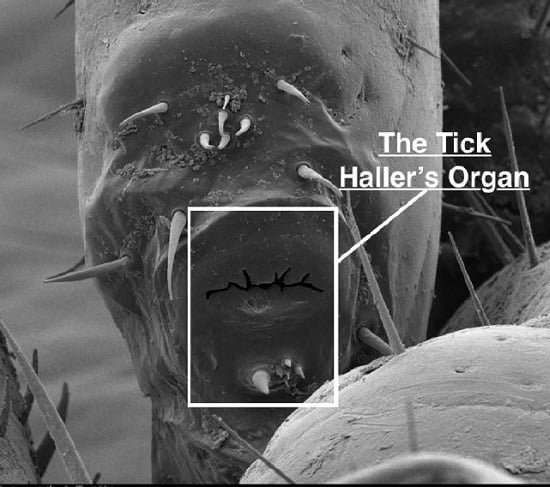
Tick Haller’s Organ, a New Paradigm for Arthropod Olfaction: How Ticks Differ from Insects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Sequencing and Transcriptomic Assembly
2.2. Top 50 Most Abundant Transcripts in the Illumina 1st and 4th Leg Transcriptomes
2.3. No Odorant Binding Proteins Found in Ticks
2.4. Haller’s Organ Not Involved in Gustation
2.5. Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors Not Involved in Haller’s Organ Olfaction
2.6. Transient Receptor Potential Channels Not Involved in Haller’s Organ Olfaction
2.7. G-Protein Coupled Receptors Associated with Chemoreception in Ticks
2.8. G-Proteins Associated with Odorant Reception
2.9. Secondary Messenger Proteins
2.10. Odorant Ion Channels
2.11. Putative Proteins Involved in Chemoreceptor Modulation
2.12. Odorant Degrading Enzymes
2.13. Potential Developmental/Hormonal Regulation of Chemoreception in the Haller’s Organ
2.14. Role of the Haller’s Organ in Tick Repellency Versus Host Attachment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Ticks
3.2. Ethics Statement
3.3. RNA Extraction
3.4. Illumina Hiseq Paired-End Sequencing
3.5. Illumina Bioinformatics
3.6. 454 1st Leg Transcriptome
3.7. Quantitative Analysis of Putative Chemosensory Transcript Levels
3.8. Repellency Bioassays
3.9. Host Attachment/Feeding Bioassays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Acronym | Species | Accession No. |
|---|---|---|
| AaGA12/13 | Anopheles aquasalis | JAA99692.1 |
| AcGPCRA | Amblyomma cajennense | JAC21379.1 |
| Adenlyate/guanylate cyclase: contig 37845 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC13610.1 |
| Adenlyate/guanylate cyclase: contig 37845 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CCD67191.1 |
| Adenlyate/guanylate cyclase: contig 37845 | Zootermopsis nevadensis | KDR07447.1 |
| Adenlyate/guanylate cyclase: contig 77721 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC01411.1 |
| Adenlyate/guanylate cyclase: contig 77721 | Danaus plexippus | EH772322.1 |
| AgGAI | Anopheles gambiae | ABA56308.1 |
| AgGAO | Anopheles gambiae | AAW50310.1 |
| AgGAQ | Anopheles gambiae | ABA56307.1 |
| AgGAS | Anopheles gambiae | ABA56309.1 |
| AgGPB1 | Aedes aegypti | EAT33735.1 |
| AgGPB2 | Aedes aegypti | EAT40134.1 |
| AgGPB5 | Aedes aegypti | EAT38001.1 |
| AtGPCRA | Amblyomma triste | JAC28848.1 |
| BmGPB1 | Apis mellifera | XM_006562979.1 |
| BmGPB2 | Apis mellifera | XM_624332.4 |
| BmGPB5 | Apis mellifera | XM_006568128.1 |
| CeGA12/13 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CCD61930.1 |
| CeGAO | Caenorhabditis elegans | CAA96595.1 |
| CeGAQ | Caenorhabditis elegans | CCD67955.1 |
| CeGAS | Caenorhabditis elegans | CCD73235.2 |
| CeGPB1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CAA35532.1 |
| CeGPB5 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CAA95824.1 |
| Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel: contig 82720 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC03664.1 |
| Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel: contig 82720 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CAB63418.2 |
| Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel: contig 82720 | Acromyrmex echinatior | EGI67156.1 |
| Cytochrome P450: contig 01691 | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | JAA56317.1 |
| Cytochrome P450: contig 01691 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CAB60436.1 |
| Cytochrome P450: contig 01691 | Cerapachys biroi | EZA58513.1 |
| Cytochrome P450: contig 06898 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC19065.1 |
| Cytochrome P450: contig 06898 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CAB07222.1 |
| Cytochrome P450: contig 06898 | Liposcelis bostrychophila | ABN80241.2 |
| Cytochrome P450: contig 14383 | Amblyomma triste | JAC34536.1 |
| Cytochrome P450: contig 14383 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CAA91268.1 |
| Cytochrome P450: contig 14383 | Bemisia tabaci | AEK21811.1 |
| Cytochrome P450: contig 69591 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC03681.1 |
| Cytochrome P450: contig 69591 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CCD68717.1 |
| Cytochrome P450: contig 69591 | Drosophila mojavensis | EDW16611.1 |
| DmGA12/13 | Drosophila melanogaster | AAA28569.1 |
| DmGAI | Drosophila melanogaster | AAA28565.1 |
| DmGAO | Drosophila melanogaster | AAA28586.1 |
| DmGAQ | Drosophila melanogaster | AAA28460.1 |
| DmGAS | Drosophila melanogaster | AAA28579.1 |
| DmGPB1 | Drosophila melanogaster | AAB59247.1 |
| DmGPB2 | Drosophila melanogaster | AAA73103.1 |
| DmGPB5 | Drosophila melanogaster | AAF46336.1 |
| Dust mite antigen EST | Amblyomma americanum | JZ171890 |
| Dust mite antigen EST | Amblyomma americanum | JZ173259 |
| Glutathione-S transferase: contig 12057 | Amblyomma triste | JAC32911.1 |
| Glutathione-S transferase: contig 04931 | Amblyomma triste | JAC32978.1 |
| Glutathione-S transferase: contig 12057 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CCD73730.1 |
| Glutathione-S transferase: contig 04931 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CCD62297.1 |
| Glutathione-S transferase: contig 12057 | Anoplophora glabripennis | JAB67323.1 |
| Glutathione-S transferase: contig 04931 | Athalia rosae | XP_012268124 |
| GPCR: contig 72702 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC06829.1 |
