Abstract
Vascular endothelial cells cover the luminal surface of blood vessels and contribute to the prevention of vascular disorders such as atherosclerosis. Metallothionein (MT) is a low molecular weight, cysteine-rich, metal-binding, inducible protein, which protects cells from the toxicity of heavy metals and active oxygen species. Endothelial MT is not induced by inorganic zinc. Adequate tools are required to investigate the mechanisms underlying endothelial MT induction. In the present study, we found that an organoantimony compound, tris(pentafluorophenyl)stibane, induces gene expression of MT-1A and MT-2A, which are subisoforms of MT in bovine aortic endothelial cells. The data reveal that MT-1A is induced by activation of both the MTF-1–MRE and Nrf2–ARE pathways, whereas MT-2A expression requires only activation of the MTF-1–MRE pathway. The present data suggest that the original role of MT-1 is to protect cells from heavy metal toxicity and oxidative stress in the biological defense system, while that of MT-2 is to regulate intracellular zinc metabolism.
1. Introduction
Metallothionein (MT) is a low molecular weight, cysteine-rich, metal-binding, and inducible protein, which was found as a protein containing cadmium and zinc from equine renal cortex [1,2]. There are four isoforms of MT—MT-1, MT-2, MT-3, and MT-4—in mammals [3], and MT-1 consists of several subisoforms: seven in human tissue but only two—MT-1A and MT-1E— in bovine tissue. Among MT isoforms, MT-3 and MT-4 exist in specific tissue: MT-3 is in the neural tissue [4] and MT-4 is in stratified squamous epithelia [3]. MT-1 and MT-2 ubiquitously exist in the liver, kidney, and other organs and are induced by heavy metals such as cadmium and zinc, oxidative stress, and other physiological factors including cytokines and growth factors [2,5,6]. MT-1 and MT-2 are considered to have the same functions and induction mechanisms [7,8]. However, several reports show the induction level is different between MT-1 and MT-2 [9,10,11,12,13,14], suggesting that these MT isoforms may be induced differently.
Mechanisms underlying transcriptional induction of MT genes are not completely understood. Metal response element-binding transcription factor-1 (MTF-1) mediates heavy metal signaling and is essentially required for MT gene expression [15]. MTF-1 is activated by zinc and binds the sequences termed metal responsive element (MRE) that exist in the upstream region of the MT gene [16,17]. Additionally, the MT gene includes sequences termed antioxidant response element (ARE) in the promoter region [2,18], which are activated by the transcriptional factor nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and regulate the expression of antioxidant genes [19]. Although ARE is involved in the transcriptional induction of MT genes by hydrogen peroxide [20], there is little information about the role of ARE in the MT induction. We hypothesize that the MTF-1–MRE and Nrf2–ARE pathways cooperatively regulate transcription of MT.
Vascular endothelial cells cover the luminal surface of blood vessels and prevent vascular disorders such as atherosclerosis by regulating the blood coagulation-fibrinolytic system and vascular tonus [21]. In addition, heavy metals may affect the vascular endothelial cell functions, which can modify the organ toxicity [22]. In fact, it has been reported that heavy metals such as cadmium and mercury cause a progression of vascular disorders [23,24]. Since MT protects cells from heavy metal toxicity [25] and oxidative stress [26], MT is considered a multifunctional protein involved in defense mechanisms. We previously studied the toxicity of heavy metals in cell culture vascular endothelial cells and found that cadmium induces MT in vascular endothelial cells and in other cell types whereas zinc—a representative MT inducer—does not induce MT in vascular endothelial cells in a serum-free medium [27,28], although the metal at high concentrations can induce MT in medium containing serum [29,30]. In addition, endothelial MT is not induced only by activation of the MTF-1–MRE pathway [28]. Therefore, inorganic zinc is not a good tool to clarify the mechanisms underlying endothelial MT induction. We hypothesized that organometallic compounds could act as good tools for analyzing endothelial MT induction as described below.
Organic-inorganic hybrid molecules are composed of an organic structure and metal(s) and are in general used as reagents in chemical synthetic reactions, since pioneers such as Grignard and Wittig used the molecules as organic synthesis reagents [31,32]. Studies on organopnictogen compounds, a type of organic-inorganic hybrid molecules, indicate that their cytotoxicity depends on intracellular accumulation and is influenced by intramolecular metal(s), organic structure, and the interaction between the metal(s) and the structure [33,34]. Organic-inorganic hybrid molecules may be useful for analyzing the mechanisms underlying endothelial MT induction. We refer to the strategy of using organic-inorganic hybrid molecules as tools to analyze biological systems as “bio-organometallics”. In the present study, we constructed a library of 28 organoantimony compounds and tested the effect on transcriptional induction of MT genes and found that tris(pentafluorophenyl)stibane (termed Sb35) induces the gene expression of the subisoforms MT-1A and MT-2A in bovine aortic endothelial cells. We analyzed the intracellular pathways involved in endothelial MT induction using Sb35.
2. Results
2.1. Transcriptional Induction of MT Isoforms by Sb35
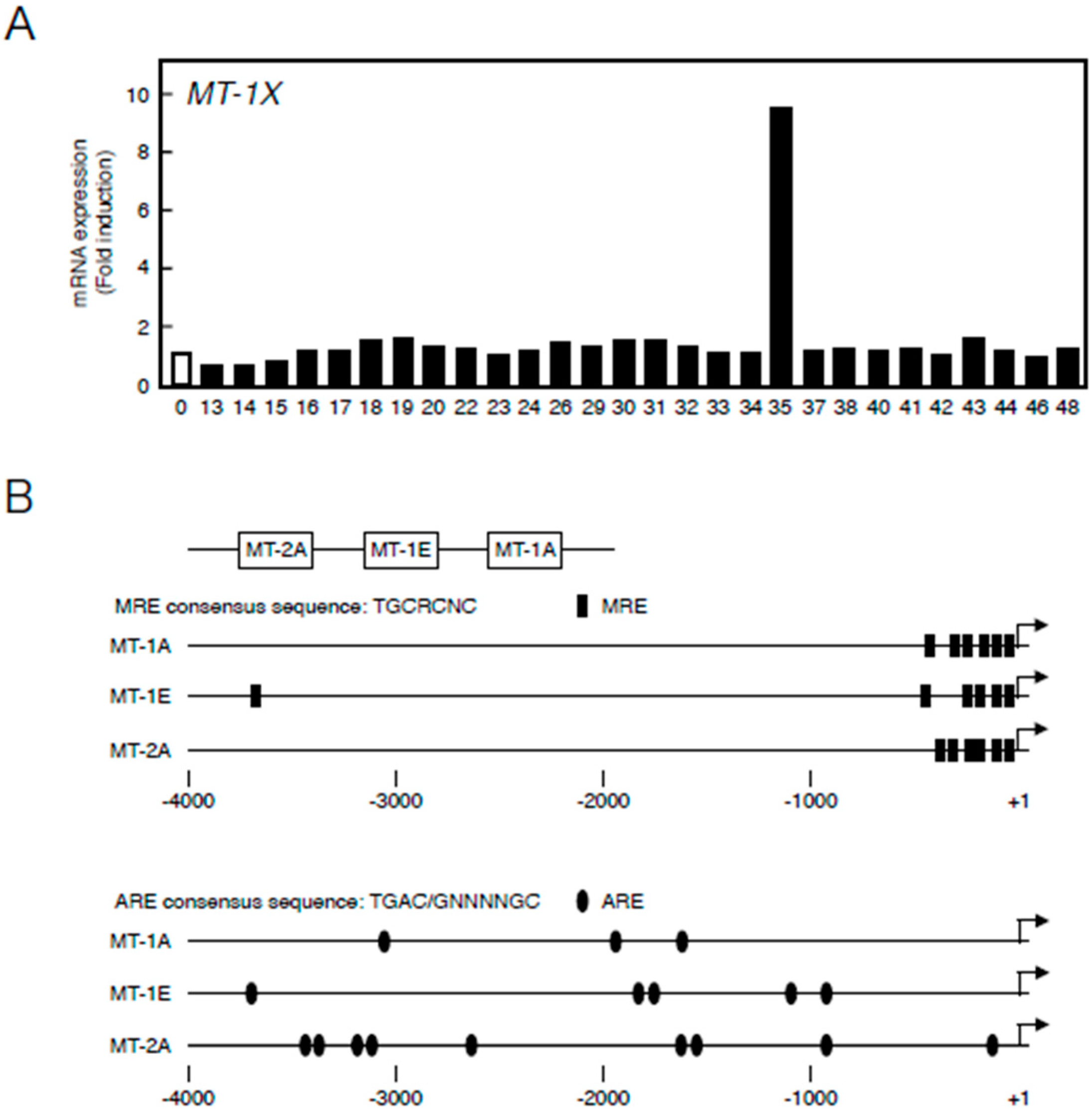
First, we constructed a library of 28 organoantimony compounds (Table 1). We used human vascular endothelial cells in the first experiment to confirm that MT induction by organoantimony compound(s) is possible in human endothelial cells as well as in bovine endothelial cells as described below. We tested the induction of expression of MT-1X—the major MT isoforms in human vascular endothelial cells [30]. As shown in Figure 1A, it was found that Sb35 induces high MT-1X gene expression. As stated below, As35 and P35 as well as Sb35 increased the expression of MT mRNAs, suggesting that the molecular structure of these hybrid molecules is required for the transcriptional induction of endothelial MT. We predict that antimony compounds, which have no ability to induce MT mRNA expression, lack the required molecular structure.

Table 1.
Organoantimony compounds used in this study.
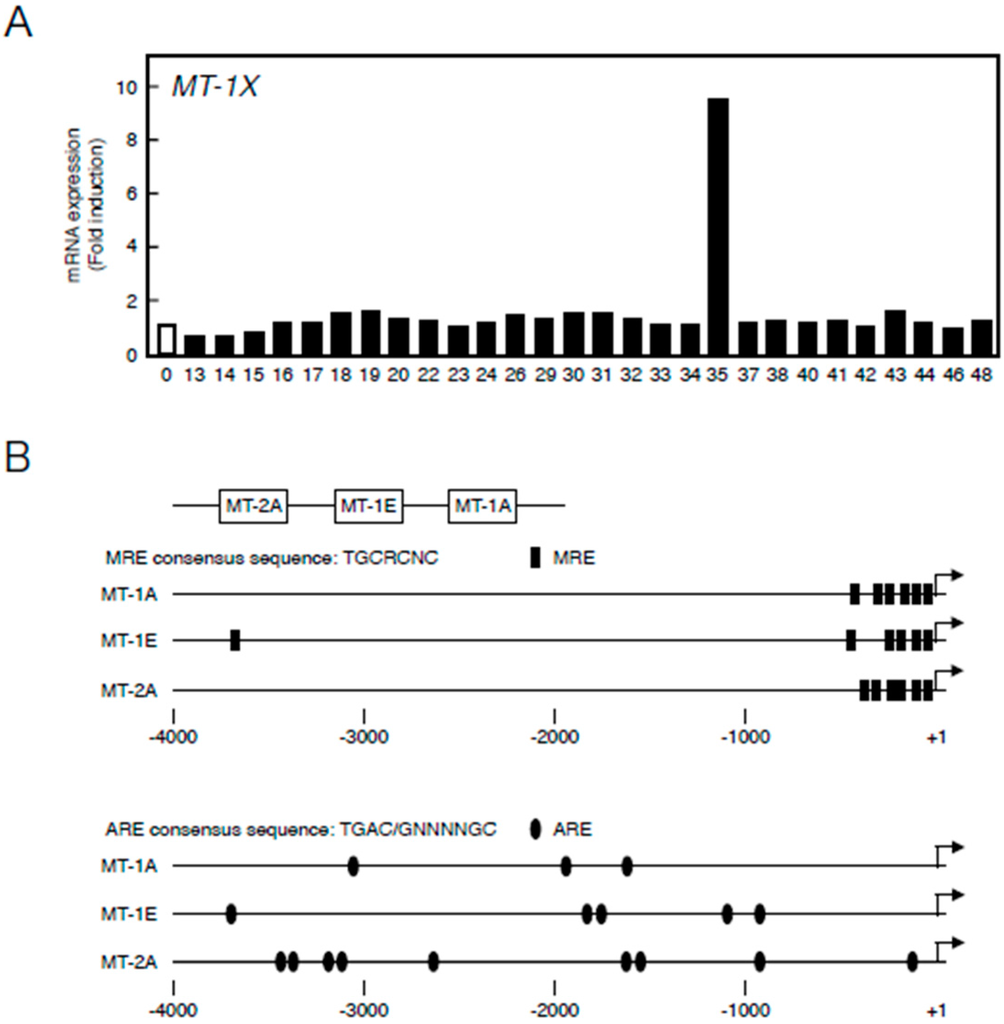
Figure 1.
