Molecular Cloning and Functional Characterization of a Hexokinase from the Oriental River Prawn Macrobrachium nipponense in Response to Hypoxia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characteristics and Phylogeny of MnHK
2.2. Tissue-Specific Expression of MnHK
2.3. Expression and Purification of Recombinant MnHK
2.4. Kinetic Characterization of rMnHK
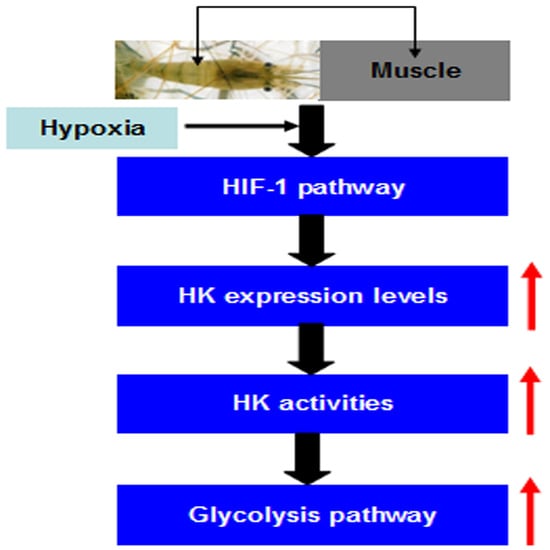
2.5. MnHK Expression and Activity in Muscles of Prawns During Hypoxia
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Ethics Statement
3.2. Experimental Animals and Hypoxia Treatment
3.3. Cloning of the MnHK cDNAs
3.4. Nucleotide Sequence and Bioinformatics Analyzes
3.5. HIF-1 Silencing and Hypoxia
3.6. qRT-PCR Analysis of MnHK Expression
3.7. Expression, Purification of MnHK and Antibody Production
3.8. Kinetic Investigations
3.9. Enzymatic Activity Assay
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HK | Hexokinase |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR |
| RACE | Rapid amplification of cDNA ends |
| HIF | Hypoxia inducible factor |
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
| DO | Dissolved oxygen |
| HRE | Hypoxia response elements |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| IPTG | Isopropyl-β-d-galactopyranoside |
| dsRNA | Double-stranded RNA |
| GPDH | Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
References
- Tsai, H.J.; Wilson, J.E. Functional organization of mammalian hexokinases: Characterization of the rat type III isozyme and its chimeric forms, constructed with the N- and C-terminal halves of the type I and type II isozymes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1997, 338, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iynedjian, P.B. Mammalian glukokinase and its gene. Biochem. J. 1993, 293, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas, M.L.; Cornish-Bowden, A.; Ureta, T. Evolution and regulatory role of the hexokinases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1401, 242–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.E. Isozymes of mammalian hexokinase: Structure, subcellular localization and metabolic function. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.E. Hexokinases. In Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology; Springer: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 1995; Volume 126, pp. 65–198. [Google Scholar]
- Soñanez-Organis, J.G.; Rodriguez-Armenta, M.; Leal-Rubio, B.; Peregrino-Uriarte, A.B.; Gómez-Jiménez, S.; Yepiz-Plascencia, G. Alternative splicing generates two lactate dehydrogenase subunits differentially expressed during hypoxia via HIF-1 in the shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Biochimie 2012, 94, 1250–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.M.; Xuan, F.J.; Ge, X.P.; Fu, H.T.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, S.Y. Identification of differentially expressed genes in hepatopancreas of oriental river prawn, Macrobrachium nipponense exposed to environmental hypoxia. Gene 2014, 534, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, P.C.; Shouche, Y.S.; Patole, M.S. Cloning of two hexokinase isoenzyme sequences from Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 31, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauera, M.M.; de Oliveira, C.B.; Yano, N.L.I.; Bianchinia, A. Copper effects on key metabolic enzymes and mitochondrial membrane potential in gills of the estuarine crab Neohelice granulata at different salinities. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2012, 156, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaxiola, G.; Cuzon, G.; Garcia, T.; Taboada, G.; Brito, R.; Chimal, M.E.; Paredes, A.; Soto, L.; Rosas, C.; van Wormhoudt, A. Factorial effects of salinity, dietary carbohydrate and moult cycle on digestive carbohydrases and hexokinases in Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2005, 140, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stetten, M. R.; Goldsmith, P.K. Two hexokinases of Homarus americanus (lobster), one having great affinity for mannose and fructose and low affinity for glucose. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1981, 657, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, D.M.; Tan, H. Molecular evolution of the vertebrate hexokinase gene family: Identification of a conserved fifth vertebrate hexokinase gene. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D 2008, 3, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.R.; Joshi, S.; Arya, R.; Kayastha, A.M.; Srivastava, K.K.; Tripathi, L.M.; Saxena, J.K. Molecular cloning and characterization of Brugia malayi hexokinase. Parasitol. Int. 2008, 57, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cáceres, A.J.; Portillo, R.; Acosta, H.; Rosales, D.; Quiñones, W.; Avilan, L.; Salazar, L.; Dubourdieu, M.; Michels, P.A.; Concepción, J.L. Molecular and biochemical characterization of hexokinase from Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2003, 126, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.Q.; Li, L.; Wang, H.C.; Wang, Z.L. Effects of hypoxia on respiratory metabolism and antioxidant capability of Macrobrachium nipponense. J. Hebei Univ. 2010, 30, 301–306, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Semenza, G.L.; Jiang, B.H.; Leung, S.W.; Passantino, R.; Concordet, J.P.; Mair, P.; Giallongo, A. Hypoxia response elements in the aldolase A, enolase 1, and lactate dehydrogenase A gene promoters contain essential binding sites for hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 32529–32537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddle, S.R.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, S.; Deeb, S.S.; Malkki, M.; Schneider, B.K.; Allen, C.B.; White, C.W. Hypoxia induces hexokinase II gene expression in human lung cell line A549. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2000, 278, L407–L416. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lonberg, N.; Gilbert, W. Intron/exon structure of the chicken pyruvate kinase gene. Cell 1985, 40, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peak, M.J.; Peak, J.G.; Stevens, F.J.; Blamey, J.; Mai, X.; Zhou, Z.H.; Adams, M.W.W. The hyperthermophilic glycolytic enzyme enolase in the archaeon, Pyrococcus furiosus: Comparison with mesophilic enolases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1994, 313, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, K.A. Evolution of the coordinate regulation of glycolytic enzyme genes by hypoxia. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 2911–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, Y.; Stao, K.; Kono, T.; Akiba, Y. Cloning and gene expression of hexokinase I and II in the chicken skeletal muscle. Anim. Sci. J. 2005, 76, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, S.; Suppola, S.; Malkki, M.; Deeb, S.S.; Jänne, J.; Laakso, M. Mouse hexokinase II gene: Structure, cDNA, promoter analysis, and expression pattern. Mamm. Genome 2000, 11, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.C. Identification, expression and bioactivity of hexokinase in amphioxus: Insights into evolution of vertebrate hexokinase genes. Gene 2014, 535, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yepiz-Plascencia, G.; Gollas-Galvan, T.; Vargas-Albores, F.; Garcia-Bañuelos, M. Synthesis of hemolymph high-Density Lipoprotein beta-Glucan binding protein by Penaeus vannamei shrimp hepatopancreas. Mar. Biotechnol. 2000, 2, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cota-Ruiz, K.; Peregrino-Uriarte, A.B.; Felix-Portillo, M.; Martínez-Quintana, J.A.; Yepiz-Plascencia, G. Expression of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase and phosphofructokinase is induced in hepatopancreas of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei by hypoxia. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 106, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renz, A.; Merlo, L.; Stitt, M. Partial purification from potato tubers of three fructokinases and three hexokinases which show differing organ and developmental specificity. Planta 1993, 190, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miernyk, J.A.; Dennis, D.T. Mitochondrial, plastid and cytosolic isozymes of hexokinase from developing endosperm of Ricinus communis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1983, 226, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.T.; Prata, R.T.N.; Williamson, J.D.; Weddington, M.; Pharr, D.M. Formation of a hexokinase complex is associated with changes in energy utilization in celery organs and cells. Physiol. Plant. 2000, 110, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncoso-Ponce, M.A.; Rivoal, J.; Dorion, S.; Moisan, M.C.; Garcés, R.; Martínez-Force, E. Cloning, biochemical characterization and expression of a sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) hexokinase associated with seed storage compounds accumulation. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Sun, M.H.; Hu, D.G.; Hao, Y.J. Molecular Cloning and Expression Analysis of a Hexokinase Gene, MdHXK1 in Apple. Hortic. Plant J. 2016, 2, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tielens, A.G.; van den Heuvel, J.M.; van Mazijk, H.J.; Wilson, J.E.; Shoemaker, C.B. The 50-kDa glucose 6-phosphate-sensitive hexokinase of Schistosoma mansoni. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 24736–24741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Misset, O.; Bos, O.J.; Opperdoes, F.R. Glycolytic enzymes of Trypanosoma brucei: Simultaneous purification, intraglycosomal concentrations and physical properties. Eur. J. Biochem. 