Abstract
The blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) reportedly contains many bioactive components of nutritional value. Water-, salt- and acid-soluble M. edulis protein fractions were obtained and the proteins were trypsinized. The resultant peptides were analyzed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time of flight tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS). 387 unique peptides were identified that matched 81 precursor proteins. Molecular mass distributions of the proteins and peptides were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacryl amide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The differences between the three protein samples were studied by Venn diagram of peptide and protein compositions. Toxicity, allergic and antithrombotic activity of peptides was predicted using database website and molecular docking respectively. The antithrombotic activity of enzymatic hydrolysate from water-, salt- and acid-soluble M. edulis protein were 40.17%, 85.74%, 82.00% at 5 mg/mL, respectively. Active mechanism of antithrombotic peptide (ELEDSLDSER) was also research about amino acid binding sites and interaction, simultaneously.
1. Introduction
Mytilus edulis (M. edulis) is a typical marine bivalve mollusk dwelling on beach rocks. It reportedly contains many types of bioactive components of nutritional value with pharmaceutical activities, e.g., nourishing the liver and kidneys, adjusting the blood pressure, curing night sweats, dizziness, impotence, etc. [1,2]. M. edulis is widely artificially cultivated and also globally popular with customers. However, the vast majority are freshly consumed, which leads to their low economic value and waste of the protein resources.
Based on the differences in solubility, the mussel protein is usually divided into a water-soluble protein fraction (sarcoplasmic protein), salt-soluble protein fraction (myofibrillar protein) [3] and water-insoluble protein fraction (matrix protein) [4,5]. At present, shellfish protein can be a natural source of bioactive peptides like milk proteins [6], peptides are very important in various food product applications.
On the other hand, bioactive peptides may be used in the treatment of the human disease and attract increasing attention because of their beneficial effects and better stability than proteins. Many studies showed that intact proteins are difficult to digest and absorb after intake by the human body because of their large molecular mass and complicated three-dimensional structure; these features significantly affect their physiological function and nutritional value [7]. Since peptide structure is simple and the molecular mass is much smaller than protein, peptides are well known as bioactive substances involved in various cellular functions in the human body. In addition, composition of allergenic food protein, e.g., wheat gluten [8], caseins [9] and β-lactoglobulin [10], are less allergic. The composition of shellfish may be developed as seafood seasoning, health food, nutritional supplement, natural medicine and protein additives in food products. These peptides may, e.g., regulate gastrointestinal motility and the immune system [11]. They possess anti-bacterial properties [12], converting enzyme inhibitory activity [13] as well as anti-cancer, anti-oxidation [14,15] and antihypertensive activity [16].
The aim of this study was to extract M. edulis proteins based on their solubility. Enzymatic hydrolysates of M. edulis were prepared from three different-solubility protein fractions and peptides in the hydrolysates were identified by ultra-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time of flight tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS). Moreover, allergic, toxicity and antithrombotic activity were predicted in silico, respectively. The antithrombotic activity and active mechanism of antithrombotic peptide were determined. This study comprised a preliminary analysis of these peptides, paving the way for a better understanding of bioactive peptide and protein.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification and Characterization of M. edulis Proteins and Identification of Peptides by Enzymatic Hydrolysis
The three protein fractions, P1–P3, isolated from the mussel represented 48.40 ± 2.76% (w/w), 17.19 ± 0% and 11.39 ± 0.64% (n = 6) of the total protein, respectively. The total protein extraction rate was 76.98 ± 3.40%. The water-soluble protein fraction (P1) was soluble both in water and a diluted salt solution, while the salt-soluble protein fraction (P2) could only be dissolved in a high-salt solution. The water-insoluble protein could be extracted with an acid or alkali. On the other hand, the protein could be also simply classed as cellular protein and extracellular protein [4,5].
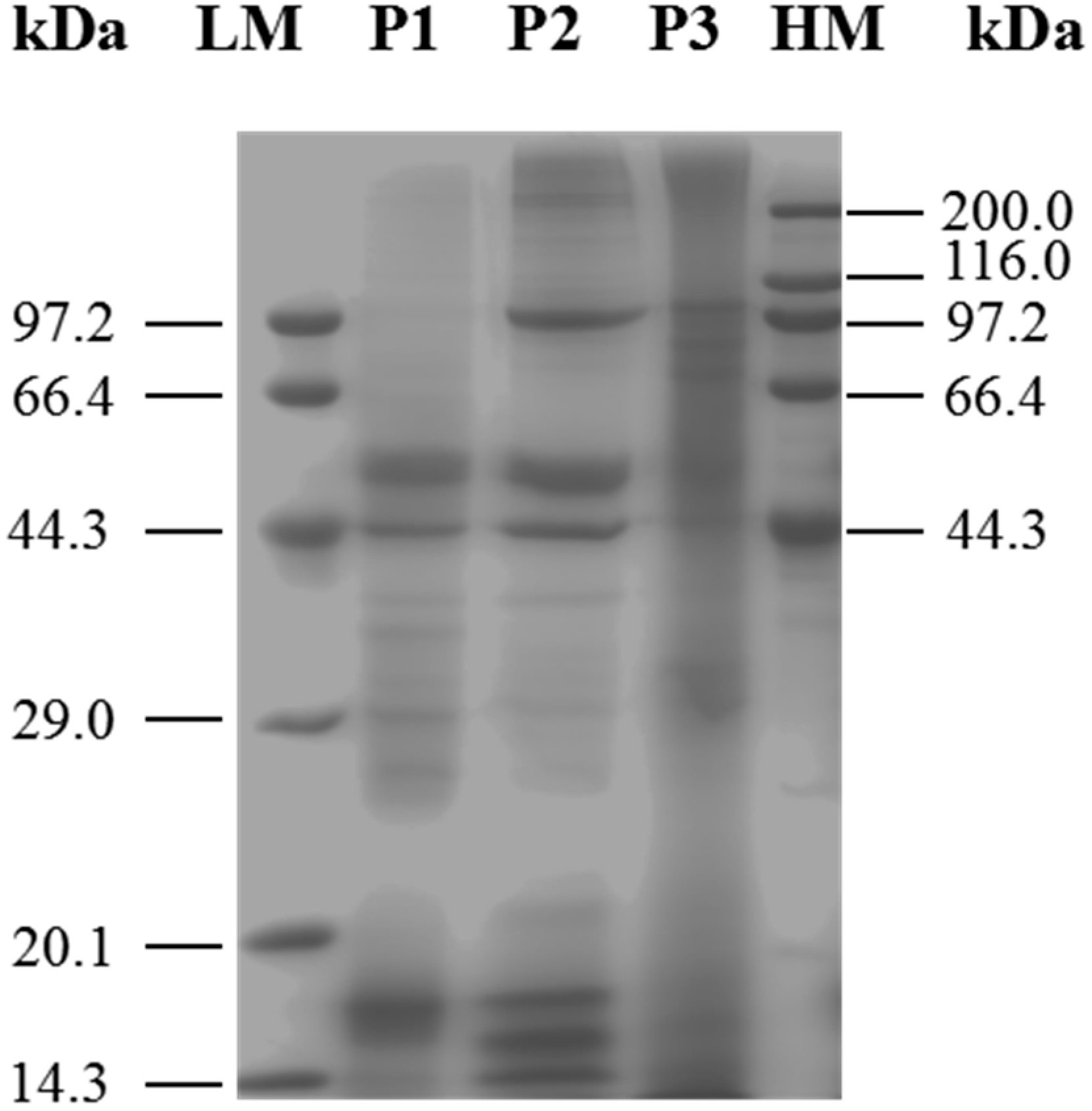
SDS-PAGE is widely used for the isolation and identification of mixed proteins [17]. After vacuum freeze-drying, the three protein fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (Figure 1). The results indicated that although these three protein fractions shared proteins of similar molecular weight, each of them also contained unique proteins. Each sample was used. Lane 1: marker; lane 2: P1; lane 3: P2; lane 4: P3. Characteristic bands of 29.51, 39.98, 44.92 and 53.67 kDa were shown in lane 2; 17,47, 44.71, 52.13, 99.7 and 215 kDa band were particularly observed in lane 3, protein bands at 75.33, 88.55, 106.69 and 177.33 kDa were identified in lane 4.
