Impact of HIV Infection and Anti-Retroviral Therapy on the Immune Profile of and Microbial Translocation in HIV-Infected Children in Vietnam
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the Subjects
2.2. Immune Status of HIV-Infected Children
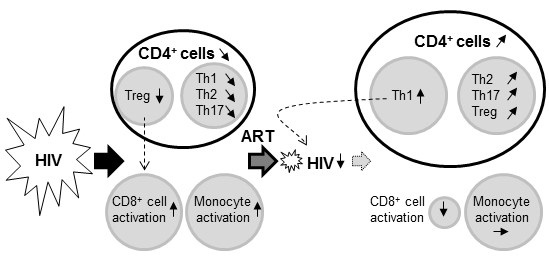
2.3. Impact of HIV Infection on Immune Profile
2.4. Impact of ART on the HIV-Induced Immune Profile
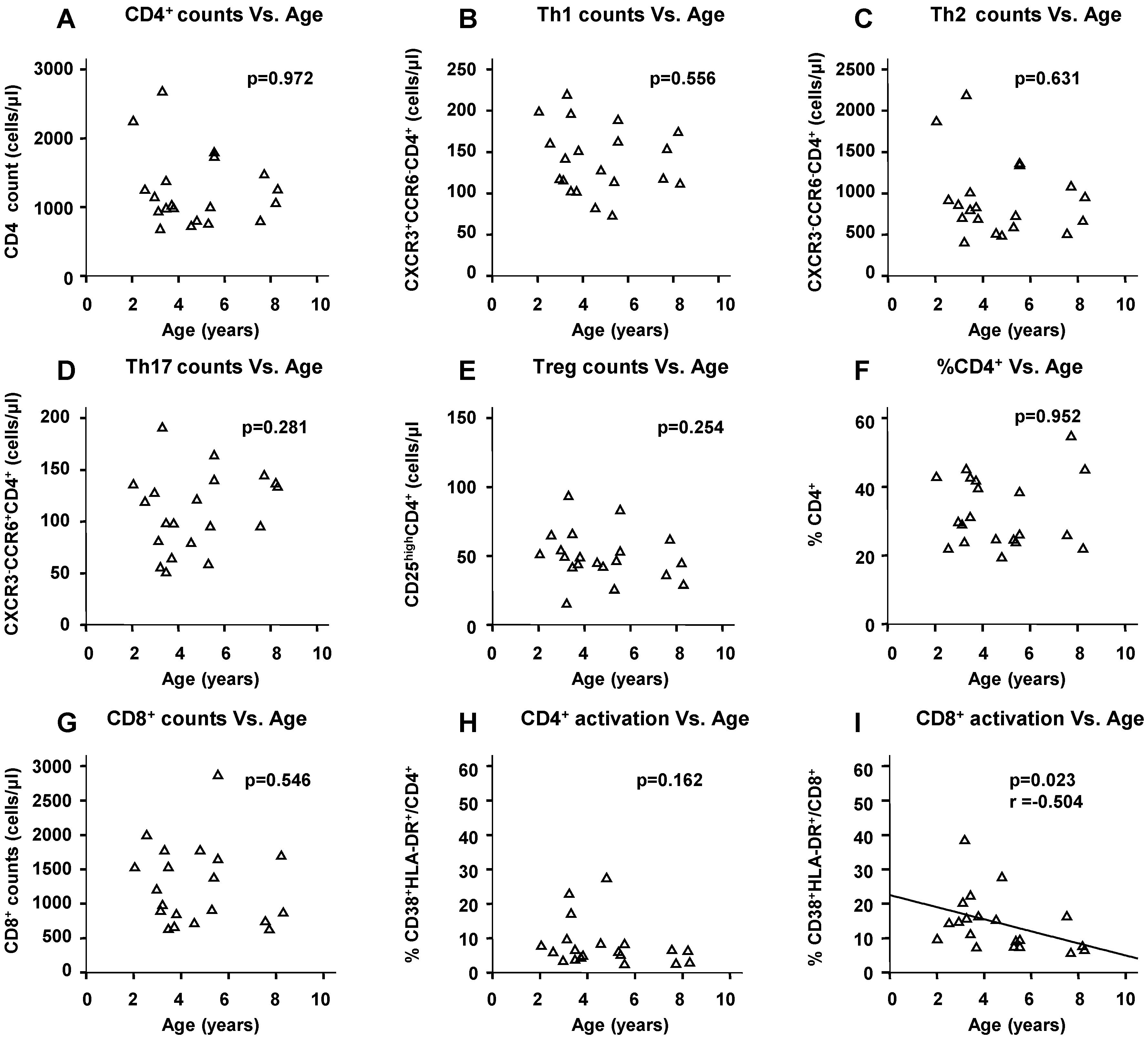
2.5. Physiological Change in Immunological Markers with Age among the HIV(−) Children
2.6. Microbial Translocation Status
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subjects and Study Design
4.2. Plasma HIV VL and sCD14 Concentration
4.3. Immunological Analysis
4.4. Detection of Bacterial Ribosomal RNA Genes (rDNA) in Plasma
4.5. Detection of Bacterial rRNA in Blood
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehandru, S.; Poles, M.A.; Tenner-Racz, K.; Horowitz, A.; Hurley, A.; Hogan, C.; Boden, D.; Racz, P.; Markowitz, M. Primary HIV-1 infection is associated with preferential depletion of CD4+ T lymphocytes from effector sites in the gastrointestinal tract. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Paiardini, M.; Knox, K.S.; Asher, A.I.; Cervasi, B.; Asher, T.E.; Scheinberg, P.; Price, D.A.; Hage, C.A.; Kholi, L.M.; et al. Differential Th17 CD4 T-cell depletion in pathogenic and nonpathogenic lentiviral infections. Blood 2008, 112, 2826–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, P.W. Th17, gut, and HIV: Therapeutic implications. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2010, 5, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.N.; Cervasi, B.; Odorizzi, P.; Silverman, R.; Aberra, F.; Ginsberg, G.; Estes, J.D.; Paiardini, M.; Frank, I.; Silvestri, G. Disruption of intestinal CD4+ T cell homeostasis is a key marker of systemic CD4+ T cell activation in HIV-infected individuals. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 5169–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, J.D.; Harris, L.D.; Klatt, N.R.; Tabb, B.; Pittaluga, S.; Paiardini, M.; Barclay, G.R.; Smedley, J.; Pung, R.; Oliveira, K.M.; et al. Damaged intestinal epithelial integrity linked to microbial translocation in pathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus infections. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Price, D.A.; Schacker, T.W.; Asher, T.E.; Silvestri, G.; Rao, S.; Kazzaz, Z.; Bornstein, E.; Lambotte, O.; Altmann, D.; et al. Microbial translocation is a cause of systemic immune activation in chronic HIV infection. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehandru, S.; Poles, M.A.; Tenner-Racz, K.; Jean-Pierre, P.; Manuelli, V.; Lopez, P.; Shet, A.; Low, A.; Mohri, H.; Boden, D.; et al. Lack of mucosal immune reconstitution during prolonged treatment of acute and early HIV-1 infection. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e484. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, X.; Suzuki, Y.; Gatanaga, H.; Oka, S. High frequency and proliferation of CD4+ FOXP3+ Treg in HIV-1-infected patients with low CD4 counts. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, N.H.; Aldrovandi, G.M. Immunology of pediatric HIV infection. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 254, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendergast, A.J.; Klenerman, P.; Goulder, P.J. The impact of differential antiviral immunity in children and adults. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunders, M.J.; van der Loos, C.M.; Klarenbeek, P.L.; van Hamme, J.L.; Boer, K.; Wilde, J.C.; de Vries, N.; van Lier, R.A.; Kootstra, N.; Pals, S.T.; et al. Memory CD4+CCR5+ T cells are abundantly present in the gut of newborn infants to facilitate mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1. Blood 2012, 120, 4383–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muenchhoff, M.; Prendergast, A.J.; Goulder, P.J. Immunity to HIV in early life. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freguja, R.; Gianesin, K.; Mosconi, I.; Zanchetta, M.; Carmona, F.; Rampon, O.; Giaquinto, C.; de Rossi, A. Regulatory T cells and chronic immune activation in human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1)-infected children. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 164, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.; Hernan, M.A.; Williams, P.L.; Seeger, J.D.; McIntosh, K.; Dyke, R.B.; Seage, G.R., 3rd. Long-term effects of highly active antiretroviral therapy on CD4+ cell evolution among children and adolescents infected with HIV: 5 years and counting. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananworanich, J.; Apornpong, T.; Kosalaraksa, P.; Jaimulwong, T.; Hansudewechakul, R.; Pancharoen, C.; Bunupuradah, T.; Chandara, M.; Puthanakit, T.; Ngampiyasakul, C.; et al. Characteristics of lymphocyte subsets in HIV-infected, long-term nonprogressor, and healthy Asian children through 12 years of age. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblatt, H.M.; Stanley, K.E.; Song, L.Y.; Johnson, G.M.; Wiznia, A.A.; Nachman, S.A.; Krogstad, P.A. Immunological response to highly active antiretroviral therapy in children with clinically stable HIV-1 infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederman, M.M.; Calabrese, L.; Funderburg, N.T.; Clagett, B.; Medvik, K.; Bonilla, H.; Gripshover, B.; Salata, R.A.; Taege, A.; Lisgaris, M.; et al. Immunologic failure despite suppressive antiretroviral therapy is related to activation and turnover of memory CD4 cells. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, H.V.; Ishizaki, A.; Nguyen, L.V.; Phan, C.T.; Phung, T.T.; Takemoto, K.; Pham, A.N.; Bi, X.; Khu, D.T.; Ichimura, H. Two-year outcome of first-line antiretroviral therapy among HIV-1 vertically-infected children in Hanoi, Vietnam. Int. J. STD AIDS 2015, 26, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearer, W.T.; Rosenblatt, H.M.; Gelman, R.S.; Oyomopito, R.; Plaeger, S.; Stiehm, E.R.; Wara, D.W.; Douglas, S.D.; Luzuriaga, K.; McFarland, E.J.; et al. Lymphocyte subsets in healthy children from birth through 18 years of age: The pediatric AIDS clinical trials group p1009 study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatorje, E.J.; Gemen, E.F.; Driessen, G.J.; Leuvenink, J.; van Hout, R.W.; de Vries, E. Paediatric reference values for the peripheral T cell compartment. Scand. J. Immunol. 