Essential Oil of Cymbopogon nardus (L.) Rendle: A Strategy to Combat Fungal Infections Caused by Candida Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical Composition of Essential Oil
2.2. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration and Minimal Fungicidal Concentration of Essential Oil of C. nardus
2.3. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration and Minimal Fungicidal Concentration of Citronellal
2.4. Inhibition on Candida albicans Hyphae Growth
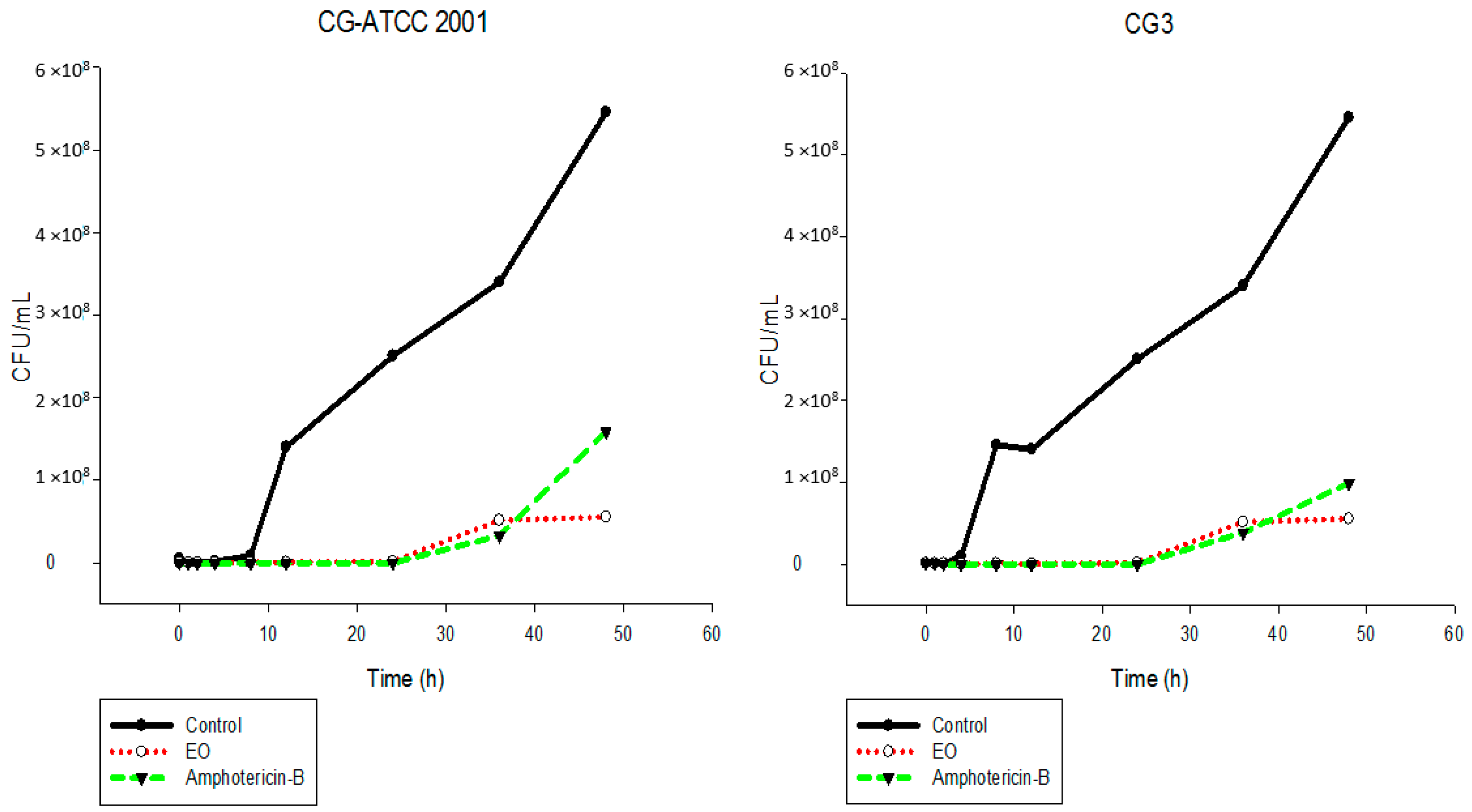
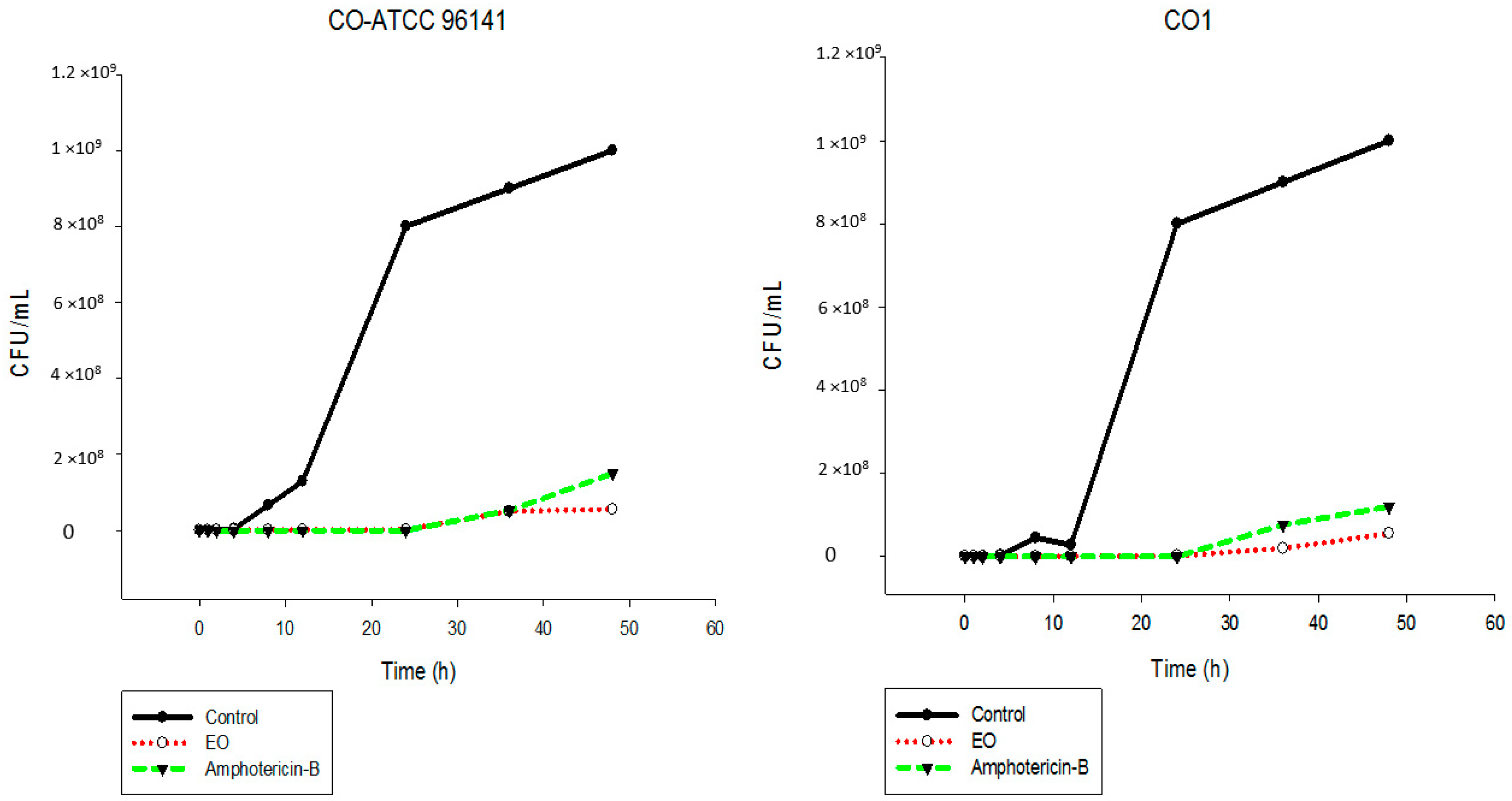
2.5. Time-Kill Assay
2.6. Biofilm
2.7. Cytotoxic Evaluation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Material
3.2. Extraction of the Essential Oil from the Leaves of C. nardus
3.3. Citronellal
3.4. Gas Chromatography Analysis of Essential Oil from the Leaves of C. nardus
3.4.1. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
3.4.2. Gas Chromatography-Flame Ionization Detector
3.5. Antifungal Activity
3.6. Fungal Strains
3.7. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
3.8. Determination of Minimum Fungicidal Concentration
3.9. Inhibition of C. albicans Hyphae Growth
3.10. Time-Kill Assay
3.11. Biofilm Assay
3.12. Cytotoxic Activity
3.12.1. Cell Lines
3.12.2. Cytotoxic Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayer, F.L.; Wilson, D.; Hube, B. Candida albicans pathogenicity mechanisms. Virulence 2013, 4, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deorukhkar, S.C.; Saini, S.; Mathew, S. Virulence factors contributing to pathogenicity of Candida tropicalis and its antifungal susceptibility profile. Int. J. Microbiol. 2014, 2014, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.; Negri, M.; Henriques, M.; Oliveira, R.; Williams, D.W.; Azeredo, J. Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis and Candida tropicalis: Biology, epidemiology, pathogenicity and antifungal resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardi, J.D.C.O.; Pitangui, N.D.S.; Rodríguez-Arellanes, G.; Taylor, M.L.; Fusco-Almeida, A.M.; Mendes-Giannini, M.J.S. Highlights in pathogenic fungal biofilms. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2014, 31, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, E.C.; Castellano, S.; Santoriello, M.; Sgherri, C.; Quartacci, M.F.; Calucci, L.; Warrilow, A.G.S.; Lamb, D.C.; Kelly, S.L.; Milite, C.; et al. Antifungal activity of azole compounds CPA18 and CPA109 against azole-susceptible and -resistant strains of Candida albicans. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, G.M.; Endo, E.H.; Cortez, D.A.G.; Ueda-nakamura, T.; Nakamura, C.V.; Filho, B.P.D.; Filho, D. Effect of plant extracts on planktonic growth and biofilm of Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 908–917. [Google Scholar]