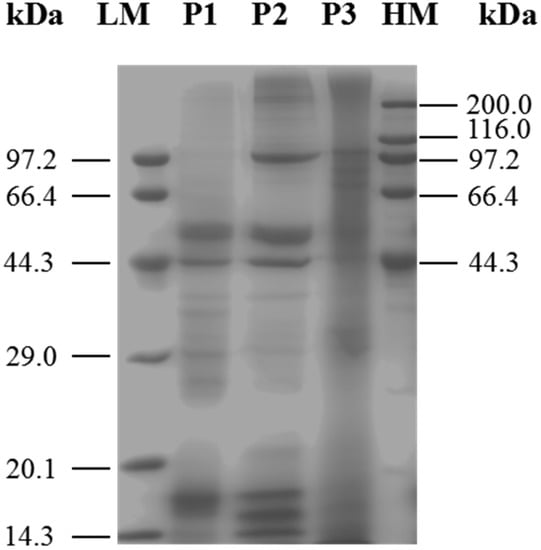
Figure 1.
SDS-PAGE analysis of different-solubility protein fractions from M. edulis was shown. P1: proteins extracted in 0.05 M PBS (pH 7); P2: proteins extracted in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7) containing 0.6 M NaCl; P3: proteins extracted in 3% (w/v) citric acid solution, with heating. LM: Premixed Protein Marker (Low, 14.3–97.2 kDa); HM: Premixed Protein Marker (High, 44.3–200.0 kDa).
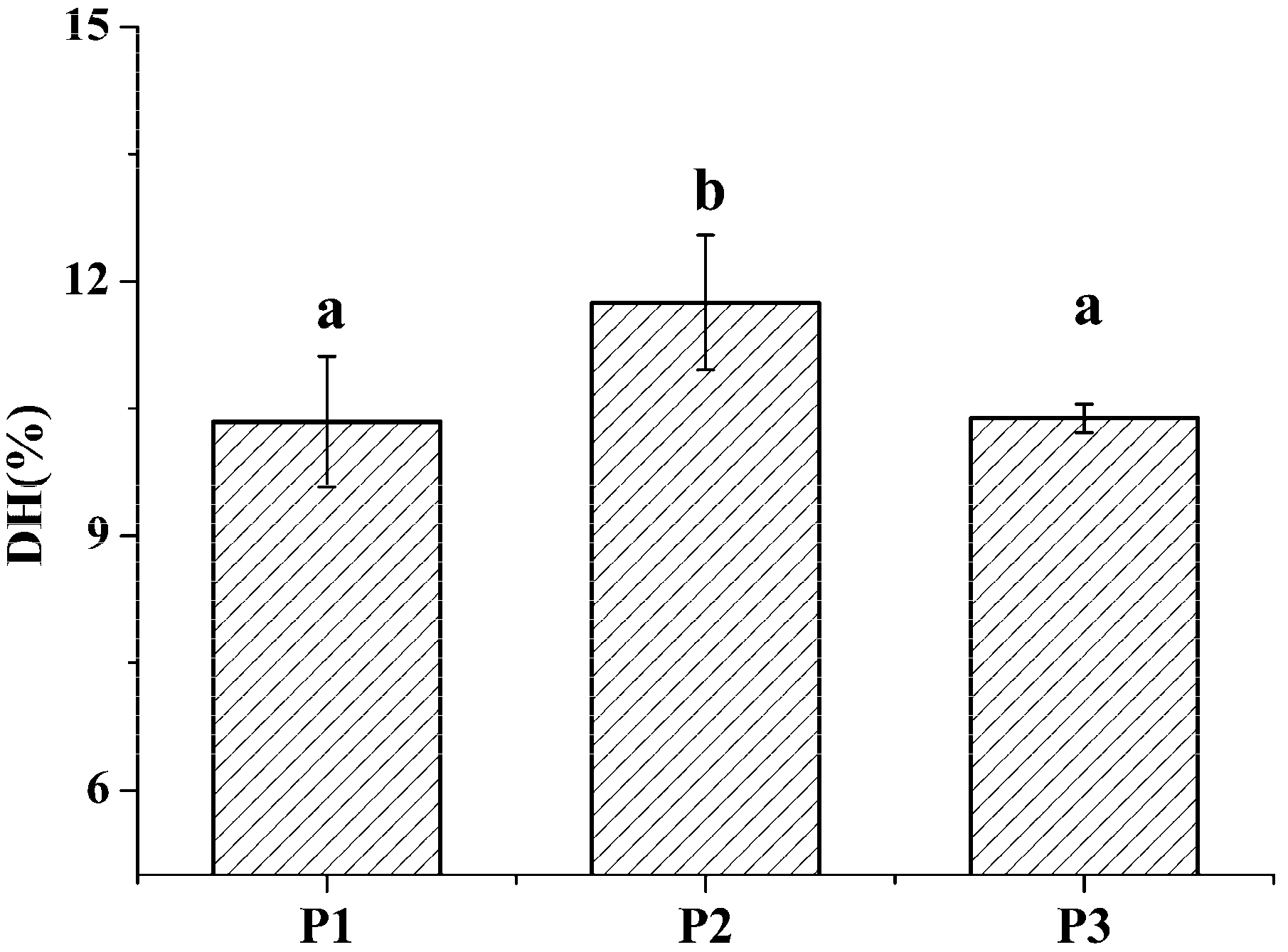
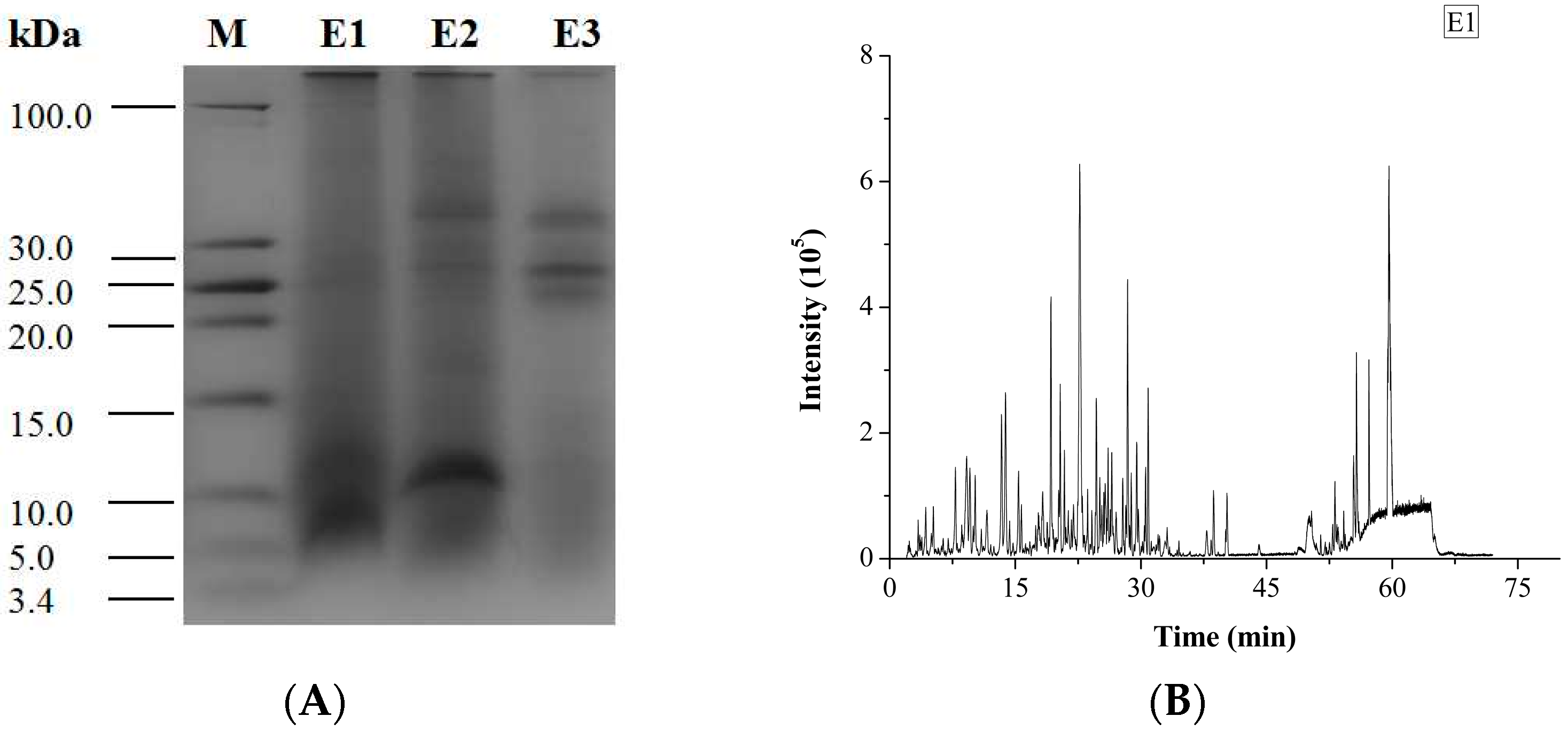
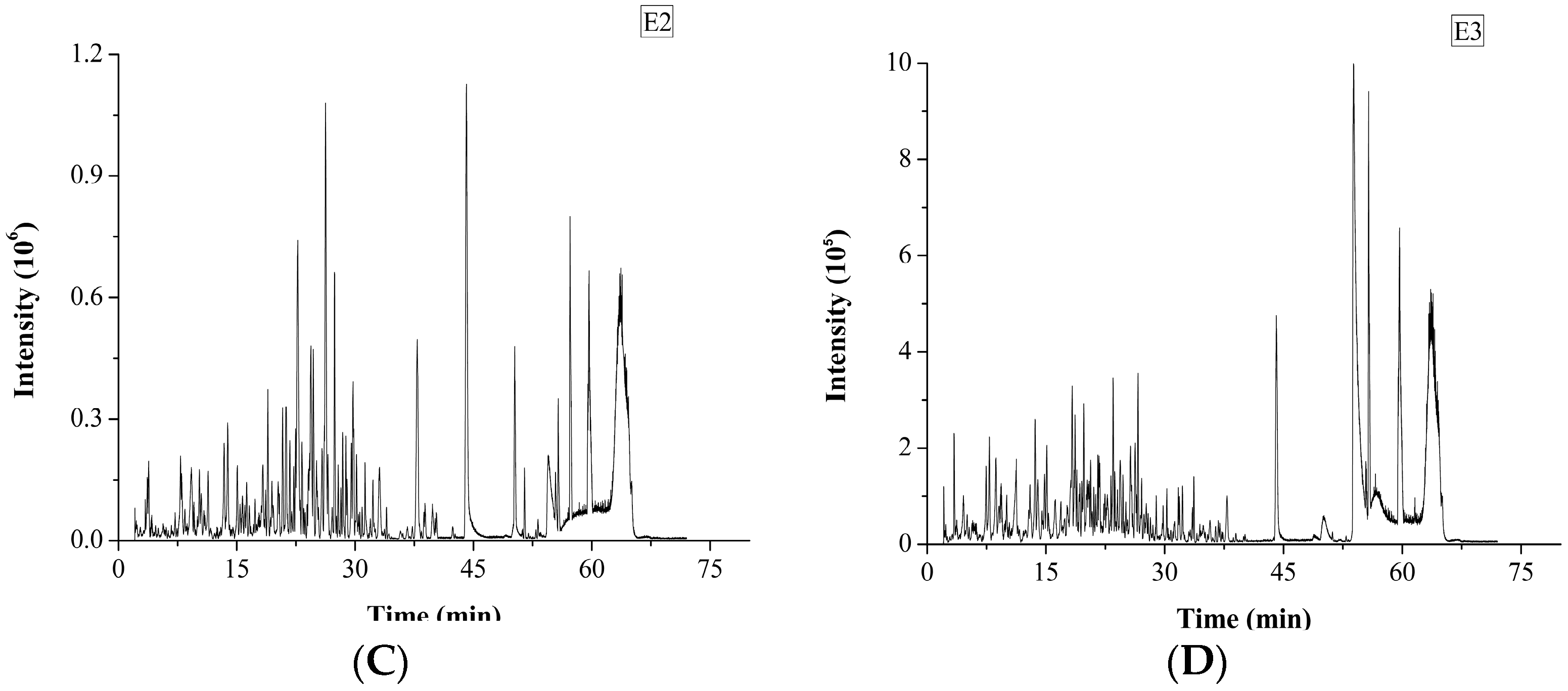
The degree of hydrolysis (DH) of different protein fractions was determined (Figure 2). Although the hydrolysis was carried out under similar conditions, some pronounced differences were observed between the samples. The DH of the salt-soluble protein fraction was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than the DH of the other two protein fractions. At the same time, there was no significant difference (p < 0.05) in the DH value of the two latter protein fractions. Tricine-SDS-PAGE analysis revealed that the enzymatic hydrolysate of the