| GPCR: contig 72702 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CCF23345.1 |
| GPCR: contig 72702 | Fopius arisanus | JAG78630.1 |
| GPCR: contig 83622 | Amblyomma sculptum | JAT99189.1 |
| GPCR: contig 83622 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CCD63420.1 |
| GPCR: contig 83622 | Drosophila melanogaster | AAF49949.2 |
| Gα protein: contig 13937 | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | JAA58325.1 |
| Gα protein: contig 13937 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CAA96595.1 |
| Gα protein: contig 13937 | Harpegnathos saltator | EFN90078.1 |
| Gβ protein: contig 24477 | Ixodes ricinus | JAB79904.1 |
| Gβ protein: contig 24477 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CAA93514.1 |
| Gβ protein: contig 24477 | Dendroctonus ponderosae | AEE61583.1 |
| Ionotropic receptor 100a | Anopheles gambiae | EAA06777.4 |
| Ionotropic receptor 141 | Anopheles gambiae | EGK96642.1 |
| Ionotropic receptor 21a | Drosophila melanogaster | AAF51569.2 |
| Ionotropic receptor 25a | Drosophila melanogaster | AGB92585.1 |
| Ionotropic receptor 25a | Anopheles gambiae | EAA13931.5 |
| Ionotropic receptor 40a | Drosophila melanogaster | ACD99552.1 |
| Ionotropic receptor 40a | Anopheles gambiae | EAA13593.5 |
| Ionotropic receptor 68a | Anopheles gambiae | EAA12883.4 |
| Ionotropic receptor 8a | Anopheles gambiae | EAA07123.4 |
| Ionotropic receptor 93a | Anopheles gambiae | EAA06694.5 |
| IR Ionotropic receptor 93a | Drosophila melanogaster | AAN71127.1 |
| IrGPCRB | Ixodes ricinus | JAB73169.1 |
| IrGPCRD1 | Ixodes scapularis | JAB74122.1 |
| IrGPCRD2 | Ixodes scapularis | JAB69073.1 |
| IsCYP21 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC15754.1 |
| IsCYP22 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC15758.1 |
| IsCYP23 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC02779.1 |
| IsCYP31 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC08584.1 |
| IsCYP32 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC17346.1 |
| IsCYP33 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC05868.1 |
| IsCYP41 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC15441.1 |
| IsCYP42 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC16313.1 |
| IsCYP43 | Ixodes scapularis | ECC15440.1 |
| IsCYPMit1 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC14261.1 |
| IsCYPMit2 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC01694.1 |
| IsCYPMit3 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC13863.1 |
| IsGPCRD | Ixodes ricinus | EEC20264.1 |
| IsGSTD1 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC06462.1 |
| IsGSTD2 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC09120.1 |
| IsGSTD3 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC15339.1 |
| IsGSTE1 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC09121.1 |
| IsGSTE2 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC09122.1 |
| IsGSTE3 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC10833.1 |
| IsGSTM1 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC05606.1 |
| IsGSTM2 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC05607.1 |
| IsGSTM3 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC12982.1 |
| IsGSTO1 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC06527.1 |
| IsGSTO2 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC08493.1 |
| IsGSTO3 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC08494.1 |
| IsGSTZ1 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC03386.1 |
| IsGSTZ2 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC17074.1 |
| IsGSTZ3 | Ixodes scapularis | EEC20054.1 |
| Lipocalin: contig 84287 | Amblyomma triste | JAC30054.1 |
| LUSH | Drosophila melanogaster | AAB58940.1 |
| Microplusin EST | Amblyomma americanum | JZ182754 |
| Microplusin EST | Amblyomma americanum | BF008203 |
| Microplusin EST | Amblyomma americanum | JZ181776 |
| Neto-like EST | Amblyomma americanum | JZ169554 |
| Niemann-Pick C2 EST | Amblyomma americanum | JZ171494 |
| Niemann-Pick C2 EST | Amblyomma americanum | BF008372 |
| OBP | Aedes aegypti | AAA29347.1 |
| OBP19a | Drosophila melanogaster | AAF50910.2 |
| OBP19d | Drosophila melanogaster | AAC46475.1 |
| OBP28a | Drosophila melanogaster | AAC46478.1 |
| OBP45 | Aedes aegypti | EAT37277.1 |
| OBP56a | Drosophila melanogaster | AAL49345.1 |
| OBP56d | Drosophila melanogaster | AAF57520.1 |
| OBP56h | Drosophila melanogaster | AAY55796.1 |
| OBP57a | Drosophila melanogaster | AAM69286.1 |
| OBP57b | Drosophila melanogaster | AAM69285.1 |
| OBP57c | Drosophila melanogaster | AAF57467.1 |
| OBP57d | Drosophila melanogaster | AAM69287.1 |
| OBP57e | Drosophila melanogaster | AAF57460.2 |
| OBP66 | Anopheles gambiae | EAU77642.1 |
| OBP67 | Anopheles gambiae | EAL42143.2 |
| OBP68 | Anopheles gambiae | EAU77839.1 |
| OBP69 | Anopheles gambiae | EGK96890.1 |
| OBP69a | Drosophila melanogaster | AAC46474.1 |
| OBP70 | Anopheles gambiae | EAA11535.2 |
| OBP71 | Anopheles gambiae | EAL42442.3 |
| OBP72 | Anopheles gambiae | EDO64833.1 |
| OBP83a | Aedes aegypti | CAF02084.1 |
| OBP83a | Drosophila melanogaster | AAC46476.1 |
| OBP84a | Drosophila melanogaster | AAC46477.1 |
| OBP99a | Drosophila melanogaster | AAM29630.1 |
| OBP99b | Drosophila melanogaster | AAM50904.1 |
| OR83b | Anopheles gambiae | AAR14938.1 |
| OR83b | Drosophila melanogaster | AAT71306.1 |
| PBP6 | Drosophila melanogaster | AAA21356.1 |
| RmGPCRC | Rhipicephalus microplus | ACV07675.1 |
| RnOBP1 | Rattus norvegicus | AAA41736.2 |