2012, 75, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenorio, A.R.; Martinson, J.; Pollard, D.; Baum, L.; Landay, A. The relationship of T-regulatory cell subsets to disease stage, immune activation, and pathogen-specific immunity in HIV infection. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2008, 48, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilakka-Kanthikeel, S.; Huang, S.; Fenton, T.; Borkowsky, W.; Cunningham, C.K.; Pahwa, S. Increased gut microbial translocation in HIV-infected children persists in virologic responders and virologic failures after antiretroviral therapy. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2012, 31, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetta, F.; Lecuroux, C.; Girault, I.; Goujard, C.; Sinet, M.; Lambotte, O.; Venet, A.; Bourgeois, C. Early and long-lasting alteration of effector CD45RA−Foxp3high regulatory T-cell homeostasis during HIV infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainwater-Lovett, K.; Nkamba, H.; Mubiana-Mbewe, M.; Moore, C.B.; Margolick, J.; Moss, W.J. Changes in cellular immune activation and memory T-cell subsets in HIV-infected Zambian children receiving HAART. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2014, 67, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourtis, A.P.; Ibegbu, C.C.; Wiener, J.; King, C.C.; Tegha, G.; Kamwendo, D.; Kumwenda, J.; Kaur, S.P.; Flax, V.; Ellington, S.; et al. Role of intestinal mucosal integrity in HIV transmission to infants through breast-feeding: The BAN Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandler, N.G.; Wand, H.; Roque, A.; Law, M.; Nason, M.C.; Nixon, D.E.; Pedersen, C.; Ruxrungtham, K.; Lewin, S.R.; Emery, S.; et al. Plasma levels of soluble CD14 independently predict mortality in HIV infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenorio, A.R.; Zheng, Y.; Bosch, R.J.; Krishnan, S.; Rodriguez, B.; Hunt, P.W.; Plants, J.; Seth, A.; Wilson, C.C.; Deeks, S.G.; et al. Soluble markers of inflammation and coagulation but not T-cell activation predict non-AIDS-defining morbid events during suppressive antiretroviral treatment. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1248–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainz, T.; Serrano-Villar, S.; Diaz, L.; Gonzalez Tome, M.I.; Gurbindo, M.D.; de Jose, M.I.; Mellado, M.J.; Ramos, J.T.; Zamora, J.; Moreno, S.; et al. The CD4/CD8 ratio as a marker T-cell activation, senescence and activation/exhaustion in treated HIV-infected children and young adults. AIDS 2013, 27, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Villar, S.; Perez-Elias, M.J.; Dronda, F.; Casado, J.L.; Moreno, A.; Royuela, A.; Perez-Molina, J.A.; Sainz, T.; Navas, E.; Hermida, J.M.; et al. Increased risk of serious non-AIDS-related events in HIV-infected subjects on antiretroviral therapy associated with a low CD4/CD8 ratio. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilakka-Kanthikeel, S.; Kris, A.; Selvaraj, A.; Swaminathan, S.; Pahwa, S. Immune activation is associated with increased gut microbial translocation in treatment-naive, HIV-infected children in a resource-limited setting. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2014, 66, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, P.W.; Martin, J.N.; Sinclair, E.; Bredt, B.; Hagos, E.; Lampiris, H.; Deeks, S.G. T cell activation is associated with lower CD4+ T cell gains in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients with sustained viral suppression during antiretroviral therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maecker, H.T.; McCoy, J.P.; Nussenblatt, R. Standardizing immunophenotyping for the human immunology project. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinter, A.; McNally, J.; Riggin, L.; Jackson, R.; Roby, G.; Fauci, A.S. Suppression of HIV-specific T cell activity by lymph node CD25+ regulatory T cells from HIV-infected individuals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3390–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Saito, M.; Tsuji, H.; Asahara, T.; Takata, O.; Fujimura, J.; Nagata, S.; Nomoto, K.; Shimizu, T. Bacterial rRNA-targeted reverse transcription-PCR used to identify pathogens responsible for fever with neutropenia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1624–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, K.; Tsuji, H.; Asahara, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Takada, T.; Nomoto, K. Establishment of an analytical system for the human fecal microbiota, based on reverse transcription-quantitative PCR targeting of multicopy rRNA molecules. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Items | HIV(+) (n = 31) | HIV(−) (n = 20) | ART(+) (n = 29) | p Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV(+) vs. HIV(−) | ART(+) vs. HIV(−) | HIV(+) vs. ART(+) | ||||
| Age (years) * | 6.2 (2.0–11.0) | 4.1 (2.0–8.3) | 6.1 (3.6–8.6) | 0.034 | 0.009 | 0.584 |
| Gender, female (n)/male (n) * | 14/17 | 8/12 | 12/17 | 0.718 | 0.920 | 0.764 |
| Height (cm) * | 109.0 (77.0–129.5) | 110.0 (80.0–130.0) | 110.0 (90.0–130.0) | 0.771 | 0.418 | 0.539 |
| Body weight (kg) * | 17.5 (10.0–27.0) | 16.0 (9.0–35.0) | 19.8 (12.0–32.8) | 0.395 | 0.140 | 0.192 |
| WHO clinical stage: 2 (n)/1 (n) | 1/30 | 5/24 | - | - | 0.098 | |
| ART duration (years) * | 3.5 (0.8–5.8) | - | - | - | ||
| Viral load (log10 copies/mL) * | 5.0 (3.2–6.5) | ** | - | - | < 0.001 | |
| % CD4+ * | 22.1 (3.6–44.5) | 29.5 (19.6–54.9) | 28.8 (12.4–47.1) | 0.001 | 0.404 | 0.010 |
| CD4+-cell counts (cells/μL) * | 698 (97–1784) | 1050 (693–2688) | 894 (244–1711) | 0.003 | 0.018 | 0.429 |
| Th1 counts (cells/μL) * | 80 (25–227) | 136 (74–220) | 147 (49–211) | 0.003 | 0.611 | 0.002 |
| Th2 counts (cells/μL) * | 537 (63–1375) | 822 (413–2196) | 553 (119–1369) | 0.016 | 0.009 | 0.970 |
| Th17 counts (cells/μL) * | 45 (6–116) | 109 (51–192) | 58 (23–144) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.016 |
| Treg counts (cells/μL) * | 14 (0–133) | 48 (16–94) | 30 (9–71) | <0.001 | 0.004 | <0.001 |
| %CD38+HLA-DR+/CD4 * | 5.6 (2.2–17.3) | 6.4 (2.7–27.6) | 4.3 (2.0–15.6) | 0.969 | 0.036 | 0.003 |
| % CD8+ * | 43.4 (29.5–61.4) | 31.4 (23.5–43.3) | 44.7 (31.1–61.4) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.464 |