(A) Transcriptional induction of MT-1X in vascular endothelial cells after treatment with organoantimony compounds shown in Table 1. Human brain microvascular endothelial cells were incubated with the organoantimony compounds at 10 µM each for 3 h, and the expression of MT-1X mRNA was determined by real-time RT-PCR; (B) The map of MRE and ARE regions in the bovine MT promoter.
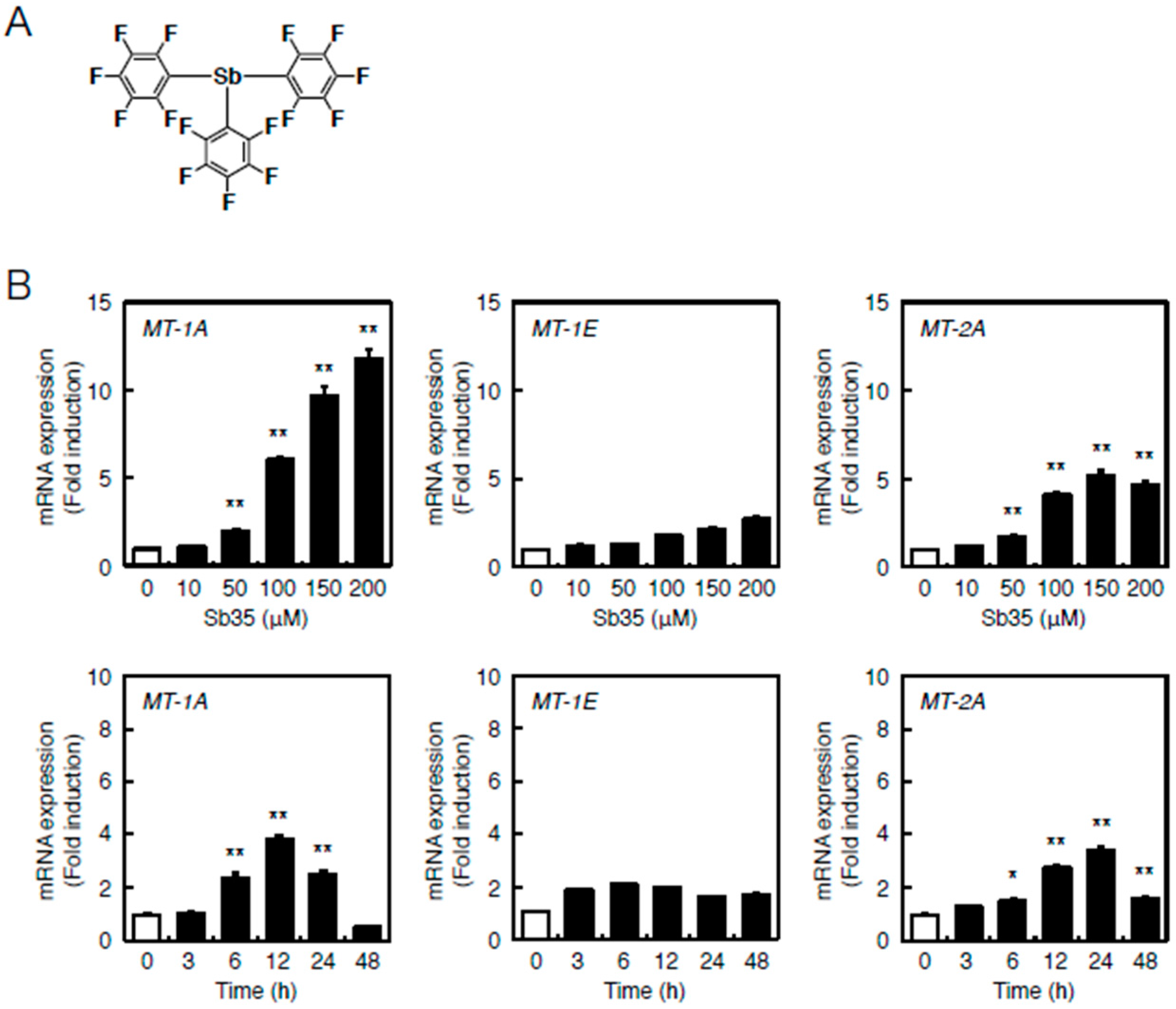
Figure 1B depicts the locations of MREs and AREs in the upstream regions of MT genes of the bovine cells. Bovine cells express three MT subisoforms—MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A—and each of their genes has MRE and ARE consensus sequences in the promoter region. The number of MT-1 subisoforms is eight in human and two in bovine cells. To investigate the difference in the intracellular signaling between MT-1 and MT-2 isoforms, the subsequent experiments were performed using bovine endothelial cells having only two subisoforms of MT-1. In bovine aortic endothelial cells, Sb35 (Figure 2a) induced MT-1A and MT-2A gene expression in a concentration-dependent manner when treated for 12 h (Figure 2b, upper panels). We observed maximum induction of MT-1A and MT-2A by 100 µM Sb35 at 12 and 24 h, respectively (Figure 2b, lower panels), indicating that Sb35 stimulates the transcriptional induction of MT-1 and MT-2 isoform genes in the cells; decrease in the induction at 48 h is possibly due to the metabolism of Sb35 and/or downregulation of the intracellular signaling activated by Sb35, although the details are unclear. However, induction of MT protein by Sb35 was not observed in Western blot analysis (Figure S1), suggesting that Sb35 compound is a tool to analyze the transcriptional induction of endothelial MT but not an agent for MT induction to protect cells from the toxicity of heavy metals and generated reactive oxygen species. In addition, Sb35 did not generate reactive oxygen species (Figure S2), suggesting that the transcriptional induction of MT by Sb35 is not mediated by reactive oxygen species. In addition, MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A mRNA levels increased by approximately 12, three, and six fold, respectively, after Sb35 treatment. On the other hand, cadmium, a typical MT inducer, increased MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A mRNA levels by approximately 1000-, 15-, and 15-fold, respectively, suggesting that Sb35 induced MT more weakly than cadmium. This appears to be the reason why Sb35 cannot induce MT at the protein level.
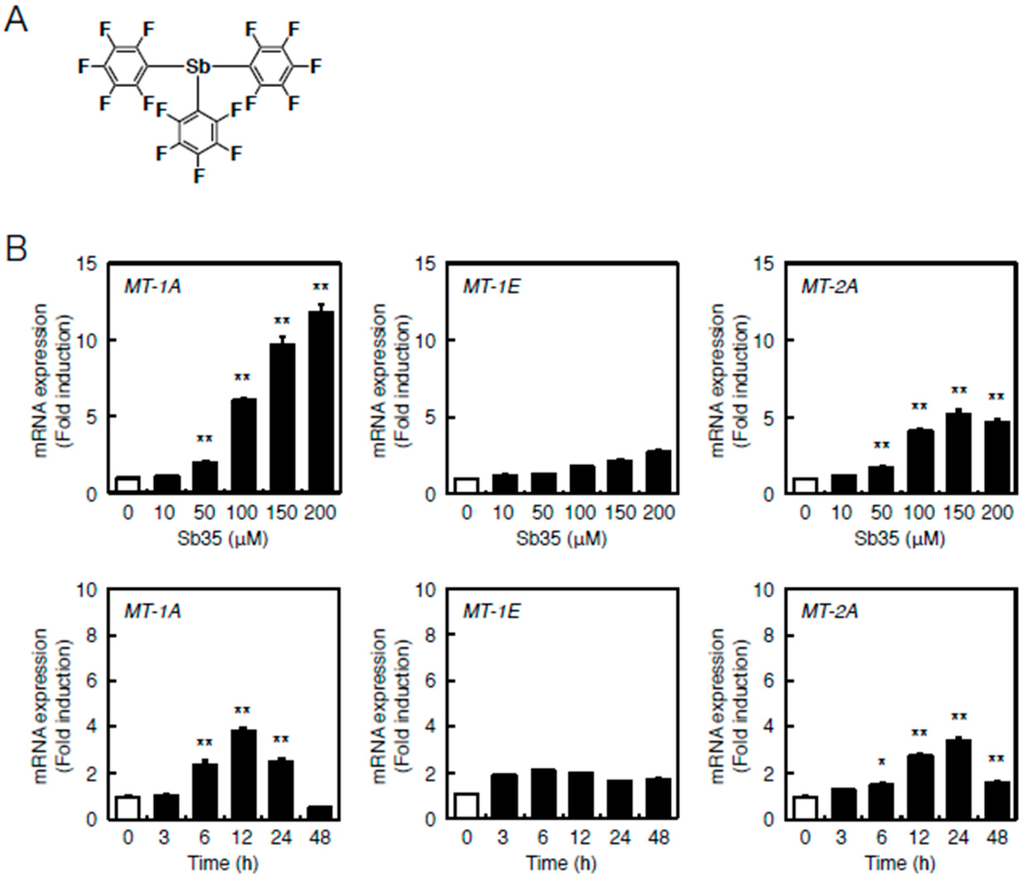
Figure 2.
Sb35-induced transcription of endothelial MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A. (A) Structure of Sb35; (B) Sb35-induced transcription of MT. Vascular endothelial cells were incubated with or without 10, 50, 100, 150, or 200 µM Sb35 for 12 h (upper panels) or 100 µM Sb35 for 3, 6, 12, 24, or 48 h (lower panels). MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A mRNA expression was determined by performing real-time RT-PCR. Data are expressed as the mean ± SE of three representative samples, with each sample obtained from three independent experiments. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 indicate significantly different from the corresponding control.
