Extracellular Vesicles as New Players in Cellular Senescence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cellular Senescence
3. Senescence Associated Secretory Phenotype
4. Extracellular Vesicles (EVs)
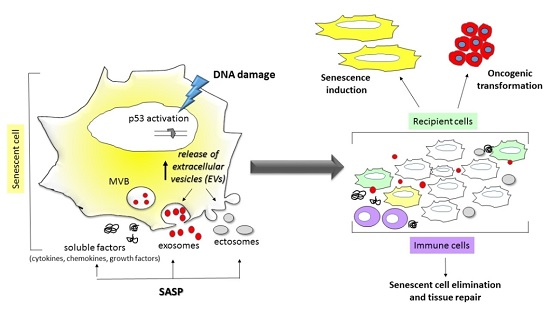
5. The Release of EVs in Cell Senescence and Aging
The Role of EVs Associated miRNA and mRNA in Senescence and Aging
6. The Role of EVs in the Blood
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ouyang, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, F.T.; Zhou, T.T.; Liu, B.; Bao, J.K. Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuilman, T.; Michaloglou, C.; Mooi, W.J.; Peeper, D.S. The essence of senescence. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2463–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campisi, J. Aging, cellular senescence, and cancer. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 685–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lujambio, A. To clear, or not to clear (senescent cells)? That is the question. Inside Cell 2016, 1, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Jurk, D.; Maddick, M.; Nelson, G.; Martin-Ruiz, C.; von Zglinicki, T. DNA damage response and cellular senescence in tissues of aging mice. Aging Cell 2009, 8, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.J.; Wijshake, T.; Tchkonia, T.; LeBrasseur, N.K.; Childs, B.G.; van de Sluis, B.; Kirkland, J.L.; van Deursen, J.M. Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive senescent cells delays ageing-associated disorders. Nature 2011, 479, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.J.; Childs, B.G.; Durik, M.; Wijers, M.E.; Sieben, C.J.; Zhong, J.; Saltness, R.A.; Jeganathan, K.B.; Verzosa, G.C.; Pezeshki, A.; et al. Naturally occurring p16(Ink4a)-positive cells shorten healthy lifespan. Nature 2016, 530, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Deursen, J.M. The role of senescent cells in ageing. Nature 2014, 509, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayflick, L. The limited in vitro lifetime of human diploid cell strains. Exp. Cell Rev. 1965, 37, 614–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Espín, D.; Serrano, M. Cellular senescence: from physiology to pathology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terman, A.; Brunk, U.T. Oxidative stress, accumulation of biological ‘garbage’, and aging. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2006, 8, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimri, G.P.; Lee, X.; Basile, G.; Acosta, M.; Scott, G.; Roskelley, C.; Medrano, E.E.; Linskens, M.; Rubelj, I.; Pereira-Smith, O.; et al. A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9363–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.Y.; Han, J.A.; Im, J.S.; Morrone, A.; Johung, K.; Goodwin, E.C.; Kleijer, W.J.; DiMaio, D.; Hwang, E.S. Senescence-associated β-galactosidase is lysosomal β-galactosidase. Aging Cell 2006, 5, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matjusaitis, M.; Chin, G.; Sarnoski, E.A.; Stolzing, A. Biomarkers to identify and isolate senescent cells. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandra, T.; Kirschner, K. Chromosome organisation during ageing and senescence. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2016, 40, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgoulis, V.G.; Halazonetis, T.D. Oncogene-induced senescence: The bright and dark side of the response. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Micco, R.; Fumagalli, M.; Cicalese, A.; Piccinin, S.; Gasparini, P.; Luise, C.; Schurra, C.; Garre, M.; Nuciforo, P.G.; Bensimon, A.; et al. Oncogene-induced senescence is a DNA damage response triggered by DNA hyper-replication. Nature 2006, 444, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roninson, I.B. Tumor cell senescence in cancer treatment. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 2705–2715. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alcorta, D.A.; Xiong, Y.; Phelps, D.; Hannon, G.; Beach, D.; Barrett, J.C. Involvement of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16 (INK4a) in replicative senescence of normal human fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 13742–13747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherr, C.J.; Roberts, J.M. CDK inhibitors: Positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campisi, J.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. Cellular senescence: When bad things happen to good cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, J.C.; Banito, A.; Wuestefeld, T.; Georgilis, A.; Janich, P.; Morton, J.P.; Athineos, D.; Kang, T.W.; Lasitschka, F.; Andrulis, M.; et al. A complex secretory program orchestrated by the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaquin, N.; Martinez, A.; Rodier, F. Keeping the senescence secretome under control: Molecular reins on the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Exp. Gerontol. 2016, 2582, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, F.; Albertini, M.C.; Orciani, M.; Ceka, A.; Cricca, M.; Procopio, A.D.; Bonafè, M. DNA damage response (DDR) and senescence: Shuttled inflamma-miRNAs on the stage of inflamm-aging. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 35509–35521. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coppé, J.P.; Kauser, K.; Campisi, J.; Beauséjour, C.M. Secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor by primary human fibroblasts at senescence. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 29568–29574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laberge, R.M.; Awad, P.; Campisi, J.; Desprez, P.Y. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by senescent fibroblasts. Cancer Microenviron. 2012, 5, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, D.; Reyes-Mugica, M.; Rebbaa, A. Role of the beta catenin destruction complex in mediating chemotherapy-induced senescence-associated secretory phenotype. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimaki, S.; Wakabayashi, T.; Takemasa, T.; Asashima, M.; Kuwabara, T. The regulation of stem cell aging by Wnt signaling. Histol. Histopathol. 2015, 30, 1411–1430. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koles, K.; Nunnari, J.; Korkut, C.; Barria, R.; Brewer, C.; Li, Y.; Leszyk, J.; Zhang, B.; Budnik, V. Mechanism of evenness interrupted (Evi)-exosome release at synaptic boutons. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 16820–16834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkut, C.; Ataman, B.; Ramachandran, P.; Ashley, J.; Barria, R.; Gherbesi, N.; Budnik, V. Trans-synaptic transmission of vesicular Wnt signals through Evi/Wntless. Cell 2009, 139, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanelli, L.; Magini, A.; Buratta, S.; Brozzi, A.; Sagini, K.; Polchi, A.; Tancini, B.; Emiliani, C. Signaling pathways in exosomes biogenesis, secretion and fate. Genes (Basel) 2013, 4, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocucci, E.; Racchetti, G.; Meldolesi, J. Shedding microvesicles: artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocucci, E.; Meldolesi, J. Ectosomes and exosomes: shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Pol, E.; Böing, A.N.; Harrison, P.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Classification, functions, and clinical relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 676–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanelli, L.; Buratta, S.; Sagini, K.; Ferrara, G.; Lanni, M.; Emiliani, C. Exosome-based strategies for diagnosis and therapy. Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal, J.; Arras, G.; Colombo, M.; Jouve, M.; Morath, J.P.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.D.; Shah, S. Methods of isolating extracellular vesicles impact down-stream analyses of their cargoes. Methods 2015, 87, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzas, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lasser, C.; Lotvall, J.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J.; et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.S.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Gho, Y.S. Proteomics, transcriptomics and lipidomics of exosomes and ectosomes. Proteomics 2013, 13, 155471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Hopmans, E.S.; Lindenberg, J.L.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Würdinger, T.; Middeldorp, J.M. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6328–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; Yao, J.; Mi, S. Exosome and exosomal microRNA: trafficking, sorting, and function. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, H.; Simpson, R.J.; Ji, H.; Aikawa, E.; Altevogt, P.; Askenase, P.; Bond, V.C.; Borràs, F.E.; Breakefield, X.; Budnik, V.; et al. Vesiclepedia: A compendium for extracellular vesicles with continuous community annotation. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.K.; Kang, B.; Kim, O.Y.; Choi, D.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.R.; Go, G.; Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, S.C.; et al. EVpedia: An integrated database of high-throughput data for systemic analyses of extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicle 2013, 2, 20384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, R.J.; Kalra, H.; Mathivanan, S. ExoCarta as a resource for exosomal research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2012, 1, 18374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Record, M.; Carayon, K.; Poirot, M.; Silvente-Poirot, S. Exosomes as new vesicular lipid transporters involved in cell-cell communication and various pathophysiologies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subra, C.; Grand, D.; Laulagnier, K.; Stella, A.; Lambeau, G.; Paillasse, M.; de Medina, P.; Monsarrat, B.; Perret, B.; Silvente-Poirot, S.; et al. Exosomes account for vesicle-mediated transcellular transport of activatable phospholipases and prostaglandins. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 2105–2120. [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli, M.; Battista, N.; Riganti, L.; Prada, I.; Antonucci, F.; Cantone, L.; Matteoli, M.; Maccarrone, M.; Verderio, C. Active endocannabinoids are secreted on extracellular membrane vesicles. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torrano, V.; Royo, F.; Peinado, H.; Loizaga-Iriarte, A.; Unda, M.; Falcón-Perez, J.M.; Carracedo, A. Vesicle-MaNiA: Extracellular vesicles in liquid biopsy and cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savina, A.; Furlan, M.; Vidal, M.; Colombo, M.I. Exosome release is regulated by a calcium dependent mechanism in K562 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20083–20090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachenal, G.; Pernet-Gallay, K.; Chivet, M.; Hemming, F.J.; Belly, A.; Bodon, G.; Blot, B.; Haase, G.; Goldberg, Y.; Sadoul, R. Release of exosomes from differentiated neurons and its regulation by synaptic glutamatergic activity. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2011, 46, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Yu, S.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Ma, R.; Cao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, J. Exosomes: Decreased sensitivity of lung cancer A549 cells to cisplatin. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Paine, M.S.; Brooks, A.M.; McCubrey, J.A.; Renegar, R.H.; Wang, R.; Terrian, D.M. Senescence-associated exosome release from human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7864–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Harris, S.L.; Levine, A.J. The regulation of exosome secretion: a novel function of thep53 protein. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4795–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lespagnol, A.; Duflaut, D.; Beekman, C.; Blanc, L.; Fiucci, G.; Marine, J.C.; Vidal, M.; Amson, R.; Telerman, A. Exosome secretion, including the DNA damage-induced p53-dependent secretory pathway, is severely compromised in TSAP6/Steap3-null mice. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Riley, T.; Levine, A. The regulation of the endosomal compartment by p53 the tumor suppressor gene. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 2201–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z. p53 regulation of the IGF-1/AKT/mTOR pathways and the endosomal compartment. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, L.; Zimmermann, M.; Mitterbauer, A.; Ellinger, A.; Gruber Narzt, M.; Zellner, M.; Gyöngyösi, M.; Madlener, S.; Simader, E.; Gabriel, C.; et al. Analysis of the secretome of apoptotic peripheral blood mononuclear cells: Impact of released proteins and exosomes for tissue regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effenberger, T.; von der Heyde, J.; Bartsch, K.; Garbers, C.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Chalaris, A.; Murphy, G.; Rose-John, S.; Rabe, B. Senescence-associated release of transmembrane proteins involves proteolytic processing by ADAM17 and microvesicle shedding. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 4847–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanelli, L.; Magini, A.; Ciccarone, V.; Trivelli, F.; Polidoro, M.; Tancini, B.; Emiliani, C. New perspectives for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov. 2009, 4, 160–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.A.; Leonardi, T.; Huang, B.; Iraci, B.; Vega, S.P. Extracellular vesicles and their synthetic analogues in aging and age-associated brain diseases. Biogerontology 2015, 16, 147–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuyama, K.; Sun, H.; Mitsutake, S.; Igarashi, Y. Sphingolipid-modulated exosome secretion promotes clearance of amyloid-B by microglia. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 10977–10989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Niel, G. Study of exosomes shed new light on physiology of amyloidogenesis. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.L.; Lukas, T.J.; Yuan, M.; Du, N.; Tso, M.O.; Neufeld, A.H. Autophagy and exosomes in the aged retinal pigment epithelium: Possible relevance to drusen formation and age-related macular degeneration. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillari, J.; Grillari-Voglauer, R. Novel modulators of senescence, aging, and longevity: Small non-coding RNAs enter the stage. Exp. Gerontol. 2010, 45, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Vikos, T.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNAs and their roles in aging. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakuchi, M.; Lowenstein, C.J. miR-34, SIRT1 and p53: the feedback loop. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugalde, A.P.; Ramsay, A.J.; de la Rosa, J.; Varela, I.; Marino, G.; Cadinanos, J.; Lu, J.; Freije, J.M.; Lopez-Otin, C. Aging and chronic DNA damage response activate a regulatory pathway involving miR-29 and p53. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 2219–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillari, J.; Hackl, M.; Grillari-Voglauer, R. miR-17~92 cluster: Ups and downs in cancer and aging. Biogerontology 2010, 11, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weilner, S.; Schraml, E.; Redl, H.; Grillari-Voglauer, R.; Grillari, J. Secretion of microvesicular miRNAs in cellular and organismal aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2013, 48, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaumik, D.; Scott, G.K.; Schokrpur, S.; Patil, C.K.; Orjalo, A.V.; Rodier, F.; Lithgow, G.J.; Campisi, J. MicroRNAs miR-146a/b negatively modulate the senescence-associated inflammatory mediators IL-6 and IL-8. Aging 2009, 1, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprott, R.L. Biomarkers of aging and disease: introduction and definitions. Exp. Gerontol. 