water-soluble protein fraction mainly consisted of 10.00 kDa peptide, while the enzymatic hydrolysate of the salt-soluble protein fraction contained a wide variety of peptides with masses from 7 to 40 kDa (Figure 3A). Further, the enzymatic hydrolysate of the P3 fraction contained peptides with masses of 30 kDa. The distribution of molecular masses of peptides in the enzymatic hydrolysates was consistent with the distribution of proteins fractions. Base Peak Chromatogram spectrum of hydrolyzed fractions was shown in Figure 3B, which indicated that peptides were well isolated. Peptides in enzymatic hydrolysates of fractions P1–P3 were analyzed; 387 different peptides were identified by UPLC-Q-TOF.
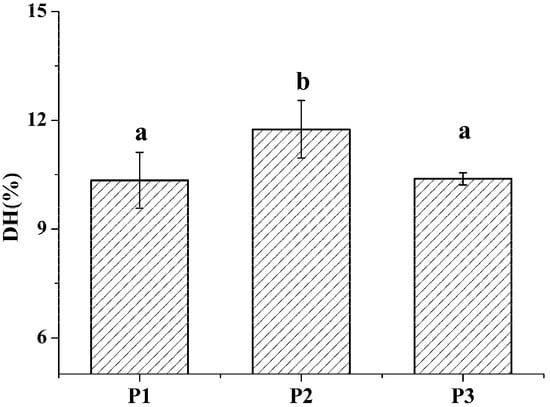
Figure 2.
The degree of hydrolysis of M. edulis proteins from different fractions was shown. Values designated by different letters (a,b) are considered statistically different (p < 0.05). All statistical tests (n = 3) were conducted using SPSS software 19.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
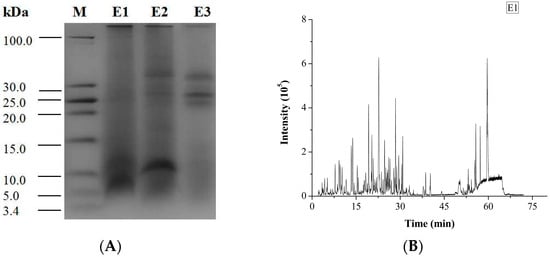
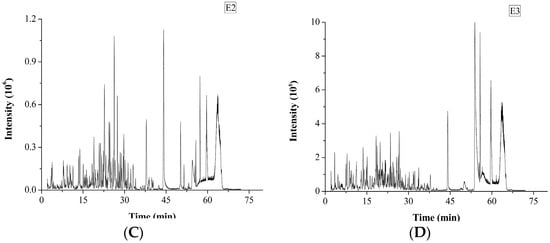
Figure 3.