2.2. Involvement of the MTF-1–MRE Pathway
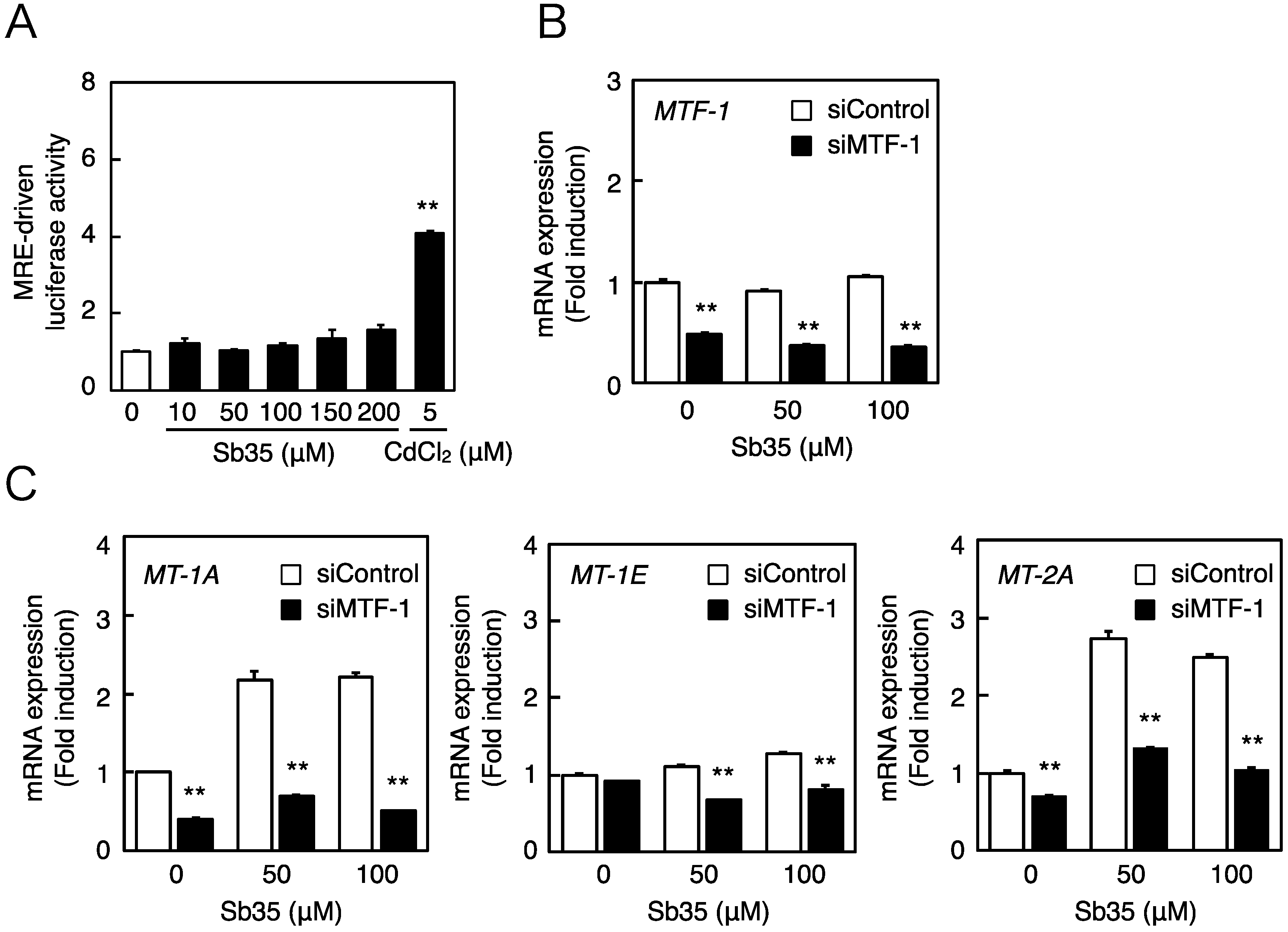
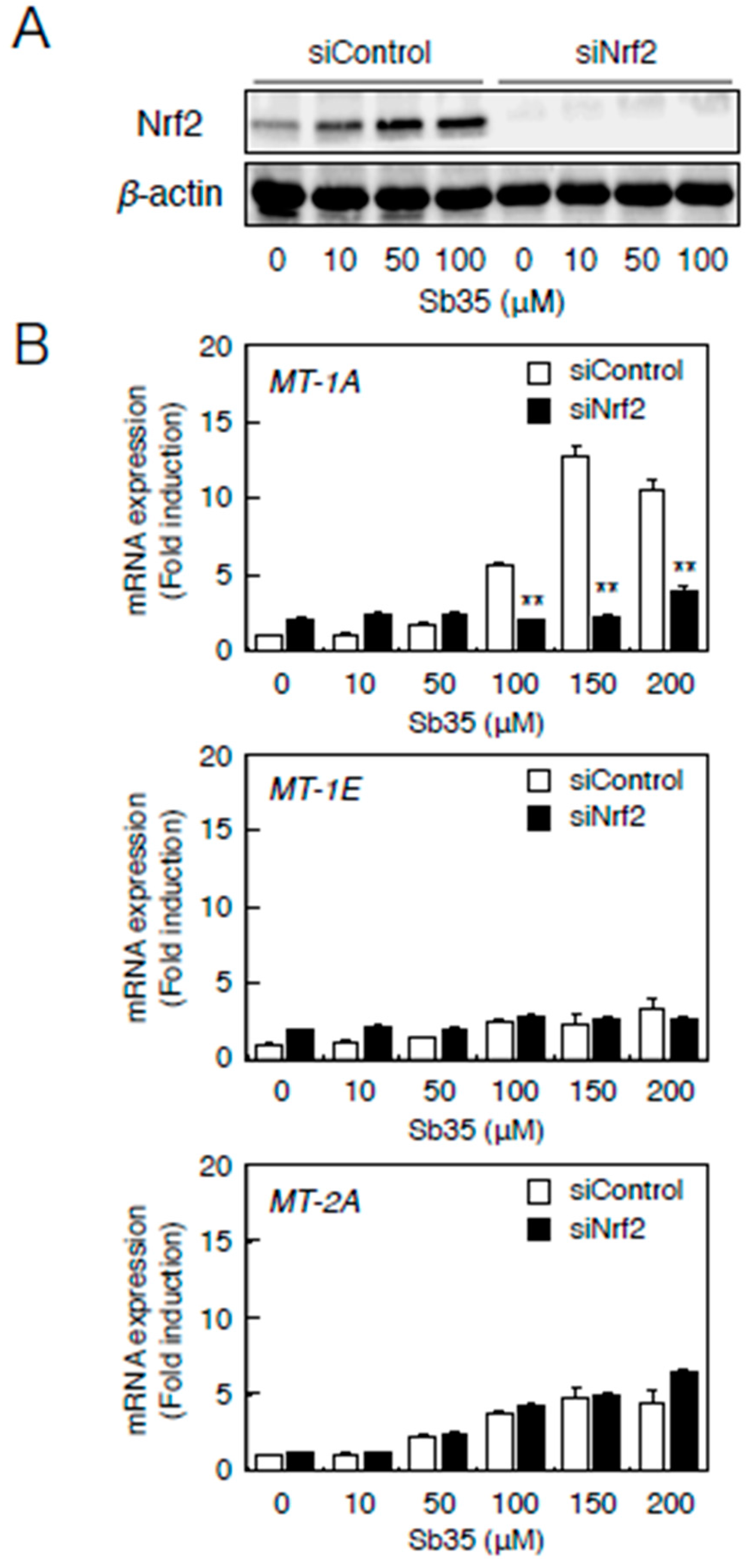
Next, we investigated whether the MTF-1–MRE pathway was involved in Sb35-induced transcription of endothelial MT isoforms. Expression of MTF-1 was detected by real-time RT-PCR because we failed to detect bovine MTF-1 protein by Western blot analysis. Sb35 only slightly increased the MRE-driven transcriptional activity (Figure 3A). In the MTF-1 knockdown (Figure 3B), Sb35-induced expression of MT-1A and MT-2A was suppressed (Figure 3C), suggesting that the constitutive expression and activity of MTF-1 is sufficient for transcriptional induction of endothelial MT-1A and MT-2A. Sb35 did not induce the transcription of MT-1E, although siRNA-mediated knockdown of MTF-1 suppressed this constitutive expression. As reported previously [35], the MTF-1–MRE pathway is involved in Sb35 induction of endothelial MT-1A and MT-2A.
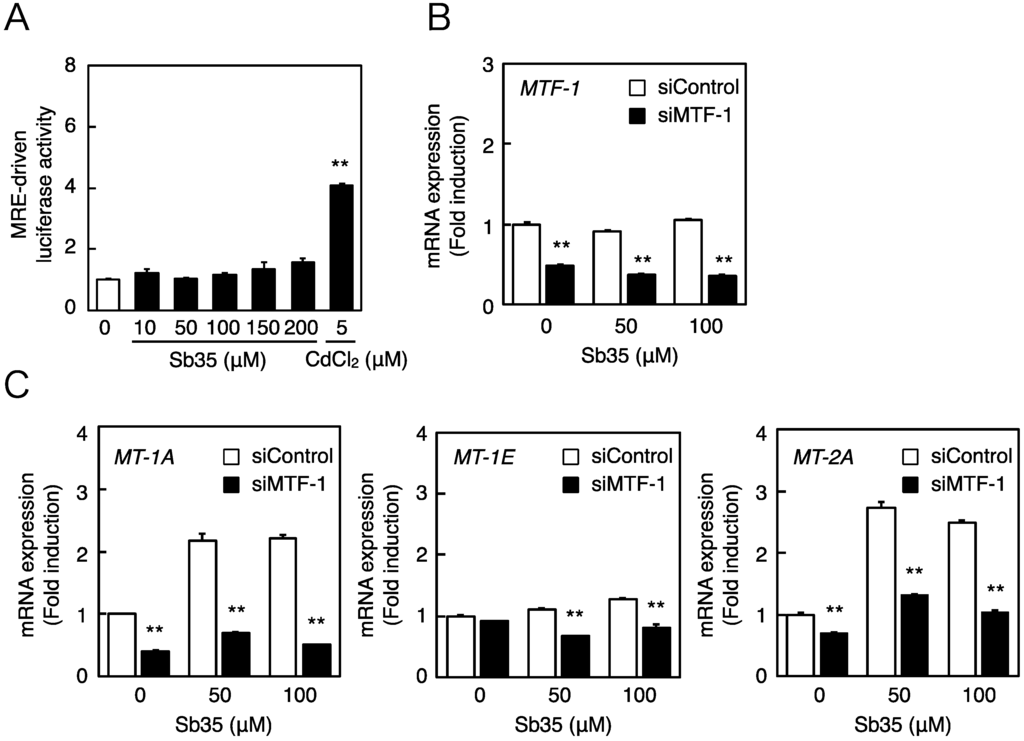
Figure 3.
The MTF-1–MRE pathway mediates Sb35-induced transcription of endothelial MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A. (A) MRE-driven transcriptional activity. Vascular endothelial cells transfected with an MRE reporter vector were treated with or without 10, 50, 100, 150, or 200 µM Sb35 or 5 µM cadmium for 12 h, and MRE-driven transcriptional activity was determined by performing the MRE-directed reporter assay; (B) siRNA-mediated MTF-1 knockdown. Vascular endothelial cells transfected with control or MTF-1 siRNA were treated with or without 50 or 100 µM Sb35 for 12 h, and expression of MTF-1 mRNA was determined by performing real-time RT-PCR. Data are expressed as the mean ± SE of three samples. ** p < 0.01 indicates significantly different from the corresponding siControl; (C) Sb35-induced transcription of endothelial MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A after MTF-1 knockdown. Vascular endothelial cells transfected with control or MTF-1 siRNA were treated with or without 50 or 100 µM Sb35 for 12 h. Data are expressed as the mean ± SE of three representative samples, with each sample obtained from three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 indicates significantly different from the corresponding siControl.
