Altered Synaptic Membrane Retrieval after Strong Stimulation of Cerebellar Granule Neurons in Cyclic GMP-Dependent Protein Kinase II (cGKII) Knockout Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Efficient SV Recycling in Boutons from Mice Cerebellar Granule Cells after Strong and Sustained Stimulation
2.2. Electron Microscopy Reveals Differences between Synapses from Wild Type and cGKII KO Mice
2.3. Altered Membrane Recycling in cGKII KO Neurons
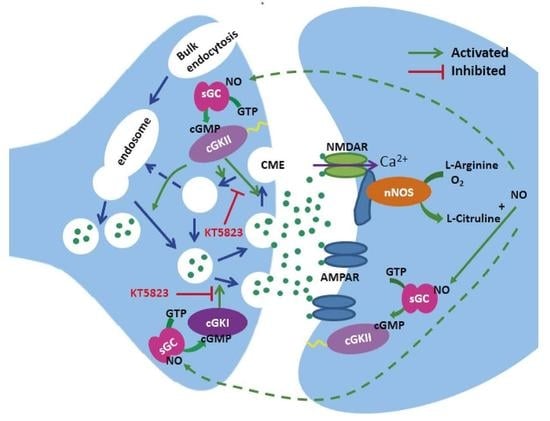
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Cell Transfection
4.3. Western Blotting
4.4. Vesicle Recycling (FM1-43)
4.5. Analysis of FM1-43
4.6. vGlut1-pHluorin (vGlut1-pH) Imaging
4.7. Electron Microscopy (EM)
4.8. KT5823 Treatment
4.9. Statistical Analyses
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADBE | Activity-dependent bulk endocytosis |
| Akt | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase activated serine/threonine kinase |
| ADBE | Activity-dependent bulk endocytosis |
| AMPAR | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor |
| AP-1/AP-3 | Adaptor protein 1 and 3 complex |
| AP-2 | Adaptor protein 2 complex |
| AP3B2 | AP-3 complex beta-2 subunit |
| AZ | Sctive zone |
| cGKI | Cyclic GMP dependent protein kinase type I |
| cGKII | Cyclic GMP dependent protein kinase type II |
| DIV | Days in vitro |
| EM | Electron Microscopy |
| FM1-43 | N-(3-Triethylammoniumpropyl)-4-(4-(Dibutylamino) Styryl) Pyridinium Dibromide |
| GSK3 | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 |
| HBM | Hepes buffered medium |
| KO | Knock out |
| N.D | No difference |
| NMDAR | N-Methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor |
| P7 | Seven days postnatal |
| pCAGGs | CAG promoter is a strong synthetic promoter frequently used to drive high levels of gene expression in mammalian expression vectors |
| sGC | Soluble guanylyl cyclase |
| SV | Synaptic vesicle |
| vGluT1-pH | pH-sensitive GFP tagged to the luminal domain of the vesicular glutamate transporter 1 |
References
- Contestabile, A.; Ciani, E. Role of nitric oxide in the regulation of neuronal proliferation, survival and differentiation. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciani, E.; Calvanese, V.; Crochemore, C.; Bartesaghi, R.; Contestabile, A. Proliferation of cerebellar precursor cells is negatively regulated by nitric oxide in newborn rat. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 3161–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Jimenez, M.E.; Bartolome-Martin, D.; Sanchez-Prieto, J.; Torres, M. Suppression of guanylyl cyclase (β1 subunit) expression impairs neurite outgrowth and synapse maturation in cultured cerebellar granule cells. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dell, T.J.; Hawkins, R.D.; Kandel, E.R.; Arancio, O. Tests of the roles of two diffusible substances in long-term potentiation: Evidence for nitric oxide as a possible early retrograde messenger. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 11285–11289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.G.; Lu, F.M.; Jin, I.; Udo, H.; Kandel, E.R.; de Vente, J.; Walter, U.; Lohmann, S.M.; Hawkins, R.D.; Antonova, I. Presynaptic and postsynaptic roles of NO, cGK, and RhoA in long-lasting potentiation and aggregation of synaptic proteins. Neuron 2005, 45, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, K.T.; Monsey, M.S.; Wu, M.S.; Schafe, G.E. Synaptic plasticity and NO-cGMP-PKG signaling regulate pre- and postsynaptic alterations at rat lateral amygdala synapses following fear conditioning. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serulle, Y.; Arancio, O.; Ziff, E.B. A role for cGMP-dependent protein kinase II in AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Channels 2008, 2, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incontro, S.; Ramirez-Franco, J.; Sanchez-Prieto, J.; Torres, M. Membrane depolarization regulates AMPA receptor subunit expression in cerebellar granule cells in culture. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnayaka, A.; Marra, V.; Bush, D.; Burden, J.J.; Branco, T.; Staras, K. Recruitment of resting vesicles into recycling pools supports NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic potentiation in cultured hippocampal neurons. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1585–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheva, K.D.; Buchanan, J.; Holz, R.W.; Smith, S.J. Retrograde regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis and recycling. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, A.M.; Giniatullin, A.R.; Sitdikova, G.F.; Zefirov, A.L. The role of cGMP-dependent signaling pathway in synaptic vesicle cycle at the frog motor nerve terminals. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 13216–13222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegenge, M.A.; Stern, M.; Bicker, G. Nitric oxide and cyclic nucleotide signal transduction modulates synaptic vesicle turnover in human model neurons. J. Neurochem. 2009, 111, 1434–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, K.; Nakanishi, S.; Takagi, H.; Taoufiq, Z.; Takahashi, T. Maturation of a PKG-dependent retrograde mechanism for exoendocytic coupling of synaptic vesicles. Neuron 2012, 74, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Milburn, P.J.; Hanna, B.T.; Graham, M.E.; Rostas, J.A.; Robinson, P.J. Phosphorylation of septin 3 on Ser-91 by cGMP-dependent protein kinase-I in nerve terminals. Biochem. J. 2004, 381, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhler, M.D. Cloning and expression of a novel cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase from mouse brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 13586–13591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wincott, C.M.; Kim, S.; Titcombe, R.F.; Tukey, D.S.; Girma, H.K.; Pick, J.E.; Devito, L.M.; Hofmann, F.; Hoeffer, C.; Ziff, E.B. Spatial memory deficits and motor coordination facilitation in cGMP-dependent protein kinase type II-deficient mice. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2013, 99, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Titcombe, R.F.; Zhang, H.; Khatri, L.; Girma, H.K.; Hofmann, F.; Arancio, O.; Ziff, E.B. Network compensation of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase II knockout in the hippocampus by Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3122–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado-Alsina, A.; Ramirez-Franco, J.; Sanchez-Prieto, J.; Torres, M. The regulation of synaptic vesicle recycling by cGMP-dependent protein kinase type II in cerebellar granule cells under strong and sustained stimulation. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 8788–8799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kan, P.L.; Gibson, A.R.; Houk, J.C. Movement-related inputs to intermediate cerebellum of the monkey. J. Neurophysiol. 1993, 69, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klingauf, J.; Kavalali, E.T.; Tsien, R.W. Kinetics and regulation of fast endocytosis at hippocampal synapses. Nature 1998, 394, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyle, J.L.; Kavalali, E.T.; Piedras-Renteria, E.S.; Tsien, R.W. Rapid reuse of readily releasable pool vesicles at hippocampal synapses. Neuron 2000, 28, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozhayeva, M.G.; Sara, Y.; Liu, X.; Kavalali, E.T. Development of vesicle pools during maturation of hippocampal synapses. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bartolome-Martin, D.; Ramirez-Franco, J.; Castro, E.; Sanchez-Prieto, J.; Torres, M. Efficient synaptic vesicle recycling after intense exocytosis concomitant with the accumulation of non-releasable endosomes at early developmental stages. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, P.Y.; Marrs, J.; Ryan, T.A. Vesicular glutamate transporter 1 orchestrates recruitment of other synaptic vesicle cargo proteins during synaptic vesicle recycling. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 22593–22601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, V.N.; Sejnowski, T.J.; Stevens, C.F. Heterogeneous release properties of visualized individual hippocampal synapses. Neuron 1997, 18, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trommershauser, J.; Schneggenburger, R.; Zippelius, A.; Neher, E. Heterogeneous presynaptic release probabilities: Functional relevance for short-term plasticity. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenowitz, S.D.; Regehr, W.G. Reliability and heterogeneity of calcium signaling at single presynaptic boutons of cerebellar granule cells. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 7888–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Wu, X.S.; Xu, J.; McNeil, B.D.; Pang, Z.P.; Yang, W.; Bai, L.; Qadri, S.; Molkentin, J.D.; Yue, D.T.; et al. The role of calcium/calmodulin-activated calcineurin in rapid and slow endocytosis at central synapses. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 11838–11847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armbruster, M.; Messa, M.; Ferguson, S.M.; De Camilli, P.; Ryan, T.A. Dynamin phosphorylation controls optimization of endocytosis for brief action potential bursts. Elife 2013, 2, e00845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.S.; Wu, L.G. The yin and yang of calcium effects on synaptic vesicle endocytosis. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 2652–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramperez, A.; Sanchez-Prieto, J.; Torres, M. Brefeldin A sensitive mechanisms contribute to endocytotic membrane retrieval and vesicle recycling in cerebellar granule cells. J. Neurochem. 2017, 141, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saviane, C.; Silver, R.A. Fast vesicle reloading and a large pool sustain high bandwidth transmission at a central synapse. Nature 2006, 439, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Steinmetz, L.M.; Gu, X.; Scharfe, C.; Davis, R.W.; Li, W.H. Role of duplicate genes in genetic robustness against null mutations. Nature 2003, 421, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado, S.; Sanchez-Prieto, J.; Torres, M. Elements of the nitric oxide/cGMP pathway expressed in cerebellar granule cells: Biochemical and functional characterisation. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlossmann, J.; Desch, M. cGK substrates. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 163–193. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Cho, O.Y.; Kim, J.A.; Chang, S. Endosome-mediated endocytic mechanism replenishes the majority of synaptic vesicles at mature CNS synapses in an activity-dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Lan, T.; Wang, Y.; Qian, H. Type II cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits epidermal growth factor-induced phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt signal transduction in gastric cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smillie, K.J.; Cousin, M.A. Akt/PKB controls the activity-dependent bulk endocytosis of synaptic vesicles. Traffic 2012, 13, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greengard, P.; Valtorta, F.; Czernik, A.J.; Benfenati, F. Synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins and regulation of synaptic function. Science 1993, 259, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bykhovskaia, M. Synapsin regulation of vesicle organization and functional pools. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.S.; McNeil, B.D.; Xu, J.; Fan, J.; Xue, L.; Melicoff, E.; Adachi, R.; Bai, L.; Wu, L.G. Ca2+ and calmodulin initiate all forms of endocytosis during depolarization at a nerve terminal. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wincott, C.M.; Abera, S.; Vunck, S.A.; Tirko, N.; Choi, Y.; Titcombe, R.F.; Antoine, S.O.; Tukey, D.S.; DeVito, L.M.; Hofmann, F.; et al. cGMP-dependent protein kinase type II knockout mice exhibit working memory impairments, decreased repetitive behavior, and increased anxiety-like traits. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2014, 114, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, A.; Aszodi, A.; Seidler, U.; Ruth, P.; Hofmann, F.; Fassler, R. Intestinal secretory defects and dwarfism in mice lacking cGMP-dependent protein kinase II. Science 1996, 274, 2082–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, J.R.; Randall, A.D. Voltage-dependent deactivation and desensitization of GABA responses in cultured murine cerebellar granule cells. J. Physiol. 1998, 506, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado, S.; Sanchez-Prieto, J.; Torres, M. Differential expression of NO-sensitive guanylyl cyclase subunits during the development of rat cerebellar granule cells: Regulation via N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3165–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsman, J.B.; Krueger, S.R.; Fitzsimonds, R.M. Automated criteria-based selection and analysis of fluorescent synaptic puncta. J. Neurosci. Methods 2006, 152, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miesenbock, G.; De Angelis, D.A.; Rothman, J.E. Visualizing secretion and synaptic transmission with pH-sensitive green fluorescent proteins. Nature 1998, 394, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atluri, P.P.; Ryan, T.A. The kinetics of synaptic vesicle reacidification at hippocampal nerve terminals. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granseth, B.; Odermatt, B.; Royle, S.J.; Lagnado, L. Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is the dominant mechanism of vesicle retrieval at hippocampal synapses. Neuron 2006, 51, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, J.; Ryan, T.A. Single-vesicle imaging reveals that synaptic vesicle exocytosis and endocytosis are coupled by a single stochastic mode. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20576–20581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Forero, D.; Montero, F.; Garcia-Morales, V.; Dominguez, G.; Gomez-Perez, L.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Moreno-Lopez, B. Endogenous Rho-kinase signaling maintains synaptic strength by stabilizing the size of the readily releasable pool of synaptic vesicles. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, K.S.; Makhlouf, G.M. Interaction of cA-kinase and cG-kinase in mediating relaxation of dispersed smooth muscle cells. Am J. Physiol. 1995, 268, C171–C180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.B.; Ruth, P.; Schlossmann, J.; Hofmann, F.; Korth, M. Protein phosphatase 2A is essential for the activation of Ca2+-activated K+ currents by cGMP-dependent protein kinase in tracheal smooth muscle and Chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 19760–19767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, R.; Torres, M. Prolonged exposure of chromaffin cells to nitric oxide down-regulates the activity of soluble guanylyl cyclase and corresponding mRNA and protein levels. BMC Biochem. 2002, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podda, M.V.; Piacentini, R.; Barbati, S.A.; Mastrodonato, A.; Puzzo, D.; D’Ascenzo, M.; Leone, L.; Grassi, C. Role of cyclic nucleotide-gated channels in the modulation of mouse hippocampal neurogenesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Wild Type | cGKII KO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k (s) | τ (s) | k (s) | τ (s) | |
| Trace A | 6.21 ± 0.51 | 7.59 ± 0.31 | 5.99 ± 0.30 | 10.92 ± 0.55 |
| Trace B | 2.80 ± 0.13 | 22.07 ± 0.93 | 6.66 ± 0.23 p < 0.0001 | 19.13 ± 0.83 |
| Trace C | 7.30 ± 0.73 | 6.93 ± 0.62 | 7.51 ± 0.74 | 15.44 ± 2.61 p = 0.0001 |
| Trace D | 5.84 ± 0.15 | 7.21 ± 0.36 | 5.69 ± 0.18 | 17.50 ± 0.76 p < 0.0001 |
| Wild Type | cGKII KO | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k (s) | τ1 (s) | τ2 (s) | k (s) | τ1 (s) | τ2 (s) | |
| Profile A | 5.42 ± 0.23 | 14.74 ± 2.40 | 10.66 ± 0.40 | 5.58 ± 0.16 | 16.94 ± 1.54 | 10.22 ± 0.70 |
| Profile B | 5.07 ± 0.20 | 57.29 ± 7.16 | 22.21 ± 1.52 | 5.17 ± 0.13 | 38.05 ± 8.70 (p = 0.00511) | 10.69 ± 0.59 (p < 0.0001) |
| Profile C | 5.13 ± 0.19 | 18.76 ± 1.06 | 5.75 ± 0.12 | 11.76 ± 0.68 (p < 0.0001) | ||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Collado-Alsina, A.; Hofmann, F.; Sánchez-Prieto, J.; Torres, M. Altered Synaptic Membrane Retrieval after Strong Stimulation of Cerebellar Granule Neurons in Cyclic GMP-Dependent Protein Kinase II (cGKII) Knockout Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112281
Collado-Alsina A, Hofmann F, Sánchez-Prieto J, Torres M. Altered Synaptic Membrane Retrieval after Strong Stimulation of Cerebellar Granule Neurons in Cyclic GMP-Dependent Protein Kinase II (cGKII) Knockout Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112281
Chicago/Turabian StyleCollado-Alsina, Andrea, Franz Hofmann, José Sánchez-Prieto, and Magdalena Torres. 2017. "Altered Synaptic Membrane Retrieval after Strong Stimulation of Cerebellar Granule Neurons in Cyclic GMP-Dependent Protein Kinase II (cGKII) Knockout Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112281
APA StyleCollado-Alsina, A., Hofmann, F., Sánchez-Prieto, J., & Torres, M. (2017). Altered Synaptic Membrane Retrieval after Strong Stimulation of Cerebellar Granule Neurons in Cyclic GMP-Dependent Protein Kinase II (cGKII) Knockout Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112281