Tricine-SDS-PAGE analysis and Base Peak Chromatogram spectrum of enzymatic hydrolysates of M. edulis protein fractions were shown. (A) The peptides were electrophoresed on 4% stacking gel and 16% separating gel. (B–D) Enzymatic hydrolysis products in samples E1, E2 and E3 correspond to the hydrolysates of P1–P3 respectively and base Peak Chromatogram spectrum of enzymatic hydrolysates of M. edulis protein fractions.
2.2. In Silico Prediction of Peptides from M. edulis
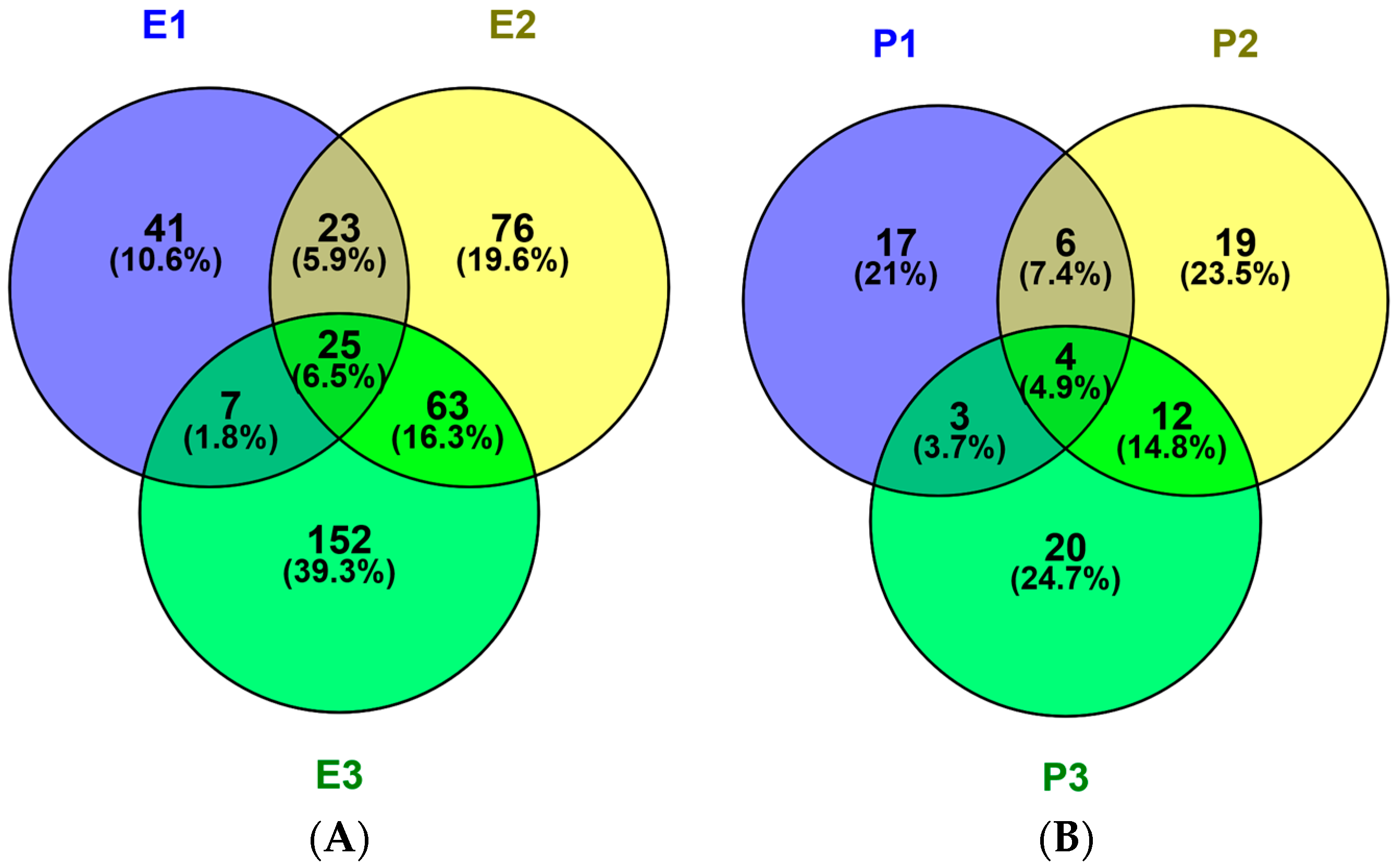
The potential toxicity and allergic of all peptides was assessed using ToxinPred and AlgPred. All peptides show no evidence of toxicity and allergic in silico (Table 1, –CDOCKER ENERGY > 150). The numbers of unique peptides identified in the E1, E2 and E3 fractions were 96,187 and 247, respectively and their activities, toxicities and allergic were predicted. The sequences, peptide sources, toxicities and allergic of peptides with –CDOCKER ENERGY score >150 were listed in Table 1. The activity became stranger as the score become larger. The number of peptides with scores more than 150 were 10, 18 and 19 identified in P1, P2 and P3, respectively. Peptides information was summarized in Figure 4A. Fractions E1, E2 and E3 contained 41, 76 and 152 unique peptides, respectively, 25 peptides were shared. So, the antithrombotic activity of E2 and E3 was different from E1 because of number and type about peptides.

Table 1.
Peptides in enzymatic hydrolysates of P1–P3 M. edulis protein fractions.
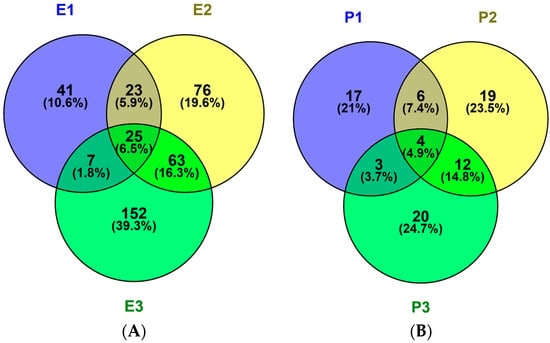
Figure 4.
Venn diagrams of peptides (A) and proteins (B) in hydrolysates of different protein fractions from M. edulis. 387 different polypeptides and 81 proteins were identified in the sarcoplasmic (P1), myofibrillar (P2) and matrix (P3) protein fractions. Venn diagrams were painted with Venny 2.1.0. Enzymatic hydrolysis products named E1, E2 and E3.
The possible protein sources of peptides were also identified. In the three protein fractions (P1, P2 and P3), 30, 41 and 39 proteins were identified, respectively in Figure 4B. Thirty M. edulis proteins were identified, including paramyosin, tropomyosin, collagen-like protein, filamin-like protein, histone, transgelin-like protein, etc. Proteins similar to proteins from other shellfish such as Crassostrea gigas, Pinctada fucata and Crassostrea angulata, were also identified. The sequence coverage for tropomyosin in the three samples, P1, P2 and P3, was 37%, 46.8% and 26.4%, respectively. More tropomyosin had been identified in P2 contrast to P1 and P3 due to its salt-soluble property. More and more proteins will be identified from M. edulis with the development of MS technology in the future.
