The ABCC6 Transporter: A New Player in Biomineralization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum: The Story of a “misnamed” Disease
3. Vascular Lesions of PXE
4. Lessons Learned from Knockout Mice
5. Molecular Aspects of ABCC6
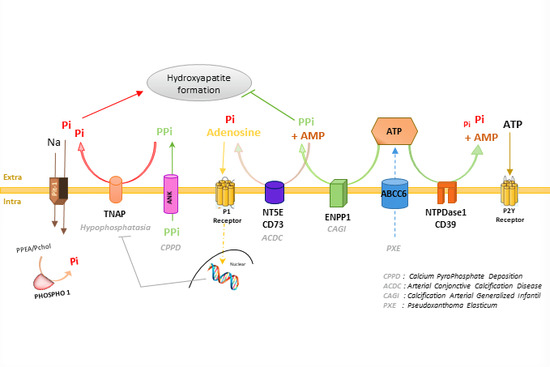
6. Pathophysiology of ABCC6
7. ABCC6 in the Context of Biomineralization
8. A Role for ABCC6 into the Pathophysiology of Vascular Calcifications in Acquired Metabolic Diseases?
9. Therapeutic Perspectives
10. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author contributions
Conflicts of interest
References
- Gheduzzi, D.; Sammarco, R.; Quaglino, D.; Bercovitch, L.; Terry, S.; Taylor, W.; Ronchetti, I.P. Extracutaneous ultrastructural alterations in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2003, 27, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, K.; Yuri, T.; Takeda, N.; Takehana, K.; Iwasaka, T.; Tsubura, A. An autopsy case of pseudoxanthoma elasticum: Histochemical characteristics. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2007, 40, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzer, F. Recherches sur les caractères anatomiques du xanthelasma. Arch. Physiol. 1884, 4, 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Chauffard, M.A. Xanthélasma disséminé et symétrique et sans insuffisance hépatique. Bull. Soc. Med. Paris 1889, 6, 412–419. [Google Scholar]
- Rigal, D. Observation pour servir à l’histoire de la chéloide diffuse xanthélasmique. Ann. Dermatol. Syphilol. 1881, 2, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Darier, J. Pseudo-xanthome élastique. III ème congrès Intern. de Dermat de Londres 1896, 23, 289–295. [Google Scholar]
- Werther. Uber pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Arch. Dermatol. Syph. 1904, 69, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Lebwohl, M.; Neldner, K.; Pope, F.M.; De Paepe, A.; Christiano, A.M.; Boyd, C.D.; Uitto, J.; McKusick, V.A. Classification of pseudoxanthoma elasticum: Report of a consensus conference. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1994, 30, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leftheriotis, G.; Omarjee, L.; Le Saux, O.; Henrion, D.; Abraham, P.; Prunier, F.; Willoteaux, S.; Martin, L. The vascular phenotype in Pseudoxanthoma elasticum and related disorders: Contribution of a genetic disease to the understanding of vascular calcification. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kranenburg, G.; de Jong, P.A.; Mali, W.P.; Attrach, M.; Visseren, F.L.; Spiering, W. Prevalence and severity of arterial calcifications in pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) compared to hospital controls. Novel insights into the vascular phenotype of PXE. Atherosclerosis 2017, 256, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leftheriotis, G.; Abraham, P.; Le Corre, Y.; Le Saux, O.; Henrion, D.; Ducluzeau, P.H.; Prunier, F.; Martin, L. Relationship between ankle brachial index and arterial remodeling in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. J. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 54, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Saux, O.; Bunda, S.; VanWart, C.M.; Douet, V.; Got, L.; Martin, L.; Hinek, A. Serum factors from pseudoxanthoma elasticum patients alter elastic fiber formation in vitro. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutouyrie, P.; Germain, D.P.; Tropeano, A.I.; Laloux, B.; Carenzi, F.; Zidi, M.; Jeunemaitre, X.; Laurent, S. Compressibility of the carotid artery in patients with pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Hypertension 2001, 38, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Berg, J.S.; Hennekam, R.C.; Cruysberg, J.R.; Steijlen, P.M.; Swart, J.; Tijmes, N.; Limburg, M. Prevalence of symptomatic intracranial aneurysm and ischaemic stroke in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2000, 10, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffenstein, G.; Pizard, A.; Le Corre, Y.; Vessieres, E.; Grimaud, L.; Toutain, B.; Labat, C.; Mauras, Y.; Gorgels, T.G.; Bergen, A.A.; et al. Disseminated arterial calcification and enhanced myogenic response are associated with abcc6 deficiency in a mouse model of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.; Hoppe, E.; Kauffenstein, G.; Omarjee, L.; Navasiolava, N.; Henni, S.; Willoteaux, S.; Leftheriotis, G. Early arterial calcification does not correlate with bone loss in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Bone 2017, 103, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persy, V.; D’Haese, P. Vascular calcification and bone disease: The calcification paradox. Trends Mol. Med. 2009, 15, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plomp, A.S.; Bergen, A.A.; Florijn, R.J.; Terry, S.F.; Toonstra, J.; van Dijk, M.R.; de Jong, P.T. