Label-Free Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Harmless and Pathogenic Strains of Infectious Microalgae, Prototheca spp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Label-Free Quantitative Proteomics
2.2. Differentially Expressed Proteins
2.3. Functional Annotation
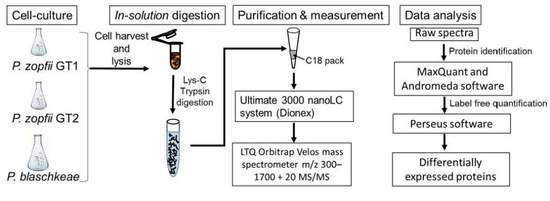
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cell Culture and Protein Extraction
3.2. In Solution Trypsin Digestion
3.3. Liquid Chromatography–Electrospray Ionization–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC–ESI–MS/MS)
3.4. Protein Identification
3.5. Differentially Expressed Proteins and Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roesler, U.; Scholz, H.; Hensel, A. Immunodiagnostic identification of dairy cows infected with Prototheca zopfii at various clinical stages and discrimination between infected and uninfected cows. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roesler, U.; Moller, A.; Hensel, A.; Baumann, D.; Truyen, U. Diversity within the current algal species Prototheca zopfii: A proposal for two Prototheca zopfii genotypes and description of a novel species, Prototheca blaschkeae sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, K.; Ooe, K.; Nagayama, H.; Makimura, K. Prototheca cutis sp. nov., a newly discovered pathogen of protothecosis isolated from inflamed human skin. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, J.R.; King, J.W.; Oberle, A.; Matsumoto, T.; Odaka, Y.; Fowler, M.; Pore, R.S.; Shahan, T.A.; Yin, L.J.; Sanusi, I.D. Protothecosis: Report of a case with 20-year follow-up, and review of previously published cases. Med. Mycol. 2012, 50, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, M.; Hirose, N.; Ishikawa, T.; Ikawa, Y.; Nishimura, K. Prototheca miyajii sp. nov., isolated from a patient with systemic protothecosis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1510–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenner, V.J.; Mackay, B.; King, T.; Barrs, V.R.D.; Irwin, P.; Abraham, L.; Swift, N.; Langer, N.; Bernays, M.; Hampson, E.; et al. Protothecosis in 17 Australian dogs and a review of the canine literature. Med. Mycol. 2007, 45, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Bergen, M.; Eidner, A.; Schmidt, F.; Murugaiyan, J.; Wirth, H.; Binder, H.; Maier, T.; Roesler, U. Identification of harmless and pathogenic algae of the genus Prototheca by MALDI-MS. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2009, 3, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugaiyan, J.; Ahrholdt, J.; Kowbel, V.; Roesler, U. Establishment of a matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry database for rapid identification of infectious achlorophyllous green micro-algae of the genus Prototheca. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Kano, R.; Sobukawa, H.; Ogawa, J.; Honda, Y.; Hosoi, Y.; Shibuya, H.; Sato, T.; Hasegawa, A.; Kamata, H. Experimental infection of bovine mammary gland with Prototheca zopfii genotype 1. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2011, 73, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Shahid, M.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Gu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zou, J.; Fanning, S.; Han, B. An Investigation of the innate immune response in bovine mammary epithelial cells challenged by Prototheca zopfii. Mycopathologia 2016, 181, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, A.; Truyen, U.; Roesler, U. Prototheca zopfii genotype 2: The causative agent of bovine protothecal mastitis? Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 120, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricchi, M.; de Cicco, C.; Buzzini, P.; Cammi, G.; Arrigoni, N.; Cammi, M.; Garbarino, C. First outbreak of bovine mastitis caused by Prototheca blaschkeae. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 997–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricchi, M.; Goretti, M.; Branda, E.; Cammi, G.; Garbarino, C.A.; Turchetti, B.; Moroni, P.; Arrigoni, N.; Buzzini, P. Molecular characterization of Prototheca strains isolated from Italian dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 4625–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobukawa, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kano, R.; Ito, T.; Suzuki, K.; Onozaki, M.; Hasegawa, A.; Kamata, H. Short communication: Molecular typing of Prototheca zopfii from bovine mastitis in Japan. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 4442–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osumi, T.; Kishimoto, Y.; Kano, R.; Maruyama, H.; Onozaki, M.; Makimura, K.; Ito, T.; Matsubara, K.; Hasegawa, A. Prototheca zopfii genotypes isolated from cow barns and bovine mastitis in Japan. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 131, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugaiyan, J.; Weise, C.; von Bergen, M.; Roesler, U. Two-dimensional proteome reference map of Prototheca zopfii revealed reduced metabolism and enhanced signal transduction as adaptation to an infectious life style. Proteomics 2013, 13, 2664–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.H.; Han, D.M.; Kudinha, T.; Kong, F.R.; Zhang, Q.Q. Isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation-based comparative proteomic analysis of human pathogenic Prototheca zopfii genotype 2 and environmental genotype 1 strains. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irrgang, A.; Weise, C.; Murugaiyan, J.; Roesler, U. Identification of immunodominant proteins of the microalgae Prototheca by proteomic analysis. New Microbes New Infect. 2015, 3, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irrgang, A.; Murugaiyan, J.; Weise, C.; Azab, W.; Roesler, U. Well-known surface and extracellular antigens of pathogenic microorganisms among the immunodominant proteins of the infectious microalgae Prototheca zopfii. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latosinska, A.; Vougas, K.; Makridakis, M.; Klein, J.; Mullen, W.; Abbas, M.; Stravodimos, K.; Katafigiotis, I.; Merseburger, A.S.; Zoidakis, J.; et al. Comparative analysis of label-free and 8-Plex iTRAQ approach for quantitative tissue proteomic analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, G.; Thippeswamy, H. Role of heat shock proteins in diseases and their therapeutic potential. Indian J. Microbiol. 2011, 51, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappsilber, J.; Ishihama, Y.; Mann, M. Stop and go extraction tips for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization, nanoelectrospray, and LC/MS sample pretreatment in proteomics. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Neuhauser, N.; Michalski, A.; Scheltema, R.A.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. Andromeda: A peptide search engine integrated into the MaxQuant environment. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Cox, J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2301–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Hein, M.Y.; Luber, C.A.; Paron, I.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Accurate proteome-wide label-free quantification by delayed normalization and maximal peptide ratio extraction, termed MaxLFQ. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 2513–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Szklarczyk, D.; Forslund, K.; Cook, H.; Heller, D.; Walter, M.C.; Rattei, T.; Mende, D.R.; Sunagawa, S.; Kuhn, M.; et al. eggNOG 4.5: A hierarchical orthology framework with improved functional annotations for eukaryotic, prokaryotic and viral sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D286–D293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doytchinova, I.A.; Flower, D.R. VaxiJen: A server for prediction of protective antigens, tumour antigens and subunit vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heberle, H.; Meirelles, G.V.; da Silva, F.R.; Telles, G.P.; Minghim, R. InteractiVenn: A web-based tool for the analysis of sets through Venn diagrams. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizcaino, J.A.; Cote, R.G.; Csordas, A.; Dianes, J.A.; Fabregat, A.; Foster, J.M.; Griss, J.; Alpi, E.; Birim, M.; Contell, J.; et al. The PRoteomics IDEntifications (PRIDE) database and associated tools: Status in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D1063–D1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| S. No | Acc. No. | Protein Names | Regulation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAG2021 (GT2) vs. SAG2063 (GT1) | SAG2064 (GT3) vs. SAG2063 (GT1) | SAG2021 (GT2) vs. SAG2064 (GT3) | |||
| 1 | A0A087SJM7 | 40S ribosomal protein S10 | (+) | (+) | |
| 2 | E1ZGA3 | 40S ribosomal protein S27 | (+) | ||
| 3 | E1ZQY4 | 40S ribosomal protein S5 | (+) | (+) | |
| 4 | A0A087SBU8 | 5-methyltetrahydropteroyltriglutamate-homocysteine methyltransferase | (+) | (+) | |
| 5 | A0A087SNV1 | 60S ribosomal protein L12-1 | (+) | (+) | |
| 6 | A0A087SKG6 | 60S ribosomal protein L6 | (+) | (+) | |