2.3. Involvement of the Nrf2–ARE Pathway
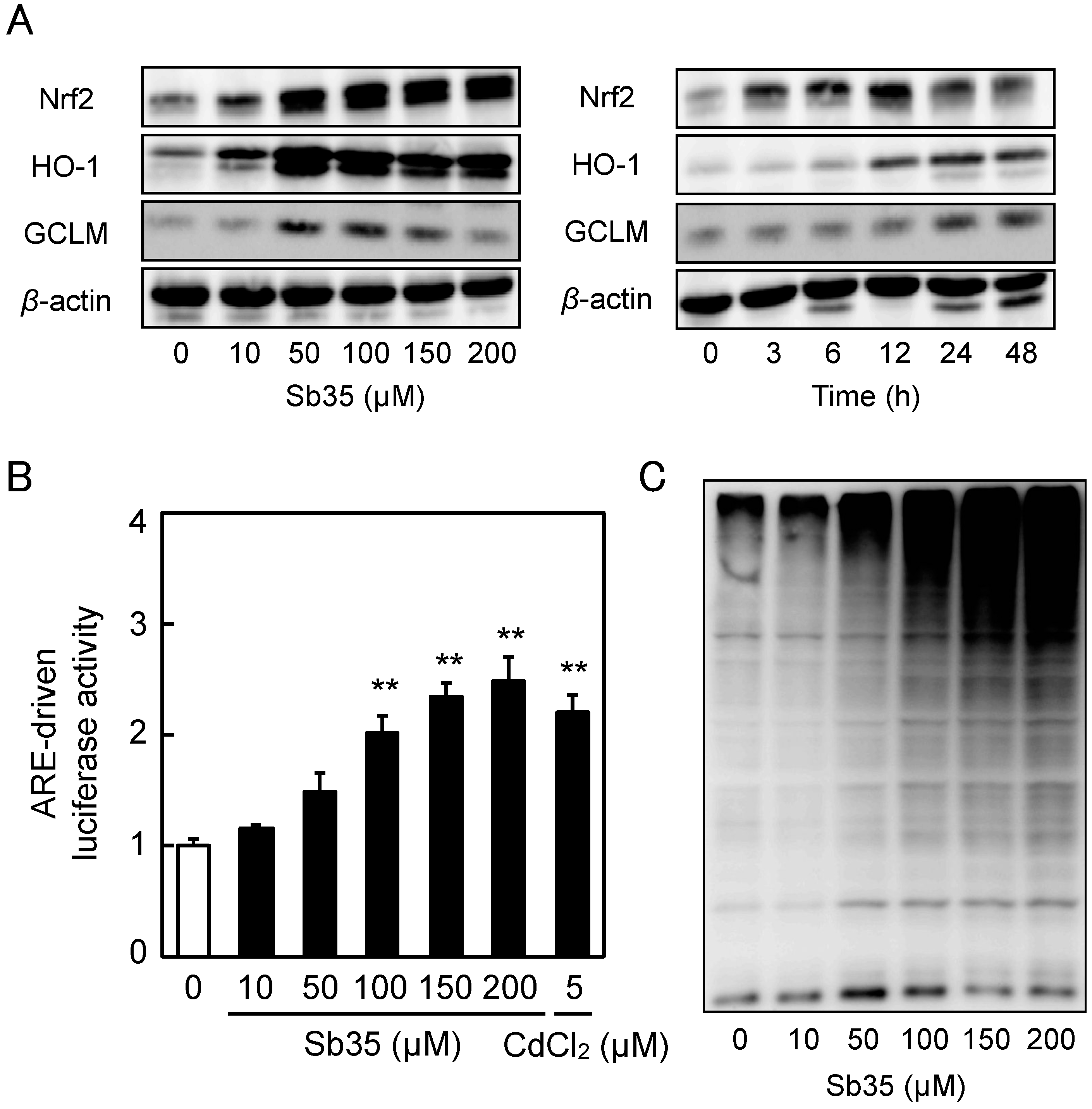
Sb35 increased the intracellular accumulation of Nrf2 in a concentration- and time-dependent manner and upregulated Nrf2 target proteins such as HO-1 and GCLM (Figure 4A). Sb35 significantly increased the ARE-driven transcriptional activity in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 4B), confirming that it activates the Nrf2–ARE pathway in vascular endothelial cells. It was shown that Sb35 exhibited proteasome inhibitory activity in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 4C), suggesting that activation of Nrf2 by Sb35 is at least partly due to the proteasome inhibition that stabilizes Nrf2. Since Sb35 did not generate reactive oxygen species (Figure S2), it is unlikely that activation of Nrf2 by Sb35 is mediated by reactive oxygen species.
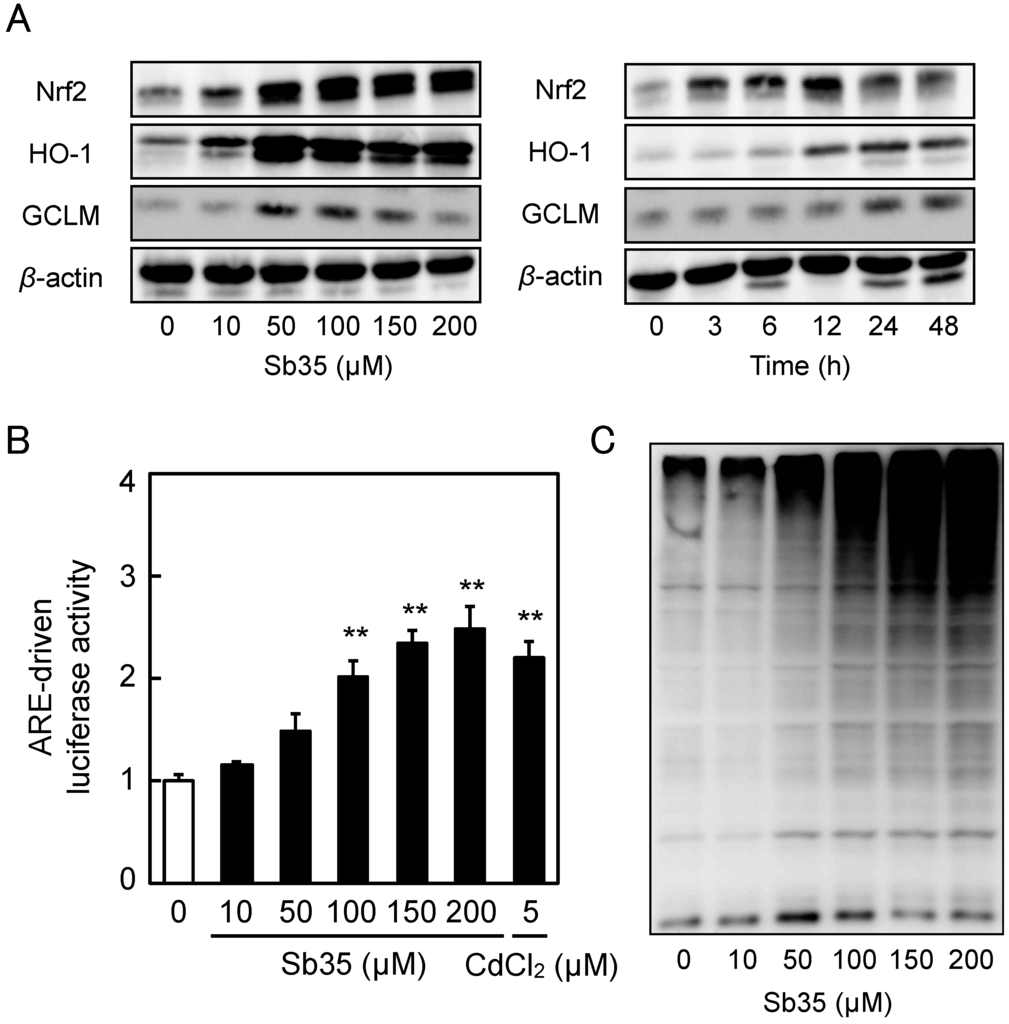
Figure 4.
Expression of Nrf2 and its downstream proteins, Sb35-induced ARE-driven transcriptional activity, and Sb35-induced proteasome inhibition in vascular endothelial cells. (A) Expression of Nrf2, HO-1, and GCLM. Vascular endothelial cells were treated with or without 10, 50, 100, 150, or 200 µM Sb35 for 12 h (left panels) or 100 µM Sb35 for 3, 6, 12, 24, or 48 h (right panels), and expression of Nrf2, HO-1, and GCLM was determined by performing Western blotting; (B) ARE-driven transcriptional activity. Vascular endothelial cells transfected with an ARE reporter vector were treated with or without 10, 50, 100, 150, or 200 µM Sb35 or 5 µM cadmium for 12 h, and ARE-driven transcriptional activity was determined by performing ARE-directed reporter assay. Data are represented as mean ± SE of three representative samples, with each sample obtained from three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 indicates significantly different from the corresponding control; (C) Sb35-induced proteasome inhibition. Vascular endothelial cells were treated with or without 10, 50, 100, 150, or 200 µM Sb35 for 24 h, and ubiquitinated proteins were determined by performing Western blotting.
Nrf2 knockdown (Figure 5A) resulted in a markedly lower expression of MT-1A in the presence of Sb35 (Figure 5b, upper panel). In contrast, MT-2A expression in the Nrf2 knockdown and in the presence of Sb35 was unaffected (Figure 5B, lower panel). Sb35 did not induce the transcription of MT-1E (Figure 5b, middle panel). Thus, the transcriptional induction of MT-1A is regulated by both the MTF-1–MRE and Nrf2–ARE pathways whereas that of MT-2A is stimulated by only the MTF-1–MRE pathway in vascular endothelial cells.
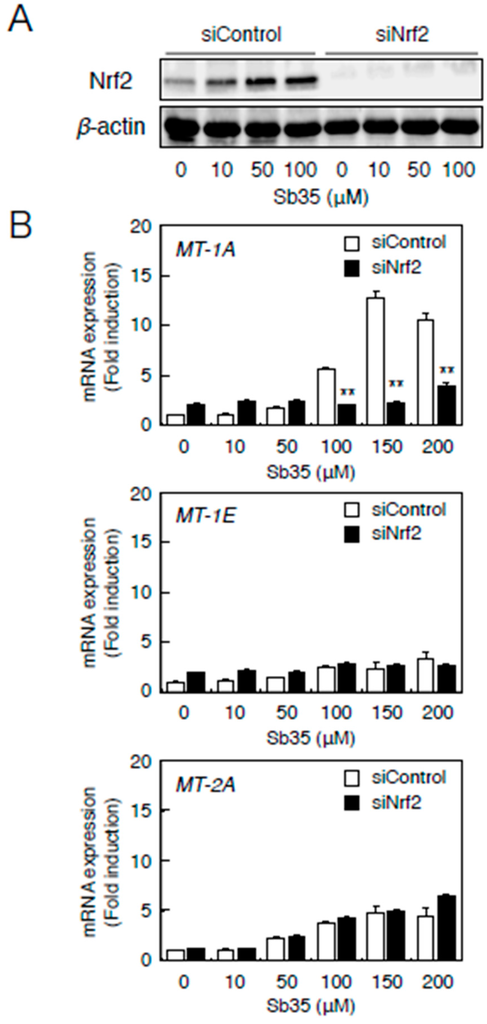
Figure 5.
The Nrf2–ARE pathway mediates Sb35-induced transcription of endothelial MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A. (A) Expression of Nrf2. Vascular endothelial cells transfected with control or Nrf2 siRNA were treated with or without 10, 50, or 100 µM Sb35 for 24 h, and expression of Nrf2 was determined by performing Western blotting; (B) Sb35-induced transcription of endothelial MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A after Nrf2 knockdown. Vascular endothelial cells transfected with control or Nrf2 siRNA were treated with or without 10, 50, 100, 150, or 200 µM Sb35 for 12 h. Data are expressed as the mean ± SE of three representative samples, with each sample obtained from three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 indicates significantly different from the corresponding siControl.