1986, 157, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loret, S.M.; Devos, P.E. Hydrolysis of G-6P by a microsomal specific phosphatase and glucose phosphorylation by a low Km hexokinase in the digestive gland of the crab Carcinus maenas. Variations during the moult cycle. J. Comp. Physiol. B 1992, 162, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, C.; Cuzon, G.; Gaxiola, G.; Le Priol, Y.; Pascual, C.; Rossignyol, J.; Contreras, F.; Sa´nchez, A.; van Wormhoudt, A. Metabolism and growth of juveniles of Litopenaeus vannamei: Effect of salinity and dietary carbohydrates level. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2001, 259, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, F.; Solares, M.; Balanza, E.; Coudert, J.; Clottes, E. Expression of lactate dehydrogenase A and B genes in different tissues of rats adapted to chronic hypobaric hypoxia. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 89, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.H.; Somero, G.N. Activity of lactate dehydrogenase but not its concentration of messenger RNA increases with body size in barred sand bass, Paralabrax nebulifer (Teleostei). Biol. Bull. 1996, 191, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClelland, G.B.; Brooks, G.A. Changes in MCT 1, MCT 4, and LDH expression are tissue specific in rats after long-term hypobaric hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 92, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.M.; Xuan, F.J.; Fu, H.T.; Ge, X.P.; Zhu, J.; Qiao, H.; Jin, S.B.; Zhang, W.Y. Molecular characterization and mRNA expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1 and cognate inhibiting factor in Macrobrachium nipponense in response to hypoxia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 2016, 196–197, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.K.; Qiao, H.; Li, F.J.; Fua, H.Y.; Jiang, S.F.; Zhang, W.Y.; Yan, Y.D.; Xiong, Y.W.; Sun, S.M.; Jin, S.B.; et al. Molecular and functional characterization of the vitellogenin receptor in oriental river prawn, Macrobrachium nipponense. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2016, 194, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, H.; Xiong, Y.W.; Zhang, W.Y.; Fu, H.G.; Jiang, S.F.; Sun, S.M.; Bai, H.K.; Jin, S.B.; Gong, Y.S. Characterization, expression, and function analysis of gonad-inhibiting hormone in Oriental River prawn, Macrobrachium nipponense and its induced expression by temperature. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2015, 185, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.M.; Gu, Z.M.; Fu, H.T.; Zhu, J.; Ge, X.P.; Xuan, F.J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and expression analysis of p53 from the oriental river prawn, Macrobrachium nipponense, in response to hypoxia. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Optimum pH | Kinetic Constant (Km) (mM) | Inhibitor Studies (Ki) (mM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | Fructose | ATP | ADP | PPi | G6P | |
| 8.46 | 0.045 ± 0.005 | 79 ± 0.6 | 0.88 ±0.6 | 0.76 | 0.011 | N.I. |
| Primer | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| MnHK-F1 (5′RACE out primer) | CAAGAAGAGGGGATGTCAAG |
| MnHK-F2 (5′RACE in primer) | GTTTCCCCACCTACGTCAGA |
| MnHK-R1 (3′RACE out primer) | GGGATGTTGTCGAGTTGCTC |
| MnHK-R2 (3′RACE in primer) | GACGGGCTCTTTGACCACAT |
| MnHK-F (Real-time PCR primer) | GGGATGTTGTCGAGTTGCTC |
| MnHK-R (Real-time PCR primer) | TCGTCCAAATCACCATCCCA |
| MnpHK CDS amplification (NdeI) | CGAGGCGAGACAAGGACCGGTCATG |
| MnpHK CDS amplification (XhoI) | ATCCTATCTTGAATTTCTTGAGGC |
| β-Actin F (Real-time PCR primer) | TATGCACTTCCTCATGCCATC |
| β-Actin R (Real-time PCR primer) | AGGAGGCGGCAGTGGTCAT |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, S.; Xuan, F.; Fu, H.; Zhu, J.; Ge, X. Molecular Cloning and Functional Characterization of a Hexokinase from the Oriental River Prawn Macrobrachium nipponense in Response to Hypoxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061256
Sun S, Xuan F, Fu H, Zhu J, Ge X. Molecular Cloning and Functional Characterization of a Hexokinase from the Oriental River Prawn Macrobrachium nipponense in Response to Hypoxia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(6):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061256
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Shengming, Fujun Xuan, Hongtuo Fu, Jian Zhu, and Xianping Ge. 2017. "Molecular Cloning and Functional Characterization of a Hexokinase from the Oriental River Prawn Macrobrachium nipponense in Response to Hypoxia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 6: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061256
APA StyleSun, S., Xuan, F., Fu, H., Zhu, J., & Ge, X. (2017). Molecular Cloning and Functional Characterization of a Hexokinase from the Oriental River Prawn Macrobrachium nipponense in Response to Hypoxia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(6), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061256