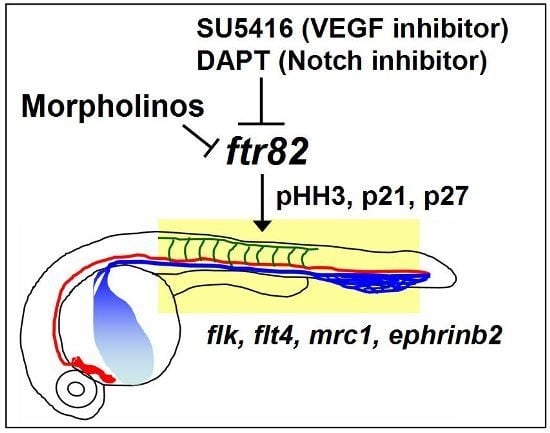
Ftr82 Is Critical for Vascular Patterning during Zebrafish Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Expression of ftr82 Is in Developing Vessels
2.2. Knockdown of ftr82 Causes Vascular Defects during Zebrafish Development
2.3. Loss of ftr82 Showed Edema, Circulation Defect, and Absent Parachordal Chain
2.4. Knockdown of ftr82 Can Be Rescued by Overexpression of ftr82
2.5. Knockdown of ftr82 Impairs the Growth of ISV Cells
2.6. Knockdown of ftr82 Affects the Expression of Vascular Markers
2.7. Regulation between ftr82 and VEGFR2-Notch Signaling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Zebrafish Line, Maintenance, and Chemicals Treatment
4.2. Embryo Morpholino and mRNA Injection
4.3. RNA Extraction, cDNA Preparation, and Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR (qPCR) Analysis
4.4. Morpholino Efficiency
4.5. Whole-Mount In Situ Hybridization and Cryosection
4.6. Imaging and Photo Processing
4.7. TUNEL Assay
4.8. Acridine Orange Staining
4.9. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting
4.10. Anti-Phospho Histone H3 Staining
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Risau, W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 1997, 386, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamik, A.; Wang, B.; Jain, M.K. Transcriptional regulators of angiogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 1936–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.H.; Alitalo, K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, C. Torturing a blood vessel. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kume, T. Specification of arterial, venous, and lymphatic endothelial cells during embryonic development. Histol. Histopathol. 2010, 25, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lawson, N.D.; Weinstein, B.M. In vivo imaging of embryonic vascular development using transgenic zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 2002, 248, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellertsdottir, E.; Lenard, A.; Blum, Y.; Krudewig, A.; Herwig, L.; Affolter, M.; Belting, H.G. Vascular morphogenesis in the zebrafish embryo. Dev. Biol. 2010, 341, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, S.; Chen, J.-N.; Garrity, D.; Fishman, M. Patterning of angiogenesis in the zebrafish embryo. Development 2002, 129, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Isogai, S.; Lawson, N.D.; Torrealday, S.; Horiguchi, M.; Weinstein, B.M. Angiogenic network formation in the developing vertebrate trunk. Development 2003, 130, 5281–5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendeville, H.; Winandy, M.; Manfroid, I.; Nivelles, O.; Motte, P.; Pasque, V.; Peers, B.; Struman, I.; Martial, J.A.; Voz, M.L. Zebrafish Sox7 and Sox18 function together to control arterial-venous identity. Dev. Biol. 2008, 317, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, N.D.; Scheer, N.; Pham, V.N.; Kim, C.H.; Chitnis, A.B.; Campos-Ortega, J.A.; Weinstein, B.M. Notch signaling is required for arterial-venous differentiation during embryonic vascular development. Development 2001, 128, 3675–3683. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhong, T.; Childs, S.; Liu, J.; Fishman, M. Gridlock signaling pathway fashions the first embryonic artery. Nature 2001, 414, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, N.D.; Vogel, A.M.; Weinstein, B.M. Sonic hedgehog and vascular endothelial growth factor act upstream of the notch pathway during arterial endothelial differentiation. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, R.E.; Childs, S. Mapping out arteries and veins. Sci. STKE 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Vazquez, J.; Kamei, M.; Weinstein, B.M. Molecular distinction between arteries and veins. Cell Tissue Res. 2003, 314, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, L.R.; Lin, F.J.; Lee, C.T.; DeMayo, F.J.; Tsai, M.J.; Tsai, S.Y. Suppression of notch signalling by the coup-tfii transcription factor regulates vein identity. Nature 2005, 435, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siekmann, A.F.; Covassin, L.; Lawson, N.D. Modulation of vegf signalling output by the notch pathway. BioEssays 2008, 30, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, H.; Golding, M.; Fruttiger, M.; Ruhrberg, C.; Lundkvist, A.; Abramsson, A.; Jeltsch, M.; Mitchell, C.; Alitalo, K.; Shima, D.; et al. Vegf guides angiogenic sprouting utilizing endothelial tip cell filopodia. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siekmann, A.F.; Lawson, N.D. Notch signalling limits angiogenic cell behaviour in developing zebrafish arteries. Nature 2007, 445, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, D.; Kim, J.; Hao, J.; Hong, C.; Bautch, V.; Jin, S. Distinct signalling pathways regulate sprouting angiogenesis from the dorsal aorta and the axial vein. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.D.; Kang, H.; Larrivee, B.; Lee, M.Y.; Mettlen, M.; Schmid, S.L.; Roman, B.L.; Qyang, Y.; Eichmann, A.; Jin, S.W. Context-dependent proangiogenic function of bone morphogenetic protein signaling is mediated by disabled homolog 2. Dev. Cell 2012, 23, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwada, T.; Fukuhara, S.; Terai, K.; Tanaka, T.; Wakayama, Y.; Ando, K.; Nakajima, H.; Fukui, H.; Yuge, S.; Saito, Y.; et al. β-catenin-dependent transcription is central to bmp-mediated formation of venous vessels. Development 2015, 142, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meroni, G.; Diez-Roux, G. Trim/rbcc, a novel class of “single protein ring finger” E3 ubiquitin ligases. BioEssays 2005, 27, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Aa, L.M.; Levraud, J.P.; Yahmi, M.; Lauret, E.; Briolat, V.; Herbomel, P.; Benmansour, A.; Boudinot, P. A large new subset of trim genes highly diversified by duplication and positive selection in teleost fish. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudinot, P.; van der Aa, L.M.; Jouneau, L.; Du Pasquier, L.; Pontarotti, P.; Briolat, V.; Benmansour, A.; Levraud, J.P. Origin and evolution of trim proteins: New insights from the complete trim repertoire of zebrafish and pufferfish. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yergeau, D.A.; Cornell, C.N.; Parker, S.K.; Zhou, Y.; Detrich, H.W., 3rd. Bloodthirsty, an RBCC/TRIM gene required for erythropoiesis in zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 2005, 283, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.L.; Lin, S.W.; Fang, H.C.; Chou, K.J.; Bee, Y.S.; Chu, T.H.; Chang, M.C.; Weng, W.T.; Wu, C.Y.; Cho, C.L.; et al. A novel poly-naphthol compound ST104P suppresses angiogenesis by attenuating matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression in endothelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 16611–16627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.F.; Wu, T.Y.; Mou, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.S.; Chen, C.L.; Wu, C.Y. Nr2f1b control venous specification and angiogenic patterning during zebrafish vascular development. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamont, R.E.; Wu, C.Y.; Ryu, J.R.; Vu, W.; Davari, P.; Sobering, R.E.; Kennedy, R.M.; Munsie, N.M.; Childs, S.J. The LIM-homeodomain transcription factor Islet2a promotes angioblast migration. Dev. Biol. 2016, 414, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Aa, L.M.; Jouneau, L.; Laplantine, E.; Bouchez, O.; Van Kemenade, L.; Boudinot, P. Fintrims, fish virus-inducible proteins with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 36, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, B.K.; Lim, H.S.; Song, R.; Yoon, M.J.; Yoon, K.J.; Moon, J.S.; Kim, Y.W.; Kwon, M.C.; Yoo, K.W.; Kong, M.P.; et al. Mind bomb 1 is essential for generating functional notch ligands to activate notch. Development 2005, 132, 