| RnOBP1 | Rattus norvegicus | ABG24236.1 |
| RnOBP1 | Rattus norvegicus | AAH86942.1 |
| RpGPCRA | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | JAA57151.1 |
| RpGPCRB | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | JAA63917.1 |
| RpGPCRC | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | JAA54919.1 |
| Str-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | AAF23508.1 |
| Superoxide dismutase | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | JAA58838.1 |
| Superoxide dismutase | Caenorhabditis elegans | CAR97839.1 |
| Superoxide dismutase | Phaedon cochleariae | AEY77316.1 |
| TRPA | Ixodes scapularis | EEC13968.1 |
| TRPA1 | Heliocoverpa armigera | AHV83756.1 |
| TRPA5_M4 | Cydia pomonella | AOR16348.1 |
| TRPA5_M43 | Cydia pomonella | AOR16350.1 |
| β-Arrestin: contig 01853 | Amblyomma cajennense | JAC21990.1 |
| β-Arrestin: contig 01853 | Caenorhabditis elegans | CCD67242.1 |
| β-Arrestin: contig 01853 | Lygus hesperus | JAG24601.1 |
References
- Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M. Biology of Ticks; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 2, ISBN 9780199744060. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Decker, C.F. Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Dis. Mon. 2012, 58, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Bonnet, S.I. Hard tick factors implicated in pathogen transmission. PLoS Neglect. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, J.L.; Cheney, L.; Keesing, F.; Killilea, M.; Logiudice, K.; Previtali, A.; Ostfeld, R.S. Molting success of Ixodes scapularis varies among individual blood meal hosts and species. J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonovich, S.A. Sensory Systems of Parasitic Ticks and Mites; Nauka Press: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, A.C.; Chao, M.Y. From odors to behavior in Caenorhabditis. In The Neurobiology of Olfaction; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 9781420071979. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, T.; Vosshall, L.B. Controversy and consensus: Non-canonical signaling mechanism in the insect olfactory system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2009, 19, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoura, S.M. Fine structure of muscles in the tick Hyalomma (Hyalomma) dromedarii (Ixodoidea: Ixodidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1989, 7, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nave, R.; Weber, K. A myofibrillar protein of insect muscle related to vertebrate titin connects Z band and A band: Purification and molecular characterization of invertebrate mini-titin. J. Cell Sci. 1990, 95, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Luo, J.; Fan, R.; Guan, G.; Fingerle, V.; Sugimoto, C.; Inoue, N.; Yin, H. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding troponin T from tick Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis (Acari: Ixodidae). Comp. Biochem. Phys. B 2008, 151, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M. Biology of Ticks; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1, ISBN 9780199744053. [Google Scholar]
- Bissinger, B.W.; Donohue, K.V.; Khalil, S.M.; Grozinger, C.M.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M. Synganglion transcriptome and developmental global gene expression in adult females of the American dog tick Dermacentor variabilis (Acari: Ixodidae). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulia-Nuss, M.; Nuss, A.B.; Meyer, J.M.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Sattelle, D.B.; de la Fuente, J.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Megy, K.; et al. Genoimc insights into the Ixodes scapularis tick vector of Lyme Disease. Nature Commun. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renthal, R.; Manghnani, L.; Bernal, S.; Qu, Y.; Griffith, W.P.; Lohmeyer, K.; Guerrero, F.D.; Borges, L.M.; Pérez de León, A. The chemosensory appendage proteome of Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) reveals putative odorant-binding and other chemoreception-related proteins. Insect Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nespoulous, C.; Briand, L.; Delage, M.M.; Tran, V.; Pernollet, J.C. Odorant binding and conformation changes of a rat odorant-binding protein. Chem. Senses 2004, 29, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egekwu, N.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Bissinger, B.W.; Roe, R.M. Transcriptome of the female synganglion of the Black-legged tick Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) with comparison between Illumina and 454 systems. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Pitts, R.J.; Bohbot, J.D.; Jones, P.L.; Wang, G.; Zwiebel, J. Distinct olfactory signaling mechanism in the malaria vector mosquito Anopheles gambiae. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Buhl, E.; Xu, M.; Croset, V.; Ress, J.S.; Lilley, K.S.; Benton, R.; Hodge, J.J.; Stanewsky, R. Drosophila ionotropic receptor 25a mediates circadian clock resetting by temperature. Nature 2015, 527, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, M.A.; Montell, C. Drosophila TRP channels and animal behavior. Life Sci. 2014, 92, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, A.M.; Bengtsson, J.M.; Montagné, N.; Jacquin-Joly, E.; Rota-Stabelli, O.; Salvagnin, U.; Bassoli, A.; Witzgall, P.; Anfora, G. TRPA5, an Ankyrin subfamily insect TRP channel, is expressed in antennae of Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in multiple splice variants. J. Insect Sci. 2016, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.J.; Fu, T.; Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.R. A TRPA1 channel that senses thermal stimulus and irritating chemicals in Heliocoverpa armigera. Insect Mol. Biol. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.A. G Protein-coupled receptors in Anopheles gambiae. Science 2002, 298, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaupp, U.B. Olfactory signaling in vertebrates and insects: Differences and commonalities. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Broeck, J.V. Insect G protein-coupled receptors and signal transduction. Arch. Insect Biochem. 2001, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, S.; Guerrero, F.D.; Kellogg, A.; Heekin, A.M.; Leung, M. Bioinformatic prediction of G protein- coupled recptor encoding sequences from the transcriptome of the foreleg, including the Haller’ organ of the cattle tick, Rhipicephalus australis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrill, C.E.; Riesgo-Escovar, J.; Pitts, R.J.; Kafatos, F.C.; Carlson, J.R.; Zwiebel, L.J. Visual arrestins in olfactory pathways of Drosophila and the malaria vector mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 99, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boto, T.; Gomez-Diaz, C.; Alcorta, E. Expression analysis of the 3 G-protein subunits Gα, Gβ, and Gγ in the olfactory receptor organs of adult Drosophila melanogaster. Chem. Sens. 2010, 35, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.; Qin, Y. Cloning and expression analysis of G-protein Gαq subunit and Gβ1 subunit from Bemisia tabaci Gennadius (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae). Arch. Insect Biochem. 2014, 87, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, J.J.; Wan, M. Molecular cloning and characterization of Gα proteins from the western tarnished plant bug, Lygus Hesperus. Insects 2015, 6, 54–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, D.M.; Yokoyama, N.; Goshima, Y.; Siddiqui, Z.K.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Kozasa, T. Identification and molecular characterization of the Gα12-ρ guanine nucleotide exchange factor pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14748–14753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rützler, M.; Lu, T.; Zwiebel, L.J. Gα encoding gene family of the malaria vector mosquito Anopheles gambiae: Expression analysis and immunolocalization of AGαq and AGαo in female antennae. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 499, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, A.; Roman, G.; Hardin, P.E. Go contributes to olfactory reception in Drosophila melanogaster. BMC Physiol. 2009, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.M.; Sleno, R.; Gora, S.; Zylbergold, P.; Laverdure, J.P.; Labbé, J.C.; Miller, G.J.; Hérbert, T.E. The expanding roles of Gβγ subunits in G protein-coupled receptor signaling and drug action. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 545–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, H.; Mori, I.; Rhee, J. Mutations in a cyclic nucleotide-gated channel lead to abnormal thermosensation and chemosensation in C. elegans. Neuron 1996, 17, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, J.T.; Grunwald, M.E.; Yau, K. Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels: An extended family with diverse functions. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1996, 58, 395–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, A.; Frings, S.; Godde, M.; Seifert, R.; Kaupp, U.B. Primary structure and functional expression of a Drosophila cyclic nucleotide-gated channel present in eyes and antennae. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 5040–5050. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fukuto, H.S.; Ferkey, D.M.; Apicella, A.J.; Lans, H.; Sharmeen, T.; Chen, W.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Jansen, G.; Schafer, W.R.; Hart, A.C. G protein-coupled receptor kinase function is essential for chemosensation in C. elegans. Neuron 2004, 42, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Krishnan, P.; Liu, L.; Krishnan, B.; Davis, R.L.; Hardin, P.E.; Roman, G. A Drosophila nonvisual arrestin is required for the maintenance of olfactory sensitivity. Chem. Senses 2006, 31, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linblom, T.H.; Dodd, A.K. Xenobiotic detoxification in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Exp. Zool. 2006, 305, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Yue, J.; Chen, F.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Zhu, S.; Wang, J.; Ran, C. Analysis of transcriptome differences between resistant and susceptible strains of the citrus red mite Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feyereisen, R. Insect CYP genes and P450 enzymes. In Insect Molecular Biology and Biochemistry; Gilbert, L.I., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 236–316. [Google Scholar]