- Piccinelli, A.C.; de Santana Aquino, D.F.; Morato, P.N.; Kuraoka-Oliveira, Â.M.; Strapasson, R.L.B.; dos Santos, É.P.; Stefanello, M.É.A.; Oliveira, R.J.; Kassuya, C.A.L. Anti-inflammatory and antihyperalgesic activities of ethanolic extract and fruticulin a from salvia lachnostachys leaves in mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, S.; Wu, T.; Guo, J.; Sha, S.; Zheng, X.; Yu, T. Effect of citronella essential oil on the inhibition of postharvest Alternaria alternata in cherry tomato. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 2441–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanthai, S.; Prachakoll, S.; Ruangviriyachai, C.; Luthria, D.L. Influence of extraction methodologies on the analysis of five major volatile aromatic compounds of citronella grass Cymbopogon nardus and lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus) grown in Thailand. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aini, M.N.N.; Said, M.I.; Nazlina, I.; Hanina, M.N.; Ahmad, I.B. Screening for Antiviral activity of sweet lemon grass (Cymbopogon nardus (L.) rendle) fractions. J. Biol. Sci. 2006, 6, 507–510. [Google Scholar]
- Innsan, M.F.M.F.; Shahril, M.H.; Samihah, M.S.; Asma, O.S.; Radzi, S.M.; Jalil, A.K.A.; Hanina, M.N. Pharmacodynamic properties of essential oils from Cymbopogon species. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, K.; Alzoreky, N.S.; Yoshihashi, T.; Nguyen, H.T.T.; Trakoontivakorn, G. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of essential oil from Cymbopogon nardus (Citronella Grass). Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2013, 37, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calo, J.R.; Crandall, P.G.; O’Bryan, C.A.; Ricke, S.C. Essential oils as antimicrobials in food systems—A review. Food Control 2015, 54, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifácio, B.V.; dos Santos Ramos, M.A.; da Silva, P.B.; Bauab, T.M. Antimicrobial activity of natural products against Helicobacter pylori: A review. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2014, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freires, I.D.A.; Murata, R.M.; Furletti, V.F.; Sartoratto, A.; de Alencar, S.M.; Figueira, G.M.; de Oliveira Rodrigues, J.A.; Duarte, M.C.T.; Rosalen, P.L. Coriandrum sativum L. (Coriander) essential oil: Antifungal activity and mode of action on Candida spp., and molecular targets affected in human whole-genome expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, F.M.; Ahmad, I.; Khan, M.S.; Al-Shabib, N.A. Trigonella foenum-graceum (Seed) extract interferes with quorum sensing regulated traits and biofilm formation in the strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Aeromonas hydrophila. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolba, H.; Moghrani, H.; Benelmouffok, A.; Kellou, D.; Maachi, R. Essential oil of algerian eucalyptus citriodora: Chemical composition, antifungal activity. J. Med. Mycol. 2015, 25, e128–e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zore, G.B.; Thakre, A.D.; Jadhav, S.; Karuppayil, S.M. Terpenoids inhibit Candida albicans growth by affecting membrane integrity and arrest of cell cycle. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewick, P.M. Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Dool, H.; Kratz, P.D. A generalization of the retention index system including linear temperature programmed gas–liquid partition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1963, 11, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry, 4th ed.; Allured Publishing Corporation: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.S.; Wee, W. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of Cymbopogon nardus citronella essential oil against systemic bacteria of aquatic animals. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2013, 5, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koba, K.; Sanda, K.; Guyon, C.; Raynaud, C.; Chaumont, J.-P.; Nicod, L. In vitro cytotoxic activity of Cymbopogon citratus L. and Cymbopogon nardus L. essential oils from Togo. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2009, 4, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, L.A.; de Araújo Oliveira, J.; de Castro, R.D.; de Oliveira Lima, E. Inhibition of adherence of C. albicans to dental implants and cover screws by Cymbopogon nardus essential oil and citronellal. Clin. Oral Investig. 2015, 19, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Viljoen, A. The in vitro antimicrobial activity of Cymbopogon essential oil (lemon grass) and its interaction with silver ions. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, D.; Taschereau, P.; Belland, R.J.; Sand, C.; Rennie, R.P. Antifungal activity of medicinal plant extracts; preliminary screening studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 115, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Shi, W.; Sun, S. A promising approach of overcoming the intrinsic resistance of Candida krusei to fluconazole (FLC)—Combining tacrolimus with FLC. FEMS Yeast Res. 2014, 14, 808–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos Ramos, M.A.; Calixto, G.M.F.; de Toledo, L.G.; Bonifácio, B.V.; dos Santos, L.C.; de Almeida, M.T.G.; Chorilli, M.; Bauab, T.M. Liquid crystal precursor mucoadhesive system as a strategy to improve the prophylactic action of Syngonanthus nitens (Bong.) Ruhland against infection by Candida krusei. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, A.F.; Costa, A.G.; Arrigoni-Blank, M.D.F.; Cavalcanti, S.C.H.; Alves, P.B.; Innecco, R.; Ehlert, P.A.D.; de Sousa, I.F. Influence of season, harvest time and drying on Java citronella (Cymbopogon winterianus Jowitt) volatile oil. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2007, 17, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileva, M.; Krumova, E.; Miteva-Staleva, J.; Kostadinova, N.; Dobreva, A.; Galabov, A.S. Chemical compounds, in vitro antioxidant and antifungal activities of some plant essential oils belonging to rosaceae family. Proc. Bulg. Acad. Sci. 2014, 67, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Mesa-Arango, A.C.; Montiel-Ramos, J.; Zapata, B.; Durán, C.; Betancur-Galvis, L.; Stashenko, E. Citral and carvone chemotypes from the essential oils of Colombian Lippia alba (Mill.) N.E. Brown: Composition, cytotoxicity and antifungal activity. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2009, 104, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Freitas Araújo, M.G.; Pacífico, M.; Vilegas, W.; Dos Santos, L.C.; Icely, P.A.; Miró, M.S.; Scarpa, M.V.C.; Bauab, T.M.; Sotomayor, C.E. Evaluation of Syngonanthus nitens (Bong.) Ruhl. extract as antifungal and in treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. Med. Mycol. 2013, 51, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, M.C.A.; de Brito Bezerra, A.P.; de Sousa, J.P.; Guerra, F.Q.S.; de Oliveira Lima, E. Evaluation of Antifungal activity and mechanism of action of citral against Candida albicans. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiCicco, M.; Neethirajan, S.; Singh, A.; Weese, J. Efficacy of clarithromycin on biofilm formation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Reference Methods for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Tests for Yeasts: Approved Standards; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Filho, N.A.; Lorenzon, E.N.; Ramos, M.A.S.; Santos, C.T.; Piccoli, J.P.; Bauab, T.M.; Fusco-Almeida, A.M.; Cilli, E.M. Synthesis and characterization of an antibacterial and non-toxic dimeric peptide derived from the C-terminal region of Bothropstoxin-I. Toxicon 2015, 103, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitangui, N.S.; Sardi, J.C.O.; Silva, J.F.; Benaducci, T.; da Silva, R.A.M.; Rodríguez-Arellanes, G.; Taylor, M.L.; Mendes-Giannini, M.J.S.; Fusco-Almeida, A.M. Adhesion of Histoplasma capsulatum to pneumocytes and biofilm formation on an abiotic surface. Biofouling 2012, 28, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Wilson, I.; Orton, T.; Pognan, F. Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5421–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Retention Time | Compound Name | AI 1 (Calculated) | AI 2 (Literature) | Concentration (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.60 | not identified | – | – | 0.09 |
| 6.74 | β-myrcene | 992 | 988 | 0.09 |
| 7.08 | n-octanal | 1004 | 998 | 0.09 |
| 7.92 | D-limonene | 1029 | 1024 | 2.47 |
| 8.21 | cis-ocimene | 1037 | 1032 | 0.27 |
| 8.56 | trans-ocimene | 1048 | 1044 | 0.17 |
| 8.75 | bergamal | 1053 | 1051 | 0.37 |
| 9.40 | not identified | – | – | 0.17 |
| 10.40 | linalool | 1101 | 1095 | 0.53 |
| 10.57 | α-pinene oxide | 1105 | 1099 | 0.11 |
| 11.51 | trans-rose oxide | 1129 | 1122 | 0.14 |
| 12.16 | neo-isopulegol | 1145 | 1144 | 0.41 |
| 12.34 | not identified | – | – | 0.27 |
| 12.54 | citronellal | 1155 | 1148 | 27.87 |
| 12.95 | not identified | – | – | 0.25 |
| 13.69 | not identified | – | – | 0.33 |
| 14.16 | cis-4-decenal | 1195 | 1193 | 0.09 |
| 14.63 | Decanal | 1207 | 1201 | 0.46 |
| 15.60 | β-citronellol | 1230 | 1223 | 11.85 |
| 16.12 | Neral | 1242 | 1235 | 11.21 |
| 16.73 | geraniol | 1257 | 1249 | 22.77 |
| 17.38 | geranial | 1273 | 1264 | 14.54 |
| 20.82 | citronellol acetate | 1355 | 1350 | 0.31 |
| 22.08 | geranyl acetate | 1385 | 1379 | 0.26 |
| 23.45 | β-cariophyllene | 1419 | 1417 | 1.28 |
| 24.81 | α-humulene | 1453 | 1452 | 0.12 |
| 27.25 | γ-cadinene | 1514 | 1513 | 1.60 |
| 27.63 | δ-cadinene | 1524 | 1522 | 0.36 |
| 27.87 | citronellyl butyrate | 1530 | 1530 | 0.24 |
| 28.60 | elemol | 1550 | 1548 | 0.11 |
| 29.11 | not identified | – | – | 0.16 |
| 29.85 | cariophyllene oxide | 1582 | 1582 | 0.55 |
| 32.08 | trans-cadinol | 1642 | 1638 | 0.16 |
| 32.54 | α-muurolol | 1654 | 1644 | 0.30 |
| Monoterpene hydrocarbons | 3.00 | |||
| Oxygen containing monoterpenes | 90.61 | |||
| Sesquiterpene hydrocarbons | 3.36 | |||
| Oxygen containing sesquiterpenes | 1.12 | |||
| Other compounds | 0.64 | |||
| Total identified | 98.73 | |||
| Candida Strains | MIC EO * | MFC EO * | MIC AmB * | MIC FLU * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA-ATCC 90028 | 1000 | 1000 | 1 | 1 |
| CA2 | 1000 | 1000 | 4 | 16 |
| CA3 | 1000 | 1000 | 1 | >64 |
| CA4 | 1000 | 1000 | 4 | 8 |
| CK-ATCC 6258 | 250 | 500 | 8 | >64 |
| CK2 | 500 | 500 | 8 | >64 |
| CK3 | 500 | 500 | 8 | >64 |
| CK4 | 250 | 250 | 4 | >64 |
| CG-ATCC 2001 | 500 | 1000 | 1 | >64 |
| CG2 | 500 | 1000 | 4 | >64 |
| CG3 | 500 | 1000 | 2 | >64 |