| CD8+-cell counts (cells/μL) * | 1368 (470–3127) | 1101 (634–2874) | 1212 (769–2064) | 0.239 | 0.290 | 0.631 |
| %CD38+HLA-DR+/CD8 * | 27.5 (12.2–53.3) | 12.9 (5.8–38.6) | 10.2 (5.0–27.7) | <0.001 | 0.329 | <0.001 |
| CD4/CD8 * | 0.50 (0.06–1.19) | 1.03 (0.45–2.34) | 0.66 (0.20–1.42) | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.181 |
| sCD14 (ng/mL) * | 1637 (1049–3003) | 1413 (944–2580) | 1964 (1281–3169) | 0.009 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Target Bacteria | HIV(+) (n = 31) | HIV(−) (n = 20) | ART(+) (n = 29) | p Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV(+) vs. HIV(−) | ART(+) vs. HIV(−) | HIV(+) vs. ART(+) | ||||
| C. coccoides group | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| C. leptum subgroup | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| B. fragilis group | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| Bifidobacterium | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| Atopobium cluster | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| Prevotella | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| Enterobacteriaceae | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| Streptococcus | 1 (3.2%) | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | 1 |
| Enterococcus | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| Staphylococcus | 7 (22.6%) | 1 (5.0%) | 0 | 0.13 | 0.41 | 0.011 |
| Pseudomonas | 1 (3.2%) | 2 (10.0%) | 0 | 0.55 | 0.16 | 1 |
| L. casei subgroup | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bi, X.; Ishizaki, A.; Nguyen, L.V.; Matsuda, K.; Pham, H.V.; Phan, C.T.T.; Ogata, K.; Giang, T.T.T.; Phung, T.T.B.; Nguyen, T.T.; et al. Impact of HIV Infection and Anti-Retroviral Therapy on the Immune Profile of and Microbial Translocation in HIV-Infected Children in Vietnam. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081245
Bi X, Ishizaki A, Nguyen LV, Matsuda K, Pham HV, Phan CTT, Ogata K, Giang TTT, Phung TTB, Nguyen TT, et al. Impact of HIV Infection and Anti-Retroviral Therapy on the Immune Profile of and Microbial Translocation in HIV-Infected Children in Vietnam. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(8):1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081245
Chicago/Turabian StyleBi, Xiuqiong, Azumi Ishizaki, Lam Van Nguyen, Kazunori Matsuda, Hung Viet Pham, Chung Thi Thu Phan, Kiyohito Ogata, Thuy Thi Thanh Giang, Thuy Thi Bich Phung, Tuyen Thi Nguyen, and et al. 2016. "Impact of HIV Infection and Anti-Retroviral Therapy on the Immune Profile of and Microbial Translocation in HIV-Infected Children in Vietnam" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 8: 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081245
APA StyleBi, X., Ishizaki, A., Nguyen, L. V., Matsuda, K., Pham, H. V., Phan, C. T. T., Ogata, K., Giang, T. T. T., Phung, T. T. B., Nguyen, T. T., Tokoro, M., Pham, A. N., Khu, D. T. K., & Ichimura, H. (2016). Impact of HIV Infection and Anti-Retroviral Therapy on the Immune Profile of and Microbial Translocation in HIV-Infected Children in Vietnam. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(8), 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081245