2.3. Antithrombotic Activity of E1–E3 and Active Mechanism of Antithrombotic Peptide
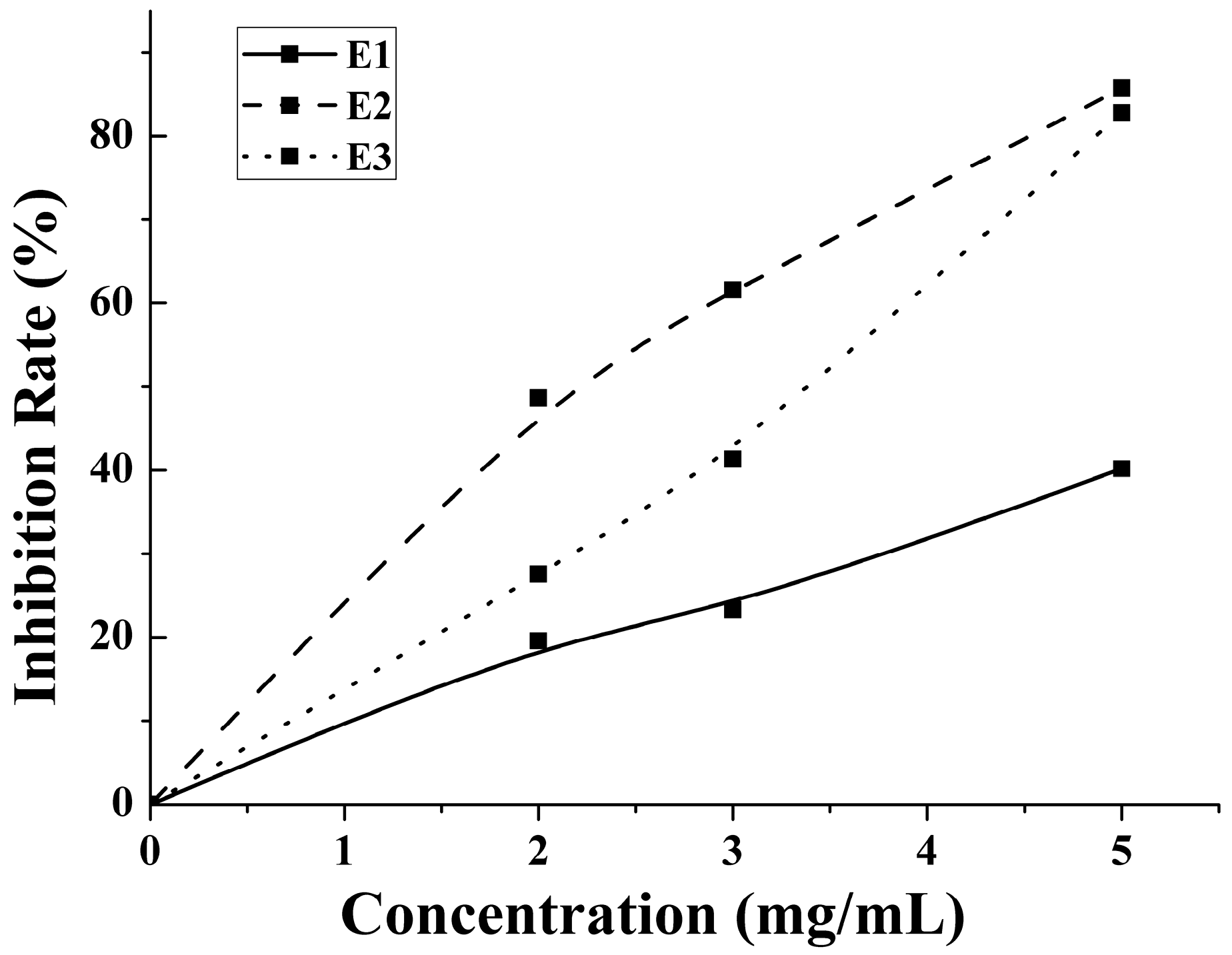
An enzymatic hydrolysis approach was proposed for the preparation of bioactive hydrolysate of M. edulis protein. The inhibition rate increased with the concentration increases. The antithrombotic activity of enzymatic hydrolysates from water-, salt- and acid-soluble M. edulis protein were 40.17%, 85.74%, 82.00% at 5 mg/mL, respectively. The inhibition rate of E2 was significantly higher than E1 and similar with E3 in Figure 5. On the one hand, the DH of P2 fraction was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than the DH of the other two protein fractions. On the other hand, the number and type of peptides from E2 and E3 were more than E1. Peptide distributions of E2 and E3 were similar in Figure 4A. In total, results showed that E3 and E2 had better activity than E1 and the antithrombotic activity of hydrolysates may be related to protein type, the DH and types and properties of peptides according to active mechanism.
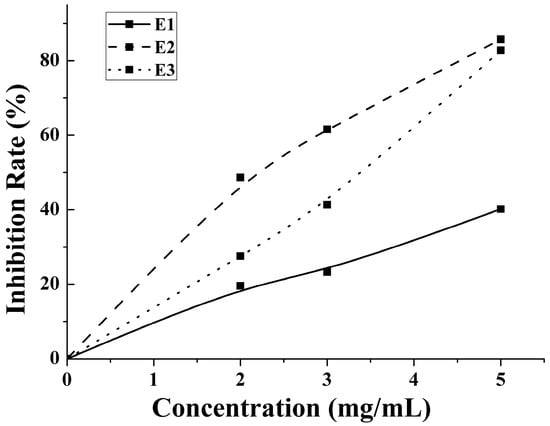
Figure 5.
The anticoagulant activity of 2, 3 and 5 mg/mL E1–E3 were determined.
There were many ways to inhibit thrombin; on the one hand, a stable thrombin-antithrombin complex formed by peptide and active sites inhibited activity of thrombin, and fibrinogen was transformed into fiber protein in order to achieve the antithrombotic activity. On the other hand, thrombin played an important role in the hydrolysis process, the enzyme cutting site of thrombin was in the middle of RG from peptide, which slowed down the process of thrombin and fibrinogen [18,19]. Peptides containing an RG structure were competitive with fibrinogen. RGILTLK, RGMVAGDSK and RGVNDELVY were hydrolyzed by thrombin which identified from E2 and E3, separately, which may also lead to higher activity.
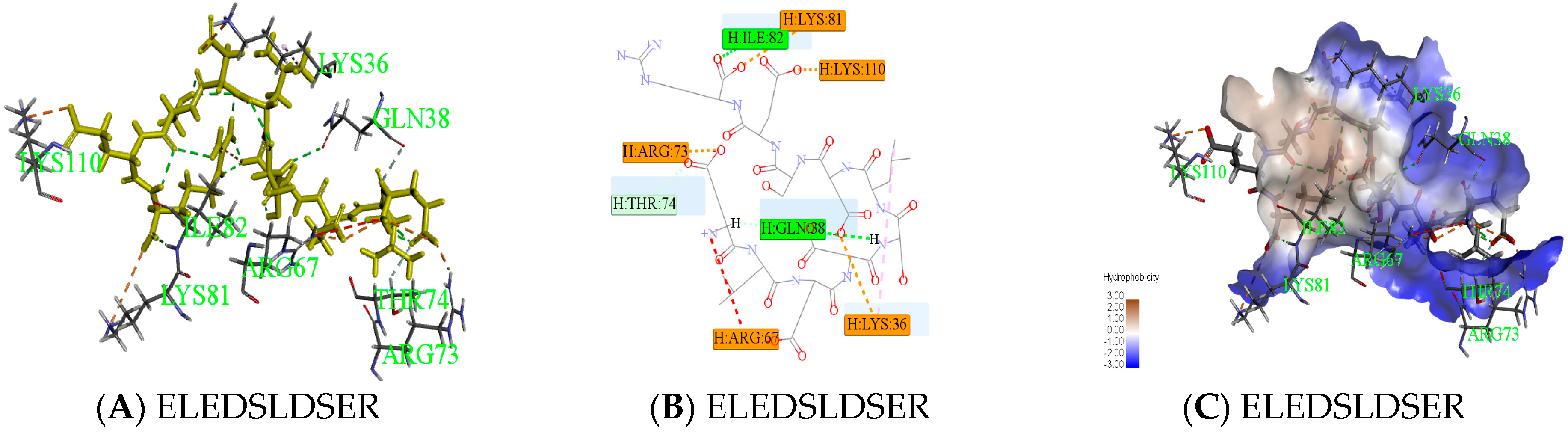
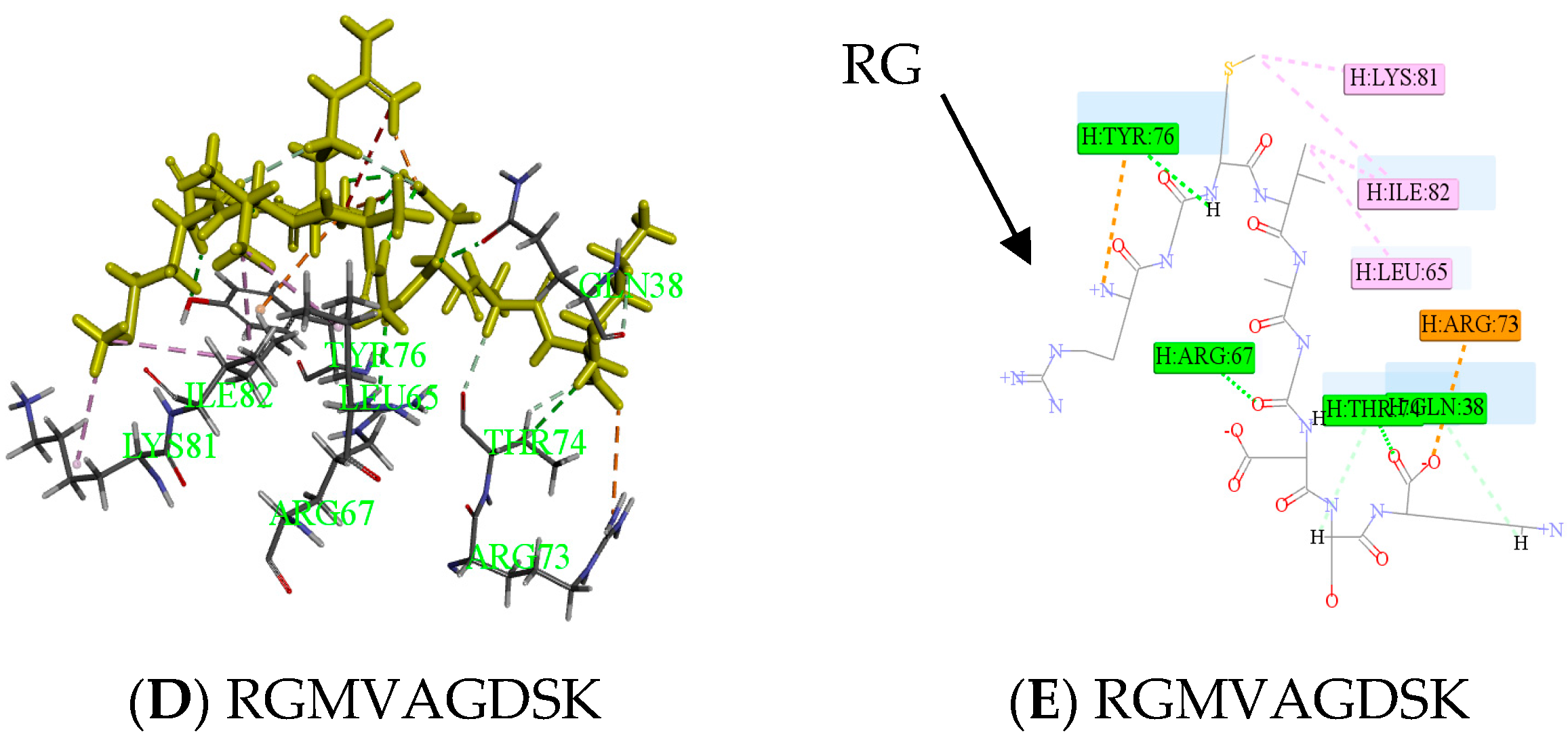
Peptides (ELEDSLDSER) appeared in result of molecular docking might be more active. Docking for the interaction of peptides with thrombin was shown in Figure 6A. Amino acids which combined from thrombin of ELEDSLDSER were Lys36-Gln38-Arg67-Arg73-Thr74 -Lys81-Ile82-Lys110. Amino acids that have hydrogen bonding were Gln38 and Ile82, the number of hydrogen bonds were 1and 1, respectively. There was a carbon hydrogen bond in Thr74, many salt bridges and attractive charges in other amino acids in Figure 6B, which made the compound more stable. So, the score of ELEDSLDSER was highest. At the same time, Gln38 and Thr74 were reported as key binding sites [20,21]. Two parts had strong hydrophilic shown in Figure 6C, which may be conducive to structural stability. Meanwhile, Peptide RGMVAGDSK came from E2, was shown in Figure 6. The amino acid combined with thrombin was Gln38-Leu65-Arg67-Arg73-Thr74 –Tyr76-Lys81-Ile82 in Figure 6D, it was worth that hydrolysis position of RG was exposed and there was no interaction between them in Figure 6E.