2.4. Determination of the Pathway Involved in the Transcriptional Induction of Endothelial MT Using Tris(pentafluorophenyl)phosphane (P35)
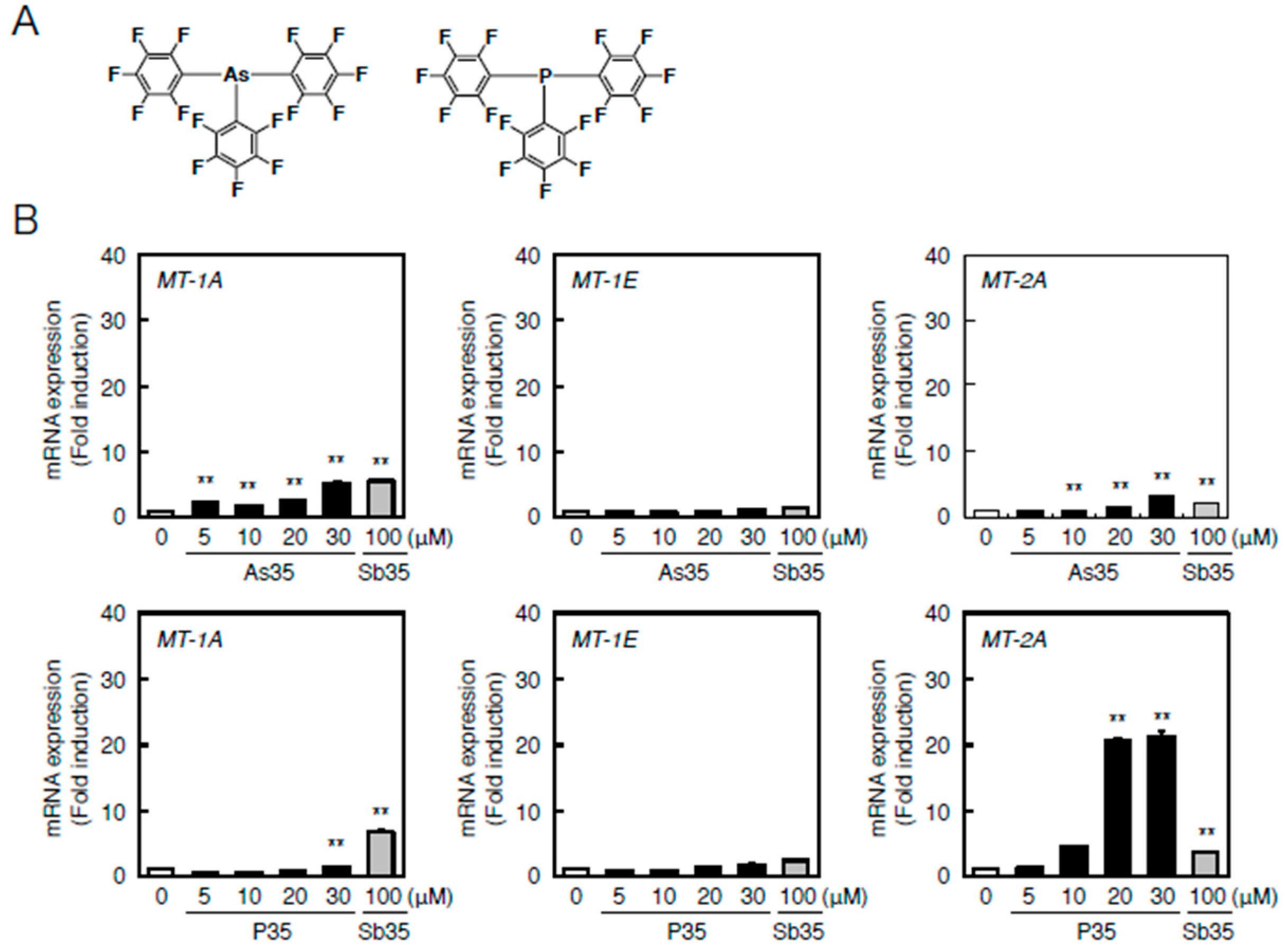
Understanding the role of the antimony atom in Sb35 molecules in endothelial MT induction is important for understanding the bioactivity of Sb35 as a hybrid molecule. In order to increase the understanding of the role of antimony atom, we next investigated the effects of pnictogen analogues—As35 and P35 (Figure 6A)—on the transcriptional induction of MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A in bovine aortic endothelial cells. As35 significantly increased MT-1A and MT-2A expression similarly to Sb35 (Figure 6B, upper panels). The transcriptional induction of MT-1A and MT-1E by P35 was very weak; however, P35 strongly induced transcription of MT-2A (Figure 6B, lower panels).
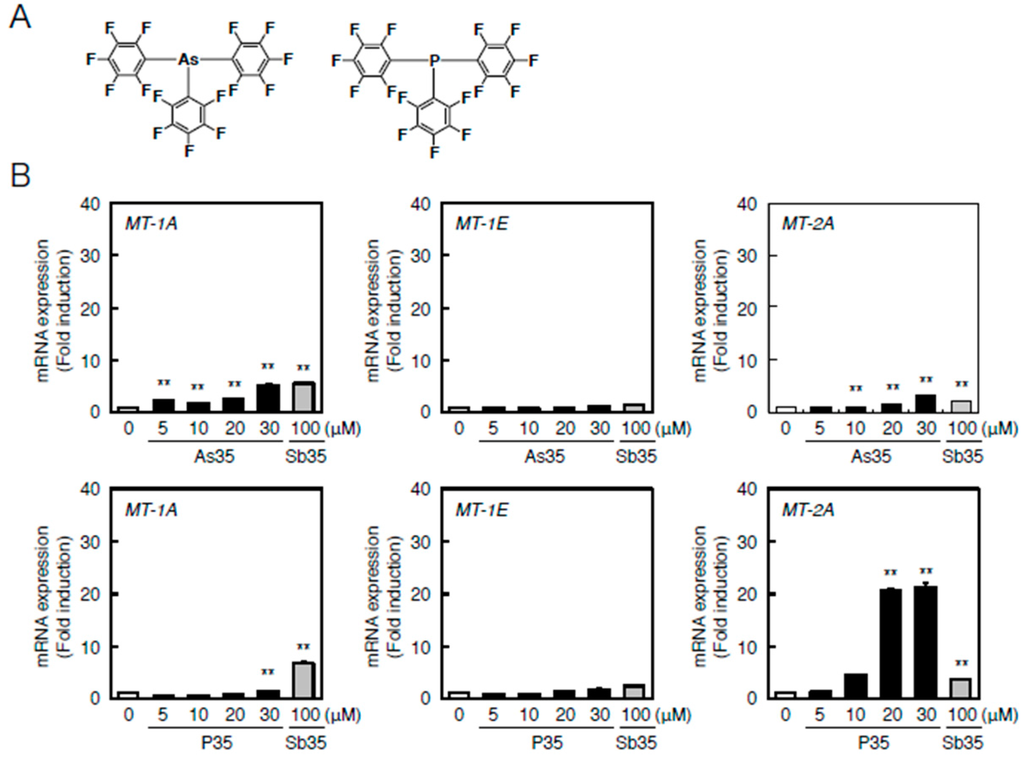
Figure 6.
As35 or P35-induced transcription of endothelial MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A. (A) Structures of As35 and P35; (B) Endothelial MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A expression after As35 (upper panels) or P35 (lower panels) treatment. Vascular endothelial cells were treated with or without 10, 20, 50, or 100 µM As35 for 12 h (upper panels) or 5, 10, 20, or 30 µM P35 or 12 h (lower panels). The cells were also treated with 100 µM Sb35, which served as a comparative control. MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A mRNA expression was determined by performing real-time RT-PCR. Data are expressed as the mean ± SE of three representative samples, with each sample obtained from three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 indicate significantly different from the corresponding control.
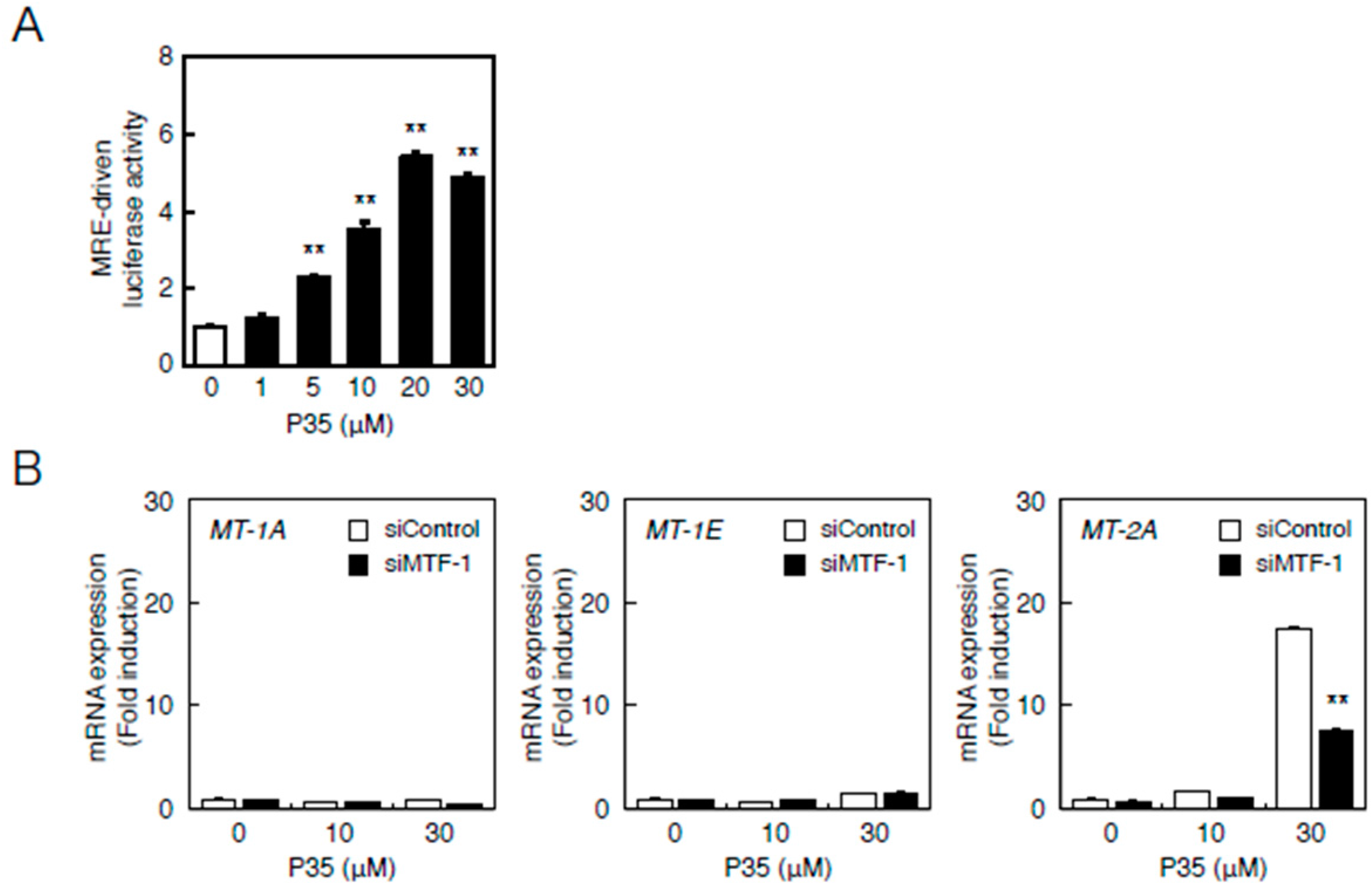
Therefore, we investigated the involvement of the MTF-1–MRE and Nrf2–ARE pathways in the transcriptional induction of MT-2A by P35. P35 significantly increased MRE-driven transcription in a concentration-dependent manner in vascular endothelial cells (Figure 7A). The transcriptional induction of MT-2A by P35 was suppressed in a siRNA-mediated knockdown of MTF-1 (Figure 7B).
