Biomarkers for Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with High Salt Intake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Association of High-Salt Diet with Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease in Hypertensive Patients and Animals
2.1. Association of High-Salt Diet with Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Patients
2.2. Association of High-Salt Diet with the Kidney in Hypertensive Patients
2.3. Association of High-Salt Diet with Blood Pressure and the Kidney in an Experimental Hypertensive Model
3. Association of High-Salt Diet with Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease in Normotensive Individuals and Animals
3.1. Association of High-Salt Diet with Blood Pressure in Normotensive Individuals
3.2. Association of High-Salt Diet with the Kidney in Normotensive Individuals
3.3. Association of High-Salt Diet with BP and the Kidney in Experimental Normotensive Model
4. Biomarkers of Salt-Induced Damages in the Progression to Chronic Kidney Disease
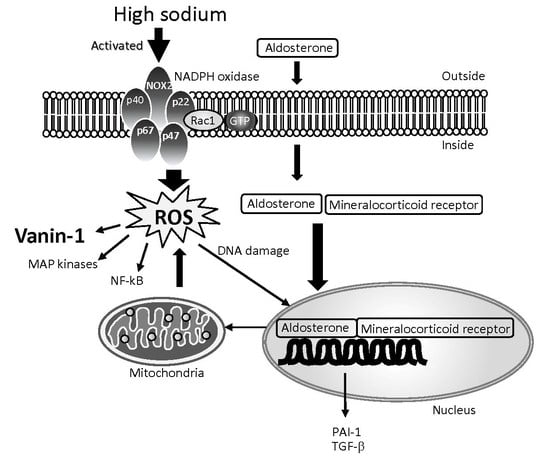
4.1. Characteristics of Damage under High Salt Intake and Its Mechanism
4.2. Biomarkers of Damage under High Salt Intake
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BP | Blood pressure |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| Kim-1 | Kidney injury molecule-1 |
| NAG | N-Acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase |
| NGAL | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin |
| RAS | Renin-angiotensin system |
| ROS | Reactive oxidative species |
| SHR | Spontaneously hypertensive rats |
| WKY | Wistar kyoto rats |
References
- Mills, K.T.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Bundy, J.D.; Chen, C.S.; Kelly, T.N.; Chen, J.; He, J. A systematic analysis of worldwide population-based data on the global burden of chronic kidney disease in 2010. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregg, E.W.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Burrows, N.R.; Ali, M.K.; Rolka, D.; Williams, D.E.; Geiss, L. Changes in diabetes-related complications in the United States, 1990–2010. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, E.J.; Bauer, J.D.; Hawley, C.M.; Isbel, N.M.; Stowasser, M.; Johnson, D.W.; Campbell, K.L. A randomized trial of dietary sodium restriction in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 2096–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inker, L.A.; Astor, B.C.; Fox, C.H.; Isakova, T.; Lash, J.P.; Peralta, C.A.; Kurella Tamura, M.; Feldman, H.I. KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, Y.; Ohta, K.; Ishizuka, A.; Hayashi, S.; Kishida, M.; Iwashima, Y.; Yoshihara, F.; Nakamura, S.; Kawano, Y. Trends in the awareness of salt restriction and actual salt intake in hypertensive patients at a hypertension clinic and general clinic: A one-year follow-up study. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2015, 37, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Delea, C.S.; Bartter, F.C.; Smith, H. The effect of high-sodium and low-sodium intakes on blood pressure and other related variables in human subjects with idiopathic hypertension. Am. J. Med. 1978, 64, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, H.; Schmelz, E.; Marrugat, J. Relationship between diet and blood pressure in a representative Mediterranean population. Eur. J. Nutr. 2002, 41, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacGregor, G.A.; Markandu, N.D.; Sagnella, G.A.; Singer, D.R.; Cappuccio, F.P. Double-blind study of three sodium intakes and long-term effects of sodium restriction in essential hypertension. Lancet 1989, 2, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGregor, G.A. Salt: Blood pressure, the kidney, and other harmful effects. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1998, 13, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, F.M.; Svetkey, L.P.; Vollmer, W.M.; Appel, L.J.; Bray, G.A.; Harsha, D.; Obarzanek, E.; Conlin, P.R.; Miller, E.R.; Simons-Morton, D.G.; et al. Effects on blood pressure of reduced dietary sodium and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. DASH-Sodium Collaborative Research Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titze, J.; Dahlmann, A.; Lerchl, K.; Kopp, C.; Rakova, N.; Schroder, A.; Luft, F.C. Spooky sodium balance. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machnik, A.; Neuhofer, W.; Jantsch, J.; Dahlmann, A.; Tammela, T.; Machura, K.; Park, J.K.; Beck, F.X.; Muller, D.N.; Derer, W.; et al. Macrophages regulate salt-dependent volume and blood pressure by a vascular endothelial growth factor-C-dependent buffering mechanism. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedler, B.; Brier, M.E.; Wiersbitzky, M.; Gruska, S.; Wolf, E.; Kallwellis, R.; Aronoff, G.R.; Luft, F.C. Sodium kinetics in salt-sensitive and salt-resistant normotensive and hypertensive subjects. J. Hypertens. 1992, 10, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, S.R.; Li, S.Y. Prevalence of severe obesity and its association with elevated blood pressure among children and adolescents in Shandong, China. Blood Press. Monit. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzati, M.; Lopez, A.D.; Rodgers, A.; Vander Hoorn, S.; Murray, C.J. Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet 2002, 360, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration. Blood pressure-lowering treatment based on cardiovascular risk: A meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet 2014, 384, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jula, A.M.; Karanko, H.M. Effects on left ventricular hypertrophy of long-term nonpharmacological treatment with sodium restriction in mild-to-moderate essential hypertension. Circulation 1994, 89, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Cailar, G.; Ribstein, J.; Mimran, A. Dietary sodium and target organ damage in essential hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2002, 15, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, T.; Kawamori, R.; Miyazaki, S.; Teramukai, S.; Shirayama, M.; Hiramatsu, K.; Kobayashi, F. Relationship between achieved blood pressure, dietary habits and cardiovascular disease in hypertensive patients treated with olmesartan: The OMEGA study. Hypertens. Res. 2012, 35, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, Y.; Tsuchihashi, T.; Kiyohara, K.; Oniki, H. High salt intake promotes a decline in renal function in hypertensive patients: A 10-year observational study. Hypertens. Res. 2013, 36, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappuccio, F.P.; Markandu, N.D.; Carney, C.; Sagnella, G.A.; MacGregor, G.A. Double-blind randomised trial of modest salt restriction in older people. Lancet 1997, 350, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengel, D.R.; Hogikyan, R.V.; Brown, M.D.; Glickman, S.G.; Supiano, M.A. Insulin sensitivity is associated with blood pressure response to sodium in older hypertensives. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, E403–E409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sowers, J.R.; Zemel, M.B.; Zemel, P.; Beck, F.W.; Walsh, M.F.; Zawada, E.T. Salt sensitivity in blacks. Salt intake and natriuretic substances. Hypertension 1988, 12, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechere-Bertschi, A.; Burnier, M. Female sex hormones, salt, and blood pressure regulation. Am. J. Hypertens. 2004, 17, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, M.R.; Dengel, D.R.; Behrens, M.T.; Goldberg, A.P. Salt-induced increases in systolic blood pressure affect renal hemodynamics and proteinuria. Hypertension 1995, 25, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, R.; Ranches, G.; Schafferer, S.; Lukasser, M.; Rudnicki, M.; Mayer, G.; Huttenhofer, A. Identification of urinary exosomal noncoding RNAs as novel biomarkers in chronic kidney disease. RNA 2017, 23, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohlich, E.D.; Varagic, J. The role of sodium in hypertension is more complex than simply elevating arterial pressure. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 2004, 1, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matavelli, L.C.; Zhou, X.; Varagic, J.; Susic, D.; Frohlich, E.D. Salt loading produces severe renal hemodynamic dysfunction independent of arterial pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 292, H814–H819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varagic, J.; Frohlich, E.D.; Susic, D.; Ahn, J.; Matavelli, L.; Lopez, B.; Diez, J. AT1 receptor antagonism attenuates target organ effects of salt excess in SHRs without affecting pressure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 294, H853–H858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonios, T.F.; MacGregor, G.A. Salt—More adverse effects. Lancet 1996, 348, 250–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.C.; Burrell, L.M.; Black, M.J.; Wu, L.L.; Dilley, R.J.; Cooper, M.E.; Johnston, C.I. Salt induces myocardial and renal fibrosis in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Circulation 1998, 98, 2621–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, S.C.; Deng, A.; Wead, L.; Richter, K.; Blantz, R.C.; Vallon, V. An unexpected role for angiotensin II in the link between dietary salt and proximal reabsorption. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susic, D.; Frohlich, E.D.; Kobori, H.; Shao, W.; Seth, D.; Navar, L.G. Salt-induced renal injury in SHRs is mediated by AT1 receptor activation. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitiyakara, C.; Chabrashvili, T.; Chen, Y.; Blau, J.; Karber, A.; Aslam, S.; Welch, W.J.; Wilcox, C.S. Salt intake, oxidative stress, and renal expression of NADPH oxidase and superoxide dismutase. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, E.Y.; Luo, Z.; Onozato, M.L.; Rudolph, E.H.; Solis, G.; Jose, P.A.; Wellstein, A.; Aslam, S.; Quinn, M.T.; Griendling, K.; et al. Effects of the antioxidant drug tempol on renal oxygenation in mice with reduced renal mass. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2012, 303, F64–F74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopkan, L.; Majid, D.S. Superoxide contributes to development of salt sensitivity and hypertension induced by nitric oxide deficiency. Hypertension 2005, 46, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majid, D.S.; Kopkan, L. Nitric oxide and superoxide interactions in the kidney and their implication in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 34, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Li, A.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Su, Z.; Bin, W.; Wilcox, C.S.; Hou, F.F. A Salt-Induced Reno-Cerebral Reflex Activates Renin-Angiotensin Systems and Promotes CKD Progression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1619–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiq, K.; Nishiyama, A.; Konishi, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Kitabayashi, C.; Kohno, M.; Masaki, T.; Mori, H.; Kobori, H.; Imanishi, M. Regression of glomerular and tubulointerstitial injuries by dietary salt reduction with combination therapy of angiotensin II receptor blocker and calcium channel blocker in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstyn, P.; Hornall, D.; Watchorn, C. Sodium and potassium intake and blood pressure. Br. Med. J. 1980, 281, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parfrey, P.S.; Markandu, N.D.; Roulston, J.E.; Jones, B.E.; Jones, J.C.; MacGregor, G.A. Relation between arterial pressure, dietary sodium intake, and renin system in essential hypertension. Br. Med. J. 1981, 283, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, A.S.; Macginley, R.J.; Schollum, J.B.; Williams, S.M.; Sutherland, W.H.; Mann, J.I.; Walker, R.J. Dietary sodium loading in normotensive healthy volunteers does not increase arterial vascular reactivity or blood pressure. Nephrology 2012, 17, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luft, F.C.; Grim, C.E.; Fineberg, N.; Weinberger, M.C. Effects of volume expansion and contraction in normotensive whites, blacks, and subjects of different ages. Circulation 1979, 59, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffman, T.M. The inextricable role of the kidney in hypertension. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2341–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuna, R.; Martinez-de-la-Maza, L.; Ponce-Coria, J.; Vazquez, N.; Ortal-Vite, P.; Pacheco-Alvarez, D.; Bobadilla, N.A.; Gamba, G. Rare mutations in SLC12A1 and SLC12A3 protect against hypertension by reducing the activity of renal salt cotransporters. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washino, S.; Hosohata, K.; Jin, D.; Takai, S.; Miyagawa, T. Early urinary biomarkers of renal tubular damage by a high-salt intake independent of blood pressure in normotensive rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Fellner, R.C.; Cook, A.K.; O'Connor, P.M.; Zhang, S.; Pollock, D.M.; Inscho, E.W. High-salt diet blunts renal autoregulation by a reactive oxygen species-dependent mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2014, 307, F33–F40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosohata, K.; Yoshioka, D.; Tanaka, A.; Ando, H.; Fujimura, A. Early urinary biomarkers for renal tubular damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats on a high salt intake. Hypertens. Res. 2016, 39, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, E.; Brady, H.R. Role of tubule epithelial cells in the pathogenesis of tubulointerstitial fibrosis induced by glomerular disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 1998, 7, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, K.A. Tubulointerstitial changes as a major determinant in the progression of renal damage. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1992, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy-Chaudhury, P.; Wu, B.; King, G.; Campbell, M.; Macleod, A.M.; Haites, N.E.; Simpson, J.G.; Power, D.A. Adhesion molecule interactions in human glomerulonephritis: Importance of the tubulointerstitium. Kidney Int. 1996, 49, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlondorff, D.; Nelson, P.J.; Luckow, B.; Banas, B. Chemokines and renal disease. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varagic, J.; Ahmad, S.; Voncannon, J.L.; Moniwa, N.; Simington, S.W., Jr.; Brosnihan, B.K.; Gallagher, P.E.; Habibi, J.; Sowers, J.R.; Ferrario, C.M. Nebivolol reduces cardiac angiotensin II, associated oxidative stress and fibrosis but not arterial pressure in salt-loaded spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 1766–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokkunuri, I.; Chugh, G.; Rizvi, I.; Asghar, M. Age-related hypertension and salt sensitivity are associated with unique cortico-medullary distribution of D1R, AT1R, and NADPH-oxidase in FBN rats. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2015, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hordijk, P.L. Regulation of NADPH oxidases: The role of Rac proteins. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, G.B.; Garvin, J.L. Rac1 mediates NaCl-induced superoxide generation in the thick ascending limb. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2010, 298, F421–F425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Circu, M.L.; Aw, T.Y. Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.W.; Wang, C.Y.; Jou, Y.J.; Yang, T.C.; Huang, S.H.; Wan, L.; Lin, Y.J.; Lin, C.W. SARS coronavirus papain-like protease induces Egr-1-dependent up-regulation of TGF-beta1 via ROS/p38 MAPK/STAT3 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Luo, N.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Bu, H.; Xu, G.; Yan, Y.; Che, X.; Jiao, Z.; Zhao, T.; et al. Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates chronic renal failure in rats by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation through ROS/MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimura, T.; Hung, C.C.; Yang, S.A.; Stevens, J.L.; Bonventre, J.V. Kidney injury molecule-1: A tissue and urinary biomarker for nephrotoxicant-induced renal injury. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2004, 286, F552–F563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Mori, K.; Ma, Q.; Kelly, C.; Barasch, J.; Devarajan, P. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: A novel early urinary biomarker for cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Am. J. Nephrol. 2004, 24, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosohata, K.; Ando, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Fujimura, A. Vanin-1: A potential biomarker for nephrotoxicant-induced renal injury. Toxicology 2011, 290, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosohata, K.; Ando, H.; Fujimura, A. Urinary vanin-1 as a novel biomarker for early detection of drug-induced acute kidney injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurrand-Lions, M.; Galland, F.; Bazin, H.; Zakharyev, V.M.; Imhof, B.A.; Naquet, P. Vanin-1, a novel GPI-linked perivascular molecule involved in thymus homing. Immunity 1996, 5, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitari, G.; Malergue, F.; Martin, F.; Philippe, J.M.; Massucci, M.T.; Chabret, C.; Maras, B.; Dupre, S.; Naquet, P.; Galland, F. Pantetheinase activity of membrane-bound Vanin-1: Lack of free cysteamine in tissues of Vanin-1 deficient mice. FEBS Lett. 2000, 483, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghaei, F.; Karimi, I.; Jouyban, A.; Samini, M. Effects of captopril on the cysteamine-induced duodenal ulcer in the rat. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosohata, K. Role of oxidative stress in drug-induced kidney injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hosohata, K. Biomarkers for Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with High Salt Intake. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102080
Hosohata K. Biomarkers for Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with High Salt Intake. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(10):2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102080
Chicago/Turabian StyleHosohata, Keiko. 2017. "Biomarkers for Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with High Salt Intake" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 10: 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102080
APA StyleHosohata, K. (2017). Biomarkers for Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with High Salt Intake. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(10), 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102080