| CG4 | 1000 | 1000 | 2 | >64 |
| CT-ATCC 13803 | 500 | 1000 | 8 | >64 |
| CT2 | >1000 | >1000 | 8 | >64 |
| CT3 | 1000 | >1000 | 4 | >64 |
| CT4 | >1000 | >1000 | 4 | >64 |
| CP-ATCC 22019 | 500 | 1000 | 4 | 8 |
| CP1 | 1000 | 1000 | 4 | 32 |
| CO-ATCC 96141 | 500 | 1000 | 8 | 32 |
| CO1 | 1000 | 1000 | 8 | 64 |
| Strains | MIC Citronellal | MFC Citronellal |
|---|---|---|
| CA-ATCC 90028 | 1000 | 1000 |
| CA3 | >1000 | >1000 |
| CK-ATCC 6258 | 500 | 1000 |
| CK4 | 500 | 500 |
| CG-ATCC 2001 | 500 | 1000 |
| CG3 | 500 | >1000 |
| CT-ATCC 13803 | >1000 | >1000 |
| CT3 | >1000 | >1000 |
| CP-ATCC 22019 | >1000 | >1000 |
| CP1 | >1000 | >1000 |
| Strains | EO (mg/mL) |
|---|---|
| CA-ATCC 90028 | 2.5 |
| CA3 | 5 |
| CK-ATCC 6258 | 2.5 |
| CK4 | 2.5 |
| CP-ATCC 22019 | 5 |
| CP1 | 10 |
| Cell Lines | (EO) IC50 * | Citronellal IC50 * | (Control) IC50 a |
|---|---|---|---|
| HepG-2 | 96.6 | 100.9 | >1000 |
| MRC-5 | 33.1 | 51 | >1000 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Toledo, L.G.; Ramos, M.A.D.S.; Spósito, L.; Castilho, E.M.; Pavan, F.R.; Lopes, É.D.O.; Zocolo, G.J.; Silva, F.A.N.; Soares, T.H.; Dos Santos, A.G.; et al. Essential Oil of Cymbopogon nardus (L.) Rendle: A Strategy to Combat Fungal Infections Caused by Candida Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081252
De Toledo LG, Ramos MADS, Spósito L, Castilho EM, Pavan FR, Lopes ÉDO, Zocolo GJ, Silva FAN, Soares TH, Dos Santos AG, et al. Essential Oil of Cymbopogon nardus (L.) Rendle: A Strategy to Combat Fungal Infections Caused by Candida Species. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(8):1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081252
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Toledo, Luciani Gaspar, Matheus Aparecido Dos Santos Ramos, Larissa Spósito, Elza Maria Castilho, Fernando Rogério Pavan, Érica De Oliveira Lopes, Guilherme Julião Zocolo, Francisca Aliny Nunes Silva, Tigressa Helena Soares, André Gonzaga Dos Santos, and et al. 2016. "Essential Oil of Cymbopogon nardus (L.) Rendle: A Strategy to Combat Fungal Infections Caused by Candida Species" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 8: 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081252
APA StyleDe Toledo, L. G., Ramos, M. A. D. S., Spósito, L., Castilho, E. M., Pavan, F. R., Lopes, É. D. O., Zocolo, G. J., Silva, F. A. N., Soares, T. H., Dos Santos, A. G., Bauab, T. M., & De Almeida, M. T. G. (2016). Essential Oil of Cymbopogon nardus (L.) Rendle: A Strategy to Combat Fungal Infections Caused by Candida Species. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(8), 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081252