3D-QSAR, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LpxC Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Systems for Simulation
2.2. CoMFA and CoMSIA Models
2.3. CoMFA and CoMSIA Contour Maps
2.4. MESP and Mulliken Charge Analyses
2.5. Molecular Docking
2.6. Stability and Flexibility of Simulation Systems
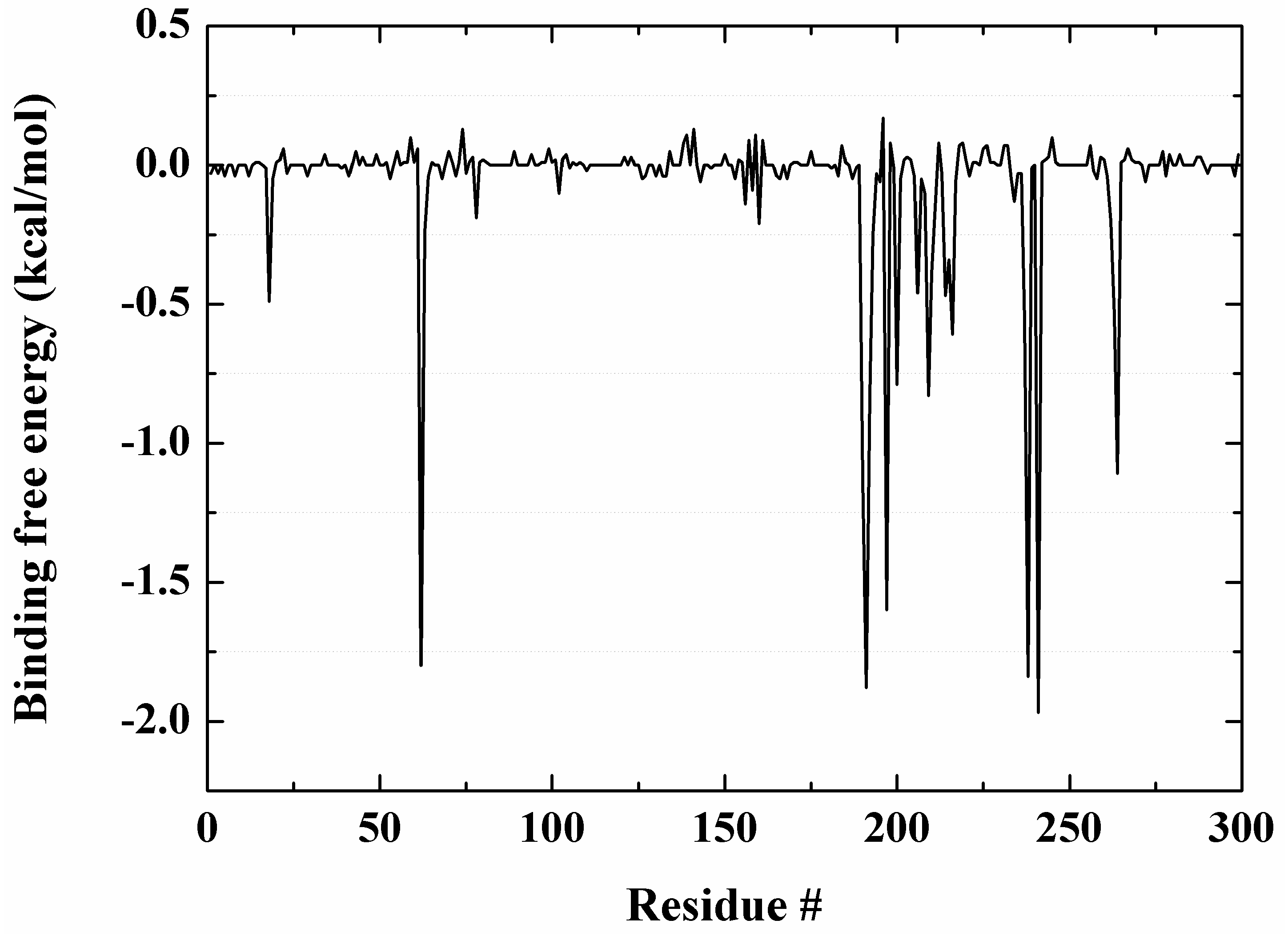
2.7. Molecular Recognition Mechanism
2.8. Conformational Change of the Systems
2.9. Water Mediated H-Bonds
2.10. Possible Inhibitory Mechanism of Cmpd # 290
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Molecular Docking
3.2. 3D-QSAR
3.3. MESP and Mulliken Charge Analyses
3.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.5. Energy Decomposition Analysis
3.6. Free Energy Landscape Analysis
3.7. Conformational Cluster Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paramythiotou, E.; Routsi, C. Association between infections caused by multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria and mortality in critically ill patients. World J. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 5, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, S.; Singh, P.; Rajurkar, M. Multidrug resistant and extensively drug resistant bacteria: A study. J. Pathog. 2016, 2016, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protic, D.; Pejovic, A.; Andjelkovic, D.; Djukanovic, N.; Savic, D.; Piperac, P.; Markovic Denic, L.; Zdravkovic, M.; Todorovic, Z. Nosocomial infections caused by Acinetobacter baumannii: Are we losing the battle? Surg. Infect. 2016, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoesser, N.; Mathers, A.J.; Moore, C.E.; Day, N.P.; Crook, D.W. Colistin resistance gene MCR-1 and pHNSHP45 plasmid in human isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labarca, J.A.; Salles, M.J.C.; Seas, C.; Guzmán-Blanco, M. Carbapenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii in the nosocomial setting in Latin America. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 276–292. [Google Scholar]
- Konya, V.; Maric, J.; Jandl, K.; Luschnig, P.; Aringer, I.; Lanz, I.; Platzer, W.; Theiler, A.; Bärnthaler, T.; Frei, R.; et al. EP4 receptor prevents endotoxin-induced neutrophil infiltration into the airways and enhances microvascular barrier function. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4454–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murzyn, K.; Pasenkiewiczgierula, M. Structural properties of the water/membrane interface of a bilayer built of the E coli Lipid A. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 5846–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.S.; Bull, H.G.; Galloway, S.M.; Kelly, T.M.; Mohan, S.; Radika, K.; Raetz, C.R. UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase of Escherichia coli. The first step of endotoxin biosynthesis is thermodynamically unfavorable. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 19858–19865. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Emiola, A.; George, J.; Andrews, S.S. A complete pathway model for lipid A biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcclerren, A.L.; Stephanie, E.; Bowman, J.L.; Andersen, N.H.; Guan, Z.; Rudolph, J.; Raetz, C.R. A slow, tight-binding inhibitor of the zinc-dependent deacetylase LpxC of lipid A biosynthesis with antibiotic activity comparable to ciprofloxacin. Biochemistry 2006, 44, 16574–16583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RCSB. Available online: www.rcsb.org (accessed on 30 February 2017).
