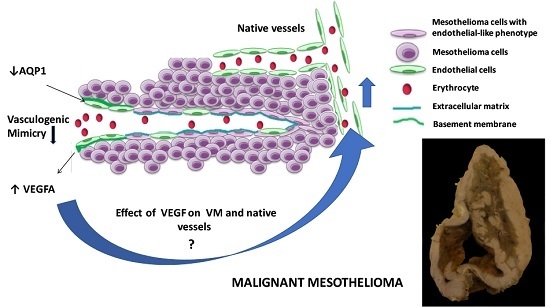
The Effect of Aquaporin 1-Inhibition on Vasculogenic Mimicry in Malignant Mesothelioma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. AQP1 Treatment Inhibits VM in Cell Lines under Hypoxic Conditions In Vitro, but not Does Inhibit VM under Normoxic Conditions in Cell Lines or Primary Cells, or Microvessel Formation In Vivo
2.2. VEGFA Is Upregulated in NCI-H28 Cells When AQP1 Is Inhibited
2.3. Inhibition of VEGFA Alone Has No Effect on VM in NCI-H28 Cells and Combined Inhibition of AQP1 and VEGF Does Not Inhibit VM in NCI-H226 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. AqB050 Aquaporin Blocker
4.3. siRNA Treatment
4.4. Matrigel VM Assay
4.5. VEGFA ELISA
4.6. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.7. Mouse Xenograft MM Model
4.8. Statistics
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MM | Malignant Mesothelioma |
| VM | Vasculogenic mimicry |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| AQP1 | Aquaporin 1 |
References
- Ohta, Y.; Shridhar, V.; Bright, R.K.; Kalemkerian, G.P.; Du, W.; Carbone, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Pass, H.I. VEGF and VEGF type C play an important role in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in human malignant mesothelioma tumours. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 81, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strizzi, L.; Catalano, A.; Vianale, G.; Orecchia, S.; Casalini, A.; Tassi, G.; Puntoni, R.; Mutti, L.; Procopio, A. Vascular endothelial growth factor is an autocrine growth factor in human malignant mesothelioma. J. Pathol. 2001, 193, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar-Singh, S.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Weyler, J.; Segers, K.; Weyn, B.; van Daele, A.; Dirix, L.Y.; van Oosterom, A.T.; van Marck, E. Evaluation of tumour angiogenesis as a prognostic marker in malignant mesothelioma. J. Pathol. 1997, 182, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalcman, G.; Mazieres, J.; Margery, J.; Greillier, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Molinier, O.; Corre, R.; Monnet, I.; Gounant, V.; et al. Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed pleural mesothelioma in the mesothelioma avastin cisplatin pemetrexed study (MAPS): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceresoli, G.L.; Zucali, P.A.; Mencoboni, M.; Botta, M.; Grossi, F.; Cortinovis, D.; Zilembo, N.; Ripa, C.; Tiseo, M.; Favaretto, A.G.; et al. Phase II study of pemetrexed and carboplatin plus bevacizumab as first-line therapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowell, J.E.; Dunphy, F.R.; Taub, R.N.; Gerber, D.E.; Ngov, L.; Yan, J.; Xie, Y.; Kindler, H.L. A multicenter phase II study of cisplatin, pemetrexed, and bevacizumab in patients with advanced malignant mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindler, H.L.; Karrison, T.G.; Gandara, D.R.; Lu, C.; Krug, L.M.; Stevenson, J.P.; Janne, P.A.; Quinn, D.I.; Koczywas, M.N.; Brahmer, J.R.; et al. Multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized phase II trial of gemcitabine/cisplatin plus bevacizumab or placebo in patients with malignant mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2509–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, L.L.; Chansky, K.; Wozniak, A.J.; Tsao, A.S.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Verschraegen, C.F.; Dasilva, M.A.; Redman, M.; Gandara, D.R. Phase II study of cediranib in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: SWOG S0509. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 1938–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, A.K.; Millward, M.J.; Creaney, J.; Francis, R.J.; Dick, I.M.; Hasani, A.; van der Schaaf, A.; Segal, A.; Musk, A.W.; Byrne, M.J. A phase II study of intermittent sunitinib malate as second-line therapy in progressive malignant pleural mesothelioma. J.Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniotis, A.J.; Folberg, R.; Hess, A.; Seftor, E.A.; Gardner, L.M.G.; Pe’er, J.; Trent, J.M.; Meltzer, P.S.; Hendrix, M.J.C. Vascular channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro: Vasculogenic mimicry. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Quan, J.; Wang, M.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Lv, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Yang, J. Tumor vasculogenic mimicry formation as an unfavorable prognostic indicator in patients with breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56408–56416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Zhou, L.; Yu, L.; Wu, S.; Song, W.; Gong, X.; Wang, D. Evaluation of the correlation of vasculogenic mimicry, aldh1, kai1 and microvessel density in the prediction of metastasis and prognosis in colorectal carcinoma. BMC Surg. 2017, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhu, B.; Wu, S.; Zhou, L.; Song, W.; Gong, X.; Wang, D. Evaluation of the correlation of vasculogenic mimicry, ALDH1, KISS-1, and MACC1 in the prediction of metastasis and prognosis in ovarian carcinoma. Diagn. Pathol. 