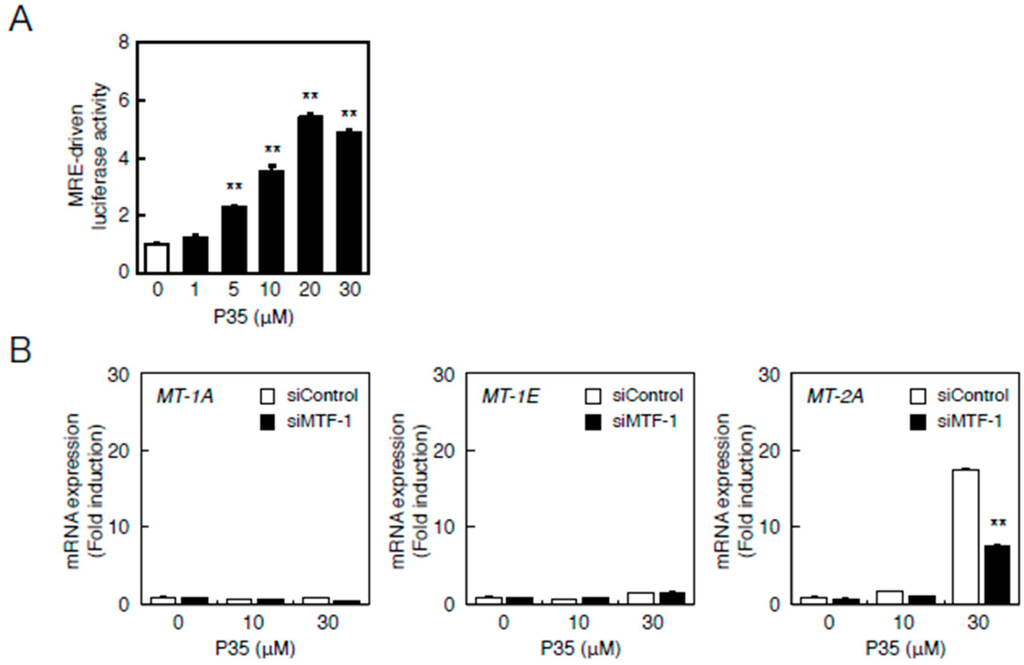
Figure 7.
The MTF-1–MRE pathway mediates P35-induced transcription of endothelial MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A. (A) Vascular endothelial cells transfected with an MRE reporter vector were treated with or without 1, 5, 10, 20, or 30 µM P35 for 12 h, and MRE-driven transcriptional activity was determined by performing the MRE-directed reporter assay. ** p < 0.01 indicates significantly different from the corresponding control; (B) P35-induced transcription of endothelial MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A after MTF-1 knockdown. Vascular endothelial cells transfected with control or MTF-1 siRNA were treated with or without 10 or 30 µM P35 for 12 h. Data are expressed as the mean ± SE of three representative samples, with each sample obtained from three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 indicates significantly different from the corresponding siControl.
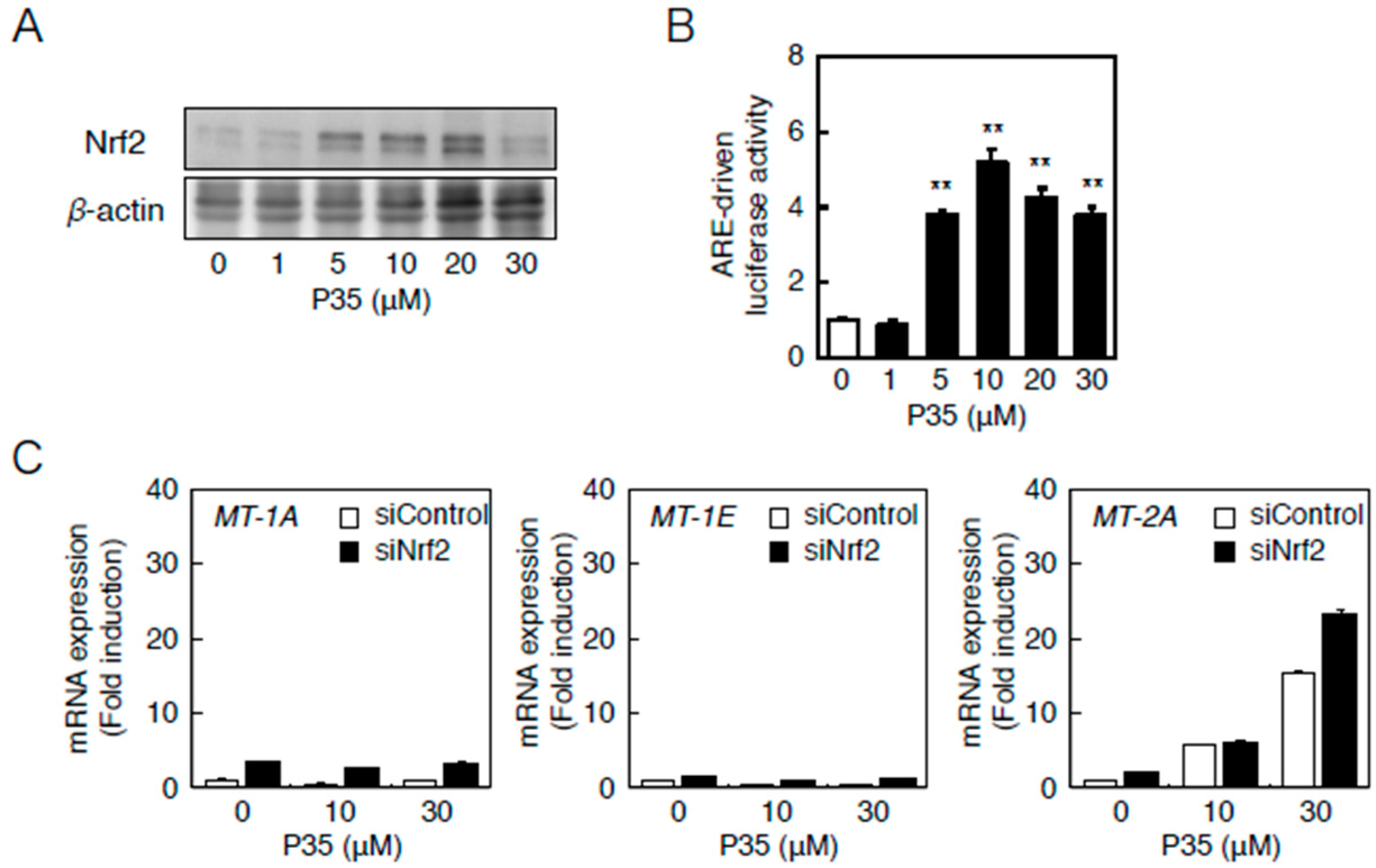
Similarly, P35 activated Nrf2 (Figure 8A) and significantly increased ARE-driven transcription in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 8B). The transcriptional induction of MT-2A by P35 was, however, unaffected in a siRNA-mediated knockdown of Nrf2 (Figure 8B), indicating that the Nrf2–ARE pathway does not transactivate MT-2A induction.
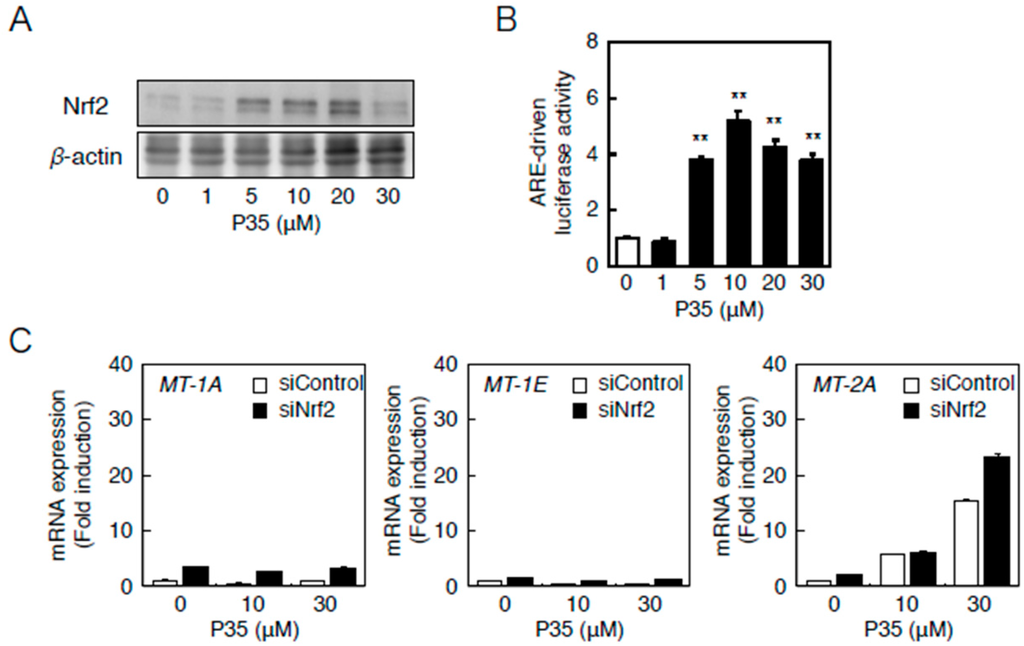
Figure 8.
The Nrf2–ARE pathway mediates P35-induced transcription of endothelial MT-2A. (A,B) ARE-driven transcriptional activity. Vascular endothelial cells transfected with an ARE reporter vector were treated with or without 1, 5, 10, 20, or 30 µM P35 for 12 h, and ARE-driven transcriptional activity was determined by performing the ARE-directed reporter assay. Data are expressed as the mean ± SE of three representative samples, with each sample obtained from three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 indicates significantly different from the corresponding control; (C) P35-induced transcription of endothelial MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A after Nrf2 knockdown. Vascular endothelial cells transfected with control or Nrf2 siRNA were treated with or without 10 or 30 µM P35 for 12 h. Data are expressed as the mean ± SE of three representative samples, with each sample obtained from three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 indicates significantly different from the corresponding siControl.
3. Discussion
MT protects cells from heavy metal toxicity and oxidative stress; however, the mechanisms underlying MT induction are not fully understood. Vascular endothelial cells regulate the blood coagulation-fibrinolytic system and vascular tone while MT likely protects the cells from functional damage, thereby preventing vascular disorders. In fact, fetal high-density lipoprotein, which is associated with the inhibition of atherosclerosis, reduces the expression of MT-1X and MT-2A in human placental endothelial cells [36]. Since zinc is not an inducer of endothelial MT synthesis [26,27], we used a library of organoantimony compounds to analyze the mechanisms of endothelial MT induction. We found that the organoantimony compound Sb35 causes transcriptional induction of MT isoforms—MT-1A and MT-2A—in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Among these MT isoforms, the transcriptional induction of MT-1A is regulated by either the MTF-1–MRE or Nrf2–ARE pathways whereas only the MTF-1–MRE pathway regulates MT-2A expression. Since sulforaphane, an Nrf2 activator, weakly induces MT isoform expression (data not shown), the MTF-1–MRE pathway is likely essential for transcriptional induction of all endothelial MT isoforms while the Nrf2–ARE pathway enhances the induction of MT-1A isoform by MTF-1. However, the increase in MRE-driven promoter activity by Sb35 was not so marked. Although the details are not clear, an assumption can be made that Sb35 may activate other regulatory pathways that induce transcription of MT genes [36] in vascular endothelial cells. Since Nrf2 is a transcriptional factor that induces the expression of antioxidant proteins such as HO-1 [37] and GCLM [38], the original role of MT-1A may be cytoprotection against oxidative damage by injury or inflammation. Alternatively, that of MT-2A may regulate zinc metabolism as well as mediate cytoprotection because the transcriptional induction requires only activation of MTF-1 by zinc. Specifically, MT-1 and MT-2 do not share these roles but the original roles may be different. A recent study suggested that MT-1, compared to MT-2, has a greater ability to bind cadmium, whereas MT-2 has higher ability to bind to zinc compared to MT-1 [39]. In addition, it was reported that cadmium increased the expression of only three genes, including MT-1E, MT-1H, and MT-1B, in human coronary artery endothelial cells by microarray analysis [35]. These reports partly support our hypothesis. Involvement of the Nrf2–ARE pathway in the transcriptional induction of MT-1A but not MT-2A is a new finding of the present study.
