Roles of Copper-Binding Proteins in Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Copper Proteins in Biology
2. Copper in Cancer
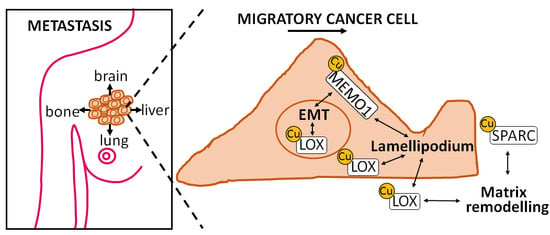
3. Copper Proteins Involved in Diverse Aspects of Cancer
4. Copper-Binding Proteins in Breast Cancer: A Clinical Perspective
5. ATOX1 in Breast Cancer
6. Summary and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grubman, A.; White, A.R. Copper as a key regulator of cell signalling pathways. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2014, 16, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohrvik, H.; Thiele, D.J. How copper traverses cellular membranes through the mammalian copper transporter 1, CTR1. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1314, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puig, S.; Thiele, D.J. Molecular mechanisms of copper uptake and distribution. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2002, 6, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.A.; Pena, M.M.; Thiele, D.J. Copper-binding motifs in catalysis, transport, detoxification and signaling. Chem. Biol. 1997, 4, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.H.; Brown, R.; Linder, M.C. Circulating ceruloplasmin is an important source of copper for normal and malignant animal cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1981, 678, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, D.; Mar, D.; Ishida, M.; Vargas, R.; Gaite, M.; Montgomery, A.; Linder, M.C. Mechanism of copper uptake from blood plasma ceruloplasmin by mammalian cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blockhuys, S.; Celauro, E.; Hildesjo, C.; Feizi, A.; Stal, O.; Fierro-Gonzalez, J.C.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Defining the human copper proteome and analysis of its expression variation in cancers. Met. Integr. Biomet. Sci. 2017, 9, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hodgkinson, V.; Zhu, S.; Weisman, G.A.; Petris, M.J. Advances in the understanding of mammalian copper transporters. Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips-Krawczak, C.A.; Singla, A.; Starokadomskyy, P.; Deng, Z.; Osborne, D.G.; Li, H.; Dick, C.J.; Gomez, T.S.; Koenecke, M.; Zhang, J.S.; et al. COMMD1 is linked to the WASH complex and regulates endosomal trafficking of the copper transporter ATP7A. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Du, J.; Zhang, P.; Ding, J. Crystal structure of human copper homeostasis protein CUTC reveals a potential copper-binding site. J. Struct. Biol. 2010, 169, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matson Dzebo, M.; Arioz, C.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Extended functional repertoire for human copper chaperones. Biomol. Concepts 2016, 7, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turski, M.L.; Thiele, D.J. New roles for copper metabolism in cell proliferation, signaling, and disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denoyer, D.; Masaldan, S.; La Fontaine, S.; Cater, M.A. Targeting copper in cancer therapy: “Copper that cancer”. Met. Integr. Biometal Sci. 2015, 7, 1459–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.; Divekar, S.D.; Storchan, G.B.; Parodi, D.A.; Martin, M.B. Metals and breast cancer. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplas. 2013, 18, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupte, A.; Mumper, R.J. Elevated copper and oxidative stress in cancer cells as a target for cancer treatment. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2009, 35, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigiracciolo, D.C.; Scarpelli, A.; Lappano, R.; Pisano, A.; Santolla, M.F.; de Marco, P.; Cirillo, F.; Cappello, A.R.; Dolce, V.; Belfiore, A.; et al. Copper activates HIF-1α/GPER/VEGF signalling in cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34158–34177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Kleer, C.G.; van Golen, K.L.; Irani, J.; Bottema, K.M.; Bias, C.; de Carvalho, M.; Mesri, E.A.; Robins, D.M.; Dick, R.D.; et al. Copper deficiency induced by tetrathiomolybdate suppresses tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4854–4859. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kenneth, N.S.; Hucks, G.E., Jr.; Kocab, A.J.; McCollom, A.L.; Duckett, C.S. Copper is a potent inhibitor of both the canonical and non-canonical NFκB pathways. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, H.M.; Xue, Y.; Robinson, C.D.; Canalizo-Hernandez, M.A.; Marvin, R.G.; Kelly, R.A.; Mondragon, A.; Penner-Hahn, J.E.; O’Halloran, T.V. Tetrathiomolybdate inhibits copper trafficking proteins through metal cluster formation. Science 2010, 327, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, G.J. The use of copper-lowering therapy with tetrathiomolybdate in medicine. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, S.; Andreux, P.; Poitry-Yamate, C.; Auwerx, J.; Hanahan, D. Bioavailable copper modulates oxidative phosphorylation and growth of tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19507–19512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Wu, C.; Dang, X.; Liu, Y. Copper depletion inhibits CoCl2-induced aggressive phenotype of MCF-7 cells via downregulation of HIF-1 and inhibition of SNAIL/TWIST-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Luo, C.; Shan, C.; You, Q.; Lu, J.; Elf, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wen, Y.; Vinkenborg, J.L.; Fan, J.; et al. Inhibition of human copper trafficking by a small molecule significantly attenuates cancer cell proliferation. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 968–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddikuzzaman; Grace, V.M.; Guruvayoorappan, C. Lysyl oxidase: A potential target for cancer therapy. Inflammopharmacology 2011, 19, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Ge, G. Lysyl oxidase, extracellular matrix remodeling and cancer metastasis. Cancer Microenviron. 2012, 5, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erler, J.T.; Bennewith, K.L.; Cox, T.R.; Lang, G.; Bird, D.; Koong, A.; Le, Q.T.; Giaccia, A.J. Hypoxia-induced lysyl oxidase is a critical mediator of bone marrow cell recruitment to form the premetastatic niche. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pez, F.; Dayan, F.; Durivault, J.; Kaniewski, B.; Aimond, G.; Le Provost, G.S.; Deux, B.; Clezardin, P.; Sommer, P.; Pouyssegur, J.; et al. The HIF-1-inducible lysyl oxidase activates HIF-1 via the Akt pathway in a positive regulation loop and synergizes with HIF-1 in promoting tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, T.R.; Rumney, R.M.; Schoof, E.M.; Perryman, L.; Hoye, A.M.; Agrawal, A.; Bird, D.; Latif, N.A.; Forrest, H.; Evans, H.R.; et al. The hypoxic cancer secretome induces pre-metastatic bone lesions through lysyl oxidase. Nature 2015, 522, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, T.R.; Gartland, A.; Erler, J.T. Lysyl oxidase, a targetable secreted molecule involved in cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levental, K.R.; Yu, H.; Kass, L.; Lakins, J.N.; Egeblad, M.; Erler, J.T.; Fong, S.F.; Csiszar, K.; Giaccia, A.; Weninger, W.; et al. Matrix crosslinking forces tumor progression by enhancing integrin signaling. Cell 2009, 139, 891–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erler, J.T.; Bennewith, K.L.; Nicolau, M.; Dornhofer, N.; Kong, C.; Le, Q.T.; Chi, J.T.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Giaccia, A.J. Lysyl oxidase is essential for hypoxia-induced metastasis. Nature 2006, 440, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, S.L.; Hendrix, M.J.; Kirschmann, D.A. Lysyl oxidase regulates actin filament formation through the p130(Cas)/Crk/Dock180 signaling complex. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 98, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iturbide, A.; Garcia de Herreros, A.; Peiro, S. A new role for LOX and LOXL2 proteins in transcription regulation. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 1768–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, D.C.; Crowe, M.S.; Turski, M.L.; Hobbs, G.A.; Yao, X.; Chaikuad, A.; Knapp, S.; Xiao, K.; Campbell, S.L.; Thiele, D.J.; et al. Copper is required for oncogenic braf signalling and tumorigenesis. Nature 2014, 509, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemieux, E.; Bergeron, S.; Durand, V.; Asselin, C.; Saucier, C.; Rivard, N. Constitutively active MEK1 is sufficient to induce epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in intestinal epithelial cells and to promote tumor invasion and metastasis. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turski, M.L.; Brady, D.C.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, B.E.; Nose, Y.; Counter, C.M.; Winge, D.R.; Thiele, D.J. A novel role for copper in RAS/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meira, M.; Masson, R.; Stagljar, I.; Lienhard, S.; Maurer, F.; Boulay, A.; Hynes, N.E. MEMO is a cofilin-interacting protein that influences PLCγ1 and cofilin activities, and is essential for maintaining directionality during ErbB2-induced tumor-cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaoui, K.; Honore, S.; Isnardon, D.; Braguer, D.; Badache, A. MEMO-Rhoa-mDia1 signaling controls microtubules, the actin network, and adhesion site formation in migrating cells. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, G.; Nalvarte, I.; Smirnova, T.; Vecchi, M.; Aceto, N.; Dolemeyer, A.; Frei, A.; Lienhard, S.; Wyckoff, J.; Hess, D.; et al. MEMO is a copper-dependent redox protein with an essential role in migration and metastasis. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, ra56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokin, A.V.; Chen, J. MEMO1, a new IRS1-interacting protein, induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3130–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okkelman, I.A.; Sukaeva, A.Z.; Kirukhina, E.V.; Korneenko, T.V.; Pestov, N.B. Nuclear translocation of lysyl oxidase is promoted by interaction with transcription repressor p66β. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 358, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S.A.; Brekken, R.A. SPARC: A matricellular regulator of tumorigenesis. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2009, 3, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraju, G.P.; Dontula, R.; El-Rayes, B.F.; Lakka, S.S. Molecular mechanisms underlying the divergent roles of SPARC in human carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, M.S.; Workman, G.; Sage, E.H. The copper binding domain of SPARC mediates cell survival in vitro via interaction with integrin β1 and activation of integrin-linked kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 22826–22837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrissey, M.A.; Jayadev, R.; Miley, G.R.; Blebea, C.A.; Chi, Q.; Ihara, S.; Sherwood, D.R. SPARC promotes cell invasion in vivo by decreasing type IV collagen levels in the basement membrane. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhoopathi, P.; Gondi, C.S.; Gujrati, M.; Dinh, D.H.; Lakka, S.S. SPARC mediates src-induced disruption of actin cytoskeleton via inactivation of small GTPases Rho-Rac-Cdc42. Cell Signal. 2011, 23, 1978–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Sluis, B.; Mao, X.; Zhai, Y.; Groot, A.J.; Vermeulen, J.F.; van der Wall, E.; van Diest, P.J.; Hofker, M.H.; Wijmenga, C.; Klomp, L.W.; et al. COMMD1 disrupts HIF-1α/β dimerization and inhibits human tumor cell invasion. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2119–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, S.; Kim, H.W.; Nakagawa, O.; Ozumi, K.; Lessner, S.M.; Aoki, H.; Akram, K.; McKinney, R.D.; Ushio-Fukai, M.; Fukai, T. Novel role of antioxidant-1 (ATOX1) as a copper-dependent transcription factor involved in cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 9157–9167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, E.A.; Assoian, R.K. Transcriptional regulation of the cyclin D1 gene at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 3853–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, S.; Ozumi, K.; Kim, H.W.; Nakagawa, O.; McKinney, R.D.; Folz, R.J.; Zelko, I.N.; Ushio-Fukai, M.; Fukai, T. Novel mechanism for regulation of extracellular sod transcription and activity by copper: Role of antioxidant-1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozumi, K.; Sudhahar, V.; Kim, H.W.; Chen, G.F.; Kohno, T.; Finney, L.; Vogt, S.; McKinney, R.D.; Ushio-Fukai, M.; Fukai, T. Role of copper transport protein antioxidant 1 in angiotensin II-induced hypertension: A key regulator of extracellular superoxide dismutase. Hypertension 2012, 60, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.F.; Sudhahar, V.; Youn, S.W.; Das, A.; Cho, J.; Kamiya, T.; Urao, N.; McKinney, R.D.; Surenkhuu, B.; Hamakubo, T.; et al. Copper transport protein antioxidant-1 promotes inflammatory neovascularization via chaperone and transcription factor function. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, T.; Urao, N.; Ashino, T.; Sudhahar, V.; McKinney, R.D.; Hamakubo, T.; Iwanari, H.; Ushio-Fukai, M.; Fukai, T. Novel role of copper transport protein antioxidant-1 in neointimal formation after vascular injury. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Ding, X.; Zhang, Z.; Kang, Y.J. Copper is required for cobalt-induced transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 342, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahra, D.; Mondol, T.; Niemiec, M.S.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Human copper chaperone ATOX1 translocates to the nucleus but does not bind DNA in vitro. Protein Pept. Lett. 2015, 22, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohrvik, H.