Akt1 Stimulates Homologous Recombination Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks in a Rad51-Dependent Manner
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
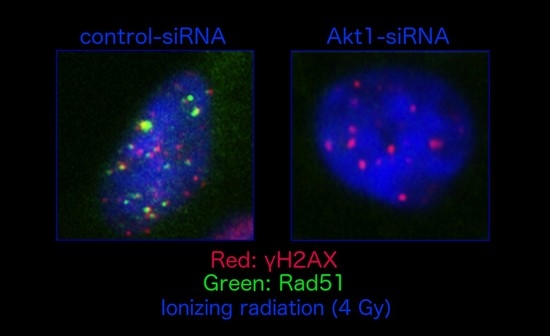
2.1. Akt1 Promotes HR-Dependent DSB Repair
2.2. Stimulation of HR Repair by Akt1 is Dependent on Rad51
2.3. Akt1 Promotes DSB Repair after Irradiation Partially by Stimulation of HR Repair
2.4. Akt1-Mediated HR Repair Plays a Minor Role in Post-Irradiation Clonogenic Survival
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Antibodies and Reagents
4.3. siRNA Transfection
4.4. Rad51, γH2AX and BRCA1 Foci Assays
4.5. HR-Reporter Assay
4.6. Subcellular Fractionation and Western Blotting
4.7. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.8. Synchronization of Cells in S/G2 Phase
4.9. Colony Formation Assay
4.10. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DNA-PKcs | DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit |
| DSB | double-strand break |
| dsDNA | double-stranded DNA |
| GFP | green fluorescent protein |
| HR | homologous recombination |
| KD | knockdown |
| MMC | Mitomycin C |
| NHEJ | non-homologous end-joining |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cancer |
| PKB | protein kinase B |
| siRNA | short-interfering RNA |
| SF | surviving fraction |
| ssDNA | single-stranded DNA |
References
- Chen, Z.; Fillmore, C.M.; Hammerman, P.S.; Kim, C.F.; Wong, K.K. Non-small-cell lung cancers: A heterogeneous set of diseases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2013, 63, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Akerley, W.; Borghaei, H.; Chang, A.C.; Cheney, R.T.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A.; Demmy, T.L.; Govindan, R.; Grannis, F.W., Jr.; et al. Non-small cell lung cancer, version 2.2013. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2013, 11, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, W.J., Jr.; Paulus, R.; Langer, C.J.; Komaki, R.; Lee, J.S.; Hauser, S.; Movsas, B.; Wasserman, T.; Rosenthal, S.A.; Gore, E.; et al. Sequential vs. Concurrent chemoradiation for stage iii non-small cell lung cancer: Randomized phase iii trial rtog 9410. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simone, C.B., II.; Burri, S.H.; Heinzerling, J.H. Novel radiotherapy approaches for lung cancer: Combining radiation therapy with targeted and immunotherapies. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vivanco, I.; Sawyers, C.L. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase akt pathway in human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, G. The role of the dysfunctional akt-related pathway in cancer: Establishment and maintenance of a malignant cell phenotype, resistance to therapy, and future strategies for drug development. Scientifica 2013, 2013, 317186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, P.Y. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-akt-mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K-AKT-MTOR) signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, E.; McGraw, T.E. The akt kinases: Isoform specificity in metabolism and cancer. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 2502–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Littlewood, T.; Bennett, M. Akt isoforms in vascular disease. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saad, S.; Donnem, T.; Al-Shibli, K.; Persson, M.; Bremnes, R.M.; Busund, L.T. Diverse prognostic roles of akt isoforms, pten and PI3K in tumor epithelial cells and stromal compartment in non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 4175–4183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toulany, M.; Kasten-Pisula, U.; Brammer, I.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Dittmann, K.; Baumann, M.; Dikomey, E.; Rodemann, H.P. Blockage of epidermal growth factor receptor-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT signaling increases radiosensitivity of k-ras mutated human tumor cells in vitro by affecting DNA repair. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4119–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toulany, M.; Kehlbach, R.; Florczak, U.; Sak, A.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Lobrich, M.; Rodemann, H.P. Targeting of AKT1 enhances radiation toxicity of human tumor cells by inhibiting DNA-pkcs-dependent DNA double-strand break repair. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toulany, M.; Lee, K.J.; Fattah, K.R.; Lin, Y.F.