Distinct Effects of Nalmefene on Dopamine Uptake Rates and Kappa Opioid Receptor Activity in the Nucleus Accumbens Following Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Exposure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
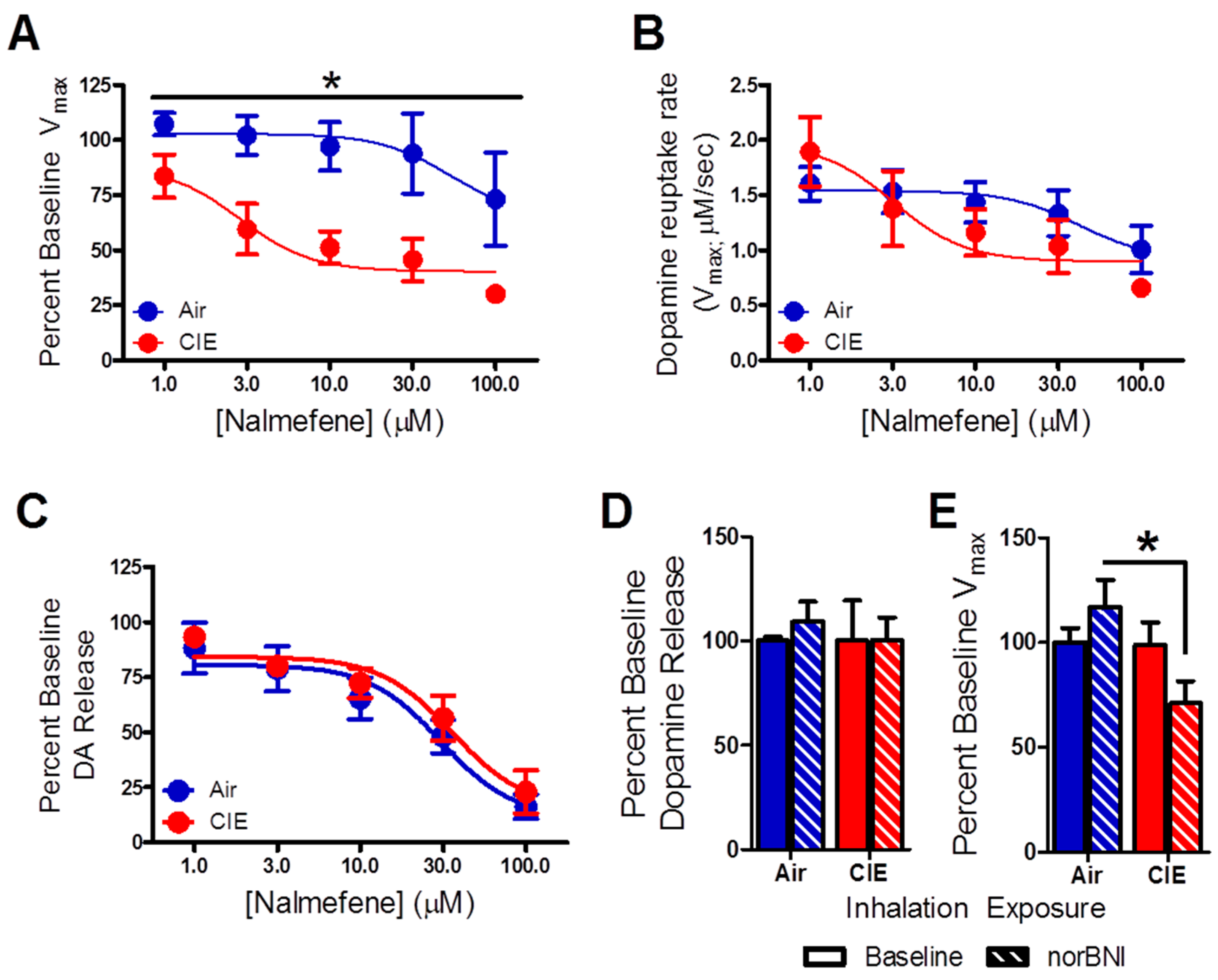
2.1. CIE Exposure Reduced Dopamine Transmission in the NAc Core
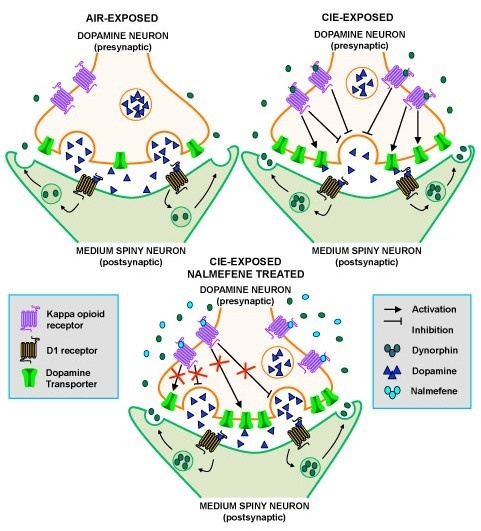
2.2. Nalmefene Slowed Dopamine Uptake Rates More in Brain Slices from CIE-Exposed Mice Than Controls
2.3. Nalmefene Reversed the Dopamine-Decreasing Effects of U50,488 in CIE-Exposed Mice
3. Discussion
3.1. Nalmefene Reduced Dopamine Release Equally in Both Inhalation Groups, but Attenuated Dopamine Uptake Rates More in Brain Slices of CIE-Exposed Mice
3.2. Dopamine Release Is Restored by Nalmefene Following KOR Activation in Brain Slices from CIE-Exposed Mice
3.3. Comparison of norBNI and Nalmefene
3.4. Behavioral Implications of the Effects of Nalmefene on Dopamine Terminal Function
4. Experimental Procedures
4.1. Subjects
4.2. Chronic Intermittent Ethanol (CIE) Exposure
4.3. Blood Ethanol Concentration (BEC) Measurement
4.4. Ex Vivo Fast Scan Cyclic Voltammetry (FSCV)
4.5. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Service Administration. The national survey on drug use and health report. 2014. Available online: http://store.samhsa.gov/shin/content//NSDUH14-0904/NSDUH14-0904.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis, A.N.; Rose, J.H.; Huggins, K.N.; Konstantopoulos, J.K.; Jones, S.R. Chronic intermittent ethanol exposure reduces presynaptic dopamine neurotransmission in the mouse nucleus accumbens. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2015, 150, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budygin, E.A.; Oleson, E.B.; Mathews, T.A.; Läck, A.K.; Diaz, M.R.; McCool, B.A.; Jones, S.R. Effects of chronic alcohol exposure on dopamine uptake in rat nucleus accumbens and caudate putamen. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 2007, 193, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, M.R.; Rodd, Z.A.; Murphy, J.M.; Simon, J.R. Chronic ethanol consumption increases dopamine uptake in the nucleus accumbens of high alcohol drinking rats. Alcohol 2006, 40, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Wang, G.J.; Fowler, J.S.; Logan, J.; Hitzemann, R.; Ding, Y.S.; Pappas, N.; Shea, C.; Piscani, K. Decreases in dopamine receptors but not in dopamine transporters in alcoholics. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1996, 20, 1594–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Wang, G.J.; Telang, F.; Fowler, J.S.; Logan, J.; Jayne, M.; Ma, Y.; Pradhan, K.; Wong, C. Profound decreases in dopamine release in striatum in detoxified alcoholics: Possible orbitofrontal involvement. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 12700–12706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulteis, G.; Markou, A.; Cole, M.; Koob, G.F. Decreased brain reward produced by ethanol withdrawal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5880–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutros, N.; Semenova, S.; Markou, A. Adolescent intermittent ethanol exposure diminishes anhedonia during ethanol withdrawal in adulthood. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.H.; Karkhanis, A.N.; Jones, S.R. Supersensitive kappa opioid receptors promote ethanol withdrawal-related behaviors and reduce dopamine signaling in the nucleus accumbens. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, C.A.; Calipari, E.S.; Cuzon Carlson, V.C.; Helms, C.M.; Lovinger, D.M.; Grant, K.A.; Jones, S.R. Voluntary ethanol intake predicts κ-opioid receptor supersensitivity and regionally distinct dopaminergic adaptations in macaques. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 5959–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, C.A.; Calipari, E.S.; Yorgason, J.T.; Lovinger, D.M.; Mateo, Y.; Jimenez, V.A.; Helms, C.M.; Grant, K.A.; Jones, S.R. Increased presynaptic regulation of dopamine neurotransmission in the nucleus accumbens core following chronic ethanol self-administration in female macaques. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 2016, 233, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blednov, Y.A.; Walker, D.; Martinez, M.; Harris, R.A. Reduced alcohol consumption in mice lacking preprodynorphin. Alcohol 2006, 40, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kissler, J.L.; Sirohi, S.; Reis, D.J.; Jansen, H.T.; Quock, R.M.; Smith, D.G.; Walker, B.M. The one-two punch of alcoholism: Role of central amygdala dynorphins/kappa-opioid receptors. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, B.M.; Zorrilla, E.P.; Koob, G.F. Systemic κ-opioid receptor antagonism by nor-binaltorphimine reduces dependence-induced excessive alcohol self-administration in rats. Addict. Biol. 2011, 16, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, B.M.; Koob, G.F. Pharmacological evidence for a motivational role of kappa-opioid systems in ethanol dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nealey, K.A.; Smith, A.W.; Davis, S.M.; Smith, D.G.; Walker, B.M. κ-opioid receptors are implicated in the increased potency of intra-accumbens nalmefene in ethanol-dependent rats. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. European Medicines Agency Recommends Approval of Medicine for Reduction of Alcohol Consumption. 2012. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Press_release/2012/12/WC500136277.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2015).