- Younus, F.; Chertemps, T.; Pearce, S.L.; Pandey, G.; Bozzolan, F.; Coppin, C.W.; Russell, R.J.; Maïbèche-Coisne, M.; Oakeshott, J.G. Identification of candidate odorant degrading gene/enzyme systems in the antennal transcriptome of Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem. Mol. 2014, 53, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlgren, M.; Miura, S.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Novel extrahepactic cytochrome P450s. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2005, 207, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, M.E.; Jani, M.K.; Vogt, R.G. An olfactory-specific glutathione S-transferase in the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. J. Exp. Biol. 1999, 202, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.Y.; Zhang, K.; Niu, J.Z.; Ding, T.B.; Zhong, R.; Xia, W.K.; Dou, W.; Wang, J.J. Identification and characterization of seven glutathione S-transferase genes from citrus red mite, Panonychus citri (McGregor). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 24255–24270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Hu, X.; Zhong, X.; Chen, Q.; Xia, Q.; Zhao, P. Antenna-specific glutathione S-transferase in male silkmoth Bombyx mori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 7429–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, B.P.; Prasad, G.B.K.S.; Raghavendra, K. In silico analysis of glutathione S-transferase supergene family revealed hitherto unreported insect specific δ- and ε-GSTs and mammalian specific μ-GSTs in Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae). Comput. Biol. Chem. 2011, 35, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumjuan, N.; McCarroll, L.; Prapanthadara, L.A.; Hemingway, J.; Ranson, H. Elevated activity of an epsilon class glutathione transferase confers DDT resistance in the dengue vector, Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. 2005, 35, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, N.S.R.; Getchell, T.V.; Getchell, M.L. Differential expression of α-class, μ-class, and π-class of glutathione S-transferases in chemosensory mucosae of rats during development. Cell Tissue Res. 1994, 275, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.C.; Liao, C.Y.; Xia, W.K.; Jiang, X.Z.; Shang, F.; Yuan, G.R.; Wang, J.J. Regulation of three isoforms of SOD gene by environmental stresses in citrus red mite, Panonychus citri. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 67, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogoma, S.B.; Moore, S.J.; Maia, M.F.A. Systematic review of mosquito coils and passive emanators: Defining recommendations for spatial repellency testing methodologies. Parasite Vector 2012, 5, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rinker, D.C.; Pitts, R.J.; Zhou, X.; Suh, E.; Rokas, A.; Zwiebel, L.J. Blood meal-induced changes to antennal transcriptome profiles reveal shifts in odor sensitivities in Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8260–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falda, M.; Toppo, S.; Pescarolo, A.; Lavezzo, E.; Di Camillo, B.; Facchinetti, A.; Cilia, E.; Velasco, R.; Fontana, P. Argot2: A large scale function prediction tool relying on semantic similarity of weighted Gene Ontology terms. BMC Bioinf. 2012, 13, S4–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview version 2: A multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriventseva, E.V.; Tegenfeldt, F.; Petty, T.J.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Simão, F.A.; Pozdnyakov, I.A.; Ioannidis, P.; Zdobnov, E.M. OrthoDB v8: Update of the hierarchical catalog of orthologs and the underlying free software. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 41, D358–D365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donohue, K.V.; Khalil, S.; Rosee, E.; Roe, R.M. Neuropeptide signaling sequences identified by pyrosequencing of the American dog tick synganglion transcriptome during blood feeding and reproduction. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Untergasser, A.; Nijveen, H.; Rao, X.; Bisseling, T.; Geurts, R.; Leunissen, J.A. Primer3Plus, an enhanced web interface to Primer3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W71–W74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, A.L.; Roe, R.M. Acarine attractants: Chemosensation, bioassay, chemistry and control. Pestic. Biochem. Phyiol. 2016, 131, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingman, V.P.; Graving, J.M.; Hebets, E.A.; Wiegmann, D.D. Importance of the antenniform legs, but not vision, for homing by the neotropical whip spider, Paraphrynus laevifrons. J. Exp. Biol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Contig | Unique Reads | Accession No. | Best Match (Lowest e-Value) to UniprotKB Database | Organism | e-Value | Conserved Domain(s) a | Putative Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 77381 | 1709234 | EAW18142 | Hypothetical protein | Neosartorya fischeri | 6E+00 | None | Unknown |
| 04832 | 439971 | EEC05627 | Putative titin | Ixodes scapularis | 00E+00 | I-set | Myofibril scaffold |
| 00022 | 410660 | JAC21803 | Putative troponin T skeletal muscle | Rhipicephalus appendiculatus | 00E+00 | Troponin | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00073 | 278198 | AAP79880 | Actin | Rhipicephalus microplus | 00E+00 | None | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00084 | 181667 | AGH19694 | Cytochrome oxidase subunit 1 | Dermacentor nitens | 00E+00 | None | Aerobic metabolism |
| 03069 | 167176 | BAK26392 | Ryanodine receptor | Tetranychus urticae | 00E+00 | Ins145_P3_rec, MIR | Intracellular cation transport |
| 00151 | 137793 | JAC30240 | Uncharacterized protein | Amblyomma triste | 00E+00 | PDZ | Unknown |
