Plasma Gelsolin Induced Glomerular Fibrosis via the TGF-β1/Smads Signal Transduction Pathway in IgA Nephropathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
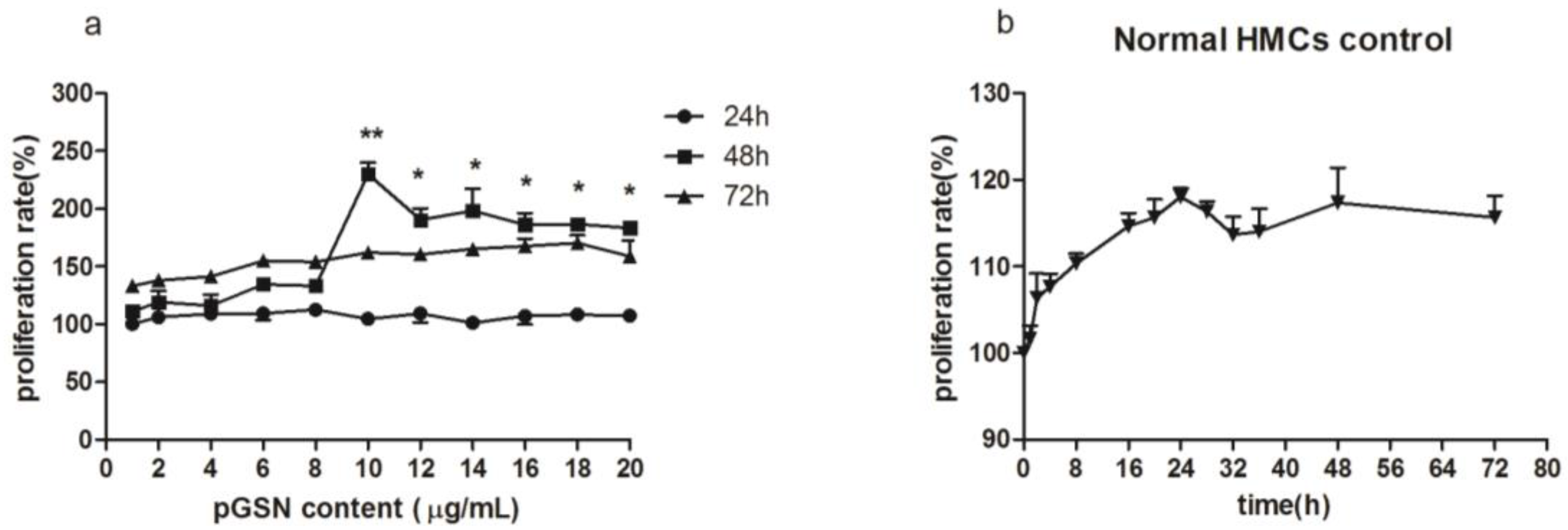
2.1. Cell Proliferation (MTT) of HMCs Cultured with pGSN
2.2. ELISA of TGF-β1 in HMCs Cultured with pGSN and/or IgA1 (from Patients or Healthy Subjects)
2.3. Electron Microscopy Detection
2.4. Immunofluorescence Detection of TGF-β1 in HMCs
2.5. Western Blot Detection of TGF-β1/Smads in HMCs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Patients and Sera
4.3. Extraction of Sera IgA1 in Patients with IgAN and Healthy Controls
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazole-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyl Tetrazoliumbromide (MTT) Assay
4.6. ELISA Detection
4.7. Electron Microscopy Detection
4.8. Immunofluorescence Detection
4.9. Western Blot Detection
4.10. Detection of the HMCs after Costimulation with pGSN and IgA1
4.11. Statistical Analysis
4.12. Ethics Statement
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barratt, J.; Feehally, J. IgA nephropathy. J. Am Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadio, J.V.; Grande, J.P. IgA nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, N.; Bruce, A.J.; Milan, T.; Jiri, M. IgA glycosylation and IgA immune complexes in the pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, N.; Hou, P.; Lv, J.C.; Zina, M.; Li, Y.F.; Krzysztof, K.; Ali, G.G.; Jan, N.; Zhang, H. The level of galactose-deficient IgA1 in the sera of patients with IgA nephropathy is associated with disease progression. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGough, A.M.; Staiger, C.J.; Min, J.K.; Simonetti, K.D. The gelsolin family of actin regulatory proteins: Modular structures, versatile functions. FEBS Lett. 2003, 552, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.L.; Stossel, T.P. Control of cytoplasmic actin gel-sol transformation by gelsolin, a calcium dependent regulatory protein. Nature 1979, 281, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhler, E.; Lin, W.; Yin, H.L.; Lee, W.M. Decreased plasma gelsolin concentrations in acute liver failure, myocardial infarction, septic shock, and myonecrosis. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 25, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mounzer, K.C.; Moncure, M.; Smith, Y.R.; Dinubile, M.J. Relationship of admission plasma gelsolin levels to clinical outcomes in patients after major trauma. Am. J.Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nubile, M.J.; Stossel, T.P.; Ljunghusen, O.C.; Ferrara, J.L.; Antin, J.H. Prognostic implications of declining plasma gelsolin levels after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2002, 100, 4367–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christofidou-Solomidou, M.; Scherpereel, A.; Solomides, C.C.; Muzykantov, V.R.; Machtay, M.; Albelda, S.M.; DiNubile, M.J. Changes in plasma gelsolin concentration during acute oxidant lung injury in mice. Lung 2002, 180, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenbach, P.A.; Dahl, B.; Schwartz, J.J.; O’Keefe, G.E.; Yamamoto, M.; Lee, W.M.; Horton, J.W.; Yin, H.L.; Turnage, R.H. Recombinant plasma gelsolin infusion attenuates burn-induced pulmonary microvascular dysfunction. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 96, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.S.; Waxman, A.B.; Cotich, K.L.; Chung, S.W.; Perrella, M.A.; Stossel, T.P. Plasma gelsolin is a marker and therapeutic agent in animal sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, T.M.; Verdrengh, M.; Stossel, T.P.; Tarkowski, A.; Bokarewa, M. Decreased levels of the gelsolin plasma isoform in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Kong, D.; Meng, H.; Han, C.; Zhu, J.; Qiao, J.; He, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Jin, X. PlasmaGelsolinPromotes Proliferation of Mesangial Cell in IgA Nephropathy. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.S.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.L.; Tang, J.; Jin, X.M. Plasma gelsolin levels are decreased and correlate with fibrosis in IgA nephropathy. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 238, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.B. The ever-increasing complexity of TGF-β signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002, 13, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Koka, V.; Lan, H.Y. Transforming growth factor-β and Smadssignalling in kidney diseases. Nephrology 2005, 10, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magistroni, R.; Furci, L.; Leonelli, M.; Rosen, R.M.; Fein, D.A. A validated model of disease progression in IgA nephropathy. J. Nephrol. 2006, 19, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.E.; Park, W.; Kim, D.C. Down-regulation of gelsolin may play a role in the progression of inverted papilloma through an antiapoptotic mechanism. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2012, 26, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, H.; Koya, R.C.; Nakagawa, K. Inhibition of Alzheimer’samyloid-βpeptide-induced reduction of mitochondrial membrane potential and neurotoxicity by gelsolin. Neurobiol. Aging 2005, 26, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwin, M.; Nowak, D.; Mazur, A.J. Gelsolin affects the migratory ability of human colon adenocarcinoma and melanoma cells. Life Sci. 2012, 90, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Jang, S.M. Gelsolin negatively regulates the activity of tumor suppressor p53 through their physical interaction in hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Shirkoohi, R.; Nakagawa, K. SiRNAgelsolin knockdown induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition with a cadherin switch in human mammary epithelial cells. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 1680–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, F.; Zhang, R.; Don, L.; Ying, K. Overexpression of gelsolin-like actin-capping protein is associated with progression of lung adenocarcinoma. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2011, 225, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.W.; Liou, Y.M. Differential role of actin-binding proteins in controlling the adipogenic differentiation of human CD105-positive Wharton’s Jelly cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silacci, P.; Mazzolai, L.; Gauci, C.; Stergiopulos, N.; Yin, H.L.; Hayoz, D. Gelsolin superfamily proteins: Key regulators of cellular functions. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philchenkov, A.A. Caspases as regulators of apoptosis and other cell functions. Biochemistry 2003, 68, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Nubile, M.J. Plasma gelsolin as a biomarker of inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juusela, P.; Tanskanen, M.; Nieminen, A. Hereditary gelsolin amyloidosis mimicking Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 8, 1351–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou, N.; Thanasopoulou, A.; Tzouvelekis, A. Gelsolin expression is necessary for the development of modelled pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Thorax 2009, 64, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos, J.; Lourido, L.; Ferna’ndez-Puente, P. Differential protein profiling of synovial fluid from rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients using LC-MALDI TOF/TOF. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2869–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.H.; Wu, C.C.; Peng, P.H. Identification of secretory gelsolin as a plasma biomarker associated with distant organ metastasis of colorectal cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Chen, R.; Brand, R.E. Multiplex targeted proteomic assay for biomarker detection in plasma: A pancreatic cancer biomarker case study. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1937–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Shen, J.N.; Peng, J.Q.; Wang, J.; Huang, G.; Li, M.T. Increased expression of serum gelsolin in patients with osteosarcoma. Chin. Med. J. 2012, 125, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.P.; Chen, Y.W.; Liu, W.H. Proteomic identification ofplasma biomarkers in uterine leiomyoma. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.F.; Liu, W.G.; Dong, X.Q.; Yang, S.B.; Fan, J. Change in plasma gelsolin level after traumatic brain injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012, 72, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.L.; Li, H.; Li, W.H.; Meng, H.X.; Fan, Y.Z.; Li, W.J.; Ji, Y.T.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L.; Jin, X.M.; et al. The value of decreased plasma gelsolinlevels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosusandrheumatoid arthritis in diagnosis and disease activity evaluation. Lupus 2013, 22, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottinger, E.P.; Bitzer, M. TGF-signaling in renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2600–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, F.; He, Y.; Kong, D.; Han, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Jin, X. Establishment of a mouse IgA nephropathy model with MBP-20-peptide fusion protein. Anat. Rec. 2010, 293, 1729–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.H.; Zhang, Y.K.; Li, X.M.; Wang, H.Y. Binding capacity and pathophysiological effects of IgA1 from patients with IgA nephropathy on human glomerular mesangial cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 136, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Han, C.; Ye, F.; He, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Jin, X. Plasma Gelsolin Induced Glomerular Fibrosis via the TGF-β1/Smads Signal Transduction Pathway in IgA Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020390
Zhang L, Han C, Ye F, He Y, Jin Y, Wang T, Wu Y, Jiang Y, Zhang F, Jin X. Plasma Gelsolin Induced Glomerular Fibrosis via the TGF-β1/Smads Signal Transduction Pathway in IgA Nephropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(2):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020390
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lei, Changsong Han, Fei Ye, Yan He, Yinji Jin, Tianzhen Wang, Yiqi Wu, Yang Jiang, Fengmin Zhang, and Xiaoming Jin. 2017. "Plasma Gelsolin Induced Glomerular Fibrosis via the TGF-β1/Smads Signal Transduction Pathway in IgA Nephropathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 2: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020390
APA StyleZhang, L., Han, C., Ye, F., He, Y., Jin, Y., Wang, T., Wu, Y., Jiang, Y., Zhang, F., & Jin, X. (2017). Plasma Gelsolin Induced Glomerular Fibrosis via the TGF-β1/Smads Signal Transduction Pathway in IgA Nephropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(2), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020390