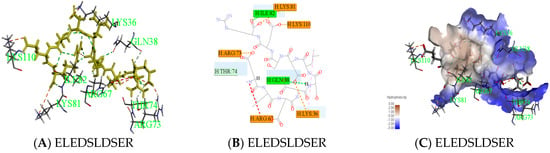
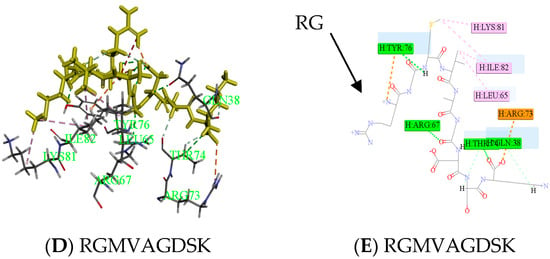
Figure 6.
Active mechanism of peptide and amino acids of thrombin interact with peptides (ELEDSLDSER and RGMVAGDSK) were shown. Yellow sticks were peptides and others were amino acids identified by the green label in (A,D). All interactions between peptides and thrombin were shown in (B,E). Different colors represented different roles. The hydrophobic interaction was done in (C). The closer the color gets to darker blue, the stronger the hydrophilic.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
M. edulis was purchased in Changxing market of Dalian. Trypsin (EC3.4.21.5, 2.5 × 105 U/g) was purchased from Solarbio (Beijing, China). Formic acid (FA) and acetonitrile (High Performance Liquid Chromatography grade) were supplied by Sigma-Aldrich Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). Cleanert C18-N solid phase extraction (SPE) column was purchased from Beijing Baoxidi Science and Technology Co., Ltd. Fibrinogen and thrombin were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). All other chemicals used in this study were analytical grade.
3.2. Preparation of M. edulis Proteins and Enzymatic Hydrolysis
Fresh mussels were washed and removed the shell and the byssus. Mussels were sheared and starched in 8000× g (IKA, Staufen, Germany). Proteins were extracted from fresh M. edulis specimens (n = 3) according to their solubility. Briefly, the extraction procedure was as follows. First, the mussel meat slurry was suspended (1:6 w/v) in 0.05 M phosphate butter solution (pH 7) and incubated for 60 min at 4 °C to extract the first proteins fraction (P1); the samples were then centrifuged (4 °C, 10,000× g, 15 min) and the supernatant was collected. The pellet was then suspended (1:9 w/v) in 0.1 M phosphate butter (pH 7) containing 0.6 M sodium chloride and incubated for 30 min at 4 °C to extract the second proteins fraction (P2); Protein solution was centrifuged and the supernatant collected. Finally, the third protein fraction (P3) was extracted from the pellet from the second centrifugation by incubating (1:15 w/v) in 3% (w/v) citric acid solution at 70 °C in a water-bath. Similarly, this solution was also centrifuged and the supernatant collected. The salt was removed from protein extracts by dialysis with a membrane with cut-off of 3000 Da. The three protein fractions were dialyzed and vacuum freeze-dried (Ningbo ShuangJia Instrument Co., Ltd., Ningbo, China). The protein content in samples was determined by the Kjeldahl method [22,23].