| 7 | A0A087SN43 | 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, decarboxylating (EC 1.1.1.44) | (+) | (+) | |
| 8 | A0A087SI38 | Acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase | (+) | (−) | |
| 9 | E1ZLA8 | Acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase (EC 6.2.1.1) | (−) | (−) | |
| 10 | A0A087SS91 | Aconitate hydratase, mitochondrial (Aconitase) (EC 4.2.1.3) | (+) | (−) | |
| 11 | A0A087SSM0 | Actin | (−) | (−) | |
| 12 | A0A087SF19 | Adenosylhomocysteinase (EC 3.3.1.1) | (−) | (+) | |
| 13 | A0A087SJV3 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 2 member B4, mitochondrial | (+) | (−) | (+) |
| 14 | A0A087SJX6 | Argininosuccinate synthase | (+) | (+) | |
| 15 | A0A087SBN0 | ATP synthase subunit beta (EC 3.6.3.14) (EC 4.2.1.24) | (+) | (−) | |
| 16 | A0A087SPA9 | Carbamoyl-phosphate synthase large chain | (+) | (+) | |
| 17 | A0A087SAK4 | Chaperone protein ClpB1 | (−) | ||
| 18 | A0A087SQR3 | Chaperonin CPN60, mitochondrial | (+) | (−) | |
| 19 | A0A087SCT6 | Citrate synthase | (−) | (−) | |
| 20 | A0A087SFG0 | Cysteine synthase, chloroplastic/chromoplastic | (−) | (−) | |
| 21 | A0A087SK74 | Elongation factor 1-α | (−) | (+) | |
| 22 | A0A087SE71 | Elongation factor Tu | (−) | ||
| 23 | A0A087S9L8 | Enolase | (−) | ||
| 24 | A0A087SHS8 | Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-10 | (+) | (+) | |
| 25 | A0A087SP16 | FK506-binding protein 1 | (−) | (−) | |
| 26 | E1ZTB0 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase (EC 4.1.2.13) | (+) | (+) | (−) |
| 27 | A0A087SG29 | Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (EC 5.3.1.9) | (−) | ||
| 28 | E1ZFZ5 | Glutamate dehydrogenase | (+) | (+) | |
| 29 | A0A087SBQ6 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, cytosolic | (+) | (−) | |
| 30 | A0A087SI84 | GTP-binding nuclear protein | (−) | ||
| 31 | A0A087SND2 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein, mitochondrial | (+) | (−) | |
| 32 | E1Z7R4 | Heat shock protein 70 | (+) | ||
| 33 | E1ZQV2 | Heat shock protein 70 | (−) | (−) | (−) |
| 34 | A0A087S9W3 | Histone H4 | (+) | ||
| 35 | A0A087SSF2 | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase 1 | (−) | ||
| 36 | A0A087SQ68 | Phosphate carrier protein, mitochondrial | (+) | (+) | |
| 37 | A0A087ST26 | Phosphoglycerate kinase (EC 2.7.2.3) | (+) | (−) | |
| 38 | E1Z5R3 | Putative uncharacterized protein | (−) | (+) | |
| 39 | E1ZCI5 | Putative uncharacterized protein | (+) | (+) | |
| 40 | E1ZD41 | Putative uncharacterized protein | (+) | ||
| 41 | E1ZG37 | Putative uncharacterized protein | (+) | (−) | (+) |
| 42 | E1ZL24 | Putative uncharacterized protein | (−) | (−) | |
| 43 | E1ZMD2 | Putative uncharacterized protein | (+) | ||
| 44 | E1ZRV3 | Putative uncharacterized protein | (+) | ||
| 45 | E1ZSM6 | Putative uncharacterized protein | (+) | ||
| 46 | A0A087SNN6 | Stress-induced-phosphoprotein 1 | (+) | (−) | |
| 47 | A0A087SIY9 | Succinyl-CoA ligase (ADP-forming) subunit α-1, mitochondrial | (+) | (−) | |
| 48 | E1ZJM1 | Tubulin β chain | (−) | (+) | |
| 49 | E1ZK88 | Ubiquitin | (−) | (−) | |
| 50 | A0A087SL21 | Ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40-2 | (−) | ||
| 51 | E1ZT42 | V-type H+ ATPase subunit A | (+) | (+) | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murugaiyan, J.; Eravci, M.; Weise, C.; Roesler, U. Label-Free Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Harmless and Pathogenic Strains of Infectious Microalgae, Prototheca spp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010059
Murugaiyan J, Eravci M, Weise C, Roesler U. Label-Free Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Harmless and Pathogenic Strains of Infectious Microalgae, Prototheca spp. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(1):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010059
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurugaiyan, Jayaseelan, Murat Eravci, Christoph Weise, and Uwe Roesler. 2017. "Label-Free Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Harmless and Pathogenic Strains of Infectious Microalgae, Prototheca spp." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 1: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010059
APA StyleMurugaiyan, J., Eravci, M., Weise, C., & Roesler, U. (2017). Label-Free Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Harmless and Pathogenic Strains of Infectious Microalgae, Prototheca spp. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(1), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010059