- Jackman, J.E.; Raetz, C.R.; Fierke, C.A. Site-directed mutagenesis of the bacterial metalloamidase UDP-(3-O-Acyl)-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase (LpxC). Identification of the zinc binding site. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittington, D.A.; Rusche, K.M.; Shin, H.; Fierke, C.A.; Christianson, D.W. Crystal structure of LpxC, a zinc-dependent deacetylase essential for endotoxin biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8146–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coggins, B.E.; Mcclerren, A.L.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Rudolph, J.; Hindsgaul, O.; Raetz, C.R.; Zhou, P. Refined solution structure of the LpxC-TU-514 complex and pKa analysis of an active site histidine: Insights into the mechanism and inhibitor design. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 1114–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coggins, B.E.; Li, X.; Mcclerren, A.L.; Hindsgaul, O.; Raetz, C.R.; Zhou, P. Structure of the LpxC deacetylase with a bound substrate-analog inhibitor. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinin, D.V.; Holl, R. Insights into the zinc-dependent deacetylase LpxC: Biochemical properties and inhibitor design. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 2379–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangherlini, G.; Torregrossa, T.; Agoglitta, O.; Köhler, J.; Melesina, J.; Sippl, W.; Holl, R. Synthesis and biological evaluation of enantiomerically pure glyceric acid derivatives as LpxC inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, H.; Gabrielli, V.; Agoglitta, O.; Holl, R. Chiral pool synthesis and biological evaluation of C-furanosidic and acyclic LpxC inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 110, 340–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, S.K.; Löppenberg, M.; Daniliuc, C.G.; Holl, R. Synthesis and biological evaluation of C-ethynyl furanosides as LpxC inhibitors. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurasaki, H.; Tsuda, K.; Shinoyama, M.; Takaya, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kishii, R.; Iwase, K.; Ando, N.; Nomura, M.; Kohno, Y. LpxC inhibitors: Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of oxazolidinones as Gram-negative antibacterial agents. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titecat, M.; Liang, X.; Lee, C.J.; Charlet, A.; Hocquet, D.; Lanbert, T.; Pagès, J.M.; Courcol, R.; Sebbane, F.; Toone, E.J.; et al. High susceptibility of MDR and XDR Gram-negative pathogens to biphenyl-diacetylene-based difluoromethyl-allo-threonyl-hydroxamate LpxC inhibitors. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2874–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Magid, A.F. LpxC inhibitors as effective therapy against multidrug resistant bacterial infections. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 1095–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Wang, W.K.; Cao, Q.; Chu, W.J.; Lan, L.F.; Hu, W.H.; Yang, Y.S. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of LpxC inhibitors with novel hydrophilic terminus. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2015, 26, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.I.; Brown, M.F.; Reilly, U.; Price, L.M.; Abramite, J.A.; Barham, R.; Che, Y.; Chen, J.M.; Chung, S.W.; Collantes, E.M.; et al. Pyridone methylsulfone hydroxamate LpxC inhibitors for the treatment of serious Gram-negative infections. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1662–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ChEMBL. Available online: www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl (accessed on 30 February 2017).
- Hu, J.P.; Gong, X.Q.; Su, J.G.; Chen, W.Z.; Wang, C.X. Study on the molecular mechanism of inhibiting HIV-1 integrase by EBR28 peptide via molecular modeling approach. Biophys. Chem. 2008, 132, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.D.; Ning, G.; Ross, P.L.; Olivier, N.B. Crystal structure of A aeolicus, LpxC with bound product suggests alternate deacetylation mechanism. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2015, 83, 1706–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.L.; Liang, X.; Chen, X.; Zheng, D.; Sang, H.J.; Chung, H.S.; Barb, A.W.; Swanson, S.M.; Nicholas, R.A.; Li, Y.; et al. Species-specific and inhibitor-dependent conformations of LpxC: Implications for antibiotic design. Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinet, J.J.; Gauld, J.W. DFT investigation on the mechanism of the deacetylation reaction catalyzed by LpxC. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 3462–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernick, M.; Gennadios, H.A.; Whittington, D.A.; Rusche, K.M.; Christianson, D.W.; Fierke, C.A. UDP-3-O-((R)-3-hydroxymyristoyl)-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase functions through a general acidbase catalyst pair mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 16969–16978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClerren, A.L.; Zhou, P.; Guan, Z.; Raetz, C.R.; Rudolph, J. Kinetic analysis of the zinc-dependent deacetylase in the lipid A biosynthetic pathway. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barb, A.W.; Zhou, P. Mechanism and inhibition of LpxC: An essential zinc-dependent deacetylase of bacterial lipid A synthesis. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2008, 9, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hale, M.R.; Hill, P.; Lahiri, S.; Miller, M.D.; Ross, P.; Alm, R.; Gao, N.; Kutschke, A.; Johnstone, M.; Prince, B.; et al. Exploring the UDP pocket of LpxC through amino acid analogs. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClure, C.P.; Rusche, K.M.; Peariso, K.; Jackman, J.E.; Fierke, C.A.; Penner-Hahn, J.E. EXAFS studies of the zinc sites of UDP-(3-Oacyl)-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2003, 94, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, G.M.; Klein, D.J.; Rickert, K.W.; Patel, S.B.; Kornienko, M.; Zugay-Murphy, J.; Reid, J.C.; Tummala, S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, S.B.; et al. Structure of the bacterial deacetylase LpxC bound to the nucleotide reaction product reveals mechanisms of oxyanion stabilization and proton transfer. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 34073–34080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennadios, H.A.; Whittington, D.A.; Li, X.; Fierke, C.A.; Christianson, D.W. Mechanistic inferences from the binding of ligands to LpxC, a metal-dependent deacetylase. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 7940–7948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SYBYL-X, version 1.3; Tripos International: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2010.