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Schaller, M.; Chen, B.P.; Chen, D.J.; Rodemann, H.P. Akt promotes post-irradiation survival of human tumor cells through initiation, progression, and termination of DNA-pkcs-dependent DNA double-strand break repair. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, R.; Tang, J.; Ma, J.G.; Chen, S.P.; Xia, L.P.; Zhou, W.J.; Li, D.D.; Feng, G.K.; Zeng, Y.X.; Zhu, X.F. Pkb/akt promotes dsb repair in cancer cells through upregulating MRE11 expression following ionizing radiation. Oncogene 2011, 30, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, P.N., Jr.; Longmate, J.; Mack, P.C.; Kelly, K.; Socinski, M.A.; Salgia, R.; Gitlitz, B.; Li, T.; Koczywas, M.; Reckamp, K.L.; et al. Phase ii study of the akt inhibitor mk-2206 plus erlotinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer who previously progressed on erlotinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4321–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Shcherba, M.; Pendurti, G.; Liang, Y.; Piperdi, B.; Perez-Soler, R. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/MTOR pathway: Potential for lung cancer treatment. Lung Cancer Manag. 2014, 3, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.K.; Reckamp, K.; Yu, H.; Figlin, R.A. Akt inhibitors in clinical development for the treatment of cancer. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2010, 19, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, K.K.; Jackson, S.P. DNA double-strand breaks: Signaling, repair and the cancer connection. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menegakis, A.; Yaromina, A.; Eicheler, W.; Dorfler, A.; Beuthien-Baumann, B.; Thames, H.D.; Baumann, M.; Krause, M. Prediction of clonogenic cell survival curves based on the number of residual DNA double strand breaks measured by gammah2ax staining. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2009, 85, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, K.; Almasan, A. Histone H2ax phosphorylation: A marker for DNA damage. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 920, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dikomey, E. Determination of DNA damage in vitro. Nukl. Nucl. Med. 2010, 49 (Suppl. S1), S64–S68. [Google Scholar]
- Paull, T.T.; Rogakou, E.P.; Yamazaki, V.; Kirchgessner, C.U.; Gellert, M.; Bonner, W.M. A critical role for histone H2ax in recruitment of repair factors to nuclear foci after DNA damage. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinner, A.; Wu, W.; Staudt, C.; Iliakis, G. Gamma-H2ax in recognition and signaling of DNA double-strand breaks in the context of chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 5678–5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podhorecka, M.; Skladanowski, A.; Bozko, P. H2ax phosphorylation: Its role in DNA damage response and cancer therapy. J. Nucleic Acids 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, W.Y.; Schumacher, S.; Rosskopf, R.; Rhein, T.; Schmidt-Petersen, F.; Gatzemeier, F.; Haag, F.; Borgmann, K.; Willers, H.; Dahm-Daphi, J. Hierarchy of nonhomologous end-joining, single-strand annealing and gene conversion at site-directed DNA double-strand breaks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 4088–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kass, E.M.; Jasin, M. Collaboration and competition between DNA double-strand break repair pathways. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3703–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahlberg, S.H.; Gustafsson, A.S.; Pendekanti, P.N.; Glimelius, B.; Stenerlow, B. The influence of akt isoforms on radiation sensitivity and DNA repair in colon cancer cell lines. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 3525–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Graham, P.H.; Hao, J.; Ni, J.; Bucci, J.; Cozzi, P.J.; Kearsley, J.H.; Li, Y. PI3K/AKT/MTOR pathway inhibitors enhance radiosensitivity in radioresistant prostate cancer cells through inducing apoptosis, reducing autophagy, suppressing nhej and hr repair pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holler, M.; Grottke, A.; Mueck, K.; Manes, J.; Jucker, M.; Rodemann, H.P.; Toulany, M. Dual targeting of AKT and MTORC1 impairs repair of DNA double-strand breaks and increases radiation sensitivity of human tumor cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothkamm, K.; Kruger, I.; Thompson, L.H.; Lobrich, M. Pathways of DNA double-strand break repair during the mammalian cell cycle. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 5706–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladenov, E.; Magin, S.; Soni, A.; Iliakis, G. DNA double-strand-break repair in higher eukaryotes and its role in genomic instability and cancer: Cell cycle and proliferation-dependent regulation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 37–38, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Scavuzzo, M.A.; Chmielowiec, J.; Sharp, R.; Bajic, A.; Borowiak, M. Enrichment of G2/M cell cycle phase in human pluripotent stem cells enhances hdr-mediated gene repair with customizable endonucleases. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieckmann, T.; Kriegs, M.; Nitsch, L.; Hoffer, K.; Rohaly, G.; Kocher, S.; Petersen, C.; Dikomey, E.; Dornreiter, I.; Dahm-Daphi, J. P53 modulates homologous recombination at i-scei-induced double-strand breaks through cell-cycle regulation. Oncogene 2013, 32, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashima, Y.; Sakuraba, M.; Koizumi, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Hayashi, M.; Honma, M. Dependence of DNA double strand break repair pathways on cell cycle phase in human lymphoblastoid cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2009, 50, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deans, A.J.; West, S.C. DNA interstrand crosslink repair and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Heyer, W.D. Homologous recombination in DNA repair and DNA damage tolerance. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasin, M.; Rothstein, R. Repair of strand breaks by homologous recombination. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a012740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ristic, D.; Kanaar, R.; Wyman, C. Visualizing rad51-mediated joint molecules: Implications for recombination mechanism and the effect of sequence heterology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.Y.; Terakawa, T.; Qi, Z.; Steinfeld, J.B.; Redding, S.; Kwon, Y.; Gaines, W.A.; Zhao, W.; Sung, P.; Greene, E.C. DNA recombination. Base triplet stepping by the Rad51/Reca family of recombinases. Science 2015, 349, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, P.; West, S.C. Role of the human Rad51 protein in homologous recombination and double-stranded-break repair. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, S.M.; Huen, M.S.; Chen, J. Palb2 is an integral component of the brca complex required for homologous recombination repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7155–7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabalier-Taste, C.; Brichese, L.; Racca, C.; Canitrot, Y.; Calsou, P.; Larminat, F. Polo-like kinase 1 mediates Brca1 phosphorylation and recruitment at DNA double-strand breaks. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 2269–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakr, A.; Oing, C.; Kocher, S.; Borgmann, K.; Dornreiter, I.; Petersen, C.; Dikomey, E.; Mansour, W.Y. Involvement of atm in homologous recombination after end resection and Rad51 nucleofilament formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 3154–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, F.; Yan, J.; Yang, Q. Akt1 inhibits homologous recombination in Brca1-deficient cells by blocking the Chk1-Rad51 pathway. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1943–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plo, I.; Laulier, C.; Gauthier, L.; Lebrun, F.; Calvo, F.; Lopez, B.S. Akt1 inhibits homologous recombination by inducing cytoplasmic retention of Brca1 and Rad51. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9404–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plo, I.; Lopez, B. Akt1 represses gene conversion induced by different genotoxic stresses and induces supernumerary centrosomes and aneuploidy in hamster ovary cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2231–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Karmakar, P. Attenuation of pten perturbs genomic stability via activation of akt and down-regulation of rad51 in human embryonic kidney cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.C.; Ciou, S.C.; Jhan, J.Y.; Cheng, C.M.; Su, Y.J.; Chuang, S.M.; Lin, S.T.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, Y.W. Roles of Mkk1/2-Erk1/2 and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-akt signaling pathways in erlotinib-induced rad51 suppression and cytotoxicity in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.C.; Chen, J.C.; Wang, T.J.; Zheng, H.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Chang, P.Y.; Lin, Y.W. Astaxanthin down-regulates rad51 expression via inactivation of AKT kinase to enhance mitomycin c-induced cytotoxicity in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 105, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.S.