Protein fractions were diluted 2% (w/v) in water and trypsinized (5000 U/g, 45 °C, pH 8.5) because of the ubiquity and controllability of trypsin [24,25]. The final degree of hydrolysis was determined at 3 h, because DH gradually increases before 3 h and there was no significant change after that. DH value was measured using the “pH-state” method as follows:
where B is the volume of consumed NaOH solution (mL), Nb is the concentration of NaOH solution, α is the degree of dissociation of α-amino acid, α = [10(pH − pK)]/[1 + 10(pH − pK)] (pH = 8.5, pK = 7.5). MP is the total mass of the substrate protein (g) and htot is the total quantity of peptide linkage unit of substrate protein (mmol/g). Three different peptide samples were named E1, E2 and E3 and the hydrolysates of them corresponded to P1, P2 and P3, respectively.
3.3. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacryl Amide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
SDS-PAGE was performed using AE-8135 (ATTO Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Premixed Protein Marker (Low, 14.3–97.2 kDa) and Premixed Protein Marker (High, 44.3–200.0 kDa) (Takara Co., Ltd., Dalian, China) were used to determine the molecular masses of proteins. The Premixed Protein Marker (3.4–100.0 kDa, Beijing Baoxidi Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) was used to determine the molecular mass of peptides. Samples of protein and peptide were mixed with 10 µL of electrophoresis buffer (0.5 M Tris-HCl, 10% SDS, glycerol, 0.5% bromophenol blue and 5% β-mercaptoethanol) and heated for 10 min at 100 °C. Tricine-SDS-PAGE gels (4% spacer gel and 16% separating gel) were used to resolve the peptide extracts. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE (5% spacer gel and 10% separating gel) [26,27]. The results were analyzed by Quantity One version 4.6.2 (Bio-Rad Technical Service Department, Oakland, CA, USA).
3.4. Activation of SPE Column
The SPE column was activated by the addition of 3 mL of methanol and equilibration with 3 mL of 0.1% (v/v) FA [28]. The peptides were then loaded onto the activated column and desalted with 1.5 mL of 0.1% FA (v/v). Finally, the peptides were eluted with 80% (v/v) methanol. Room temperature was operating condition. The eluted fractions were dried under a stream of nitrogen and dissolved in 0.1% FA (v/v) before detection by MS.
3.5. Peptide Identification by UPLC-Q-TOF
UPLC-Q-TOF method was developed to identify peptides from protein hydrolysates. The peptides were analyzed using MS/MS (Bruker Scientific Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) with ESI ion source [28] coupled with an LC system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, California, USA) [29]. Peptide sequences were deduced based on MS/MS fragmentation data. The liquid phase-adopting gradient elution program was carried using a C18 column (Guangzhou Phenomenex science instrument Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China). The program time was 70 min. The mobile phase was 0.1% FA in water (eluent A) and 0.1% FA in acetonitrile (eluent B). The flow rate was 0.3 mL/min. The organic phase was increased from 5% to 10% for 12 min and changed 35% for 35 min, then reached 50% and organic phase was increased from 50% to 85% using 2 min and 85% remained 8 min, then quickly returned to 5% using 2 min. The resulting files were searched using the Mascot search software as the following: (1) Protein database were set from National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/); (2) the enzyme was set as Trypsin; (3) the significance threshold was set up as p < 0.05. The peptides sequence was identified through database matching as well as the manual interpretation of its MS/MS spectrum. Peptides with ion scores more than the identity threshold (score > 35) were regarded as identity peptides. The MS spectra were acquired under the positive ESI conditions [30].
Swiss-Prot database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/?term=Swiss-Port) and Bivalvia database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/?term=Bivalvia) were searched using the MASCOT server (Peptide tol: ±10.0 ppm, MS/MS tol: ±0.03 Da; Defined by user: 35.0; http://192./68.1.6/mascot/). Peptides mass fingerprints and sequence queries were analyzed and MS/MS ion search was performed, using MASCOT [31].
3.6. In Silico Predictions of Peptide Toxicity, Allergic and Antithrombotic Activity
The potential character of the identified peptides from E1–E3 samples was analyzed using ToxinPred (http://www.imtech.res.in/raghava/toxinpred/) and AlgPred (http://crdd.osdd.net/raghava//algpred/) [32,33]. In addition, the antithrombotic activity of the peptides was assessed using molecular docking. Molecular docking of the estimated antithrombotic peptides was carried out using Discovery Studio 2017 software (Neo trident Technology Ltd., Beijing China) according to a method described by Tu et al. [34] with some modifications. The peptides were processed by this software whose structures were energy minimized using steepest decent and conjugate gradient techniques. The corresponding receptor protein was from PDB database (http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/home/home.do) and also treated by completing the missing amino acids, removing water molecules and so on. Docking was performed using CDOCKER docking tool of Discovery Studio software (Neo Trident Technology Ltd., Beijing, China). The best ranked docking pose of peptides in the active site of antithrombotic was obtained according to the score of binding-energy value [35].
3.7. Determination of Thrombin Inhibitory Activity
The antithrombotic activity of 2, 3 and 5 mg/mL E1–E3 were determined. A microplate reader was set at a wavelength of 405 nm, at 37 °C. The fibrinogen, thrombin and E1–E3 were all dissolved in 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.4) containing 0.154 mM NaCl. 0.1% fibrinogen solution (140 μL) and 40 μL sample solution with various concentrations were added into the plate wells, mixed and then the absorbance of the sample blank was measured. Next, 10μL thrombin solution (12 U/mL) was added and incubated in 37 °C. Finally, the absorbance of 405 was measured after 10 min [36,37,38]. The control treatment contained 40 μL of Tris-HCl buffer instead of the sample solution. Inhibition rates were calculated according to the following equation; C, Cb, S, Sb represent the absorbance of control, control blank, sample, sample blank, respectively.
3.8. Statistical Analysis
Values are expressed as the mean ± SD (n ≥ 3). Following the assessment of significant differences between samples by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), the level of significance was set at p < 0.05. All statistical tests were conducted using SPSS software 19.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
4. Conclusions
Three M. edulis protein fractions and their enzymatic hydrolysis products were obtained and analyzed. The content of sarcoplasmic, myofibrillar and matrix proteins in M. edulis was different and the peptide compositions of three kinds of proteins were also different by Venn diagrams. Altogether, 387 peptides were identified in enzymatic hydrolysates of M. edulis protein; none of the peptides were toxic and allergic. E3 and E2 showed better activity than E1 and results showed that the antithrombotic activity of hydrolysates may be related to protein type, the DH and types and properties of peptides according to active mechanism. The enzymatic hydrolysates of M. edulis proteins can be exploited by the food industry to improve nutritional value as a functional component. On the other hand, ELEDSLDSER was screened as an antithrombotic peptide and the described optimized preparation of bioactive peptides from different M. edulis protein fractions comprised a good theoretical basis for development of M. edulis protein and may be applied to further the research into bioactive peptides from mollusks.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the State Key Research and Development Plan Modern Food Processing and Food Storage and Transportation Technology and Equipment (2017YFD0400200) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31771926).
Author Contributions
Meiling Qiao conceived and designed the experiments, performed the experiments, analyzed the data, contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools, wrote the paper, prepared figures and tables and reviewed drafts of the paper. Ming Du conceived and designed the experiment, analyzed the data, contributed/reagent/materials/analysis tools, reviewed drafts of the paper. Maolin Tu, Zhenyu Wang, Fengjiao Mao, Hui Chen, Lei Qin have reviewed drafts of the paper, provided constructive suggestions for this research.
Conflicts of Interest
There is no conflict of interest.