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: Wide phenotypic variation in homozygotes and no signs in heterozygotes for the c.3775delT mutation in ABCC6. Genet. Med. 2009, 11, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finger, R.P.; Charbel Issa, P.; Ladewig, M.S.; Gotting, C.; Szliska, C.; Scholl, H.P.; Holz, F.G. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: Genetics, clinical manifestations and therapeutic approaches. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2009, 54, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prunier, F.; Terrien, G.; Le Corre, Y.; Apana, A.L.; Biere, L.; Kauffenstein, G.; Furber, A.; Bergen, A.A.; Gorgels, T.G.; Le Saux, O.; et al. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: Cardiac findings in patients and Abcc6-deficient mouse model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klement, J.F.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Jiang, Q.J.; Terlizzi, J.; Choi, H.Y.; Fujimoto, N.; Li, K.; Pulkkinen, L.; Birk, D.E.; Sundberg, J.P.; et al. Targeted ablation of the abcc6 gene results in ectopic mineralization of connective tissues. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 8299–8310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgels, T.G.; Hu, X.; Scheffer, G.L.; van der Wal, A.C.; Toonstra, J.; de Jong, P.T.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Levelt, C.N.; de Wolf, A.; Loves, W.J.; et al. Disruption of Abcc6 in the mouse: novel insight in the pathogenesis of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Corre, Y.; Le Saux, O.; Froeliger, F.; Libouban, H.; Kauffenstein, G.; Willoteaux, S.; Leftheriotis, G.; Martin, L. Quantification of the calcification phenotype of Abcc6-deficient mice with microcomputed tomography. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 2208–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kupetsky, E.A.; Rincon, F.; Uitto, J. Rate of change of carotid intima-media thickness with magnesium administration in Abcc6(-)/(-) mice. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2013, 6, 485–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aherrahrou, Z.; Doehring, L.C.; Ehlers, E.M.; Liptau, H.; Depping, R.; Linsel-Nitschke, P.; Kaczmarek, P.M.; Erdmann, J.; Schunkert, H. An alternative splice variant in Abcc6, the gene causing dystrophic calcification, leads to protein deficiency in C3H/He mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 7608–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doehring, L.C.; Kaczmarek, P.M.; Ehlers, E.; Mayer, B.; Erdmann, J.; Schunkert, H.; Aherrahrou, Z. Arterial calcification in mice after freeze-thaw injury. Ann. Anat. 2006, 188, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, G.J.; Custer, R.P.; Johnson, F.N.; Stabenow, K.T. Dystrophic cardiac calcinosis in mice: Genetic, hormonal, and dietary influences. Am. J. Pathol. 1978, 90, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Vera, I.; Che, N.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.S.; Ingram-Drake, L.; Schadt, E.E.; Drake, T.A.; Lusis, A.J. Identification of Abcc6 as the major causal gene for dystrophic cardiac calcification in mice through integrative genomics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4530–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everitt, J.I.; Olson, L.M.; Mangum, J.B.; Visek, W.J. High mortality with severe dystrophic cardiac calcinosis in C3H/OUJ mice fed high fat purified diets. Vet. Pathol. 