3459–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; McGill, M.A.; Dermer, M.; Dho, S.E.; Wolting, C.D.; McGlade, C.J. Lnx functions as a ring type E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets the cell fate determinant numb for ubiquitin-dependent degradation. Embo J. 2002, 21, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi, N.; Helker, C.; Ehling, M.; Behrens, A.; Herzog, W.; Adams, R.H. Fbxw7 controls angiogenesis by regulating endothelial notch activity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhler, A.; Kustermann, M.; Bummer, T.; Rottbauer, W.; Sandri, M.; Just, S. Atrogin-1 deficiency leads to myopathy and heart failure in zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamont, R.E.; Vu, W.; Carter, A.D.; Serluca, F.C.; MacRae, C.A.; Childs, S. Hedgehog signaling via angiopoietin1 is required for developmental vascular stability. Mech. Dev. 2010, 127, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.J.; Chiu, C.C.; Chen, C.L.; Wang, W.D.; Wang, J.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Liu, W.; Chang, H.W.; Wu, C.Y. Nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group f member 1a (nr2f1a) is required for vascular development in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, B.L.; Pham, V.N.; Lawson, N.D.; Kulik, M.; Childs, S.; Lekven, A.C.; Garrity, D.M.; Moon, R.T.; Fishman, M.C.; Lechleider, R.J.; et al. Disruption of acvrl1 increases endothelial cell number in zebrafish cranial vessels. Development 2002, 129, 3009–3019. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Dong, L.; Ahn, J.; Dao, D.; Hammerschmidt, M.; Chen, J.N. Foxh1 negatively modulates flk1 gene expression and vascular formation in zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 2007, 304, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proulx, K.; Lu, A.; Sumanas, S. Cranial vasculature in zebrafish forms by angioblast cluster-derived angiogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2010, 348, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jowett, T.; Lettice, L. Whole-mount in situ hybridizations on zebrafish embryos using a mixture of digoxigenin- and fluorescein-labelled probes. Trends Genet. 1994, 10, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thisse, C.; Thisse, B. High-resolution in situ hybridization to whole-mount zebrafish embryos. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.S.; Proulx, K.; Rost, M.S.; Sumanas, S. Identification of vasculature-specific genes by microarray analysis of etsrp/etv2 overexpressing zebrafish embryos. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 1836–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, H.-W.; Wang, W.-D.; Chiu, C.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Wang, Y.-S.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Liu, W.; Tai, M.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Wu, C.-Y. Ftr82 Is Critical for Vascular Patterning during Zebrafish Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010156
Chang H-W, Wang W-D, Chiu C-C, Chen C-H, Wang Y-S, Chen Z-Y, Liu W, Tai M-H, Wen Z-H, Wu C-Y. Ftr82 Is Critical for Vascular Patterning during Zebrafish Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(1):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010156
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Hsueh-Wei, Wen-Der Wang, Chien-Chih Chiu, Chiou-Hua Chen, Yi-Shan Wang, Zih-Ying Chen, Wangta Liu, Ming-Hong Tai, Zhi-Hong Wen, and Chang-Yi Wu. 2017. "Ftr82 Is Critical for Vascular Patterning during Zebrafish Development" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 1: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010156
APA StyleChang, H.-W., Wang, W.-D., Chiu, C.-C., Chen, C.-H., Wang, Y.-S., Chen, Z.-Y., Liu, W., Tai, M.-H., Wen, Z.-H., & Wu, C.-Y. (2017). Ftr82 Is Critical for Vascular Patterning during Zebrafish Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(1), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010156