| 00696 | 137289 | JAC22297 | Putative titin | Amblyomma cajennense | 00E+00 | I-set, fn3 | Myofibril scaffold |
| 13661 | 118729 | AAD23988 | Beta-actin | Tupaia belangeri | 2E-79 | None | Cytoskeleton |
| 00033 | 112728 | ABB89211 | Troponin I | Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides | 8E-49 | None | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00545 | 109190 | XP_003739692 | Uncharacterized protein | Metaseiulus occidentalis | 6E-17 | None | Unknown |
| 18048 | 94602 | CCW16442 | Xanthine dehydrogenase | Sphingobium japonicum | 1.2E+00 | None | Amino acid metabolism |
| 15573 | 94585 | JAC34970 | Putative myosin class II heavy chain | Amblyomma triste | 7E-27 | Myosin_head | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 04953 | 85346 | JAA60593 | Putative 24 kDa family member | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 4E-38 | None | Unknown |
| 27862 | 82021 | JAB83083 | Putative myosin class I heavy chain | Ixodes ricinus | 3E-33 | Myosin_head | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00452 | 80428 | ECC00524 | Myosin heavy chain, skeletal muscle or cardiac muscle | Ixodes scapularis | 3E-26 | Myosin_N | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00140 | 79270 | JAA57343 | Calcium transporting ATPase | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 00E+00 | Cation ATPase_N | Organelle cation transporter |
| 00619 | 78855 | JAC31893 | Putative actin binding cytoskeleton protein filamin | Amblyomma triste | 00E+00 | CH, filamin | Cytoskeleton |
| 51899 | 78108 | ETM32796 | Uncharacterized protein | Phytophthora parasitica | 8E+00 | None | Unknown |
| 08708 | 77869 | ELU14970 | Uncharacterized protein | Capitella teleta | 1E+00 | None | Unknown |
| 02127 | 75107 | JAC34859 | Putative mitogen inducible protein product | Amblyomma triste | 00E+00 | FERM_M | Unknown |
| 00589 | 74222 | JAA62349 | Uncharacterized protein | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 1E-112 | None | Unknown |
| 00036 | 72607 | JAT93369 | Putative myosin class I heavy chain | Amblyomma aureolatum | 00E+00 | None | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00430 | 72504 | JAC31335 | Putative myosin regulatory light chain | Amblyomma triste | 1E-133 | EF-hand_6 | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00017 | 72240 | AAD17324 | Tropomyosin | Rhipicephalus microplus | 00E+00 | None | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00471 | 66789 | JAC94084 | Putative endocytosis/signaling protein | Ixodes ricinus | 00E+00 | None | Endocytosis |
| 73407 | 64871 | XP_657842 | Uncharacterized protein | Emericella nidulans | 2E-10 | None | Unknown |
| 00449 | 62738 | AEO34581 | Uncharacterized protein | Amblyomma maculatum | 00E+00 | None | Unknown |
| 00975 | 62079 | JAB81899 | Nucleolar GTP-binding protein | Ixodes ricinus | 00E+00 | NOGCT | Biogenesis of 60 s |
| 00477 | 61091 | JAC34490 | Putative alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase agt2 | Amblyomma triste | 00E+00 | Aminotran_3 | Amino acid metabolism |
| 28761 | 60162 | EEC00415 | Putative ornithine decarboxylase | Ixodes scapularis | 9E-126 | Orn_Arg_deC_N, Orn_DAP_Arg_deC | Polyamine synthesis |
| 07560 | 60258 | JAC93558 | Uncharacterized protein | Ixodes ricinus | 1E-6 | None | Unknown |
| 00055 | 60152 | JAC22069 | Elongation factor 1-alpha | Amblyomma cajennense | 00E+00 | GTP_EFTU, GTP_EFTU_D2, GTP_EFTU_D3 | Elongation and nuclear export |
| 10926 | 60100 | JAC29751 | Putative alpha crystallins | Amblyomma triste | 5E-65 | HSP20 | Stress response |
| 01517 | 58463 | EEC19998 | Putative titin | Ixodes scapularis | 00E+00 | I-set, fn3 | Myofibril scaffold |
| 00690 | 55986 | EEC04237 | Putative cuticular protein | Ixodes scapularis | 3E-69 | CBM_14 | Chitin metabolism |
| 00310 | 55692 | JAA60289 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4a2 | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 00E+00 | DEAD | Translation initiation |
| 00960 | 55150 | EEC14479 | Putative stearoyl-CoA desaturase | Ixodes scapularis | 00E+00 | FA_desaturase | Iron binding/fatty acid metabolism |
| 17549 | 54635 | AAF81900 | Beta-actin | Aspergillus terreus | 2E-121 | None | Cytoskeleton |
| 00233 | 54395 | JAC22444 | Putative myosin class II heavy chain | Amblyomma cajennense | 00E+00 | None | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00080 | 53133 | JAC30913 | Putative secreted protein | Amblyomma triste | 4E-17 | None | Unknown |
| 00060 | 52729 | JAC34970 | Putative myosin class II heavy chain | Amblyomma triste | 00E+00 | Myosin_head | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00355 | 52661 | JAA61741 | Putative eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4g2 | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 00E+00 | MIF4G | Translation initiation |
| 43456 | 51562 | EKN64830 | Uncharacterized protein | Bacillus azotoformans | 2E-1 | None | Unknown |
| 03024 | 50391 | JAC22994 | Putative secreted protein | Amblyomma cajennense | 3E-9 | None | Unknown |
| 00517 | 50298 | JAA60286 | Putative amb caj-77 translation factor | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 00E+00 | None | Translation |
| 37644 | 50066 | JAA56007 | Putative der and -36 heat shock-related protein | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 9E-75 | None | Stress response |
| 00954 | 49578 | JAC26141 | Putative enolase | Amblyomma parvum | 00E+00 | Enolase_C, enolase_N | Glycolysis |
