A Review of Structure Construction of Silk Fibroin Biomaterials from Single Structures to Multi-Level Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physicochemical Properties of Silk Fibroin as Biomaterials
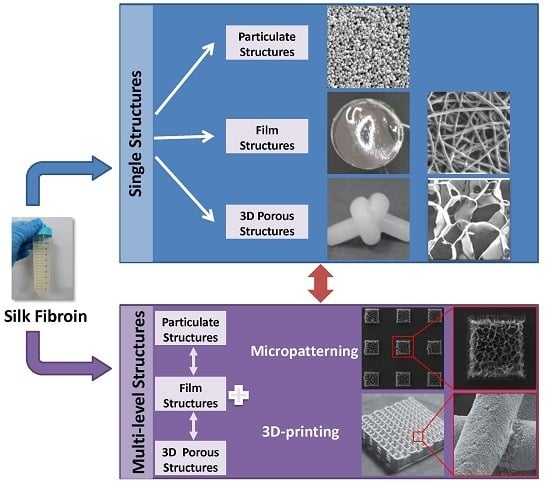
3. Structure Design of Silk Fibroin-Based Biomaterials
3.1. Single Structures
3.1.1. Particulate Structures
3.1.2. Film Structures
3.1.3. Three-Dimensional Structures
3.2. Multi-Level Structures
3.2.1. Micropatterning Structures
3.2.2. Three-Dimensional Printing Structures
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kundu, B.; Rajkhowa, R.; Kundu, S.C.; Wang, X. Silk fibroin biomaterials for tissue regenerations. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, G.H.; Diaz, F.; Jakuba, C.; Calabro, T.; Horan, R.L.; Chen, J.; Lu, H.; Richmond, J.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk-based biomaterials. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vepari, C.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk as a biomaterial. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melke, J.; Midha, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ito, K.; Hofmann, S. Silk fibroin as biomaterial for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2016, 31, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Porter, D.; Vollrath, F. Morphology and structure of silkworm cocoons. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.; Vollrath, F. Silk as a Biomimetic Ideal for Structural Polymers. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinel, L.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk constructs for delivery of musculoskeletal therapeutics. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. New Opportunities for an Ancient Material. Science 2010, 329, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Xie, M. Silk Fibroin-Based Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 4880–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Sato, M.; Takahashi, R.; Aytemiz, D.; Takabayashi, C.; Tamura, T.; Enomoto, S.; Sata, M.; Asakura, T. Development of Small-Diameter Vascular Grafts Based on Silk Fibroin Fibers from Bombyx mori for Vascular Regeneration. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. E 2011, 22, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, D.; Kang, S.; Kim, J.; Kwon, Y.; Young Kweon, H.; Lee, K.; Park, Y.; Baek, R.; Heo, C.; Choe, J.; et al. Wound healing effect of silk fibroin/alginate-blended sponge in full thickness skin defect of rat. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, B.B.; Kaplan, D.L. High-strength silk protein scaffolds for bone repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7699–7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seal, B.L.; Otero, T.C.; Panitch, A. Polymeric biomaterials for tissue and organ regeneration. Mat. Sci. Eng. R 2001, 34, 147–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, B.; Kurland, N.E.; Bano, S.; Patra, C.; Engel, F.B.; Yadavalli, V.K.; Kundu, S.C. Silk proteins for biomedical applications: Bioengineering perspectives. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolind, K.; Leong, K.W.; Besenbacher, F.; Foss, M. Guidance of stem cell fate on 2D patterned surfaces. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6626–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikkhah, M.; Edalat, F.; Manoucheri, S.; Khademhosseini, A. Engineering microscale topographies to control the cell–substrate interface. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5230–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metavarayuth, K.; Sitasuwan, P.; Zhao, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Q. Influence of Surface Topographical Cues on the Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Vitro. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, R.J.; Wann, A.; Thompson, C.L.; Connelly, J.T.; Knight, M.M. Surface topography regulates wnt signaling through control of primary cilia structure in mesenchymal stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, S.; Traub, W.; Wagner, H.D. Lamellar Bone: Structure–Function Relations. J. Struct. Biol. 1999, 126, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubin-Tam, M.E.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Structure and function of nanoparticle-protein conjugates. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 34001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badylak, S.F.; Freytes, D.O.; Gilbert, T.W. Extracellular matrix as a biological scaffold material: Structure and function. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Song, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, Z.; Pu, D.; Lin, S.; Zhou, C.; You, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Silk structure and degradation. Colloid Surface B 2015, 131, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, L.; Cheng, Y.; Teng, C.; Khin, Y.; Loh, X.; Tee, S.; Low, M.; Ye, E.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Structures, mechanical properties and applications of silk fibroin materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 46, 86–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Tanaka, K.; Kikuchi, Y.; Waga, M.; Waga, S.; Mizuno, S. Production of a Chimeric Fibroin Light-chain Polypeptide in a Fibroin Secretion-deficient Naked Pupa Mutant of the SilkwormBombyx mori. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 251, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Inoue, S.; Mizuno, S. Hydrophobic interaction of P25, containing Asn-linked oligosaccharide chains, with the H–L complex of silk fibroin produced by Bombyx mori. Insect. Biochem. Mol. 1999, 29, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Tanaka, K.; Arisaka, F.; Kimura, S.; Ohtomo, K.; Mizuno, S. Silk fibroin of Bombyx mori is secreted, assembling a high molecular mass elementary unit consisting of H-chain, L-chain, and P25, with a 6:6:1 molar ratio. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 40517–40528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.Z.; Confalonieri, F.; Jacquet, M.; Perasso, R.; Li, Z.G.; Janin, J. Silk fibroin: Structural implications of a remarkable amino acid sequence. Proteins 2001, 44, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkov, V.; Ferreira, A.V.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. On the Routines of Wild-Type Silk Fibroin Processing Toward Silk-Inspired Materials: A Review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2015, 300, 1199–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valluzzi, R.; Gido, S.P.; Muller, W.; Kaplan, D.L. Orientation of silk III at the air-water interface. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 24, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummy, L.F.; Phillips, D.M.; Stone, M.O.; And, B.L.F.; Naik, R.R. Thermally Induced α-Helix to β-Sheet Transition in Regenerated Silk Fibers and Films. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3328–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numata, K.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Mechanism of enzymatic degradation of beta-sheet crystals. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2926–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, D.M.; Drummy, L.F.; Naik, R.R.; Long, H.C.D.; Fox, D.M.; Trulove, P.C.; Mantz, R.A. Regenerated silk fiber wet spinning from an ionic liquid solution. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 4206–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.B.; Kundu, S.C. A novel method for dissolution and stabilization of non-mulberry silk gland protein fibroin using anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 99, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.; Yang, Y.; Shao, Z. Physically Crosslinked Biocompatible Silk-Fibroin-Based Hydrogels with High Mechanical Performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Parker, S.T.; Wang, X.; Kaplan, D.L.; Lewis, J.A. Direct-Write Assembly of Microperiodic Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Mechanism of silk processing in insects and spiders. Nature 2003, 424, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Chen, X.; Yao, J.; Huang, L.; Shao, Z. The preparation of regenerated silk fibroin microspheres. Soft Matter 2007, 3, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, P.C.; Balmayor, E.R.; Azevedo, H.S.; Nürnberger, S.; Casal, M.; van Griensven, M.; Reis, R.L.; Redl, H. Silk fibroin microparticles as carriers for delivery of human recombinant BMPs. Physical characterization and drug release. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2010, 4, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Goh, J.C.H. Self-assembled silk fibroin particles: Tunable size and appearance. Powder Technol. 2012, 215–216, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammel, A.S.; Hu, X.; Park, S.; Kaplan, D.L.; Scheibel, T.R. Controlling silk fibroin particle features for drug delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4583–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, D.; Pan, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, K. Controlling silk fibroin microspheres via molecular weight distribution. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 50, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Wen, J.; Xia, Z.; Xin, C.; Shao, Z.; Jiang, J.J. A pilot study of macrophage responses to silk fibroin particles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101A, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkhowa, R.; Gil, E.S.; Kluge, J.; Numata, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Kaplan, D.L. Reinforcing Silk Scaffolds with Silk Particles. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 10, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, J.; Chung, Y.I.; Kim, Y.H.; Tae, G.; Kundu, S.C. Silk fibroin nanoparticles for cellular uptake and control release. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 388, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, J.; Lee, K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.Y. Simple preparation and characteristics of silk fibroin microsphere. Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenk, E.; Wandrey, A.J.; Merkle, H.P.; Meinel, L. Silk fibroin spheres as a platform for controlled drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Aseh, A.; Rios, C.N.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Mathur, A.B. Fabrication and characterization of silk fibroin-derived curcumin nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2009, 4, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, H.; Song, D.W.; Kwak, H.W.; Yun, H.; Um, I.C.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, K.H. Effect of shear viscosity on the preparation of sphere-like silk fibroin microparticles by electrospraying. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, O.J.; Kim, J.; Moon, B.M.; Chao, J.R.; Yoon, J.; Ju, H.W.; Lee, J.M.; Park, H.J.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Fabrication and characterization of hydrocolloid dressing with silk fibroin nanoparticles for wound healing. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 13, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Mitropoulos, A.N.; Marelli, B.; Simpson, D.A.; Tran, P.A.; Omenetto, F.G.; Tomljenovic-Hanic, S. Fluorescent Nanodiamond Silk Fibroin Spheres: Advanced Nanoscale Bioimaging Tool. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoura, N.; Tsukada, M.; Nagura, M. Physico-chemical properties of silk fibroin membrane as a biomaterial. Biomaterials 1990, 11, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, D.; Yokoyama, Y.; Hattori, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Tamada, Y. The outermost surface properties of silk fibroin films reflect ethanol-treatment conditions used in biomaterial preparation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagnella, A.; Pistone, A.; Bonetti, S.; Donnadio, A.; Saracino, E.; Nocchetti, M.; Dionigi, C.; Ruani, G.; Muccini, M.; Posati, T. Effect of different fabrication methods on the chemo-physical properties of silk fibroin films and on their interaction with neural cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 9304–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, X.; Gunawidjaja, R.; Lin, Y.H.; Gupta, M.K.; Kaplan, D.L.; Naik, R.R.; Tsukruk, V.V. Mechanical Properties of Robust Ultrathin Silk Fibroin Films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demura, M.; Asakura, T. Immobilization of glucose oxidase with Bombyx mori silk fibroin by only stretching treatment and its application to glucose sensor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1989, 33, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.J.; Park, J.; Karageorgiou, V.; Kim, U.J.; Valluzzi, R.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Water-Stable Silk Films with Reduced β-Sheet Content. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Kluge, J.A.; Lu, S.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Water-insoluble silk films with silk I structure. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Shi, L.; Zhong, J.; Zhu, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, P.; Cao, C.; He, D. Regenerated Silk Fibroin Films with Controllable Nanostructure Size and Secondary Structure for Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2014, 6, 21813–21821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Chen, J.; Karageorgiou, V.; Altman, G.H.; Kaplan, D.L. Human bone marrow stromal cell responses on electrospun silk fibroin mats. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Shao, H.; Hu, X. Morphology and structure of electrospun mats from regenerated silk fibroin aqueous solutions with adjusting pH. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2007, 41, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessrino, A.; Marelli, B.; Arosio, C.; Fare, S.; Tanzi, M.C.; Freddi, G. Electrospun Silk Fibroin Mats for Tissue Engineering. Eng. Life Sci. 2008, 8, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, H.; Hu, X. Electrospun ultra-fine silk fibroin fibers from aqueous solutions. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 5359–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meechaisue, C.; Wutticharoenmongkol, P.; Waraput, R.; Huangjing, T.; Ketbumrung, N.; Pavasant, P.; Supaphol, P. Preparation of electrospun silk fibroin fiber mats as bone scaffolds: A preliminary study. Biomed. Mater. 2007, 2, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chuanbao, C.; Xilan, M.; Yin, T.; Hesun, Z. Preparation of non-woven mats from all-aqueous silk fibroin solution with electrospinning method. Polymer 2006, 47, 6322–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, L.; Yao, J. Electrospinning of Bombyx mori silk fibroin nanofiber mats reinforced by cellulose nanowhiskers. Fiber Polym. 2011, 12, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttayarat, P.; Jetawattana, S.; Suwanmala, P.; Eamsiri, J.; Tangthong, T.; Pongpat, S. Antimicrobial electrospun silk fibroin mats with silver nanoparticles for wound dressing application. Fiber Polym. 2012, 13, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jao, W.; Yang, M.; Lin, C.; Hsu, C. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun silk fibroin/TiO2 nanofibrous mats for wound dressings. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 23, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinel, L.; Hofmann, S.; Karageorgiou, V.; Kirker-Head, C.; McCool, J.; Gronowicz, G.; Zichner, L.; Langer, R.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Kaplan, D.L. The inflammatory responses to silk films in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, H.; Ha, H.C.; Um, I.C.; Park, Y.H. Physical properties of silk fibroin/chitosan blend films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Fan, L.; He, C.; Zhang, K.; Mo, X.; Wang, H. Vitamin E-loaded silk fibroin nanofibrous mats fabricated by green process for skin care application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 56, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safdari, M.; Shakiba, E.; Kiaie, S.H.; Fattahi, A. Preparation and characterization of Ceftazidime loaded electrospun silk fibroin/gelatin mat for wound dressing. Fiber Polym. 2016, 17, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, C.; Yao, C.; Chung, S.; Yao, J.; Lee, I.; Kong, X. Silk fibroin membrane used for guided bone tissue regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Ghezzi, C.E.; Kaplan, D.L. Optimization of silk films as substrate for functional corneal epithelium growth. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2016, 104, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Kluge, J.A.; Leisk, G.G.; Kaplan, D.L. Sonication-induced gelation of silk fibroin for cell encapsulation. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yucel, T.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Vortex-Induced Injectable Silk Fibroin Hydrogels. Biophys. J. 2009, 97, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keene, E.C.; Evans, J.S.; Estroff, L.A. Silk Fibroin Hydrogels Coupled with the n16N−β-Chitin Complex: An in Vitro Organic Matrix for Controlling Calcium Carbonate Mineralization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 5169–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; de Moraes, M.A.; Beppu, M.M.; Garcia, M.P.; Fernandes, M.H.; Monteiro, F.J.; Ferraz, M.P. Development of silk fibroin/nanohydroxyapatite composite hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, J.; Poole-Warren, L.A.; Martens, P.; Kundu, S.C. Silk fibroin/poly(vinyl alcohol) photocrosslinked hydrogels for delivery of macromolecular drugs. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1720–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, M.; Zuo, B.; Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk fibroin electrogelation mechanisms. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2394–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, U.; Park, J.; Li, C.; Jin, H.; Valluzzi, R.; Kaplan, D.L. Structure and Properties of Silk Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, A.; Chen, J.; Collette, A.L.; Kim, U.; Altman, G.H.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Mechanisms of Silk Fibroin Sol−Gel Transitions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 21630–21638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.H.; Song, D.W.; Kim, M.J.; Ryu, S.J.; Um, I.C.; Ki, C.S.; Park, Y.H. Effect of silk fibroin molecular weight on physical property of silk hydrogel. Polymer 2016, 90, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partlow, B.P.; Hanna, C.W.; Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; Moreau, J.E.; Applegate, M.B.; Burke, K.A.; Marelli, B.; Mitropoulos, A.N.; Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. Highly Tunable Elastomeric Silk Biomaterials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4615–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Oliveira, J.M.; Oliveira, A.L.; Reis, R.L. Core-shell silk hydrogels with spatially tuned conformations as drug-delivery system. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazarov, R.; Jin, H.; Kaplan, D.L. Porous 3-D Scaffolds from Regenerated Silk Fibroin. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kim, U.; Blasioli, D.J.; Kim, H.; Kaplan, D.L. In vitro cartilage tissue engineering with 3D porous aqueous-derived silk scaffolds and mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 7082–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, U.; Park, J.; Joo Kim, H.; Wada, M.; Kaplan, D.L. Three-dimensional aqueous-derived biomaterial scaffolds from silk fibroin. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2775–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, B.B.; Kundu, S.C. Cell proliferation and migration in silk fibroin 3D scaffolds. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2956–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamada, Y. New Process to Form a Silk Fibroin Porous 3-D Structure. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3100–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Oliveira, J.M.; Oliveira, A.L.; Caridade, S.G.; Mano, J.F.; Reis, R.L. Macro/microporous silk fibroin scaffolds with potential for articular cartilage and meniscus tissue engineering applications. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutolf, M.P.; Gilbert, P.M.; Blau, H.M. Designing materials to direct stem-cell fate. Nature 2009, 462, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Silva-Correia, J.; Ribeiro, V.P.; Miranda-Gonçalves, V.; Correia, C.; Da Silva Morais, A.; Sousa, R.A.; Reis, R.M.; Oliveira, A.L.; Oliveira, J.M.; et al. Tumor Growth Suppression Induced by Biomimetic Silk Fibroin Hydrogels. Sci. Rep. (UK) 2016, 6, 31037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yan, S.; You, R.; Kaplan, D.L.; Liu, Y.; Qu, J.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Multichannel silk protein/laminin grafts for spinal cord injury repair. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2016, 104, 3045–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Ning, H.; Liu, S.; Lu, Q.; Fan, Z.; Lu, H.; Lu, G.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk Biomaterials with Vascularization Capacity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.G. The cultivation of tissues in extraneous media as a method of morpho-genetic study. Anat. Rec. 1912, 6, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Weng, Y.; Chen, G.; Hu, Z. Guiding the behaviors of human umbilical vein endothelial cells with patterned silk fibroin films. Colloid Surf. B 2014, 122, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; You, R.; Luo, Z.; Chen, G.; Li, M. Silk fibroin scaffolds with a micro-/nano-fibrous architecture for dermal regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2903–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Ding, J. Preparation of hydroxyapatite micropatterns for the study of cell–biomaterial interactions. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 2220–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, S.; Marelli, B.; Lee, M.; Kim, T.; Oh, H.; Jeon, H.; Omenetto, F.G.; Kim, S. Eco-friendly photolithography using water-developable pure silk fibroin. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 39330–39334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M.; Ostuni, E.; Takayama, S.; Jiang, X.; Ingber, D.E. Soft lithography in biology and biochemistry. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 3, 335–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.K.; Khokhar, S.K.; Phillips, D.M.; Sowards, L.A.; Drummy, L.F.; Kadakia, M.P.; Naik, R.R. Patterned Silk Films Cast from Ionic Liquid Solubilized Fibroin as Scaffolds for Cell Growth. Langmuir 2007, 23, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, H.; Gopinath, A.; Kaplan, D.L.; Dal Negro, L.; Omenetto, F.G. Nano- and Micropatterning of Optically Transparent, Mechanically Robust, Biocompatible Silk Fibroin Films. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3070–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, G.; Ye, X.; He, D.; Zhong, J. Micropattern of nano-hydroxyapatite/silk fibroin composite onto Ti alloy surface via template-assisted electrostatic spray deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ahmed, H. Fabrication of 5–7 nm wide etched lines in silicon using 100 keV electron-beam lithography and polymethylmethacrylate resist. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 62, 1499–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinerd, V.M.; Collins, A.M.; Skaer, N.J.; Gheysens, T.; Mann, S. Silk inverse opals from template-directed β-sheet transformation of regenerated silk fibroin. Soft Matter 2007, 3, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, R.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Lu, S.; Li, M. Response of filopodia and lamellipodia to surface topography on micropatterned silk fibroin films. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 4206–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Ma, M.; Zhou, J.; Wei, D.; Yan, Z.; He, D. Tip-Induced Micropatterning of Silk Fibroin Protein Using In Situ Solution Atomic Force Microscopy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2013, 5, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; He, J.; Nichol, J.W.; Wang, L.; Hutson, C.B.; Wang, B.; Du, Y.; Fan, H.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis and characterization of photocrosslinkable gelatin and silk fibroin interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2384–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.Y.; Chuah, Y.J.; Goh, J.C.H.; Li, J.L.; Xu, H. Design and engineering of silk fibroin scaffolds with biomimetic hierarchical structures. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wüst, S.; Müller, R.; Hofmann, S. Controlled Positioning of Cells in Biomaterials—Approaches Towards 3D Tissue Printing. J. Funct. Biomater. 2011, 2, 119–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.X.F.; Mo, X.M.; Teoh, S.; Hutmacher, D.W. Scaffold development using 3D printing with a starch-based polymer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2002, 20, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.V.; Atala, A. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Parker, S.T.; Syoji, D.; Wang, X.; Lewis, J.A.; Kaplan, D.L. Direct-Write Assembly of 3D Silk/Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds for Bone Co-Cultures. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suntivich, R.; Drachuk, I.; Calabrese, R.; Kaplan, D.L.; Tsukruk, V.V. Inkjet Printing of Silk Nest Arrays for Cell Hosting. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Pati, F.; Choi, Y.; Rijal, G.; Shim, J.; Kim, S.W.; Ray, A.R.; Cho, D.; Ghosh, S. Bioprintable, cell-laden silk fibroin–gelatin hydrogel supporting multilineage differentiation of stem cells for fabrication of three-dimensional tissue constructs. Acta Biomater. 2015, 11, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.J.; Brown, J.; Giordano, J.; Lin, S.J.; Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk based bioinks for soft tissue reconstruction using 3-dimensional (3D) printing with in vitro and in vivo assessments. Biomaterials 2017, 117, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Y.; Wang, H.; Wei, K.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, R.-Y.; Kim, I.S.; Zhang, K.-Q. A Review of Structure Construction of Silk Fibroin Biomaterials from Single Structures to Multi-Level Structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030237
Qi Y, Wang H, Wei K, Yang Y, Zheng R-Y, Kim IS, Zhang K-Q. A Review of Structure Construction of Silk Fibroin Biomaterials from Single Structures to Multi-Level Structures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(3):237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030237
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Yu, Hui Wang, Kai Wei, Ya Yang, Ru-Yue Zheng, Ick Soo Kim, and Ke-Qin Zhang. 2017. "A Review of Structure Construction of Silk Fibroin Biomaterials from Single Structures to Multi-Level Structures" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 3: 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030237
APA StyleQi, Y., Wang, H., Wei, K., Yang, Y., Zheng, R.-Y., Kim, I. S., & Zhang, K.-Q. (2017). A Review of Structure Construction of Silk Fibroin Biomaterials from Single Structures to Multi-Level Structures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(3), 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030237