- Bart, G.; Schluger, J.H.; Borg, L.; Ho, A.; Bidlack, J.M.; Kreek, M.J. Nalmefene induced elevation in serum prolactin in normal human volunteers: Partial kappa opioid agonist activity? Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 2254–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, W.C., 3rd; Lopez, M.F.; Becker, H.C. Intensity and durations of chronic ethanol xposure is critical for subsequent escalation of voluntary ethanol drinking in mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.T. Mechanistic explanation for the unique pharmacologic properties of receptor partial agonists. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2005, 59, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvey, T.N.; Williams, N.E. Drug Action, in Principles and Practice of Pharmacology for Anaesthetists, 5th ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Spanagel, R.; Herz, A.; Shippinberg, T.S. Opposing tonically active endogenous opioid systems modulate the mesolimbic dopaminergic pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2046–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hipólito, L.; Sánchez-Catalán, M.J.; Zanolini, I.; Polache, A.; Granero, L. Shell/core differences in mu- and delta-opioid receptor modulation of dopamine efflux in nucleus accumbens. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilts, R.P.; Kalivas, P.W. Autoradiographic localization of delta opioid receptors within the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system using radioiodinated [2-d-penicillamine, 5-d-penicillamine] enkephalin (125I-DPDPE). Synapse 1990, 6, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusa, K.; Takahashi, I.; Watanabe, S.; Aono, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Saigusa, T.; Nagase, H.; Suzuki, T.; Koshikawa, N.; Cools, A.R. The non-peptidic delta opioid receptor agonist TAN-67 enhances dopamine efflux in the nucleus accumbens of freely moving rats via a mechanism that involves both glutamate and free radicals. Neuroscience 2005, 130, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svingos, A.L.; Moriwaki, A.; Wang, J.B.; Uhl, G.R.; Pickel, V.M. Mu opioid receptors are localized to extrasynaptic plasma membranes of GABAergic neurons and their targets in the rat nucleus accumbens. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 2585–2594. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Britt, J.P.; McGehee, D.S. Presynaptic opioid and nicotinic receptor modulation of dopamine overflow in the nucleus accumbens. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruchas, M.R.; Chavkin, C. Kinase cascades and ligand-directed signaling at the kappa opioid receptor. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 2010, 210, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivell, B.; Uzelac, Z.; Sundaramurthy, S.; Rajamanickam, J.; Ewald, A.; Chefer, V.; Jaligam, V.; Bolan, E.; Simonson, B.; Annamalai, B. Salvinorin A regulates dopamine transporter function via a kappa opioid receptor and ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. Neuropharmacology 2014, 86, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.C.; Zapata, A.; Justice, J.B., Jr.; Vaughan, R.A.; Sharpe, L.G.; Shippenberg, T.S. Kappa-opioid receptor activation modifies dopamine uptake in the nucleus accumbens and opposes the effects of cocaine. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 9333–9340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chefer, V.I.; Czyzyk, T.; Bolan, E.A.; Moron, J.; Pintar, J.E.; Shippenberg, T.S. Endogenous kappa-opioid receptor systems regulate mesoaccumbal dopamine dynamics and vulnerability to cocaine. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 5029–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Rogers, J.; Michael-Titus, A.T. Comparative study of the effects of mu, delta and kappa opioid agonists on 3H-dopamine uptake in rat striatum and nucleus accumbens. Neuropharmacology 1994, 33, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudapongse, N.; Kim, S.Y.; Kramer, R.E.; Ho, I.K. Nonspecific effects of the selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist U-50,488H on dopamine uptake and release in PC12 cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 93, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beadles-Bohling, A.S.; Wiren, K.M. Alteration of kappa-opioid receptor system expression in distinct brain regions of a genetic model of enhanced ethanol withdrawal severity. Brain Res. 2005, 1046, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chartoff, E.; Sawyer, A.; Rachlin, A.; Potter, D.; Pliakas, A.; Carlezon, W.A. Blockade of kappa opioid receptors attenuates the development of depressive-like behaviors induced by cocaine withdrawal in rats. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.M.; Liang, M.T.; Fields, H.L. A single injection of the kappa opioid antagonist norbinaltorphimine increases ethanol consumption in rats. Psychopharmacology 2005, 182, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.; Tseng, A.; Marquez, P.; Hamid, A.; Lutfy, K. The role of endogenous dynorphin in ethanol-induced state-dependent CPP. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 227, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkhanis, A.N.; Rose, J.H.; Weiner, J.L.; Jones, S.R. Early-Life Social Isolation Stress Increases Kappa Opioid Receptor Responsiveness and Downregulates the Dopamine System. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 2263–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, B.J.; Ritvo, E.C.; Morgan, R.O.; Salvato, F.R.; Goldberg, G.; Welch, B.; Mantero-Atienza, E. A double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral nalmefene HCl for alcohol dependence. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1994, 18, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karhuvaara, S.; Simojoki, K.; Virta, A.; Rosberg, M.; Löyttyniemi, E.; Nurminen, T.; Kallio, A.; Mäkelä, R. Targeted nalmefene with simple medical management in the treatment of heavy drinkers: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled multicenter study. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.R.; Gainetdinov, R.R.; Wightman, R.M.; Caron, M. Mechanisms of amphetamine action revealed in mice lacking the dopamine transporter. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mittleman, G.; Call, S.B.; Cockroft, J.L.; Goldowitz, D.; Matthews, D.B.; Blaha, C.D. Dopamine dynamics associated with, and resulting from, schedule-induced alcohol self-administration: Analyses in dopamine transporter knockout mice. Alcohol 2011, 45, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingman, K.; Hagelberg, N.; Aalto, S.; Någren, K.; Juhakoski, A.; Karhuvaara, S.; Kallio, A.; Oikonen, V.; Hietala, J.; Scheinin, H. Prolonged central mu-opioid receptor occupancy after single and repeated nalmefene dosing. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gual, A.; He, Y.; Torup, L.; van den Brink, W.; Mann, K.; ESENSE 2 Study Group. A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, efficacy study of nalmefene, as-needed use, in patients with alcohol dependence. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 23, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, K.; Bladström, A.; Torup, L.; Gual, A.; van den Brink, W. Extending the treatment options in alcohol dependence: A randomized controlled study of as-needed nalmefene. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 73, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Brink, W.; Aubin, H.J.; Bladström, A.; Torup, L.; Gual, A.; Mann, K. Efficacy of as-needed nalmefene in alcohol-dependent patients with at least a high drinking risk level: Results from a subgroup analysis of two randomized controlled 6-month studies. Alcohol Alcohol. 2013, 48, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, B.J.; Salvato, F.R.; Williams, L.D.; Ritvo, E.C.; Cutler, R.B. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of oral nalmefene for alcohol dependence. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1999, 56, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flurkey, K.; Currer, J.M.; Harrison, D.E. Chapter 20: Mouse models in aging research. In The Mouse in Biomedical Research, History, Wild Mice and Genetics, 2nd ed.; Fox, J.G., Davisson, M.T., Quimby, F.W., Barthold, S.W., Newcomer, C.E., Smith, A.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2007; pp. 637–672. [Google Scholar]
- Workman, A.D.; Charvet, C.J.; Clancy, B.; Darlington, R.B.; Finlay, B.L. Modeling transformations of neurodevelopmental sequences across mammalian species. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 7368–7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.I.; Lopez, M.F.; Becker, H.C. Stress-Induced Enhancement of Ethanol Intake in C57BL/6J Mice with a History of Chronic Ethanol Exposure: Involvement of Kappa Opioid Receptors. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Reith, M.E.; Wightman, R.M.; Kawagoe, K.T.; Garris, P.A. Determination of release and uptake parameters from electrically evoked dopamine dynamics measured by real-time voltammetry. J. Neurosci. Methods 2001, 112, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorgason, J.T.; España, R.A.; Jones, S.R. Demon voltammetry and analysis software: Analysis of cocaine-induced alterations in dopamine signaling using multiple kinetic measures. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 202, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtigfeld, F.J.; Gillman, M.A. Role of dopamine mesolimbic system in opioid action of psychotropic analgesic nitrous oxide in alcohol and drug withdrawal. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 1996, 19, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rose, J.H.; Karkhanis, A.N.; Steiniger-Brach, B.; Jones, S.R. Distinct Effects of Nalmefene on Dopamine Uptake Rates and Kappa Opioid Receptor Activity in the Nucleus Accumbens Following Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081216
Rose JH, Karkhanis AN, Steiniger-Brach B, Jones SR. Distinct Effects of Nalmefene on Dopamine Uptake Rates and Kappa Opioid Receptor Activity in the Nucleus Accumbens Following Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Exposure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(8):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081216
Chicago/Turabian StyleRose, Jamie H., Anushree N. Karkhanis, Björn Steiniger-Brach, and Sara R. Jones. 2016. "Distinct Effects of Nalmefene on Dopamine Uptake Rates and Kappa Opioid Receptor Activity in the Nucleus Accumbens Following Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Exposure" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 8: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081216
APA StyleRose, J. H., Karkhanis, A. N., Steiniger-Brach, B., & Jones, S. R. (2016). Distinct Effects of Nalmefene on Dopamine Uptake Rates and Kappa Opioid Receptor Activity in the Nucleus Accumbens Following Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Exposure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(8), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081216