| 02045 | 49068 | JAA60432 | Putative tick thioester protein | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 00E+00 | A2M_comp, thiol-ester_cl | Fatty acid metabolism |
| 02199 | 48695 | JAA59973 | Putative ATP | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 00E+00 | ABC_tran, ABC_tran_2 | ATPase activity |
| Contig | Unique Reads | Accession No. | Best Match (Lowest e-Value) to UniprotKB Database | Organism | e-Value | Conserved Domain(s) a | Putative Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20107 | 3060443 | EEH50655 | Uncharacterized protein | Paracoccidioides brasiliensis | 6E-5 | None | Unknown |
| 03297 | 2068585 | EDW75348 | GK19734 | Drosophila willistoni | 5.9E+00 | None | Unknown |
| 29927 | 1571479 | ABQ96857 | Uncharacterized protein | Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis | 5E-5 | None | Unknown |
| 06805 | 425907 | EEC05627 | Putative titin | Ixodes scapularis | 00E+00 | I-set | Myofibril scaffold |
| 00086 | 344474 | JAT93369 | Putative myosin class I heavy chain | Amblyomma aureolatum | 00E+00 | None | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00042 | 316355 | JAC21803 | Putative troponin T skeletal muscle | Rhipicephalus appendiculatus | 00E+00 | Troponin | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 13801 | 259741 | EAU34989 | TATA-box binding protein | Aspergillus terreus | 6E-72 | TBP | DNA binding/transcription |
| 02472 | 200303 | Not available | Uncharacterized protein | Tetranychus urticae | 00E+00 | Ins145_P3_rec, MIR | Intracellular cation transport |
| 03579 | 194590 | EEC12543 | Uncharacterized protein | Ixodes scapularis | 1E-28 | None | Unknown |
| 89009 | 165386 | JAA56423 | Uncharacterized protein | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 6E-58 | None | Unknown |
| 0194 | 150153 | ABB89211 | Putative troponin I | Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides | 2E-24 | None | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00250 | 149220 | EPQ15604 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | Myotis brandtii | 2E-120 | None | Cytoskeleton component |
| 00146 | 146196 | AAP79880 | Actin | Rhipicephalus microplus | 00E+00 | None | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00082 | 133507 | JAA57343 | Calcium-transporting ATPase | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 00E+00 | Cation ATPase_N | Organelle cation transporter |
| 27571 | 132321 | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | None | Unknown | |
| 10067 | 131184 | JAC31684 | Arginyl tRNA protein transferase 1 | Amblyomma triste | 8E-162 | None | Amino acid metabolism |
| 00824 | 130575 | JAC34993 | Putative neural cell adhesion molecule L1 | Amblyomma triste | 00E+00 | I-set, fn3 | Cytoskeleton component |
| 00023 | 126693 | AGH19694 | Cytochrome C oxidase | Dermacentor nitens | 00E+00 | None | Aerobic metabolism |
| 00680 | 126367 | JAB71798 | Putative titin | Ixodes ricinus | 3E-14 | I-set | Myofibril scaffold |
| 00424 | 124358 | AGH19696 | Cytochrome C oxidase subunit 2 | Dermacentor nitens | 6E-109 | COX2 | Aerobic metabolism |
| 51752 | 122349 | EEC14950 | Uncharacterized protein | Ixodes scapularis | 5E-14 | None | Unknown |
| 00375 | 118647 | JAC94084 | Putative endocytosis/signaling protein | Ixodes ricinus | 00E+00 | None | Endocytosis |
| 00468 | 117492 | JAC34970 | Putative myosin class II heavy chain | Amblyomma triste | 2E-175 | Myosin_head | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 01684 | 112255 | JAC29985 | Uncharacterized protein | Amblyomma triste | 1E-81 | None | Unknown |
| 02213 | 109709 | JAC26409 | Uncharacterized protein | Amblyomma parvum | 00E+00 | A2M_comp, thiol_ester_d | Unknown |
| 17461 | 109466 | EFG04290 | Threonine dehydrogenase | Streptomyces clavuligerus | 7.2E+00 | None | Amino acid metabolism |
| 01153 | 108934 | Not available | Uncharacterized protein | Xenopus tropicalis | 1.8E-1 | None | Unknown |
| 03566 | 108685 | AAK73728 | Uncharacterized protein | Oryza sp. | 4.2+00 | None | Unknown |
| 00808 | 107982 | EEC14479 | Putative stearoyl-CoA desaturase | Ixodes scapularis | 00E+00 | FA_desaturase | Iron binding/fatty acid metabolism |
| 15365 | 107585 | JAB79130 | Putative mitochondrial enolase | Ixodes ricinus | 00E+00 | MR_MLE, MR_MLE_C MR_MLE_N | Glycolysis |
| 00182 | 105261 | JAA59820 | Uncharacterized protein | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 00E+00 | Orn_Arg_deC_N, Orn_DAP_Arg_deC | Unknown |
| 00543 | 105012 | JAA64874 | Uncharacterized protein | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 00E+00 | NOGCT | Unknown |
| 00574 | 103671 | JAC34490 | Putative alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase agt2 | Amblyomma triste | 00E+00 | Aminotran_3 | Amino acid metabolism |
| 00516 | 103502 | JAC34859 | Putative mitogen inducible protein product | Amblyomma triste | 00E+00 | FERM_M | Unknown |
| 00006 | 100338 | JAC22069 | Elongation factor 1-alpha | Amblyomma cajennense | 00E+00 | GTP_EFTU, GTP_EFTU_D2, GTP_EFTU_D3 | Elongation and nuclear export |
| 15671 | 94282 | BAC31766 | Uncharacterized protein | Mus musculus | 1E-50 | None | Unknown |
| 00912 | 93884 | AEO34581 | Uncharacterized protein | Amblyomma maculatum | 00E+00 | None | Unknown |
| 04838 | 93041 | KGG51869 | Uncharacterized protein | Microsporidia sp. | 2E-24 | None | Unknown |
| 02211 | 92976 | ECC04237 | Putative cuticular protein | Ixodes scapularis | 3E-69 | CBM_14 | Chitin metabolism |
