Mollugin Has an Anti-Cancer Therapeutic Effect by Inhibiting TNF-?-Induced NF-?B Activation
Abstract
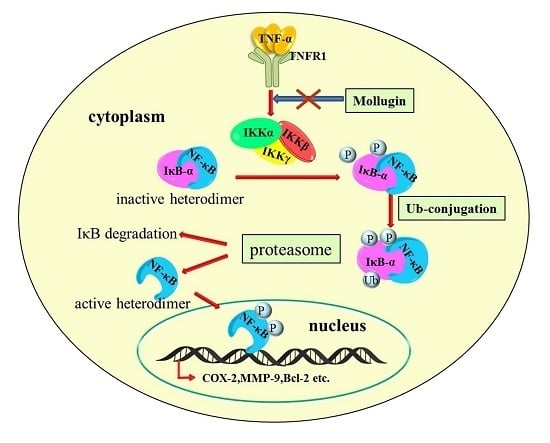
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
2.2. Plasmids, Transfections, and Luciferase Assay
2.3. Measurement of Cell Viability by MTT Assay
2.4. Apoptosis Assays
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Immunofluorescence of NF-κB p65
2.7. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.8. EdU Labeling and Immunofluorescence
2.9. Colony Formation Assay
2.10. In Vivo Xenograft Assay
2.11. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Mollugin Inhibits the TNF-α-Induced Expression of an NF-κB Reporter Gene
3.2. Mollugin Inhibits TNF-α-Induced Phosphorylation and Nuclear Translocation of p65, Phosphorylation and Degradation of IκBα, and IKK Phosphorylation
3.3. Mollugin Inhibits the Expression of TNF-α-Induced NF-κB-Regulated Genes
3.4. Mollugin Potentiates TNF-α-Induced Apoptosis
3.5. Mollugin Inhibits Cell Proliferation
3.6. Mollugin Inhibits Growth of HeLa Cells in a Xenograft Tumor Model
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κB |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| IκBα | Inhibitor of NF-κB alpha |
| cIAP-1 | Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein-1 |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| MMP-9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Sarkar, F.H.; Li, Y. Harnessing the fruits of nature for the development of multi-targeted cancer therapeutics. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2009, 35, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efferth, T.; Li, P.C.; Konkimalla, V.S.; Kaina, B. From traditional Chinese medicine to rational cancer therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, R.; Sun, C.; Pan, Y. An effective high-speed countercurrent chromatographic method for preparative isolation and purification of mollugin directly from the ethanol extract of the Chinese medicinal plant Rubia cordifolia. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Park, H.S.; Jun, D.Y.; Woo, H.J.; Woo, M.H.; Yang, C.H.; Kim, Y.H. Mollugin induces apoptosis in human Jurkat T cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated activation of JNK and caspase-12 and subsequent activation of mitochondria-dependent caspase cascade regulated by Bcl-xL. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 241, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, G.S.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, D.C.; Jahng, Y.; Son, J.K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.C. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of mollugin via up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1 in mouse hippocampal and microglial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 654, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.J.; Lee, J.S.; Kwak, M.K.; Choi, H.G.; Yong, C.S.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, Y.R.; Lyoo, W.S.; Park, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory action of mollugin and its synthetic derivatives in HT-29 human colonic epithelial cells is mediated through inhibition of NF-κB activation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 622, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Harhaj, E.W.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-κB2 p100. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.D. Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-κB and IKK function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, M.J.; Marienfeld, R.B.; Ghosh, S. Characterization of the IκB-kinase NEMO binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 45992–46000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, G.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-κB activation: From bench to bedside. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saika, K.; Sobue, T. Cancer statistics in the world. Cancer Chemother. 2013, 40, 2475–2480. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-κB: The enemy within. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikarsky, E.; Porat, R.M.; Stein, I.; Abramovitch, R.; Amit, S.; Kasem, S.; Gutkovich-Pyest, E.; Urieli-Shoval, S.; Galun, E.; Ben-Neriah, Y. NF-κB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature 2004, 431, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Bai, L.; Chen, W.; Xu, S. The NF-κB activation pathways, emerging molecular targets for cancer prevention and therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Ma, J.; Wang, K.S.; Mi, C.; Lee, J.J.; Jin, X. Blockade of TNF-α-induced NF-κB signaling pathway and anti-cancer therapeutic response of dihydrotanshinone I. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.R.; Jin, S.Z.; Cai, X.F.; Li, D.; Wu, X.; Nan, J.X.; Lee, J.J.; Jin, X. Cryptopleurine targets NF-κB pathway, leading to inhibition of gene products associated with cell survival, proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, K.S.; Mi, C.; Wang, Z.; Piao, L.X.; Xu, G.H.; Li, X.; Lee, J.J.; Jin, X. Baicalein inhibits TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation and expression of NF-κB-regulated target gene products. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2771–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; May, M.J.; Kopp, E.B. NF-κB and Rel proteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 225–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lenardo, M.J. Roles of caspases in apoptosis, development, and cytokine maturation revealed by homozygous gene deficiencies. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Son, J.K.; Jung, S.J.; Jung, J.H.; Fang, Z.; Lee, C.S.; Seo, C.S.; Moon, D.C.; Min, B.S.; Kim, M.R.; Woo, M.H. Anticancer constituents from the roots of Rubia cordifolia L. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, W.P.; Cheng, C.H.; Che, C.T.; Zhao, M.; Lin, Z.X. Induction of apoptosis underlies the Radix Rubiae-mediated anti-proliferative action on human epidermal keratinocytes: Implications for psoriasis treatment. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 20, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Ding, K. Mollugin induces tumor cell apoptosis and autophagy via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K and ERK signaling pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M.; Auh, Q.S.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Jung, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, E.C. Involvement of Nrf2-mediated upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 in mollugin-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis in human oral cancer cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 210604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: The control of NF-κB activity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 621–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Song, M.S.; MacTavish, D.; Jhamandas, J.H.; Kar, S. Role of calpain and caspase in β-amyloid-induced cell death in rat primary septal cultured neurons. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Wang, H.G. Tissue transglutaminase serves as an inhibitor of apoptosis by cross-linking caspase 3 in thapsigargin-treated cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.; Arundine, M.; Sun, H.S.; Jones, M.; Tymianski, M. Inhibition of caspase-mediated apoptosis by peroxynitrite in traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 11540–11553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, F.; Gotte, K.; Schwalb, J.; Bergler, W.; Hormann, K. Expression of 92-kDa type IV collagenase correlates with angiogenic markers and poor survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2000, 17, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Aggarwal, B.B. Evodiamine abolishes constitutive and inducible NF-κB activation by inhibiting IκBα kinase activation, thereby suppressing NF-κB-regulated antiapoptotic and metastatic gene expression, up-regulating apoptosis, and inhibiting invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 17203–17212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Li, M.Y.; Mi, C.; Wang, K.S.; Ma, J.; Jin, X. Mollugin Has an Anti-Cancer Therapeutic Effect by Inhibiting TNF-?-Induced NF-?B Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081619
Wang Z, Li MY, Mi C, Wang KS, Ma J, Jin X. Mollugin Has an Anti-Cancer Therapeutic Effect by Inhibiting TNF-?-Induced NF-?B Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(8):1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081619
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhe, Ming Yue Li, Chunliu Mi, Ke Si Wang, Juan Ma, and Xuejun Jin. 2017. "Mollugin Has an Anti-Cancer Therapeutic Effect by Inhibiting TNF-?-Induced NF-?B Activation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 8: 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081619
APA StyleWang, Z., Li, M. Y., Mi, C., Wang, K. S., Ma, J., & Jin, X. (2017). Mollugin Has an Anti-Cancer Therapeutic Effect by Inhibiting TNF-?-Induced NF-?B Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(8), 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081619