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Identification of new potential interaction partners for human cytoplasmic copper chaperone ATOX1: Roles in gene regulation? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 16728–16739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.T.; Wen, X.; Han, T.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, S.B.; Wang, J.G.; Liu, X.P. Expression of CPEB4 in invasive ductal breast carcinoma and its prognostic significance. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 3499–3506. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Zapater, E.; Pineda, D.; Martinez-Bosch, N.; Fernandez-Miranda, G.; Iglesias, M.; Alameda, F.; Moreno, M.; Eliscovich, C.; Eyras, E.; Real, F.X.; et al. Key contribution of CPEB4-mediated translational control to cancer progression. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callebaut, I.; Courvalin, J.C.; Mornon, J.P. The BAH (bromo-adjacent homology) domain: A link between DNA methylation, replication and transcriptional regulation. FEBS Lett. 1999, 446, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Helps, N.R.; Cohen, P.T.; Barford, D. Crystal structure of the protein serine/threonine phosphatase 2C at 2.0 A resolution. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 6798–6809. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Duan, X.; Liang, Y.Y.; Su, Y.; Wrighton, K.H.; Long, J.; Hu, M.; Davis, C.M.; Wang, J.; Brunicardi, F.C.; et al. PPM1A functions as a Smad phosphatase to terminate tgfβ signaling. Cell 2006, 125, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.W.; Chen, S.F.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, D.R.; Lee, J.H. Serum and tissue trace elements in patients with breast cancer in taiwan. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2002, 89, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, G.M.; Othman, M.; Fox, B.P.; Alsaber, R.; Pellegrino, C.M.; Zeng, Y.; Khanna, R.; Tamburini, P.; Swaroop, A.; Kandpal, R.P. Gene expression signatures and biomarkers of noninvasive and invasive breast cancer cells: Comprehensive profiles by representational difference analysis, microarrays and proteomics. Oncogene 2006, 25, 2328–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzaki, A.; Toi, M.; Neamati, N.; Miyashita, H.; Oubu, M.; Nakayama, K.; Bando, H.; Ogawa, K.; Mutoh, M.; Mori, S.; et al. Copper-transporting P-type adenosine triphosphatase (ATP7B) is expressed in human breast carcinoma. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2002, 93, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm-Espling, M.E.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Reaction of platinum anticancer drugs and drug derivatives with a copper transporting protein, ATOX1. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm-Espling, M.E.; Andersson, C.D.; Bjorn, E.; Linusson, A.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Determinants for simultaneous binding of copper and platinum to human chaperone ATOX1: Hitchhiking not hijacking. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, M.E.; Weise, C.F.; Lundin, C.; Wingsle, G.; Nygren, Y.; Bjorn, E.; Naredi, P.; Wolf-Watz, M.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Cisplatin binds human copper chaperone ATOX1 and promotes unfolding in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6951–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, C.L.; Wang, H.; Wong, A.H.; Vazquez-Ortiz, G.; Chen, W.; Xu, X.; Deng, C.X. Ammonium tetrathiomolybdate treatment targets the copper transporter ATP7A and enhances sensitivity of breast cancer to cisplatin. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 84439–84452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Haibi, C.P.; Bell, G.W.; Zhang, J.; Collmann, A.Y.; Wood, D.; Scherber, C.M.; Csizmadia, E.; Mariani, O.; Zhu, C.; Campagne, A.; et al. Critical role for lysyl oxidase in mesenchymal stem cell-driven breast cancer malignancy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17460–17465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, S.L.; Fogelgren, B.; Hess, A.R.; Seftor, E.A.; Wiley, E.L.; Fong, S.F.; Csiszar, K.; Hendrix, M.J.; Kirschmann, D.A. Lysyl oxidase regulates breast cancer cell migration and adhesion through a hydrogen peroxide-mediated mechanism. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 11429–11436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollosi, P.; Yakushiji, J.K.; Fong, K.S.; Csiszar, K.; Fong, S.F. Lysyl oxidase-like 2 promotes migration in noninvasive breast cancer cells but not in normal breast epithelial cells. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.J.; Finney, J.; Xu, L.; Moore, D.; Welch, D.R.; Mure, M. MCF-7 cells expressing nuclear associated lysyl oxidase-like 2 (LOXL2) exhibit an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) phenotype and are highly invasive in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 30000–30008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.G.; Dong, S.M.; Oshima, A.; Kim, W.H.; Lee, H.M.; Lee, S.A.; Kwon, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Jeong, J.; et al. LOXL2 expression is associated with invasiveness and negatively influences survival in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 141, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, H.E.; Chang, J.; Cox, T.R.; Lang, G.; Bird, D.; Nicolau, M.; Evans, H.R.; Gartland, A.; Erler, J.T. LOXL2-mediated matrix remodeling in metastasis and mammary gland involution. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Bueno, G.; Salvador, F.; Martin, A.; Floristan, A.; Cuevas, E.P.; Santos, V.; Montes, A.; Morales, S.; Castilla, M.A.; Rojo-Sebastian, A.; et al. Lysyl oxidase-like 2 (LOXL2), a new regulator of cell polarity required for metastatic dissemination of basal-like breast carcinomas. EMBO Mol. Med. 2011, 3, 528–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, A.; MacDonald, G.; Lund, I.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Hynes, N.E.; Nalvarte, I. MEMO interacts with c-src to control estrogen receptor α sub-cellular localization. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 56170–56182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Wang, S.; Ning, K.; Zhou, L.; Lin, J.; Zhong, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Mediator of ErbB2-driven cell motility (MEMO) promotes extranuclear estrogen receptor signaling involving the growth factor receptors IGF1R and ErbB2. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 24590–24599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttlein, L.N.; Benedetti, L.G.; Fresno, C.; Spallanzani, R.G.; Mansilla, S.F.; Rotondaro, C.; Raffo Iraolagoitia, X.L.; Salvatierra, E.; Bravo, A.I.; Fernandez, E.A.; et al. Predictive outcomes for HER2-enriched cancer using growth and metastasis signatures driven by SPARC. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarrio, D.; Rodriguez-Pinilla, S.M.; Hardisson, D.; Cano, A.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Palacios, J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer relates to the basal-like phenotype. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, G.; Douglas-Jones, A.; Bryce, R.; Mansel, R.E.; Jiang, W.G. Increased levels of SPARC (osteonectin) in human breast cancer tissues and its association with clinical outcomes. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat. Acids 2005, 72, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.D.; Balleine, R.L.; Milliken, J.S.; Bilous, A.M.; Clarke, C.L. Expression of osteonectin mRNA in human breast tumours is inversely correlated with oestrogen receptor content. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, L.Y.; Lim, S.; Chong, P.K.; Wong, C.Y.; Shah, N.; Lim, Y.P. Proteome-wide profiling of the MCF10AT breast cancer progression model. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blockhuys, S.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Copper chaperone ATOX1 plays role in breast cancer cell migration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Sudhahar, V.; Chen, G.F.; Kim, H.W.; Youn, S.W.; Finney, L.; Vogt, S.; Yang, J.; Kweon, J.; Surenkhuu, B.; et al. Endothelial antioxidant-1: A key mediator of copper-dependent wound healing in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neve, R.M.; Chin, K.; Fridlyand, J.; Yeh, J.; Baehner, F.L.; Fevr, T.; Clark, L.; Bayani, N.; Coppe, J.P.; Tong, F.; et al. A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blockhuys, S.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Roles of Copper-Binding Proteins in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040871
Blockhuys S, Wittung-Stafshede P. Roles of Copper-Binding Proteins in Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(4):871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040871
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlockhuys, Stéphanie, and Pernilla Wittung-Stafshede. 2017. "Roles of Copper-Binding Proteins in Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 4: 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040871
APA StyleBlockhuys, S., & Wittung-Stafshede, P. (2017). Roles of Copper-Binding Proteins in Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(4), 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040871