References
- Field, I.A. Biology and economic value of the sea mussel Mytilus edulis. Bull. U. S. Bur. Fish. 1922, 38, 127–259. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Ahn, C.B.; Je, J.Y. Anti-inflammatory action of high molecular weight Mytilus edulis hydrolysates fraction in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophage via NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Food Chem. 2016, 202, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darewicz, M.; Borawska, J.; Vegarud, G.E.; Minkiewica, P.; Iwaniak, A. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity and ACE Inhibitory Peptides of Salmon (Salmosalar) Protein Hydrolysates Obtained by Human and Porcine Gastrointestinal Enzymes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 14077–14101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Obaidi, J.R.; Saidi, N.B.; Rokhiyah, S.; Nahadatul, S.; Yusoff, N.M.; Idris, A.S. Comparison of Different Protein Extraction Methods for Gel-Based Proteomic Analysis of Ganoderma spp. Protein J. 2016, 35, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alu’datt, M.H.; Rababah, T.; Alhamad, M.N.; Gammoh, S.; Ereifej, K.; Alodat, M.; Hussein, N.M.; Kubow, S.; Torley, P.J. Antioxidant and antihypertensive properties of phenolic–protein complexes in extracted protein fractions from Nigella damascena and Nigella arvensis. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 56, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziuba, B.; Dziuba, M. New Milk Protein-Derived Peptides with Potential Antimicrobial Activity: An Approach Based on Bioinformatic Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 14531–14545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skripnikov, A.Y.; Kazakov, N.A.; Dolgovx, S.V.; Ziganshin, R.K.; Govorum, V.M.; Ivanov, V.T. The search for and identification of peptides from the moss Physcomitrella patens. Russ. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 37, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanska, I.; PiaseckaJóźwiak, K.; Kotyrba, D.; Kolenda, M.; Stecka, K.M. Selection of lactic acid bacteria strains for the hydrolysis of allergenic proteins of wheat flour. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3897–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, A.; Boye, J. Simultaneous detection of multi-allergens in an incurred food matrix using ELISA, multiplex flow cytometry and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC–MS). Food Chem. 2015, 175, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zellal, D.; Kaddouri, H.; Grar, H.; Belarbi, H.; Kheroua, O.; Saidi, D. Allergenic changes in β-lactoglobulin induced by microwave irradiation under different pH conditions. Food. Agric. Immunol. 2007, 22, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.L.; Liu, Q.T.; Cao, R.B.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Y.P.; Liu, K.; Liu, X.D.; Wei, J.C.; Li, X.F.; Chen, P.Y. Characterization and immunomodulatory function comparison of various bursal-derived peptides iolated from the humoral central immune Organ. Peptides 2012, 33, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Fan, M.H.; Sun, J.J.; Shen, W. Molecular characterization of a novel antimicrobial peptide from Mytilus coruscus. Fish Shellish Immunol. 2013, 34, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, W.; Ma, H.; Jia, J.; He, R.; Luo, L.; Pan, Z. Enzymolysis kinetics and activities of ACE inhibitory peptides from wheat germ protein prepared with SFP Ultrasound-assisted processing. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleekayai, T.; Harnedy, P.A.; O’Keeffe, M.B.; Poyarkov, A.A.; Cunhaneves, A.; Suntornsuk, A.X.; FitzGerald, R.J. Extraction of antioxidant and ACE inhibitory peptides from pthai traditional fermented shrimp pastes. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.X.; Wu, H.; Ling, Y.F.; Lu, R.R. Isolation and identification of antioxidant peptides derived from whey protein enzymatic hydrolysate by consecutive chromatography and Q-TOF MS. J. Dairy Res. 2013, 80, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, M.; Naramoto, K.; Nakajima, T.; Aoyama, T.; Watanabe, M.; Nakamura, K. Purification and identification of antihypertensive peptides from fermented buckwheat sprouts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3013–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Wu, H.; Lai, F.R.; Yang, M.Y.; Li, X.F.; Tang, Y.Q. Isolation and identification of a novel anticoagulant peptide from enzymatic hydrolysates of scorpion (Buthusmartensii Karsch) protein. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Wu, W.J.; Zhang, M.M.; Wu, H.; Li, X.F. Identification and characterization of novel anticoagulant peptide with thrombolytic effect and nutrient oligopeptides with high branched chain amino acid from Whitmaniapigra protein. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 2657–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, T.; Junker, H.D.; Keil, O.; Burkert, K.; Ottleben, H.; Gamer, J.; Sekul, R.; Deppr, H.; Feurer, A.; Tomandl, D.; et al. Discovery of thrombin inhibitor fragments from chemical microarray screening. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2005, 2, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, W. Structure and interaction modes of thrombin. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2006, 36, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjeldahl, J. Neuemethodezurbestimmung des stickstoffs in organischenKörpern (New method for the determination of nitrogen in organic substances). Z. Anal. Chem. 1883, 22, 366–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.M.; Barbano, D.M. Kjeldahlnitrogen analysis as a reference method for protein determination in dairy products. J. AOAC Int. 1999, 82, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khaket, T.P.; Singh, J. Potential of plant’s dipeptidyl peptidase I & II homologs in generation of ace inhibitory peptides. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2016, 1, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Hörnaeus, K.; Guillemant, J.; Mi, J.; Hernroth, B.; Bergquist, J.; Bergstrom, L. Mass spectrometry data from a quantitative analysis of protein expression in gills of immuno-challenged blue mussels (Mytilus edulis). Data Brief 2016, 8, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.M.; Zhu, B.W.; Wu, H.T.; Yu, L.; Zhou, D.Y.; Dong, X.; Yang, J.-F.; Li, D.-M.; Ye, W.-X.; Murata, Y. Purification and characterization of cathepsin B from the gut of the sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicas). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbaix, H.; Budinger, D.; Dieu, M.; Fumiere, O.; Gillard, N.; Delahaut, P.; Mauro, S.; Raes, M. Identification of proteins and peptide biomarkers for detecting banned processed animal proteins (PAPs) in meat and bone meal by mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2405–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Li, W.; Ullah, K.; Hasan, M.; Linna, G.; Awan, U.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Batool, S.; Qing, H.; Deng, Y.L. Study of rat hypothalamic proteome by HPLC/ESI ion trap and HPLC/ESI-Q-TOF MS. Proteomics 2013, 13, 2455–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Zheng, W.; Li, J.; Wang, L.C.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.Z.; Shi, L. Rapid identification of bioactive peptides with antioxidant activity from the enzymatic hydrolysate of mactraveneriformis by UHPLC-Q-TOF mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougatef, A.; Balti, R.; Nedjar-Arroume, N.; Ravallec, R.; Adje, E.Y.; Souissi, N.; Lassoued, I.; Guillochon, D.; Nasri, M. Evaluation of Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activities of smooth hound (Mustelusmustelus) muscle protein hydrolysates generated by gastrointestinal proteases: Identification of the most potent active peptide. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 231, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aivaliotis, M.; Gevaert, K.; Falb, M.; Tebbe, A.; Konstantinidis, K.; Bisle, B.; Klein, C.; Martens, L.; Staes, A.; Timmerman, E.; et al. Large-scale identification of N-terminal peptides in the Halophilic Archaea Halobacterium salinarum and Natronomonas pharaonis. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 2195–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Kapoor, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Gautam, A.; Kumar, R. In Silico Approach for predicting toxicity of peptides and proteins. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafarga, T.; Wilm, M.; Wynne, K.; Hayes, W. Bioactive hydrolysates from bovine blood globulins: Generation, characterisation, and in silico prediction of toxicity and allergenicity. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 24, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.L.; Feng, T.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Qiao, M.L.; Shahidi, F.; Lu, W.H.; Du, M. Sequence analysis and molecular docking of antithrombotic peptides from casein hydrolysate by trypsin digestion. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 32, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Zhang, L.W.; Han, X.; Cheng, D.Y. Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from protease hydrolysates of Qula casein: Quantitative structure-activity relationship modeling and molecular docking study. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 32, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.G.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S.Y. A new method for determination of antithrombotic activity of egg white protein hydrolysate by microplate reader. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2007, 18, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.B.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S.Y. Antioxidant and antithrombotic activities of rapeseed peptides. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2008, 85, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, R.S.T.; Padmanabhan, K.; Arni, R.V. Structure of tick anticoagulant peptide at 1.6 Å resolution complexed with bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Protein Sci. 2000, 9, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, W.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.Z.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.W. Production and functional characterization of a novel fungal immunomodulatory protein FIP-SN15 shuffled from two genes of ganoderma species. Appl. Microbiol. Biol. 2014, 98, 5967–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).