Recently, we found that the Nrf2–ARE pathway is involved in the cadmium mediated induction of endothelial MT isoforms including MT-1E and MT-2A [40]. Cadmium modifies Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1, a negative regulator of Nrf2, and activates Nrf2, which is recruited to ARE1 and ARE5 of the promoter region of endothelial MT-2A. However, induction of both MT-2A and MT-1E is reinforced by ARE activation. Since MT-1E is located next to MT-2A in the genome, we speculated that recruitment of Nrf2 to the AREs of the MT-2 promoter region stimulates the transcriptional activity of MT-1 and MT-2A. In the present study, the Nrf2–ARE pathway increases the induction of MT-1A and MT-1E but not MT-2A. Although we have not identified AREs to which Nrf2 is recruited in the presence of Sb35, we speculate that Sb35 modifies Nrf2 and alters AREs to be recruited. For example, Nrf2 might be recruited to the promoter region of MT-1 rather than that of MT-2 in the presence of Sb35. In fact, Nrf2 is regulated by acetylation [41]. Proteasome inhibition results in Nrf2 stabilization [42] and acetylation [43]. We confirmed that in bovine aortic endothelial cells after 12 h Sb35 (>50 µM) inhibits proteasome activity whereas cadmium (<10 µM) does not [44]. It is likely that the degree of acetylation of Nrf2 is responsible for the differences in involvement of the Nrf2–ARE pathway in the MT isoform transcriptional induction between Sb35 and cadmium, although other mechanisms might also be involved.
P35’s induction of endothelial MT-2A transcription is unaffected by the Nrf2–ARE pathway. If P35-activated Nrf2 is recruited to AREs in the promoter regions of MT-1A/E genes, transcription of MT-1A/E would be stimulated, as is the case when Sb35 is present. Even if Nrf2 is recruited to MT-2A AREs, transcription of MT-1A/E would be stimulated, as is the case for cadmium. Although it is not known why P35-activated Nrf2 does not stimulate MT-1A/E transcription, the present data suggest that there is a mechanism by which only MT-2A is induced in vascular endothelial cells. In other words, both Sb35 and P35 activate the Nrf2–ARE pathway but only Sb35 may be able to act on the mechanism that is required for MT-1A gene expression. On the other hand, As35 increased the transcriptional induction of MT-1A and MT-2A similarly to Sb35, but at concentrations lower than that of Sb35. The properties of arsenic as an element are very similar to those of antimony. In our previous study, however, it was shown that intracellular accumulation of As35 was higher than that of Sb35 in cultured vascular endothelial cells [33]. It is suggested that the mechanisms underlying transcriptional induction of MT-1A and MT-2A by As35 and Sb35 are similar, but the induction by As35 can occur at lower concentrations because of the higher intracellular accumulation. Although it is certain that the intramolecular elements can modify the bioactivities of organometallic compounds, the mechanisms underlying the modifications remain to be determined.
In the present study, we demonstrate the intracellular signaling pathways for transcriptional induction of endothelial MT isoforms using the organic-inorganic hybrid molecules Sb35 and P35. We found that there are two signaling pathways—the MTF-1–MRE and Nrf2–ARE pathways—that regulate the transcription of endothelial MT. The MTF-1–MRE pathway is essential for induction of all isoforms and the Nrf2–ARE pathway reinforces this induction. In addition, there is a mechanism by which only MT-2A is induced in vascular endothelial cells. It is suggested that MT-1A/E and MT-2A could have different functions. Additionally, proteasome inhibition could be involved in transcriptional regulation by modulating Nrf2 recruitment to AREs in the promoter regions of MT genes via Nrf2 acetylation. In addition, MTF-1 is activated by zinc; zinc binds to the zinc finger domain of MTF-1 to recruit transcription factors to the MREs [45,46]. Zinc is the only heavy metal that can induce MTF-1 binding to MREs [47]. Although the origin of zinc, which activates MTF-1 after P35 treatment, is unclear, two mechanisms are possible. First, the zinc ion could be supplied to MTF-1 by intracellular proteins that bind zinc ions nonspecifically. The difference in MTF-1 activating activity between Sb35 and P35 may be due to the different capacity to release zinc from zinc-binding proteins. Second, recently, a family of zinc transporters was identified [48], which are expressed on the transmembrane [49], Golgi apparatus [50], and endoplasmic reticulum [51] and may regulate the intracellular concentration of zinc. It is possible that either Sb35, As35, or P35 activates or induces zinc transporter(s), which releases the zinc ion into the cytoplasm, thereby activating MTF-1. Although the mechanisms for endothelial MT induction remain to be elucidated, our present study revealed the exact role of the Nrf2–ARE pathway in endothelial MT transcriptional induction by using an organometallic compound as an endothelial MT inducer. This suggests that the strategy of bio-organometallics, in which organic-inorganic hybrid molecules are used as tools for analysis of biological functions, is effective to reveal unknown biological mechanisms.
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Synthesis of Sb35, P35, and As35
Sb35, tris(pentafluorophenyl)arsane (As35), and tris(pentafluorophenyl)phosphane (P35) were synthesized according to previously reported procedures [52,53,54,55].
4.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
Bovine aortic endothelial cells (Cell Applications, CA, USA) were cultured at 37 °C in 5% CO2 in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) until confluent. The cells were treated with or without Sb35 (10, 50, 100, 150, or 200 µM), As35 (5, 10, 20, or 30 µM), or P35 (5, 10, 20, or 30 µM) at 37 °C for 3, 6, 12, 24, or 48 h in serum-free Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium after washing twice with serum-free Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium. In another experiment, confluent cultures of human brain microvascular endothelial cells were treated with 28 organoantimony compounds (Table 1) at 10 µM for 3 h in HuMedia EG-2 (Kurabo, Osaka, Japan), and MT-1X mRNA expression was determined by real-time RT-PCR as described below. The primer pair was 5′-TTGATCGGGAACTCCTGCTTCT-3′ (forward) and 5′-ACACTTGGCACAGCCCACA-3′ (reverse). Since the organometallic compounds used in this study were insoluble in water, they were dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide and then added to the culture medium. The final concentration of dimethylsulfoxide was less than 0.1%.
4.3 Transfection
Vascular endothelial cells were cultured and were transfected with small-interfering RNAs (siRNAs; Bioneer, Daejeon, Korea) by using RNAiMAX reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), according to the manufacturer's instructions. After transfection, the cells were treated with Sb35, As35, or P35 for 12 h. Sequences of the sense and antisense strands of siRNAs are as follows: bovine Nrf2 siRNA, 5′-CCAUUGAUCUCUCUGAUCUdTdT-3′ (sense) and 5′-AGAUCAGAGAGAUCAAUGGGC-3′ (antisense); bovine MTF-1 siRNA, 5′-GAGAACACUUGCCUUUUCUdTdT-3′ (sense) and 5′-AGAAAAGGCAAGUGUUCUCCG-3′ (antisense). A nonspecific sequence was used as negative control siRNA (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA).
4.4. Luciferase Assay
MRE and ARE-driven reporter assays by using firefly reporter plasmids pGL4.12-MREd4 and pGL4.12-ARE4 × 3 [56,57] were performed as described previously [58]. After transfection with the MRE or ARE reporter vector, vascular endothelial cells were treated with Sb35, P35, or CdCl2 for 12 h. The cells were then lysed, and luciferase activity was measured using Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) and GloMax 20/20n luminometer (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Luminescence of pRL-SV40 and pRL-TK (Promega) was used to normalize MRE- and ARE-driven transcriptional activities, respectively.
4.5. Real-Time RT-PCR
mRNA expression of endothelial MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A was analyzed by performing real-time RT-PCR. Total RNA was extracted from Sb35-, As35-, or P35-treated vascular endothelial cells that were transfected with or without the siRNAs by using RNeasy Lipid Tissue Mini kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA). Complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized using High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Real-time PCR was performed using Gene Ace SYBR qPCR Mixα (Nippon Gene, Tokyo, Japan), 10 ng cDNA, and 100 nM primers in a StepOnePlus RT-PCR system (Applied Biosystems). Sequences of primer pairs used have been described previously [58].
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
Protein expression of Nrf2, glutamate-cysteine ligase, modifier subunit (GCLM), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), ubiquitin, and β-actin was analyzed by performing Western blotting, as described previously [58]. The following primary antibodies were used: anti-Nrf2 antibody (H-300; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), anti-GCLM antibody (FL-274; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), anti-HO-1 antibody (ADI-SPA-895; Enzo Life Sciences, Farmingdale, NY, USA), anti-ubiquitin monoclonal antibody (ADI-SPA-203; Enzo Life Sciences), and anti-β-actin antibody (A5060; Sigma-Aldrich Chemical, St. Louis, MO, USA). Expression of MT protein was analyzed using a method described by Stitt et al. [59] with a mouse monoclonal anti-MT-1/2 antibody (E9; DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark). An apoprotein of MT was detected in this experiment because metals bound to MT were chelated by EDTA and because thiols of cysteine residues in MT were alkylated by iodoacetamide before performing sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni-type multiple t-test. p values less than 0.05 were considered significant.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be found at www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/17/9/1381/s1.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI as follows: Grant-in-Aids for Challenging Exploratory Research #24659058 (to Toshiyuki Kaji) and #15K14992 (to Toshiyuki Kaji); a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) #24390034 (to Toshiyuki Kaji); and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) #15K08047 (to Chika Yamamoto).
