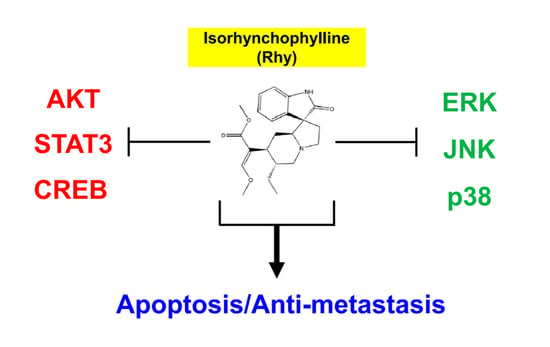
Isorhynchophylline, a Potent Plant Alkaloid, Induces Apoptotic and Anti-Metastatic Effects in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through the Modulation of Diverse Cell Signaling Cascades
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Rhy Suppressed the Cell Viability in Variety of Tumor Cells
2.2. Rhy Repressed the Expression of Various Proteins Involved in Anti-Apoptosis, Proliferation, Metastasis and Angiogenesis
2.3. Rhy Induced the Expression of Bax and p21 Proteins
2.4. Rhy Activated Caspase-3 and Caused PARP Cleavage
2.5. Overexpression of Bcl-2 Attenuated Rhy-Mediated Apoptosis
2.6. Rhy Caused the Accumulation of the Cells in the Sub-G1 Phase
2.7. Rhy Promoted Substantial Apoptotic Cell Death
2.8. Rhy Suppressed the Proliferative Activity of HepG2 Cells
2.9. Rhy Suppressed HepG2 Cells Migration and Invasion
2.10. Rhy Decreased the Phosphorylation Levels of Various Kinase Phosphorylation Sites in HepG2 Cells
2.11. Rhy Inhibited Phosphorylation of p38, ERK, JNK, CREB, c-Jun, Akt, STAT3, and Enhanced Phosphorylation of p53 in HepG2 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Lines
4.3. MTT Assay
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Transfection with pEGFP-Bcl-2 Plasmids
4.6. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.7. Annexin V Assay
4.8. TUNEL Assay
4.9. Real-Time Cell Proliferation Analysis
4.10. Live and Dead Assay
4.11. Wound Healing Assay
4.12. Invasion Assay
4.13. Human Phospho-Kinase Array
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.J.; Xu, J.; Feng, F.; Qu, W. Medicinal uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of the genus Uncaria. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 173, 48–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Zhou, S.W. Isorhynchophylline: A plant alkaloid with therapeutic potential for cardiovascular and central nervous system diseases. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, S.; Carvalho, A.R.; Pittol, V.; Dietrich, F.; Manica, F.; Machado, M.M.; de Oliveira, L.F.; Oliveira Battastini, A.M.; Ortega, G.G. Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of oxindole alkaloids from Uncaria tomentosa (cat’s claw): Chemotype relevance. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 189, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Ma, B.; Wu, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Wu, L.; Kano, Y. Alkaloids from the leaves of Uncaria rhynchophylla and their inhibitory activity on NO production in lipopolysaccharide-activated microglia. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1271–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Ma, B.; Yang, J.Y.; Xie, Y.Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.J.; Kano, Y.; Wu, C.F. Anti-inflammatory effects of rhynchophylline and isorhynchophylline in mouse N9 microglial cells and the molecular mechanism. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Chai, E.Z.; Kanchi, M.M.; Kar, S.; Arfuso, F.; Dharmarajan, A.; Kumar, A.P.; Ramar, P.S.; Looi, C.Y.; et al. Cancer prevention and therapy through the modulation of transcription factors by bioactive natural compounds. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishayee, A.; Sethi, G. Bioactive natural products in cancer prevention and therapy: Progress and promise. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, J.C. Mechanisms of apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1415–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igney, F.H.; Krammer, P.H. Death and anti-death: Tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Kannaiyan, R.; Sethi, G. Targeting cell signaling and apoptotic pathways by dietary agents: Role in the prevention and treatment of cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thushara, R.M.; Hemshekhar, M.; Santhosh, M.S.; Devaraja, S.; Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S. Differential action of phytochemicals on platelet apoptosis: A biological overview. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes-Hernandez, T.Y.; Giampieri, F.; Gasparrini, M.; Mazzoni, L.; Quiles, J.L.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Battino, M. The effects of bioactive compounds from plant foods on mitochondrial function: A focus on apoptotic mechanisms. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 154–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Xi, C.; Wang, W.; Fu, X.; Jinqiang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Jin, J.; Xu, J.; Huang, Z. Triptolide-induced oxidative stress involved with Nrf2 contribute to cardiomyocyte apoptosis through mitochondrial dependent pathways. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 230, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. The Bcl-2 protein family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science 1998, 281, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinou, J.C.; Green, D.R. Breaking the mitochondrial barrier. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Hurwitz, J.; Massague, J. Cell-cycle inhibition by independent CDK and PCNA binding domains in p21Cip1. Nature 1995, 375, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, H.; Iwasaki, K.; Furukawa, K.; Seki, T.; He, M.; Maruyama, M.; Tomita, N.; Kudo, Y.; Higuchi, M.; Saido, T.C.; et al. Uncaria rhynchophylla, a Chinese medicinal herb, has potent antiaggregation effects on Alzheimer’s β-amyloid proteins. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 84, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.J.; Yu, J.Y.; Hwang, B.Y.; Ye, S.K.; Shujuan, L.; Gao, L.; Pyo, M.Y.; Yun, Y.P. Corynoxeine isolated from the hook of Uncaria rhynchophylla inhibits rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through the blocking of extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Son, D.; Lee, P.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, C.J.; Lim, E. Alkaloid fraction of Uncaria rhynchophylla protects against N-methyl-d-aspartate-induced apoptosis in rat hippocampal slices. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 348, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Ahn, J.S.; Chang, Y.S. Inhibition of phospholipase cγ1 and cancer cell proliferation by triterpene esters from Uncaria rhynchophylla. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornberry, N.A.; Lazebnik, Y. Caspases: Enemies within. Science 1998, 281, 1312–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, B.B.; Green, D.R. Suicidal tendencies: Apoptotic cell death by caspase family proteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 20049–20052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamzami, N.; Brenner, C.; Marzo, I.; Susin, S.A.; Kroemer, G. Subcellular and submitochondrial mode of action of Bcl-2-like oncoproteins. Oncogene 1998, 16, 2265–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.; Zha, J.; Jockel, J.; Boise, L.H.; Thompson, C.B.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Bad, a heterodimeric partner for Bcl-XL and Bcl-2, displaces Bax and promotes cell death. Cell 1995, 80, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.W.; Chen, J.T.; Hong, C.Y.; Lin, Y.L.; Wang, K.T.; Yao, C.J.; Lai, G.M.; Chen, R.M. Honokiol traverses the blood-brain barrier and induces apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells via an intrinsic bax-mitochondrion-cytochrome c-caspase protease pathway. Neuro-Oncology 2012, 14, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, B.W.; Duckett, C.S. The IAP proteins: Caspase inhibitors and beyond. Sci. STKE 2000, 2000, pe1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.L.; Li, X.M. The IAP family: Endogenous caspase inhibitors with multiple biological activities. Cell Res. 2000, 10, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, J.C. Bcl-2 family proteins: Regulators of apoptosis and chemoresistance in hematologic malignancies. Semin. Hematol. 1997, 34, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Proudfoot, A.E. Chemokine receptors: Multifaceted therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brummer, O.; Athar, S.; Riethdorf, L.; Loning, T.; Herbst, H. Matrix-metalloproteinases 1, 2, and 3 and their tissue inhibitors 1 and 2 in benign and malignant breast lesions: An in situ hybridization study. Virchows Arch. 1999, 435, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liotta, L.A.; Steeg, P.S.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: An imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell 1991, 64, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, G.; O’Byrne, K.J. Matrix metalloproteinases and cancer. Anticancer Res. 2001, 21, 4207–4219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Egeblad, M.; Werb, Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.X.; Wei, D.; Liu, M.; Gao, A.C.; Ali-Osman, F.; Sawaya, R.; Huang, S. STAT3 activation regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tumor invasion and metastasis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 3550–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam, H.S.; Arand, G.; Lippman, M.E.; Thompson, E.W. Association of MMP-2 activation potential with metastatic progression in human breast cancer cell lines independent of MMP-2 production. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1993, 85, 1758–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, Y.F.; Lin, Z.X.; Mao, Q.Q.; Chen, J.N.; Su, Z.R.; Lai, X.P.; Ip, P.S. Isorhynchophylline Protects PC12 cells against β-amyloid-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 163057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Deng, W.; Xu, D.; Han, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.; et al. Isorhynchophylline protects against pulmonary arterial hypertension and suppresses PASMCs proliferation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.B.; Nabha, S.M.; Atanaskova, N. Role of MAP kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Li, B.X.; Mitton, B.; Ikeda, A.; Sakamoto, K.M. Targeting CREB for cancer therapy: Friend or foe. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2010, 10, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarthout, J.T.; Tyson, D.R.; Jefcoat, S.C., Jr.; Partridge, N.C. Induction of transcriptional activity of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein by parathyroid hormone and epidermal growth factor in osteoblastic cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2002, 17, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, E.Z.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Dharmarajan, A.; Wang, C.; Kumar, A.P.; Samy, R.P.; Lim, L.H.; Wang, L.; Goh, B.C.; et al. Targeting transcription factor STAT3 for cancer prevention and therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 162, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, N.E.; Lane, H.A. ERBB receptors and cancer: The complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, J.G.; Ehlting, C.; Haussinger, D. The macrophage response towards LPS and its control through the p38(MAPK)-STAT3 axis. Cell Signal. 2012, 24, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierenga, A.T.; Vogelzang, I.; Eggen, B.J.; Vellenga, E. Erythropoietin-induced serine 727 phosphorylation of STAT3 in erythroid cells is mediated by a MEK-, ERK-, and MSK1-dependent pathway. Exp. Hematol. 2003, 31, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, L.P.; Mollenauer, M.N.; Xu, Z.; Turck, C.W.; Weiss, A. Akt-dependent phosphorylation specifically regulates Cot induction of NF-kappa B-dependent transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 5962–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, B.H.; Shi, X. Role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in the cell cycle progression of human prostate cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 310, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downward, J. Targeting RAS signalling pathways in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelstein, B.; Lane, D.; Levine, A.J. Surfing the p53 network. Nature 2000, 408, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, D.; Oren, M. The p53 and Mdm2 families in cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002, 12, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Nakazato, T.; Yamato, K.; Miyakawa, Y.; Yamada, T.; Hozumi, N.; Segawa, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Kizaki, M. Induction of apoptosis in leukemic cells by homovanillic acid derivative, capsaicin, through oxidative stress: Implication of phosphorylation of p53 at Ser-15 residue by reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Ko, J.-H.; Lee, S.-G.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Yang, W.M.; Um, J.-Y.; et al. Isorhynchophylline, a Potent Plant Alkaloid, Induces Apoptotic and Anti-Metastatic Effects in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through the Modulation of Diverse Cell Signaling Cascades. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051095
Lee H, Baek SH, Lee JH, Kim C, Ko J-H, Lee S-G, Chinnathambi A, Alharbi SA, Yang WM, Um J-Y, et al. Isorhynchophylline, a Potent Plant Alkaloid, Induces Apoptotic and Anti-Metastatic Effects in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through the Modulation of Diverse Cell Signaling Cascades. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(5):1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051095
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hanwool, Seung Ho Baek, Jong Hyun Lee, Chulwon Kim, Jeong-Hyeon Ko, Seok-Geun Lee, Arunachalam Chinnathambi, Sulaiman Ali Alharbi, Woong Mo Yang, Jae-Young Um, and et al. 2017. "Isorhynchophylline, a Potent Plant Alkaloid, Induces Apoptotic and Anti-Metastatic Effects in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through the Modulation of Diverse Cell Signaling Cascades" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 5: 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051095
APA StyleLee, H., Baek, S. H., Lee, J. H., Kim, C., Ko, J.-H., Lee, S.-G., Chinnathambi, A., Alharbi, S. A., Yang, W. M., Um, J.-Y., Sethi, G., & Ahn, K. S. (2017). Isorhynchophylline, a Potent Plant Alkaloid, Induces Apoptotic and Anti-Metastatic Effects in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through the Modulation of Diverse Cell Signaling Cascades. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(5), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051095