- Hu, J.P.; He, H.Q.; Tang, D.Y.; Sun, G.F.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Fan, J.; Chang, S. Study on the interactions between diketo-acid inhibitors and prototype foamy virus integrase-DNA complex via molecular docking and comparative molecular dynamics simulation methods. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2013, 31, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Martins, D.; Forli, S.; Ramos, M.J.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4Zn: An improved AutoDock force field for small-molecule docking to zinc metalloproteins. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 2371–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossi, M.; Rega, N.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V. Energies, structures, and electronic properties of molecules in solution with the C-PCM solvation model. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, D.A.; Betz, R.M.; Botello-Smith, W.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Darden, T.A.; Duke, R.E.; Giese, T.J.; Gohlke, H.; Goetz, A.W.; et al. AMBER 2016; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Merz, K.M. MCPB.py: A python based metal center parameter builder. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryckaert, J.P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H.J.C. Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: Molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollman, P.A.; Massova, I.; Reyes, C.; Kuhn, B.; Huo, S.; Chong, L.; Lee, M.; Lee, T.; Duan, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Calculating structures and free energies of complex molecules: Combining molecular mechanics and continuum models. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonson, T. Macromolecular electrostatics: Continuum models and their growing pains. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2001, 11, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, J.; Shenkin, P.S.; Still, W.C. Approximate atomic surfaces from linear combinations of pairwise overlaps (LCPO). J. Comput. Chem. 1999, 20, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.H.; Derrenumaux, P. Configurational entropy: An improvement of the quasiharmonic approximation using configurational temperature. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlow, P.N.; Steinkasserer, A.; Norman, D.G.; Kieffer, B.; Wiles, A.P.; Sim, R.B.; Campbell, I.D. Solution structure of a pair of complement modules by nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 232, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feig, M.; Karanicolas, J.; Brooks, C.L., III. MMTSB tool set: Enhanced sampling and multiscale modeling methods for applications in structural biology. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2004, 22, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daura, X.; Gademann, K.; Jaun, B.; Seebach, D.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; Mark, A.E. Peptide folding: When simulation meets experiment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, K.; Liang, L.; Du, W.; Sun, X.; Liu, W.; Gou, X.; Wan, H.; Hu, J. 3D-QSAR, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LpxC Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18050761
Zuo K, Liang L, Du W, Sun X, Liu W, Gou X, Wan H, Hu J. 3D-QSAR, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LpxC Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(5):761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18050761
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Ke, Li Liang, Wenyi Du, Xin Sun, Wei Liu, Xiaojun Gou, Hua Wan, and Jianping Hu. 2017. "3D-QSAR, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LpxC Inhibitors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 5: 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18050761
APA StyleZuo, K., Liang, L., Du, W., Sun, X., Liu, W., Gou, X., Wan, H., & Hu, J. (2017). 3D-QSAR, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LpxC Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(5), 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18050761




