acid in the treatment of bone metastases in patients with advanced cancer (excluding breast and prostate cancer) or multiple myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopeck, A.T.; Lipton, A.; Body, J.J.; Steger, G.G.; Tonkin, K.; de Boer, R.H.; Lichinitser, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Yardley, D.A.; Viniegra, M.; et al. Denosumab compared with zoledronic acid for the treatment of bone metastases in patients with advanced breast cancer: A randomized, double-blind study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 5132–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Hughes, M.; Kammula, U.; Royal, R.; Sherry, R.M.; Topalian, S.L.; Suri, K.B.; Levy, C.; Allen, T.; Mavroukakis, S.; et al. Ipilimumab (anti-CTLA4 antibody) causes regression of metastatic renal cell cancer associated with enteritis and hypophysitis. J. Immunother. 2007, 30, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Nivolumab for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Results of a randomized phase II trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, M.P.; Tsao, M.N.; Whelan, T.J.; Morris, D.E.; Hayman, J.A.; Flickinger, J.C.; Mills, M.; Rogers, C.L.; Souhami, L. The american society for therapeutic radiology and oncology (astro) evidence-based review of the role of radiosurgery for brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 63, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taunk, N.K.; Spratt, D.E.; Bilsky, M.; Yamada, Y. Spine radiosurgery in the management of renal cell carcinoma metastases. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2015, 13, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Bilsky, M.H.; Lovelock, D.M.; Venkatraman, E.S.; Toner, S.; Johnson, J.; Zatcky, J.; Zelefsky, M.J.; Fuks, Z. High-dose, single-fraction image-guided intensity-modulated radiotherapy for metastatic spinal lesions. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 71, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, A.; Giuliano, G.; Scuderi, V.; Motta, S.; Crisafi, R.; Coppolino, F.; Mundo, E.; Banna, G.; di Raimondo, F.; Patti, M.T. Cementoplasty in the management of painful extraspinal bone metastases: Our experience. Radiol. Med. 2008, 113, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangi, A.; Kastler, B.; Klinkert, A.; Dietemann, J.L. Injection of alcohol into bone metastases under CT guidance. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1994, 18, 932–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenemeyer, D.H.; Schirp, S.; Gevargez, A. Image-guided percutaneous thermal ablation of bone tumors. Acad. Radiol. 2002, 9, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.J.; Dupuy, D.E.; Mayo-Smith, W.W. Microwave ablation: Principles and applications. Radiographics 2005, 25 (Suppl. 1), S69–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callstrom, M.R.; Atwell, T.D.; Charboneau, J.W.; Farrell, M.A.; Goetz, M.P.; Rubin, J.; Sloan, J.A.; Novotny, P.J.; Welch, T.J.; Maus, T.P.; et al. Painful metastases involving bone: Percutaneous image-guided cryoablation—Prospective trial interim analysis. Radiology. 2006, 241, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyota, N.; Naito, A.; Kakizawa, H.; Hieda, M.; Hirai, N.; Tachikake, T.; Kimura, T.; Fukuda, H.; Ito, K. Radiofrequency ablation therapy combined with cementoplasty for painful bone metastases: Initial experience. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2005, 28, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, M.; Delea, T.E.; Saville, M.W.; Chung, K. Healthcare utilization and costs associated with skeletal-related events in prostate cancer patients with bone metastases. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2013, 16, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, N.; Gore, M.E.; Sohaib, S.A. Imaging in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 189, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.-C.; Kuo, P.-L. Bone Metastasis from Renal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060987
Chen S-C, Kuo P-L. Bone Metastasis from Renal Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(6):987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060987
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Szu-Chia, and Po-Lin Kuo. 2016. "Bone Metastasis from Renal Cell Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 6: 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060987
APA StyleChen, S.-C., & Kuo, P.-L. (2016). Bone Metastasis from Renal Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(6), 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060987