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chiu, Y.F.; Su, Y.C.; Lin, Y.W. Down-regulation of rad51 expression overcomes drug resistance to gemcitabine in human non-small-cell lung cancer cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moynahan, M.E.; Cui, T.Y.; Jasin, M. Homology-directed DNA repair, mitomycin-c resistance, and chromosome stability is restored with correction of a brca1 mutation. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4842–4850. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Short, S.C.; Giampieri, S.; Worku, M.; Alcaide-German, M.; Sioftanos, G.; Bourne, S.; Lio, K.I.; Shaked-Rabi, M.; Martindale, C. Rad51 inhibition is an effective means of targeting DNA repair in glioma models and cd133+ tumor-derived cells. Neuro-Oncology 2011, 13, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, R.; Iwakawa, R.; Tang, M.; Kohno, T.; Angulo, B.; Pio, R.; Montuenga, L.M.; Minna, J.D.; Yokota, J.; Sanchez-Cespedes, M. A gene-alteration profile of human lung cancer cell lines. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toulany, M.; Minjgee, M.; Saki, M.; Holler, M.; Meier, F.; Eicheler, W.; Rodemann, H.P. Erk2-dependent reactivation of akt mediates the limited response of tumor cells with constitutive k-ras activity to pi3k inhibition. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toulany, M.; Iida, M.; Keinath, S.; Iyi, F.F.; Mueck, K.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Mansour, W.Y.; Schaller, M.; Wheeler, D.L.; Rodemann, H.P. Dual targeting of pi3k and mek enhances the radiation response of k-ras mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 43746–43761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, T.; Kowalczykowski, S.C. Rad52 protein associates with replication protein a (RPA)-single-stranded DNA to accelerate rad51-mediated displacement of rpa and presynaptic complex formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 31663–31672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, C.J.; Ashworth, A. Rad51, brca2 and DNA repair: A partial resolution. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamo, A.; Collis, S.J.; Adelman, C.A.; Silva, N.; Horejsi, Z.; Ward, J.D.; Martinez-Perez, E.; Boulton, S.J.; La Volpe, A. Preventing nonhomologous end joining suppresses DNA repair defects of fanconi anemia. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.C.; Tsai, M.S.; Weng, S.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chiu, Y.F.; Lin, Y.W. Curcumin enhances the mitomycin c-induced cytotoxicity via downregulation of Mkk1/2-Erk1/2-mediated Rad51 expression in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 255, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladenov, E.; Tsaneva, I.; Anachkova, B. Cell cycle-dependent association of rad51 with the nuclear matrix. DNA Cell Biol. 2007, 26, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Nastasi, A.; Shen, Z.; Brenneman, M.; Crissman, H.; Chen, D.J. Cell cycle-dependent protein expression of mammalian homologs of yeast DNA double-strand break repair genes Rad51 and Rad52. Mutat. Res. 1997, 384, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flygare, J.; Benson, F.; Hellgren, D. Expression of the human Rad51 gene during the cell cycle in primary human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1312, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.R.; Shim, H.J.; Yu, H.N.; Song, E.K.; Park, J.; Kwon, K.B.; Park, J.W.; Rho, H.W.; Park, B.H.; Han, M.K.; et al. Dimethylsulfoxide induces upregulation of tumor suppressor protein pten through nuclear factor-kappab activation in hl-60 cells. Leuk. Res. 2005, 29, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankenberg-Schwager, M.; Gebauer, A.; Koppe, C.; Wolf, H.; Pralle, E.; Frankenberg, D. Single-strand annealing, conservative homologous recombination, nonhomologous DNA end joining, and the cell cycle-dependent repair of DNA double-strand breaks induced by sparsely or densely ionizing radiation. Radiat. Res. 2009, 171, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Enriquez, S.; Ramon, Y.C.T.; Alonso, C.; Corral, A.; Carrasco, P.; Cornet, M.; Sanz, J.; Ribas, M.; Baiget, M.; Diez, O. Ionizing radiation or mitomycin-induced micronuclei in lymphocytes of Brca1 or Brca2 mutation carriers. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 127, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.K. Modulation of radiation-induced and mitomycin c-induced chromosome damage by apigenin in human lymphocytes in vitro. J. Radiat. Res. 2013, 54, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahaney, B.L.; Meek, K.; Lees-Miller, S.P. Repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks by non-homologous end-joining. Biochem. J. 2009, 417, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeggo, P.A.; Geuting, V.; Lobrich, M. The role of homologous recombination in radiation-induced double-strand break repair. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 101, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Galick, H.; Wallace, S.S. Attempted base excision repair of ionizing radiation damage in human lymphoblastoid cells produces lethal and mutagenic double strand breaks. DNA Repair 2004, 3, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaachouay, H.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Toulany, M.; Schaller, M.; Multhoff, G.; Rodemann, H.P. Ampk-independent autophagy promotes radioresistance of human tumor cells under clinical relevant hypoxia in vitro. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 116, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhu, H.; Guo, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, H.; Sun, X. Autophagy and its function in radiosensitivity. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 4079–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerniglia, G.J.; Karar, J.; Tyagi, S.; Christofidou-Solomidou, M.; Rengan, R.; Koumenis, C.; Maity, A. Inhibition of autophagy as a strategy to augment radiosensitization by the dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor NVP-Bez235. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.K.; Kwong, A.; Tam, K.F.; Cheung, A.N.; Ngan, H.Y.; Xia, W.; Wong, A.S. Brca1 deficiency induces protective autophagy to mitigate stress and provides a mechanism for Brca1 haploinsufficiency in tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 2014, 346, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteve, J.M.; Armengod, M.E.; Knecht, E. Brca1 negatively regulates formation of autophagic vacuoles in Mcf-7 breast cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 2618–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaoka, M.; Iwai-Kanai, E.; Katamura, M.; Okawa, Y.; Mita, Y.; Matoba, S. An alpha-adrenergic agonist protects hearts by inducing AKT1-mediated autophagy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 456, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Ju, J.H.; Lee, K.M.; Nam, K.; Oh, S.; Shin, I. Protein kinase b/akt1 inhibits autophagy by down-regulating uvrag expression. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, T.M.; Iida, M.; Luthar, N.; Wleklinski, M.J.; Starr, M.M.; Wheeler, D.L. Mapping C-terminal transactivation domains of the nuclear her family receptor tyrosine kinase her3. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.C.; Hung, M.C. Characterization of a novel tripartite nuclear localization sequence in the egfr family. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10432–10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| % of Cells ± SEM | Con-si | Akt1-si | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Synch. | S/G2-Synch | Non-Synch. | S/G2-Synch | |
| G1 | 53.7 ± 1.3 | 20.9 ± 0.4 | 56.3 ± 0.8 | 33.6 ± 1.9 |
| S | 11.2 ± 0.6 | 23.0 ± 1.6 | 8.1 ± 0.6 | 16.7 ± 1.2 |
| G2 | 32.3 ± 1.4 | 52.1 ± 2.1 | 33.9 ± 0.8 | 47.3 ± 2.7 |
| subG1 | 2.7 ± 0.9 | 4.0 ± 1.0 | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 2.5 ± 0.3 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mueck, K.; Rebholz, S.; Harati, M.D.; Rodemann, H.P.; Toulany, M. Akt1 Stimulates Homologous Recombination Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks in a Rad51-Dependent Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112473
Mueck K, Rebholz S, Harati MD, Rodemann HP, Toulany M. Akt1 Stimulates Homologous Recombination Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks in a Rad51-Dependent Manner. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112473
Chicago/Turabian StyleMueck, Katharina, Simone Rebholz, Mozhgan Dehghan Harati, H. Peter Rodemann, and Mahmoud Toulany. 2017. "Akt1 Stimulates Homologous Recombination Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks in a Rad51-Dependent Manner" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112473
APA StyleMueck, K., Rebholz, S., Harati, M. D., Rodemann, H. P., & Toulany, M. (2017). Akt1 Stimulates Homologous Recombination Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks in a Rad51-Dependent Manner. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112473