2017, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Jin, Z.; Xu, T.; Gao, Y.; Wei, H.; Li, C.; Hou, W.; Hua, B. Association between tumor vasculogenic mimicry and the poor prognosis of gastric cancer in China: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2408645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulford, E.; Hocking, A.; Griggs, K.; McEvoy, J.; Bonder, C.; Henderson, D.W.; Klebe, S. Vasculogenic mimicry in malignant mesothelioma: An experimental and immunohistochemical analysis. Pathology 2016, 48, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.J.; Ward, J.H.; Tan, C.; Grundy, R.G.; Rahman, R. Endothelial-like malignant glioma cells in dynamic three dimensional culture identifies a role for VEGF and FGFR in a tumor-derived angiogenic response. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 22191–22205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cai, X.; Qian, Z.; Huang, H.; Huang, W. VEGF-sirna silencing induces apoptosis, inhibits proliferation and suppresses vasculogenic mimicry in osteosarcoma in vitro. Exp. Oncol. 2008, 30, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schnegg, C.I.; Yang, M.H.; Ghosh, S.K.; Hsu, M.Y. Induction of vasculogenic mimicry overrides VEGF-A silencing and enriches stem-like cancer cells in melanoma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkman, A.S. Physiological importance of aquaporin water channels. Ann. Med. 2002, 34, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klebe, S.; Griggs, K.; Cheng, Y.; Driml, J.; Henderson, D.W.; Reid, G. Blockade of aquaporin 1 inhibits proliferation, motility, and metastatic potential of mesothelioma in vitro but not in an in vivo model. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 286719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzani, E.; Bazzotti, R.; Perego, C.; LA Porta, C.A. AQP1 is not only a water channel: It contributes to cell migration through lin7/β-catenin. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Yang, B.; Matthay, M.A.; Ma, T.; Verkman, A.S. Role of aquaporin water channels in pleural fluid dynamics. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Phys. 2000, 279, C1744–C1750. [Google Scholar]
- Driml, J.; Pulford, E.; Moffat, D.; Karapetis, C.; Kao, S.; Griggs, K.; Henderson, D.W.; Klebe, S. Usefulness of aquaporin 1 as a prognostic marker in a prospective cohort of malignant mesotheliomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, S.C.; Armstrong, N.; Condon, B.; Griggs, K.; McCaughan, B.; Maltby, S.; Wilson, A.; Henderson, D.W.; Klebe, S. Aquaporin 1 is an independent prognostic factor in pleural malignant mesothelioma. Cancer 2012, 118, 2952–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagirdar, R.; Solenov, E.I.; Hatzoglou, C.; Molyvdas, P.A.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Zarogiannis, S.G. Gene expression profile of aquaporin 1 and associated interactors in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Gene 2013, 517, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, S.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Hara-Chikuma, M.; Verkman, A.S. Impairment of angiogenesis and cell migration by targeted aquaporin-1 gene disruption. Nature 2005, 434, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCicco-Skinner, K.L.; Henry, G.H.; Cataisson, C.; Tabib, T.; Gwilliam, J.C.; Watson, N.J.; Bullwinkle, E.M.; Falkenburg, L.; O’Neill, R.C.; Morin, A.; et al. Endothelial cell tube formation assay for the in vitro study of angiogenesis. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, e51312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staton, C.A.; Reed, M.W.R.; Brown, N.J. A critical analysis of current in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis assays. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2009, 90, 195–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agre, P.; Sasaki, S.; Chrispeels, M.J. Aquaporins: A family of water channel proteins. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 265, F461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deen, P.M.; Weghuis, D.O.; Geurs van Kessel, A.; Wieringa, B.; van Os, C.H. The human gene for water channel aquaporin 1 (AQP1) is localized on chromosome 7p15->p14. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1994, 65, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y. Aquaporin-1 activity of plasma membrane affects HT20 colon cancer cell migration. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorward, H.S.; Du, A.; Bruhn, M.A.; Wrin, J.; Pei, J.V.; Evdokiou, A.; Price, T.J.; Yool, A.J.; Hardingham, J.E. Pharmacological blockade of aquaporin-1 water channel by AqB013 restricts migration and invasiveness of colon cancer cells and prevents endothelial tube formation in vitro. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.L.; Semenza, G.L. Purification and characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.E.; Gu, J.; Schau, M.; Bunn, H.F. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α is mediated by an O2-dependent degradation domain via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7987–7992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.H.; Rue, E.; Wang, G.L.; Roe, R.; Semenza, G.L. Dimerization, DNA binding, and transactivation properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 17771–17778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klabatsa, A.; Sheaff, M.T.; Steele, J.P.; Evans, M.T.; Rudd, R.M.; Fennell, D.A. Expression and prognostic significance of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) in malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM). Lung Cancer 2006, 51, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, K.; Yagui, K.; Tanaka, A.; Yoshihara, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Takahashi, K.; Bujo, H.; Sakurai, K.; Saito, Y. Aquaporin 1 is required for hypoxia-inducible angiogenesis in human retinal vascular endothelial cells. Microvasc. Res. 2008, 75, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echevarría, M.; Muñoz-Cabello, A.M.; Sánchez-Silva, R.; Toledo-Aral, J.J.; López-Barneo, J. Development of cytosolic hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor stabilization are facilitated by aquaporin-1 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 30207–30215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, N.; Tabata, C.; Tabata, R.; Maeda, R.; Yasumitsu, A.; Yamada, S.; Kuribayashi, K.; Fukuoka, K.; Nakano, T. Pleural effusion VEGF levels as a prognostic factor of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, S.; Herbst, R.S.; Shinohara, H.; Knighton, B.; Bucana, C.D.; Killion, J.J.; Wood, J.; Fidler, I.J. Treatment for malignant pleural effusion of human lung adenocarcinoma by inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Masood, R.; Kundra, A.; Zhu, S.; Xia, G.; Scalia, P.; Smith, D.L.; Gill, P.S. Malignant mesothelioma growth inhibition by agents that target the VEGF and VEGF-c autocrine loops. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 104, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yano, S.; Ogino, H.; Wang, W.; Uehara, H.; Nishioka, Y.; Sone, S. The therapeutic efficacy of anti vascular endothelial growth factor antibody, bevacizumab, and pemetrexed against orthotopically implanted human pleural mesothelioma cells in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5918–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Du, J.; Guo, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Hao, X. Vasculogenic mimicry is associated with high tumor grade, invasion and metastasis, and short survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 16, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Bao, M.; Miele, L.; Sarkar, F.H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Q. Tumour vasculogenic mimicry is associated with poor prognosis of human cancer patients: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3914–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidner, N. Current pathologic methods for measuring intratumoral microvessel density within breast carcinoma and other solid tumors. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1995, 36, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pulford, E.; McEvoy, J.; Hocking, A.; Prabhakaran, S.; Griggs, K.; Klebe, S. The Effect of Aquaporin 1-Inhibition on Vasculogenic Mimicry in Malignant Mesothelioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112293
Pulford E, McEvoy J, Hocking A, Prabhakaran S, Griggs K, Klebe S. The Effect of Aquaporin 1-Inhibition on Vasculogenic Mimicry in Malignant Mesothelioma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112293
Chicago/Turabian StylePulford, Emily, James McEvoy, Ashleigh Hocking, Sarita Prabhakaran, Kim Griggs, and Sonja Klebe. 2017. "The Effect of Aquaporin 1-Inhibition on Vasculogenic Mimicry in Malignant Mesothelioma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112293
APA StylePulford, E., McEvoy, J., Hocking, A., Prabhakaran, S., Griggs, K., & Klebe, S. (2017). The Effect of Aquaporin 1-Inhibition on Vasculogenic Mimicry in Malignant Mesothelioma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112293