| 02753 | 92396 | JAA62349 | Uncharacterized protein | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 8E-124 | None | Unknown |
| 00216 | 89994 | JAA60289 | Eukaryotic transcription initiation factor 4a2 | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 00E+00 | DEAD | Translation initiation |
| 51752 | 89524 | JAC25392 | Putative wings up A | Amblyomma parvum | 7E-32 | None | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 07344 | 89354 | JAA54211 | Putative similar to chymotrypsin-elastase inhibitor ixodidin | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 6E-44 | TIL | Immune response |
| 00239 | 89239 | AAD17324 | Tropomyosin | Rhipicephalus microplus | 00E+00 | None | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 01350 | 88374 | JAA61741 | Putative eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 2 | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 00E+00 | None | Translation initiation |
| 74084 | 86871 | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | 3E-63 | None | Unknown |
| 52616 | 85798 | EEC03672 | Putative gamma-glutamyltransferase | Ixodes scapularis | 4E-23 | None | Antioxidant metabolism |
| 00355 | 85082 | AAL75582 | Ferritin | Dermacentor variabilis | 1E-115 | Ferritin | Iron homeostasis |
| 00079 | 83955 | JAC34970 | Putative myosin class II heavy chain | Amblyomma triste | 2E-175 | Myosin_head | Skeletal muscle contraction |
| 00043 | 83765 | JAA55363 | Acetyl Co-enzyme A oxidase | Rhipicephalus pulchellus | 00E+00 | Acyl_CoA_dh_1, Acyl_CoA_M, Acyl_CoA_ox_N | Metabolism |
| Chemoreceptor Signal Transduction & Stimuli Adaption | Protein | Contig (Length, bp) | Top Tick Hit a %ID & e-Value | Top C. elegans Hit b %ID & e-Value | Top Insect Hit c %ID & e-Value | Contig Conserved Domain(s) d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Lipocalin | 84287 (279) | A. triste 48% & 12.00E-12 | No match | No match | None found |
| OR, Odorant receptor: G-protein coupled receptor | 72702 (271) | I. scapularis 92% & 2.30E-30 | C. elegans 25% & 2.00E-3 | F. arisanus 35% & 8.50E-4 | None found | |
| RP, Receptor protein: Gα protein | 13937 (7348) | R. pulchellus 99% & 0.00E+00 | C. elegans 89% & 0.00E+00 | H. saltator 75% & 8.00E-166 | G_alpha | |
| RP: Gβ protein | 24477 (354) | I. ricinus 75% & 4.70E-28 | C. elegans 73% & 4.00E-25 | D. ponderosae 94% & 3.40E-36 | WD40 | |
| SP, Secondary protein: Adenylate/guanylate cyclase | 77721 (242) | I. scapularis 70% & 1.90E-30 | No match | D. plexippus 58% & 4.60E-7 | None found | |
| 37845 (534) | I. scapularis 92% & 1.60E-105 | C. elegans 36% & 2.00E-19 | Z. nevadensis 61% & 6.20E-67 | Guanylate_cyc, HNOBA | ||
| IC, Ion channel: Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel | 82720 (266) | I. scapularis 99% & 3.00E-51 | C. elegans 61% & 8.00E-26 | A. echinatior 93% & 3.00E-49 | cNMP_binding | |
| TP, Terminator protein: β-Arrestin | 1853 (3390) | A. cajennense 93% & 0.00E+00 | C. elegans 63% & 5.80E-160 | L. hesperus 83% & 0.00E+00 | Arrestin_C, Arrestin_N |
| Odorant Degradation Enzymes, ODE | Protein | Contig (Length, bp) | Top Tick Hit a %Identity & e-Value | Top C. elegans Hit b %Identity & e-Value | Top Insect Hit c %Identity & e-Value | Contig Conserved Domain(s) d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ODE, Cytochrome P450 | 69591 (575) | I. scapularis 57% & 1.30E-69 | C. elegans 43% & 2.00E-39 | D. mojavensis 42% & 1.30E-48 | p450 |
| 1691 (1001) | R. pulchellus 90% & 4.80E-79 | C. elegans 30% & 7.00E-7 | C. biroi 32% & 2.70E-9 | p450 | ||
| 6898 (1170) | I. scapularis 64% & 6.10E-123 | C. elegans 33% & 3.00E-30 | L. bostrychophila 40% & 3.0E-54 | p450 | ||
| 14383 (1167) | A. triste 69% & 2.30E-157 | C. elegans 31% & 2.00E-27 | B. tabaci 33% & 2.70E-41 | p450 | ||
| ODE, Glutathione S-transferase | 12057 (902) | A. triste 74% & 5.00E-110 | C. elegans 31% & 6.00E-7 | A. glabripennis 34% & 7.80E-38 | GST_C_3, GST_N | |
| 4931 (2250) | A. triste 88% & 3.30E-140 | C. elegans 30% & 7.00E-18 | A. rosae 31% & 1.00E-13 | GST_C, GST_N | ||
| ODE, Superoxide dismutase | 83534 (332) | R. pulchellus 70%, 2.20E-38 | C. elegans 55%, 3.00E-26 | P. cochleariae 65% & 4.90E-36 | Sod_Cu |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carr, A.L.; D. Mitchell III, R.; Dhammi, A.; Bissinger, B.W.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M. Tick Haller’s Organ, a New Paradigm for Arthropod Olfaction: How Ticks Differ from Insects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071563
Carr AL, D. Mitchell III R, Dhammi A, Bissinger BW, Sonenshine DE, Roe RM. Tick Haller’s Organ, a New Paradigm for Arthropod Olfaction: How Ticks Differ from Insects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(7):1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071563
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarr, Ann L., Robert D. Mitchell III, Anirudh Dhammi, Brooke W. Bissinger, Daniel E. Sonenshine, and R. Michael Roe. 2017. "Tick Haller’s Organ, a New Paradigm for Arthropod Olfaction: How Ticks Differ from Insects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 7: 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071563
APA StyleCarr, A. L., D. Mitchell III, R., Dhammi, A., Bissinger, B. W., Sonenshine, D. E., & Roe, R. M. (2017). Tick Haller’s Organ, a New Paradigm for Arthropod Olfaction: How Ticks Differ from Insects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(7), 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071563