2010, 45, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weilner, S.; Schraml, E.; Wieser, M.; Messner, P.; Schneider, K.; Wassermann, K.; Micutkova, L.; Fortschegger, K.; Maier, A.B.; Westendorp, R.; et al. Secreted microvesicular miR-31 inhibits osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, B.; Sun, X.; Li, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Chen, X. Differentially expressed microRNAs in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles in young and older rats and their effect on tumor growth factor-β1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HK2 cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner-Gorzel, K.; Dempsey, E.; Milewska, M.; McGoldrick, A.; Toh, V.; Walsh, A.; Lindsay, S.; Gubbins, L.; Cannon, A.; Sharpe, D.; et al. Overexpression of the microRNA miR-433 promotes resistance to paclitaxel through the induction of cellular senescence in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Balkom, B.W.; de Jong, O.G.; Smits, M.; Brummelman, J.; den Ouden, K.; de Bree, P.M.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Pegtel, D.M.; Stoorvogel, W.; Würdinger, T.; et al. Endothelial cells require miR-214 to secrete exosomes that suppress senescence and induce angiogenesis in human and mouse endothelial cells. Blood 2013, 121, 3997–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machida, T.; Tomofuji, T.; Ekuni, D.; Maruyama, T.; Yoneda, T.; Kawabata, Y.; Mizuno, H.; Miyai, H.; Kunitomo, M.; Morita, M. MicroRNAs in salivary exosome as potential biomarkers of aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21294–21309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuhashi, M.; Taub, D.D.; Kapogiannis, D.; Eitan, E.; Zukley, L.; Mattson, M.P.; Ferrucci, L.; Schwartz, J.B.; Goetzl, E.J. Aging enhances release of exosomal cytokine mRNAs by Aβ1–42-stimulated macrophages. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 5141–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation: Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burnier, L.; Fontana, P.; Kwak, B.R.; Angelillo-Scherrer, A. Cell-derived microparticles in haemostasis and vascular medicine. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 101, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pienimaeki-Roemer, A.; Ruebsaamen, K.; Boettcher, A.; Orsó, E.; Scherer, M.; Liebisch, G.; Kilalic, D.; Ahrens, N.; Schmitz, G. Stored platelets alter glycerophospholipid and sphingolipid species, which are differentially transferred to newly released extracellular vesicles. Transfusion 2013, 53, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pienimaeki-Roemer, A.; Kuhlmann, K.; Böttcher, A.; Konovalova, T.; Black, A.; Orsó, E.; Liebisch, G.; Ahrens, M.; Eisenacher, M.; Meyer, H.E.; et al. Lipidomic and proteomic characterization of platelet extracellular vesicle subfractions from senescent platelets. Transfusion 2015, 55, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forest, A.; Pautas, E.; Ray, P.; Bonnet, D.; Verny, M.; Amabile, N.; Boulanger, C.; Riou, B.; Tedgui, A.; Mallat, Z.; et al. Circulating microparticles and procoagulant activity in elderly patients. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2010, 65, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.L.; Rak, J.W. Shedding of tissue factor (TF)-containing microparticles rather than alternatively spliced TF is the main source of TF activity released from human cancer cells. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 2, 2065–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlaftis, V.; Attard, C.; Summerhayes, R.; Monagle, P.; Ignjatovic, V. The microparticle-specific procoagulant phospholipid activity changes with age. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2014, 36, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosman, G.J.; Lasonder, E.; Groenen-Döpp, Y.A.; Willekens, F.L.; Were, J.M. The proteome of erythrocyte-derived microparticles from plasma: New clues for erythrocyte aging and vesiculation. J. Proteom. 2012, 76, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weilner, S.; Keider, V.; Winter, M.; Harreither, E.; Salzer, B.; Weiss, F.; Schraml, E.; Messner, P.; Pietschmann, P.; Hildner, F.; et al. Vesicular Galectin-3 levels decrease with donor age and contribute to the reduced osteo-inductive potential of human plasma derived extracellular vesicles. Aging 2016, 8, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urbanelli, L.; Buratta, S.; Sagini, K.; Tancini, B.; Emiliani, C. Extracellular Vesicles as New Players in Cellular Senescence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091408
Urbanelli L, Buratta S, Sagini K, Tancini B, Emiliani C. Extracellular Vesicles as New Players in Cellular Senescence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(9):1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091408
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrbanelli, Lorena, Sandra Buratta, Krizia Sagini, Brunella Tancini, and Carla Emiliani. 2016. "Extracellular Vesicles as New Players in Cellular Senescence" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 9: 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091408
APA StyleUrbanelli, L., Buratta, S., Sagini, K., Tancini, B., & Emiliani, C. (2016). Extracellular Vesicles as New Players in Cellular Senescence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(9), 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091408