1988, 25, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aherrahrou, Z.; Axtner, S.B.; Kaczmarek, P.M.; Jurat, A.; Korff, S.; Doehring, L.C.; Weichenhan, D.; Katus, H.A.; Ivandic, B.T. A locus on chromosome 7 determines dramatic up-regulation of osteopontin in dystrophic cardiac calcification in mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivandic, B.T.; Utz, H.F.; Kaczmarek, P.M.; Aherrahrou, Z.; Axtner, S.B.; Klepsch, C.; Lusis, A.J.; Katus, H.A. New Dyscalc loci for myocardial cell necrosis and calcification (dystrophic cardiac calcinosis) in mice. Physiol. Genom. 2001, 6, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Korff, S.; Schoensiegel, F.; Riechert, N.; Weichenhan, D.; Katus, H.A.; Ivandic, B.T. Fine mapping of Dyscalc1, the major genetic determinant of dystrophic cardiac calcification in mice. Physiol. Genom. 2006, 25, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Kingman, J.; van de Wetering, K.; Tannouri, S.; Sundberg, J.P.; Uitto, J. Abcc6 Knockout Rat Model Highlights the Role of Liver in PPi Homeostasis in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Sadowski, S.; Frank, M.; Chai, C.; Varadi, A.; Ho, S.Y.; Lou, H.; Dean, M.; Thisse, C.; Thisse, B.; et al. The abcc6a gene expression is required for normal zebrafish development. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2561–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Saux, O.; Urban, Z.; Tschuch, C.; Csiszar, K.; Bacchelli, B.; Quaglino, D.; Pasquali-Ronchetti, I.; Pope, F.M.; Richards, A.; Terry, S.; et al. Mutations in a gene encoding an ABC transporter cause pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uitto, J.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Q. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: Molecular genetics and putative pathomechanisms. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symmons, O.; Varadi, A.; Aranyi, T. How segmental duplications shape our genome: Recent evolution of ABCC6 and PKD1 Mendelian disease genes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 2601–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulkkinen, L.; Nakano, A.; Ringpfeil, F.; Uitto, J. Identification of ABCC6 pseudogenes on human chromosome 16p: Implications for mutation detection in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Hum. Genet. 2001, 109, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranyi, T.; Ratajewski, M.; Bardoczy, V.; Pulaski, L.; Bors, A.; Tordai, A.; Varadi, A. Identification of a DNA methylation-dependent activator sequence in the pseudoxanthoma elasticum gene, ABCC6. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 18643–18650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boussac, H.; Ratajewski, M.; Sachrajda, I.; Koblos, G.; Tordai, A.; Pulaski, L.; Buday, L.; Varadi, A.; Aranyi, T. The ERK1/2-hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha axis regulates human ABCC6 gene expression in hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22800–22808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douet, V.; VanWart, C.M.; Heller, M.B.; Reinhard, S.; Le Saux, O. HNF4alpha and NF-E2 are key transcriptional regulators of the murine Abcc6 gene expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1759, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratajewski, M.; de Boussac, H.; Sachrajda, I.; Bacquet, C.; Kovacs, T.; Varadi, A.; Pulaski, L.; Aranyi, T. ABCC6 Expression Is Regulated by CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Activating a Primate-Specific Sequence Located in the First Intron of the Gene. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 131, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Li, K.; Uitto, J. Transcriptional regulation and characterization of the promoter region of the human ABCC6 gene. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.; Douet, V.; VanWart, C.M.; Heller, M.B.; Le Saux, O. A mouse model of beta-thalassemia shows a liver-specific down-regulation of Abcc6 expression. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, E.; Forni, G.L.; Guerrini, G.; Borgna-Pignatti, C. Pseudoxanthoma-elasticum-like syndrome and thalassemia: An update. Dermatol. Online J. 2009, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Veto, B.; Bojcsuk, D.; Bacquet, C.; Kiss, J.; Sipeki, S.; Martin, L.; Buday, L.; Balint, B.L.; Aranyi, T. The transcriptional activity of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha is inhibited via phosphorylation by ERK1/2. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilias, A.; Urban, Z.; Seidl, T.L.; Le Saux, O.; Sinko, E.; Boyd, C.D.; Sarkadi, B.; Varadi, A. Loss of ATP-dependent transport activity in pseudoxanthoma elasticum-associated mutants of human ABCC6 (MRP6). J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 16860–16867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomozi, V.; Brampton, C.; Fulop, K.; Chen, L.H.; Apana, A.; Li, Q.; Uitto, J.; Le Saux, O.; Varadi, A. Analysis of pseudoxanthoma elasticum-causing missense mutants of ABCC6 in vivo; pharmacological correction of the mislocalized proteins. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pomozi, V.; Brampton, C.; Szeri, F.; Dedinszki, D.; Kozak, E.; van de Wetering, K.; Hopkins, H.; Martin, L.; Varadi, A.; Le Saux, O. Functional Rescue of ABCC6 Deficiency by 4-Phenylbutyrate Therapy Reduces Dystrophic Calcification in Abcc6−/− Mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Saux, O.; Fulop, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ilias, A.; Szabo, Z.; Brampton, C.N.; Pomozi, V.; Huszar, K.; Aranyi, T.; Varadi, A. Expression and in vivo rescue of human ABCC6 disease-causing mutants in mouse liver. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madon, J.; Hagenbuch, B.; Landmann, L.; Meier, P.J.; Stieger, B. Transport function and hepatocellular localization of mrp6 in rat liver. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beck, K.; Hayashi, K.; Dang, K.; Hayashi, M.; Boyd, C.D. Analysis of ABCC6 (MRP6) in normal human tissues. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 123, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kool, M.; van der Linden, M.; de Haas, M.; Baas, F.; Borst, P. Expression of human MRP6, a homologue of the multidrug resistance protein gene MRP1, in tissues and cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maher, J.M.; Cherrington, N.J.; Slitt, A.L.; Klaassen, C.D. Tissue distribution and induction of the rat multidrug resistance-associated proteins 5 and 6. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2219–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, J.M.; Slitt, A.L.; Cherrington, N.J.; Cheng, X.; Klaassen, C.D. Tissue distribution and hepatic and renal ontogeny of the multidrug resistance-associated protein (Mrp) family in mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, Y.; Nakano, A.; Jiang, Q.J.; Pulkkinen, L.; Uitto, J. Tissue-specific expression of the ABCC6 gene. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomozi, V.; Le Saux, O.; Brampton, C.; Apana, A.; Ilias, A.; Szeri, F.; Martin, L.; Monostory, K.; Paku, S.; Sarkadi, B.; et al. ABCC6 is a basolateral plasma membrane protein. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, e148–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, K.; Hayashi, K.; Nishiguchi, B.; Le Saux, O.; Hayashi, M.; Boyd, C.D. The distribution of Abcc6 in normal mouse tissues suggests multiple functions for this ABC transporter. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2003, 51, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belinsky, M.G.; Kruh, G.D. MOAT-E (ARA) is a full-length MRP/cMOAT subfamily transporter expressed in kidney and liver. Bri. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffer, G.L.; Hu, X.; Pijnenborg, A.C.; Wijnholds, J.; Bergen, A.A.; Scheper, R.J. MRP6 (ABCC6) detection in normal human tissues and tumors. Lab. Investig. 2002, 82, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Endo, M.; Dibra, F.; Wang, K.; Uitto, J. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is a metabolic disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Oldenburg, R.; Otsuru, S.; Grand-Pierre, A.E.; Horwitz, E.M.; Uitto, J. Parabiotic heterogenetic pairing of Abcc6−/−/Rag1−/− mice and their wild-type counterparts halts ectopic mineralization in a murine model of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Grange, D.K.; Armstrong, N.L.; Whelan, A.J.; Hurley, M.Y.; Rishavy, M.A.; Hallgren, K.W.; Berkner, K.L.; Schurgers, L.J.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Mutations in the GGCX and ABCC6 genes in a family with pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like phenotypes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanakker, O.M.; Martin, L.; Gheduzzi, D.; Leroy, B.P.; Loeys, B.L.; Guerci, V.I.; Matthys, D.; Terry, S.F.; Coucke, P.J.; Pasquali-Ronchetti, I.; et al. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like phenotype with cutis laxa and multiple coagulation factor deficiency represents a separate genetic entity. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, Q.; Grand-Pierre, A.E.; Schurgers, L.J.; Uitto, J. Administration of vitamin K does not counteract the ectopic mineralization of connective tissues in Abcc6−/− mice, a model for pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brampton, C.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Vanakker, O.; Van Laer, L.; Chen, L.H.; Thakore, M.; De Paepe, A.; Pomozi, V.; Szabo, P.T.; Martin, L.; et al. Vitamin K does not prevent soft tissue mineralization in a mouse model of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jansen, R.S.; Duijst, S.; Mahakena, S.; Sommer, D.; Szeri, F.; Varadi, A.; Plomp, A.; Bergen, A.A.; Oude Elferink, R.P.; Borst, P.; et al. ABCC6-mediated ATP secretion by the liver is the main source of the mineralization inhibitor inorganic pyrophosphate in the systemic circulation-brief report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1985–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, R.S.; Kucukosmanoglu, A.; de Haas, M.; Sapthu, S.; Otero, J.A.; Hegman, I.E.; Bergen, A.A.; Gorgels, T.G.; Borst, P.; van de Wetering, K. ABCC6 prevents ectopic mineralization seen in pseudoxanthoma elasticum by inducing cellular nucleotide release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20206–120211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, E.H.; Prat, A.G.; Gerweck, L.; Seneveratne, T.; Arceci, R.J.; Kramer, R.; Guidotti, G.; Cantiello, H.F. The multidrug resistance (mdr1) gene product functions as an ATP channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AI-Awqati, Q. Regulation of ion channels by ABC transporters that secrete ATP. Science 1995, 269, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutsch, F.; Ruf, N.; Vaingankar, S.; Toliat, M.R.; Suk, A.; Hohne, W.; Schauer, G.; Lehmann, M.; Roscioli, T.; Schnabel, D.; et al. Mutations in ENPP1 are associated with “idiopathic” infantile arterial calcification. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St Hilaire, C.; Ziegler, S.G.; Markello, T.C.; Brusco, A.; Groden, C.; Gill, F.; Carlson-Donohoe, H.; Lederman, R.J.; Chen, M.Y.; Yang, D.; et al. NT5E mutations and arterial calcifications. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleisch, H.; Russell, R.G.; Straumann, F. Effect of pyrophosphate on hydroxyapatite and its implications in calcium homeostasis. Nature 1966, 212, 901–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomashvili, K.A.; Narisawa, S.; Millan, J.L.; O’Neill, W.C. Vascular calcification is dependent on plasma levels of pyrophosphate. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, S.G.; Ferreira, C.R.; MacFarlane, E.G.; Riddle, R.C.; Tomlinson, R.E.; Chew, E.Y.; Martin, L.; Ma, C.T.; Sergienko, E.; Pinkerton, A.B.; et al. Ectopic calcification in pseudoxanthoma elasticum responds to inhibition of tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedinszki, D.; Szeri, F.; Kozak, E.; Pomozi, V.; Tokesi, N.; Mezei, T.R.; Merczel, K.; Letavernier, E.; Tang, E.; Le Saux, O.; et al. Oral administration of pyrophosphate inhibits connective tissue calcification. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, A.M.; Johnson, M.D.; Kingsley, D.M. Role of the Mouse ank Gene in Control of Tissue Calcification and Arthritis. Science 2000, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, M.W.; Feigl, E.O.; Buffington, C.W. Human plasma ATP concentration. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, S.P.; Thaning, P.; Nyberg, M.; Saltin, B.; Hellsten, Y. Local release of ATP into the arterial inflow and venous drainage of human skeletal muscle: Insight from ATP determination with the intravascular microdialysis technique. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohman, A.W.; Billaud, M.; Isakson, B.E. Mechanisms of ATP release and signalling in the blood vessel wall. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 95, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Kingman, J.; Sundberg, J.P.; Uitto, J.; Li, Q. Plasma PPi Deficiency is the Major, But Not the Exclusive, Cause of Ectopic Mineralization in an Abcc6−/− Mouse Model of PXE. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alem, A.M.; Sherrard, D.J.; Gillen, D.L.; Weiss, N.S.; Beresford, S.A.; Heckbert, S.R.; Wong, C.; Stehman-Breen, C. Increased risk of hip fracture among patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stehman-Breen, C.O.; Sherrard, D.J.; Alem, A.M.; Gillen, D.L.; Heckbert, S.R.; Wong, C.S.; Ball, A.; Weiss, N.S. Risk factors for hip fracture among patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 2200–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, E.; Arfai, K.; Liu, X.; Sayre, J.; Gilsanz, V. Aortic calcification and the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 4246–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiel, D.P.; Kauppila, L.I.; Cupples, L.A.; Hannan, M.T.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Wilson, P.W. Bone loss and the progression of abdominal aortic calcification over a 25 year period: The Framingham Heart Study. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2001, 68, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanholder, R.; Annemans, L.; Brown, E.; Gansevoort, R.; Gout-Zwart, J.J.; Lameire, N.; Morton, R.L.; Oberbauer, R.; Postma, M.J.; Tonelli, M.; et al. Reducing the costs of chronic kidney disease while delivering quality health care: A call to action. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, A.S.; Chertow, G.M.; Fan, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hsu, C.Y. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvinkel, P. Chronic kidney disease: A public health priority and harbinger of premature cardiovascular disease. J. Intern. Med. 2010, 268, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agatston, A.S.; Janowitz, W.R.; Hildner, F.J.; Zusmer, N.R.; Viamonte, M., Jr.; Detrano, R. Quantification of coronary artery calcium using ultrafast computed tomography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1990, 15, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budoff, M.J.; Shaw, L.J.; Liu, S.T.; Weinstein, S.R.; Mosler, T.P.; Tseng, P.H.; Flores, F.R.; Callister, T.Q.; Raggi, P.; Berman, D.S. Long-term prognosis associated with coronary calcification: Observations from a registry of 25,253 patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1860–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.; Oldendorf, M.; Moshage, W.; Heidler, R.; Zeitler, E.; Luft, F.C. Electron beam computed tomography in the evaluation of cardiac calcification in chronic dialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1996, 27, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsnefes, M.M. Cardiovascular disease in children with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moranne, O.; Froissart, M.; Rossert, J.; Gauci, C.; Boffa, J.J.; Haymann, J.P.; M’Rad, M.B.; Jacquot, C.; Houillier, P.; Stengel, B.; et al. Timing of onset of CKD-related metabolic complications. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomashvili, K.A.; Khawandi, W.; O’Neill, W.C. Reduced plasma pyrophosphate levels in hemodialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, W.C.; Sigrist, M.K.; McIntyre, C.W. Plasma pyrophosphate and vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, W.L.; Liu, S.; Vaziri, N.D. Chronic kidney disease results in deficiency of ABCC6, the novel inhibitor of vascular calcification. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 40, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomashvili, K.A.; Garg, P.; Narisawa, S.; Millan, J.L.; O’Neill, W.C. Upregulation of alkaline phosphatase and pyrophosphate hydrolysis: Potential mechanism for uremic vascular calcification. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haarhaus, M.; Brandenburg, V.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Stenvinkel, P.; Magnusson, P. Alkaline phosphatase: A novel treatment target for cardiovascular disease in CKD. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais, R.; Barritt, A.S., 4th; Calmus, Y.; Scatton, O.; Runge, T.; Lebray, P.; Poynard, T.; Ratziu, V.; Conti, F. NAFLD and liver transplantation: Current burden and expected challenges. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Nien, C.K.; Yang, C.C.; Yeh, Y.H. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and coronary artery calcification. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1752–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assy, N.; Djibre, A.; Farah, R.; Grosovski, M.; Marmor, A. Presence of coronary plaques in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Radiology 2010, 254, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Arcaro, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2007, 191, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazo, M.; Hernaez, R.; Bonekamp, S.; Kamel, I.R.; Brancati, F.L.; Guallar, E.; Clark, J.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and mortality among US adults: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2011, 343, d6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanova, M.; Younossi, Z.M. Independent association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular disease in the US population. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiba, H.; Sumida, Y.; Kataoka, S.; Kuroda, M.; Akabame, S.; Tomiyasu, K.; Tanaka, M.; Arai, M.; Taketani, H.; Seko, Y.; et al. Association of coronary artery calcification with liver fibrosis in Japanese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, S.; Celikbilek, M.; Yilmaz, Y.K.; Sarikaya, S.; Zararsiz, G.; Serin, H.I.; Borekci, E.; Akyol, L.; Pirti, I.; Davarci, S.E. Association between liver fibrosis and coronary heart disease risk in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.C.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Han, K.H. Hepatic fibrosis assessed using transient elastography independently associated with coronary artery calcification. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, W.R.; Kim, H.J.; Therneau, T.M. Association between noninvasive fibrosis markers and mortality among adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez-Pinto, H.; Chatham, J.; Chacko, V.P.; Arnold, C.; Rashid, A.; Diehl, A.M. Alterations in liver ATP homeostasis in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A pilot study. JAMA 1999, 282, 1659–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliaki, C.; Roden, M. Hepatic energy metabolism in human diabetes mellitus, obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2013, 379, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherer, D.W.; Singer, G.; Uribarri, J.; Phelps, R.G.; Sapadin, A.N.; Freund, K.B.; Yanuzzi, L.; Fuchs, W.; Lebwohl, M. Oral phosphate binders in the treatment of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 53, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Blum, R.R.; Singer, G.K.; Stern, D.K.; Emanuel, P.O.; Fuchs, W.; Phelps, R.G.; Terry, S.F.; Lebwohl, M.G. A randomized controlled trial of oral phosphate binders in the treatment of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 65, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRusso, J.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Uitto, J. Elevated dietary magnesium prevents connective tissue mineralization in a mouse model of pseudoxanthoma elasticum (Abcc6−/−). J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomozi, V.; Brampton, C.; van de Wetering, K.; Zoll, J.; Calio, B.; Pham, K.; Owens, J.B.; Marh, J.; Moisyadi, S.; Varadi, A.; et al. Pyrophosphate Supplementation Prevents Chronic and Acute Calcification in ABCC6-Deficient Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 1258–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, W.C.; Lomashvili, K.A.; Malluche, H.H.; Faugere, M.C.; Riser, B.L. Treatment with pyrophosphate inhibits uremic vascular calcification. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, M.D.; Russell, R.G.; Fleisch, H. Diphosphonates inhibit formation of calcium phosphate crystals in vitro and pathological calcification in vivo. Science 1969, 165, 1264–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Sundberg, J.P.; Levine, M.A.; Terry, S.F.; Uitto, J. The effects of bisphosphonates on ectopic soft tissue mineralization caused by mutations in the ABCC6 gene. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albright, R.A.; Stabach, P.; Cao, W.; Kavanagh, D.; Mullen, I.; Braddock, A.A.; Covo, M.S.; Tehan, M.; Yang, G.; Cheng, Z.; et al. ENPP1-Fc prevents mortality and vascular calcifications in rodent model of generalized arterial calcification of infancy. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeer, C.; Braam, L. Role of K vitamins in the regulation of tissue calcification. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2001, 19, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fodor, D.; Albu, A.; Poanta, L.; Porojan, M. Vitamin K and vascular calcifications. Acta Physiol. Hung. 2010, 97, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sequence Variations at Protein Level | Transport Activity | Wild-Type-Like Localization | Mutations Responding to 4-PBA | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p.R1114P | Yes | No | Yes | [48,49] |
| p.S1121W | Yes | No | Yes | [48,49] |
| p.R1138Q | Yes | No | No | [48,50] |
| p.V1298F | No | Yes | Nd | [47,50] |
| p.T1301I | Yes | No | No | [48] |
| p.G1302R | No | Nd | Nd | [47] |
| p.R1314W | Yes | No | Yes | [47,48,49] |
| p.G1321S | No | No | Nd | [47,48,50] |
| p.R1339C | Nd | Not stable | No | [48,50] |
| p.Q1347H | Yes | No | Yes | [48,49] |
| p.R1459C | Yes | Yes | Nd | [48] |
| Human Disease | Protein | OMIM | Localization of Symptomatic Calcifications | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) | ATP-binding cassette transporter, subfamily C, member 6 (ABCC6) | 264800 | Skin, arteries | None |
| Craniometaphyseal dysplasia, autosomal dominant (CMDD) or Chondrocalcinosis 2 (CCAL2) | Inorganic pyrophosphate transport regulator (ANKH) | 118600 or 123000 | Cartilage (joints) | None |
| Generalized arterial calcification in infancy (GACI) | Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (ENPP1) | 208000 | Arteries | Bisphoshonate |
| Arterial calcification due to deficiency of CD73 (ACDC) | Ecto 5’ nucleotidase (NT5E) alias CD73 | 21288095 | Arteries and distal joints | None |
| Keutel syndrome | Matrix Gla Protein (MGP) | 245150 | Cartilage (trachea, bronchiae, rib) | None |
| Juvenil Paget Disease/Hyperostosis corticalis deformans juvenilis | Osteoprotegerin (OPG) | 239000 | Bone | Bisphoshonate |
| Tumoral calcinosis, hyperphosphatemic | Klotho or fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) or polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyl-transferase 3 (GALNT3) | 211900 | Arteries | None |
| Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) | Laminin A (LMNA) | 176670 | Arteries, aortic valves | None |
| Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) | Activin A receptor type 1 (ACVR1) | 135100 | Skeletal muscle, fascia, tendons and ligaments | Glucocorticoids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| Coeliac disease with epilepsy and cerebral calcifications (CEC) | Unknown | 226810 | Brain (occipital area) | None |
| Idiopathic basal ganglia calcification (IBGC) | Sodium-dependent Pi co-transporter 2 (PiT-2) or platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) or (platelet derived growth factor receptor B) PDGFRB | 158378 or 190040 or 173410 | Brain (basal ganglia, thalamus, cerebellum) | None |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Favre, G.; Laurain, A.; Aranyi, T.; Szeri, F.; Fulop, K.; Le Saux, O.; Duranton, C.; Kauffenstein, G.; Martin, L.; Lefthériotis, G. The ABCC6 Transporter: A New Player in Biomineralization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091941
Favre G, Laurain A, Aranyi T, Szeri F, Fulop K, Le Saux O, Duranton C, Kauffenstein G, Martin L, Lefthériotis G. The ABCC6 Transporter: A New Player in Biomineralization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(9):1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091941
Chicago/Turabian StyleFavre, Guillaume, Audrey Laurain, Tamas Aranyi, Flora Szeri, Krisztina Fulop, Olivier Le Saux, Christophe Duranton, Gilles Kauffenstein, Ludovic Martin, and Georges Lefthériotis. 2017. "The ABCC6 Transporter: A New Player in Biomineralization" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 9: 1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091941
APA StyleFavre, G., Laurain, A., Aranyi, T., Szeri, F., Fulop, K., Le Saux, O., Duranton, C., Kauffenstein, G., Martin, L., & Lefthériotis, G. (2017). The ABCC6 Transporter: A New Player in Biomineralization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(9), 1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091941