Author Contributions
Tomoya Fujie and Masaki Murakami performed the gene expression experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. Eiko Yoshida performed the gene expression experiments and analyzed the data. Tomoki Kimura performed the luciferase assay and analyzed the data. Shuji Yasuike chemically synthesized Sb35, P35, As35 and the other organic-inorganic hybrid molecules. Yasuyuki Fujiwara and Chika Yamamoto analyzed the data and designed the experiments. Toshiyuki Kaji analyzed the data, designed the experiments with Yasuyuki Fujiwara and Chika Yamamoto, coordinated this research, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| ARE | Antioxidant Response Element |
| As35 | Tris(pentafluorophenyl)arsane |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehydes-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| GCLM | Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase, Modifier subunit |
| HO-1 | Heme Oxygenase-1 |
| MRE | Metal Responsive Element |
| MTF-1 | Metal response element-binding Transcription Factor-1 |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear Factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| P35 | Tris(pentafluorophenyl)phosphane |
| Sb35 | Tris(pentafluorophenyl)stibane |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
References
- Margoshes, M.; Vallee, B.L. A cadmium protein from equine kidney cortex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 4813–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blindauer, C.A.; Metallothionein, F. Transport and Storage of Metal Ions in Biological Cells (RSC Metallobiology Series 2); Maret, W., Wedd, A., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 606–665. [Google Scholar]
- Quaife, C.J.; Findley, S.D.; Erickson, J.C.; Froelick, G.J.; Kelly, E.J.; Zambrowicz, B.P.; Palmiter, R.D. Induction of a new metallothionein isoform (MT-IV) occurs during differentiation of stratified squamous epithelia. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 7250–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeiser, E.C.; Fitch, C.A.; Horning, M.S.; Rutkoski, N.; Levenson, C.W. Regulation of metallothionein-3 mRNA by thyroid hormone in developing rat brain and primary cultures of rat astrocytes and neurons. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 1999, 115, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kägi, J.M. Overview of metallothionein. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 205, 613–626. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M.; Bremner, I. Oxygen free radicals and metallothionein. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1993, 14, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, P.F.; Davison, B.L.; Stuart, G.W.; Wilkie, T.M.; Norstedt, G.; Palmiter, R.D. Regulation, linkage, and sequence of mouse metallothionein I and II genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1984, 4, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagle, M.K.; Palmiter, R.D. Coordinate regulation of mouse metallothionein I and II genes by heavy metals and glucocorticoids. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1985, 5, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Sayato-Suzuki, J. Isolation of mouse isometallothioneins—A comparison of isometallothioneins in growing cells and post-mitotic cells. Biochem. J. 1988, 251, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw, W.C.; Lehman-McKeeman, L.D.; Klaassen, C.D. Hepatic isometallothioneins in mice: Induction in adults and postnatal ontogeny. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1990, 104, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahroudi, N.; Foster, R.; Price-Haughey, J.; Beitel, G.; Gedamu, L. Cell-type specific and differential regulation of the human metallothionein genes. Correlation with DNA methylation and chromatin structure. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 6506–6511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cavigelli, M.; Kägi, J.H.; Hunziker, P.E. Cell- and inducer-specific accretion of human isometallothioneins. Biochem. J. 1993, 292, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somji, S.; Sens, M.A.; Lamm, D.L.; Garrett, S.H.; Sens, D.A. Metallothionein isoform 1 and 2 gene expression in the human bladder: Evidence for regulation of MT-1X mRNA in bladder cancer. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2001, 25, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.; Phann, T.T.; Yip, G.W.; Bay, B.H. Up-regulation of metallothionein isoforms in keloid keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 17, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauchel, R.; Radtke, F.; Georgiev, O.; Stark, G.; Aguet, M.; Schaffner, W. The transcription factor MTF-1 is essential for basal and heavy metal-induced metallothionein gene expression. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 2870–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart, G.W.; Searle, P.F.; Palmiter, R.D. Identification of multiple metal regulatory elements in mouse metallothionein-I promoter by assaying synthetic sequences. Nature 1985, 317, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culotta, V.C.; Hamer, D.H. Fine mapping of a mouse metallothionein gene metal response element. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1989, 9, 1376–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmiter, R.D. Molecular biology of metallothionein gene expression. Exp. Suppl. 1987, 52, 63–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuji, M.; Katsuoka, F.; Kobayashi, A.; Aburatani, H.; Hayes, J.D.; Yamamoto, M. Nrf1 and Nrf2 play distinct roles in activation of antioxidant response element-dependent genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 33554–33562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, T.; Palmiter, R.D.; Andrews, G.K. Transcriptional induction of the mouse metallothionein-1 gene in hydrogen peroxide-treated Hepa cells involves a composite major late transcription factor/antioxidant response element and metal response promoter element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 5016–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harker, L.A.; Schwartz, S.M.; Ross, R. Endothelium and arteriosclerosis. Clin. Haematol. 1981, 10, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kägi, J.M.; Schaffer, A. Biochemistry of metallothionein. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 8509–8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messner, B.; Knoflach, M.; Seubert, A.; Ritsch, A.; Pfller, K.; Henderson, B.; Shen, Y.H.; Zeller, I.; Willeit, G.; Laufer, G.; et al. Cadmium is a novel and independent risk factor for early atherosclerosis mechanisms and in vivo relevance. Atherioscler. Thromb. Res. 2009, 29, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, M.C. Role of mercury toxicity in hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and stroke. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2011, 13, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornalley, P.J.; Vasák, M. Possible role for metallothionein in protection against radiation-induced oxidative stress. Kinetics and mechanism of its reaction with superoxide and hydroxyl radicals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 21, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, T.; Mishima, A.; Koyanagi, E.; Yamamoto, C.; Sakamoto, M.; Kozuka, H. Possible mechanism for zinc protection against cadmium cytotoxicity in cultured vascular endothelial cells. Toxicology 1992, 76, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujie, T.; Segawa, Y.; Uehara, A.; Nakamura, T.; Kimura, T.; Yoshida, E.; Yamamoto, C.; Uchiyama, M.; Naka, H.; Kaji, T. Zinc diethyldithiocarbamate as an inducer of metallothionein in cultured vascular endothelial cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 41, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobilya, D.J.; Reynolds, J.T.; Faia, K.L.; Briske-Anderson, M.; Reeves, P.G. Zinc-related metallothionein metabolism in bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1999, 10, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulkens, I.A.; Castricum, K.C.M.; Weijers, E.M.; Koolwijk, P.; Griffioen, A.W.; Thijssen, V.L. Expression, regulation and function of human metallothioneins in endothelial cells. J. Vasc. Res. 2014, 51, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grignard, V. Some new organometallic combinations of magnesium and their application to the synthesis of alcohols and hydrocarbons. C. R. Acad. Sci. 1900, 130, 1322–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Wittig, G.; Schöllkopf, U. Triphenylphosphinemethylene as an olefin-forming reagent. Chem. Ber. 1954, 97, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohri, K.; Yoshida, E.; Yasuike, S.; Fujie, T.; Yamamoto, C.; Kaji, T. The cytotoxicity of organobismuth compounds with certain molecular structures can be diminished by replacing the bismuth atom with an antimony atom in the molecules. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 40, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Fujie, T.; Matsumura, M.; Yoshida, E.; Yamamoto, C.; Fujiwara, Y.; Yasuike, S.; Kaji, T. Comparative cytotoxicity of triphenylstibane and fluorine-substituted triarylpnictogens in cultured vascular endothelial cells. Fundam. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 2, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, V.; Lindert, U.; Schaffner, W. The taste of heavy metals: Gene regulation by MTF-1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 1416–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizkova, S.; Kepinska, M.; Emri, G.; Rodrigo, M.A.M.; Tmejova, K.; Nerudova, D.; Kizek, R.; Adam, V. Microarray analysis of metallothionein in human diseases. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 117, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsutani, K.; Ito, N.; Kanekiyo, M.; Muto, N.; Tanaka, K. Requirement for cooperative interaction of interleukin-6 responsive element type 2 and glucocorticoid responsive element in the synergistic activation of mouse metallothionein-1 gene by interleukin-6 and glucocorticoid. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1998, 151, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, J.; Stewart, D.; Touchard, C.; Boinapally, S.; Choi, S.M.K.; Cook, J.L. Nrf2, a Cap’n’Collar transcription factor, regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 26071–26078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, A.M.; Nevarea, Z.; Gipp, J.J.; Muleahy, R.T. Identification of a variant antioxidant response element in the promoter of the human glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30730–30737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artells, E.; Palacos, O.; Capdevila, M.; Atrian, S. Mammalian MT1 and MT2 metallothioneins differ in their metal binding abilities. Metallomics 2013, 5, 1397–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkai, Y.; Kimura, T.; Itagaki, A.; Yamamoto, C.; Taguchi, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Kumagai, Y.; Kaji, T. Partial contribution of the Keap1-Nrf2 system to cadmium-mediated metallothionein expression in vascular endothelial cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 295, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Chin, Y.E.; Zhang, D.D. Acetylation of Nrf2 by p300/CBP augments promoter-specific DNA binding of Nrf2 during the antioxidant response. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 2658–2672. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, D.; Killeen, E.; Naquin, R.; Alam, S.; Alam, J. Degradation of transcription factor Nrf2 via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and stabilization by cadmium. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2396–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercado, N.; Thimmulappa, R.; Thomas, C.M.R.; Fenwick, P.S.; Chana, K.K.; Donnelly, L.E.; Biswal, S.; Ito, K.; Barnes, P.J. Decreased histone deacetylase 2 impairs Nrf2 activation by oxidative stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 406, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujie, T.; Murakami, M.; Yoshida, E.; Tachinami, T.; Shinkai, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Yamamoto, C.; Kumagai, Y.; Naka, H.; Kaji, T. Copper diethyldithiocarbamate as an activator of Nrf2 in cultured vascular endothelial cells. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 21, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Agarwal, A.; Giedroc, D.P. Structural and functional heterogeneity among the zinc fingers of human MRE-binding transcription factor-1. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 11152–11161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittel, D.; Smirnova, I.V.; Andrew, G.K. Functional heterogeneity in the zinc finger of metalloregulatory protein metal response element-binding transcription factor-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 37194–37201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittel, D.; Dalton, T.; Samson, S.L.; Gedamu, L.; Andrews, G.K. The DNA binding activity of metal response element-binding transcription factor-1 is activated in vivo and in vitro by zinc, but not by other transition metals. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 7127–7133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotz, N.; Fox, T.; Connolly, E.; Park, W.; Guerinot, M.L.; Eide, D. Identification of a family of zinc transporter genes from Arabidopsis that respond to zinc deficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7220–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukada, T.; Kambe, T. Molecular and genetic features of zinc transporters in physiology and pathogenesis. Metallomics 2011, 3, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, M.; Fukunaka, A.; Hagihara, M.; Watanabe, K.; Kamino, S.; Kambe, T.; Enomoto, S.; Hironuma, M. Essential role of the zinc transporter ZIP9/SLC39A9 in regulating the activations of Akt and Erk in B-cell receptor signaling pathway in DT40 cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.M.; Hiscox, S.; Nicholson, R.I.; Hogstrand, C.; Kille, P. Structure-function analysis of HKE4, a member of the new LIV-1 subfamily of zinc transporters. Biochem. J. 2004, 377, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fild, M.; Glemser, O.; Christoph, G. Synthesis of tris(pentafluorophenyl)arsine, -stibine, and -phosphine and of pentafluorophenyl-trimethylsilane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1964, 3, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, R.; Singhal, K.; Shukla, S.K.; Chandrashekar, K.; Saxena, A.K.; Ranjan, A.; Raj, P. Synthesis and biological activity of a novel compound: (C6F5)2SbPh. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2008, 183, 2029–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.; Reißmann, M.; Schäfer, A.; Saak, W.; Haase, D.; Müller, T. A new synthesis of triarylsilylium ions and their application in dihydrogen activation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 12636–12638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Yin, H.; Wang, F.; Han, Z.; Wang, F.; Cheng, S.; Hong, M. Novel tetranuclear triarylantimony(V) complexes with (±)-mandelic acid ligands: Synthesis, characterization, in vitro cytotoxicity and DNA binding properties. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 8563–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, T.; Itoh, N.; Takehara, M.; Oguro, I.; Ishizaki, J.; Nakanishi, T.; Tanaka, K. MRE-binding transcription factor-1 is activated during endotoxemia: A central role for metallothionein. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 129, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Kawasaki, Y.; Okumura, F.; Sone, T.; Natsuki, R.; Isobe, M. Ethanol-induced expression of glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit gene is mediated by NF-κB. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 185, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujie, T.; Segawa, Y.; Yoshida, E.; Fujiwara, Y.; Yamamoto, C.; Satoh, M.; Naka, H.; Kaji, T. Induction of metallothionein isoforms by copper diethyldithiocarbamate in cultured vascular endothelial cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 41, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stitt, M.S.; Wasserloos, K.J.; Tang, X.; Liu, X.; Pitt, B.R.; St. Croix, C.M. Nitric oxide-induced nuclear translocation of the metal responsive transcription factor, MTF-1 is mediated by zinc release from metallothionein. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 44, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).