The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Valproic Acid Exerts a Synergistic Cytotoxicity with the DNA-Damaging Drug Ellipticine in Neuroblastoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
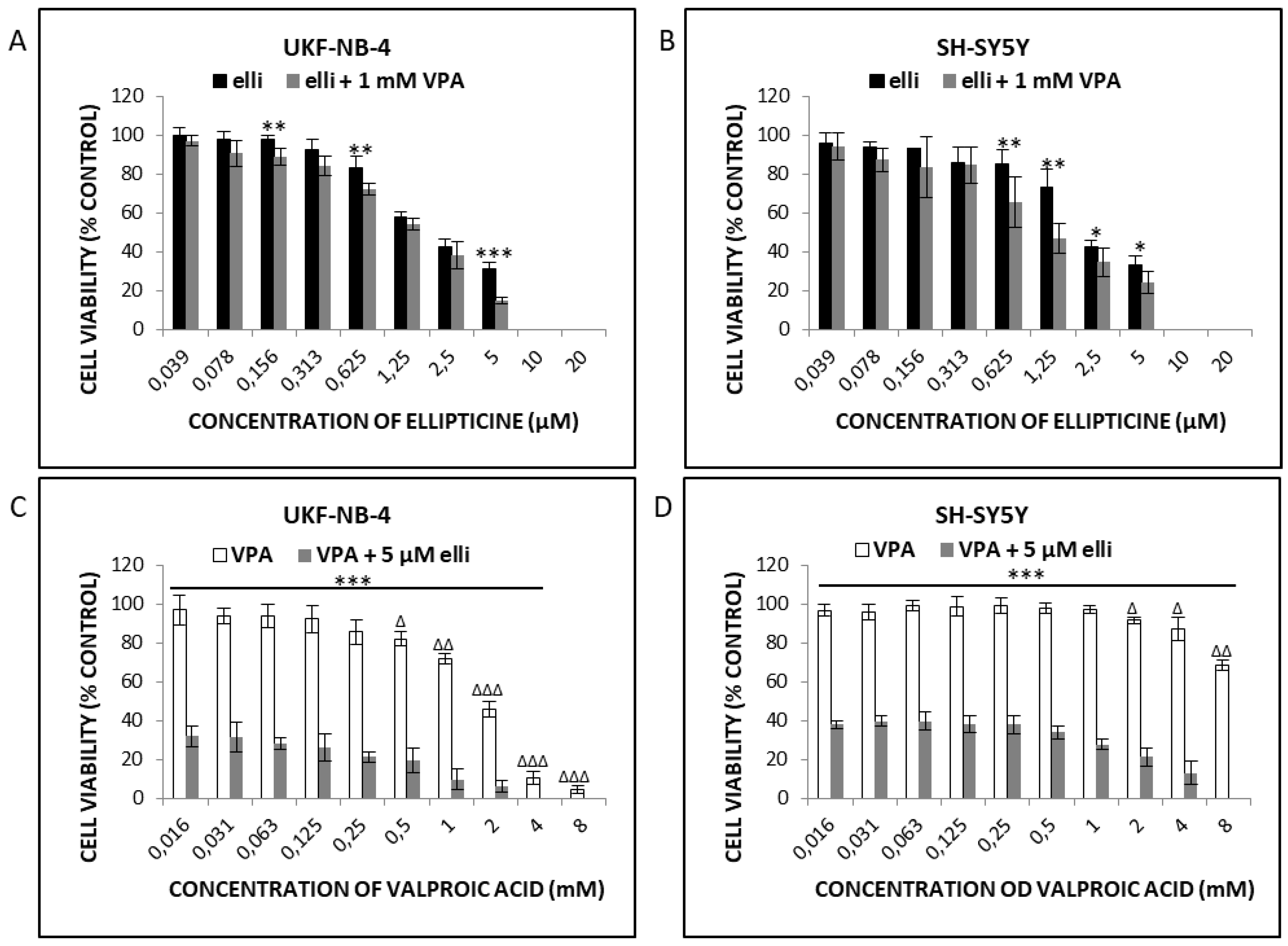
2.1. VPA Enhances Cytotoxicity of Ellipticine in Human UKF-NB-4 and SH-SY5Y NBL Cells
2.2. VPA and Ellipticine Produce Different Effects on the Cell Cycle Distribution in UKF-NB-4 and SH-SY5Y Cells
2.3. Acetylation of Histones H3 and H4 in UKF-NB-4 and SH-SY5Y Cells Exposed to VPA, Ellipticine and Their Combination
2.4. The Effect of VPA on Ellipticine-Induced DNA Damage in UKF-NB-4 and SH-SY5Y Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures and Chemicals
4.2. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Assay
4.3. Annexin V/DAPI Double Staining Assay
4.4. Real-Time Monitoring of Cell Viability
4.5. Detection of Active Caspase-3
4.6. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.7. Determination of Contents of Acetylated Histones H3 and H4
4.8. Determination of Histone H2AX Phosphorylation Status
4.9. Detection of Ellipticine-DNA Adducts by 32P-Postlabeling
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brodeur, G.M. Neuroblastoma: Biological insights into a clinical enigma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, M.; Westermann, F.; Hero, B.; Berthold, F. Neuroblastoma: Biology and molecular and chromosomal pathology. Lancet Oncol. 2003, 4, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maris, J.M.; Hogarty, M.D.; Bagatell, R.; Cohn, S.L. Neuroblastoma. Lancet 2007, 369, 2106–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furchert, S.E.; Lanvers-Kaminsky, C.; Jürgens, H.; Jung, M.; Loidl, A.; Frühwald, M.C. Inhibitors of histone deacetylases as potential therapeutic tools for high-risk embryonal tumors of the nervous system of childhood. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decock, A.; Ongenaert, M.; Vandesompele, J.; Speleman, F. Neuroblastoma epigenetics: From candidate gene approaches to genome-wide screenings. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, V.; Gozzini, A.; Ferrari, G. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Molecular and biological activity as a premise to clinical application. Curr. Drug Metab. 2007, 8, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portela, A.; Esteller, M. Epigenetic modifications and human disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouzarides, T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 2007, 128, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perri, F.; Longo, F.; Giuliano, M.; Sabbatino, F.; Favia, G.; Ionna, F.; Addeo, R.; Della Vittoria Scarpati, G.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Pisconti, S. Epigenetic control of gene expression: Potential implications for cancer treatment. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 111, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glozak, M.A.; Sengupta, N.; Zhang, X.; Seto, E. Acetylation and deacetylation of non-histone proteins. Gene 2005, 363, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretsovali, A.; Hadjimichael, C.; Charmpilas, N. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cell pluripotency, differentiation, and reprogramming. Stem Cells Int. 2012, 2012, 1841154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckschlager, T.; Plch, J.; Stiborova, M.; Hrabeta, J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.L.; Sung, J.; Cohen, M.; Chowdhury, W.H.; Sachs, M.D.; Li, Y.; Lakshmanan, Y.; Yung, B.Y.; Lupold, S.E.; Rodriguez, R. Valproic acid inhibits invasiveness in bladder cancer but not in prostate cancer cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 319, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockhausen, M.T.; Sjölund, J.; Manetopoulos, C.; Axelson, H. Effects of the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid on Notch signalling in human neuroblastoma cells. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiborova, M.; Eckschlager, T.; Poljakova, J.; Hrabeta, J.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R.; Frei, E. The Synergistic effects of DNA-targeted chemotherapeutics and histone deacetylase inhibitors as therapeutic strategies for cancer treatment. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 4218–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmaca, A.; Al-Batran, S.-E.; Maurer, A.; Neumann, A.; Heinzel, T.; Hentsch, B.; Schwarz, S.E.; Hövelmann, S.; Göttlicher, M.; Knuth, A.; et al. Valproic acid (VPA) in patients with refractory advanced cancer: A dose escalating phase I clinical trial. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munster, P.; Marchion, D.; Bicaku, E.; Lacevic, M.; Kim, J.; Centeno, B.; Daud, A.; Neuger, A.; Minton, S.; Sullivan, D. Clinical and biological effects of valproic acid as a histone deacetylase inhibitor on tumor and surrogate tissues: Phase I/II trial of valproic acid and epirubicin/FEC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2488–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocca, A.; Minucci, S.; Tosti, G.; Croci, D.; Contegno, F.; Ballarini, M.; Nolè, F.; Munzone, E.; Salmaggi, A.; Goldhirsch, A.; et al. A phase I-II study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid plus chemoimmunotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandermeers, F.; Hubert, P.; Delvenne, P.; Mascaux, C.; Grigoriu, B.; Burny, A.; Scherpereel, A.; Willems, L. Valproate, in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin, provides additional efficacy to the treatment of malignant mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2818–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Blake, M.; Baek, J.H.; Kohlhagen, G.; Pommier, Y.; Carrier, F. Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase Increases Cytotoxicity to Anticancer Drugs Targeting DNA. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7291–7300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Munshi, A.; Kurland, J.F.; Nishikawa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Hobbs, M.L.; Tucker, S.L.; Ismail, S.; Stevens, C.; Meyn, R.E. Histone deacetylase inhibitors radiosensitize human melanoma cells by suppressing DNA repair activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 4912–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, C.M.; Zage, P.E.; Taylor, P.; Aguilera, D.; Wolff, J.E.; Lee, D.; Gopalakrishnan, V. Chromatin remodelling at the topoisomerase II-beta promoter is associated with enhanced sensitivity to etoposide in human neuroblastoma cell lines. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 2771–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poljakova, J.; Hrebackova, J.; Dvorakova, M.; Moserova, M.; Eckschlager, T.; Hrabeta, J.; Göttlicherova, M.; Kopejtkova, B.; Frei, E.; Kizek, R.; et al. Anticancer agent ellipticine combined with histone deacetylase inhibitors, valproic acid and trichostatin A, is an effective DNA damage strategy in human neuroblastoma. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 2011, 32, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cipro, Š.; Hřebačková, J.; Hraběta, J.; Poljaková, J.; Eckschlager, T. Valproic acid overcomes hypoxia-induced resistance to apoptosis. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groh, T.; Hrabeta, J.; Poljakova, J.; Eckschlager, T.; Stiborova, M. Impact of histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid on the anticancer effect of etoposide on neuroblastoma cells. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 2012, 33, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Groh, T.; Hrabeta, J.; Khalil, M.A.; Doktorova, H.; Eckschlager, T.; Stiborova, M. The synergistic effects of DNA-damaging drugs cisplatin and etoposide with a histone deacetylase inhibitor valproate in high-risk neuroblastoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 4, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Edwards, H.; Caldwell, J.T.; Buck, S.A.; Qing, W.Y.; Taub, J.W.; Ge, Y.; Wang, Z. Panobinostat synergistically enhances the cytotoxic effects of cisplatin, dexorubicin or etoposide on high-risk neuroblastoma cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76662. [Google Scholar]
- Hrabeta, J.; Stiborova, M.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R.; Eckschlager, T. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. A review. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2014, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New, M.; Olzscha, H.; La Thangue, N.B. HDAC inhibitor-based therapies: Can we interpret the code? Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poljaková, J.; Eckschlager, T.; Hraběta, J.; Hrebacková, J.; Smutný, S.; Frei, E.; Martínek, V.; Kizek, R.; Stiborová, M. The mechanism of cytotoxicity and DNA adduct formation by the anticancer drug ellipticine in human neuroblastoma cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 1466–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiborová, M.; Rupertová, M.; Frei, E. Cytochrome P450- and peroxidase-mediated oxidation of anticancer alkaloid ellipticine dictates its anti-tumor efficiency. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1814, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procházka, P.; Libra, A.; Zemanová, Z.; Hřebačková, J.; Poljaková, J.; Hraběta, J.; Bunček, M.; Stiborová, M.; Eckschlager, T. Mechanisms of ellipticine-mediated resistance in UKF-NB-4 neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiborova, M.; Frei, E. Ellipticines as DNA-targeted chemotherapeutics. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabeta, J.; Groh, T.; Khalil, M.A.; Poljakova, J.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R.; Uhlik, J.; Doktorova, H.; Cerna, T.; Frei, E.; et al. Vacuolar-ATPase-mediated intracellular sequestration of ellipticine contributes to drug resistance in neuroblastoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auclair, C. Multimodal action of antitumor agents on DNA: The ellipticine series. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1987, 259, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbett, N.C.; Graves, D.E. Extending nature's leads: The anticancer agent ellipticine. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti-Cancer Agents 2004, 4, 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tmejova, K.; Krejcova, L.; Hynek, D.; Adam, V.; Babula, P.; Trnková, L.; Stiborova, M.; Eckschlager, T.; Kizek, R. Electrochemical study of ellipticine interaction with single and double stranded oligonucleotides. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwelling, L.A.; Michaels, S.; Kerrigan, D.; Pommier, Y.; Kohn, K.W. Protein-associated deoxyribonucleic acid strand breaks produced in mouse leukemia L1210 cells by ellipticine and 2-methyl-9-hydroxyellipticinium. Biochem. Pharm. 1982, 31, 3261–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiborová, M.; Sejbal, J.; Borek-Dohalská, L.; Aimová, D.; Poljaková, J.; Forsterová, K.; Rupertová, M.; Wiesner, J.; Hudecek, J.; Wiessler, M.; et al. The anticancer drug ellipticine forms covalent DNA adducts, mediated by human cytochromes P450, through metabolism to 13-hydroxyellipticine and ellipticine N2-oxide. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 8374–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiborová, M.; Poljaková, J.; Ryslavá, H.; Dracínský, M.; Eckschlager, T.; Frei, E. Mammalian peroxidases activate anticancer drug ellipticine to intermediates forming deoxyguanosine adducts in DNA identical to those found in vivo and generated from 12-hydroxyellipticine and 13-hydroxyellipticine. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiborová, M.; Rupertová, M.; Aimová, D.; Ryslavá, H.; Frei, E. Formation and persistence of DNA adducts of anticancer drug ellipticine in rats. Toxicology 2007, 236, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiborová, M.; Indra, R.; Moserová, M.; Cerná, V.; Rupertová, M.; Martínek, V.; Eckschlager, T.; Kizek, R.; Frei, E. Cytochrome b5 increases cytochrome P450 3A4-mediated activation of anticancer drug ellipticine to 13-hydroxyellipticine whose covalent binding to DNA is elevated by sulfotransferases and N,O-acetyltransferases. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiborová, M.; Poljaková, J.; Martínková, E.; Ulrichová, J.; Simánek, V.; Dvořák, Z.; Frei, E. Ellipticine oxidation and DNA adduct formation in human hepatocytes is catalyzed by human cytochromes P450 and enhanced by cytochrome b5. Toxicology 2012, 302, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizek, R.; Adam, V.; Hrabeta, J.; Eckschlager, T.; Smutny, S.; Burda, J.V.; Frei, E.; Stiborova, M. Anthracyclines and ellipticines as DNA-damaging anticancer drugs: Recent advances. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 133, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotrbová, V.; Mrázová, B.; Moserová, M.; Martínek, V.; Hodek, P.; Hudeček, J.; Frei, E.; Stiborová, M. Cytochrome b5 shifts oxidation of the anticancer drug ellipticine by cytochromes P450 1A1 and 1A2 from its detoxication to activation, thereby modulating its pharmacological efficacy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, L.; Ke, X.X.; Gong, X.Y.; Wan, J.H.; Hao, X.W.; Xu, M.; Xiang, Z.; Cui, Z.B.; Cui, H. DNA-damaging drug-induced apoptosis sensitized by N-myc in neuroblastoma cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2012, 36, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.A.; Hrabeta, J.; Groh, T.; Prochazka, P.; Doktorova, H.; Eckschlager, T. Valproic acid increases CD133 positive cells that show low sensitivity to cytostatics in neuroblastoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earnshaw, W.C.; Martins, L.M.; Kaufmann, S.H. Mammalian caspases: Structure, activation, substrates, and functions during apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999, 68, 383–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, A.G.; Jänicke, R.U. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slee, E.A.; Adrain, C.; Martin, S.J. Executioner caspase-3, -6, and -7 perform distinct, non-redundant roles during the demolition phase of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7320–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, A.J.; Rao, V.A.; Pommier, Y.; Bonner, W.M. The complexity of phosphorylated H2AX foci formation and DNA repair assembly at DNA double-strand breaks. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, K.; Almasan, A. Histone H2AX phosphorylation: A marker for DNA damage. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 920, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stiborová, M.; Indra, R.; Frei, E.; Kopečková, K.; Schmeiser, H.H.; Eckschlager, T.; Adam, V.; Heger, Z.; Arlt, V.M.; et al. Cytochrome b5 plays a dual role in the reaction cycle of cytochrome P450 3A4 during oxidation of the anticancer drug ellipticine. Monatsh. Chem. 2017, 148, 1983–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchenko, V.L.; Salcido, C.D.; Zhang, Y.; Agama, K.; Komlodi-Pasztor, E.; Murphy, R.F.; Giaccone, G.; Pommier, Y.; Bates, S.E.; et al. Schedule-dependent synergy of histone deacetylase inhibitors with DNA damaging agents in small cell lung cancer. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, W.; Fulda, S.; Jeremias, I.; Debatin, K.M.; Schwab, M. MycN and IFN cooperate in apoptosis of human neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene 1998, 17, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroni, M.; Veschi, V.; Prodosmo, A.; Rinaldo, C.; Massimi, I.; Carbonari, M.; Dominici, C.; McDowell, H.P.; Rinaldi, C.; et al. MYCN sensitizes human neuroblastoma to apoptosis by HIPK2 activation through a DNA damage response. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, M.I.; Ali, A.M.; Sayed, H.A.; Zaky, E.M. Treatment results and prognostic factors of pediatric neuroblastoma: A retrospective study. Int. Arch. Med. 2010, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poljaková, J.; Groh, T.; Gudino, Z.O.; Hraběta, J.; Bořek-Dohalská, L.; Kizek, R.; Doktorová, H.; Eckschlager, T.; Stiborová, M. Hypoxia-mediated histone acetylation and expression of N-myc transcription factor dictate aggressiveness of neuroblastoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1928–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinatl, J., Jr.; Cinatl, J.; Driever, P.H.; Kotchetkov, R.; Pouckova, P.; Kornhuber, B.; Schwabe, D. Sodium valproate inhibits in vivo growth of human neuroblastoma cells. Anticancer Drugs 1997, 8, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, N.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Abassi, Y.A. The xCELLigence system for real-time and label-free monitoring of cell viability. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 740, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shechter, D.; Dormann, H.L.; Allis, C.D.; Hake, S.B. Extraction, purification and analysis of histones. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1445–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosenbrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frei, E.; Bieler, C.A.; Arlt, V.M.; Wiessler, M.; Stiborová, M. Covalent binding of the anticancer drug ellipticine to DNA in V79 cells transfected with human cytochrome P450 enzymes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 64, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poljaková, J.; Frei, E.; Gomez, J.E.; Aimová, D.; Eckschlager, T.; Hrabeta, J.; Stiborová, M. DNA adduct formation by the anticancer drug ellipticine in human leukemia HL-60 and CCRF-CEM cells. Cancer Lett. 2007, 252, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

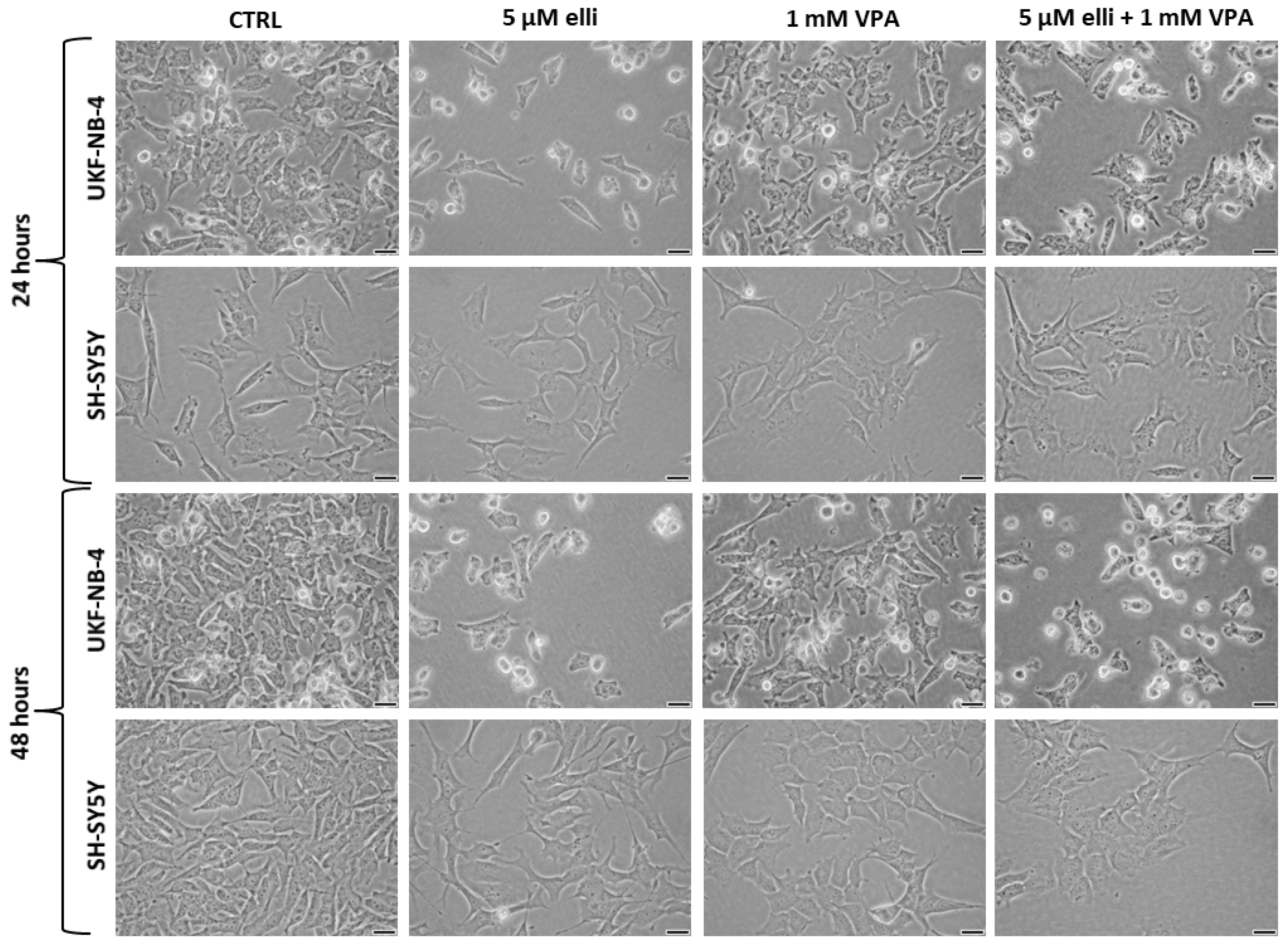
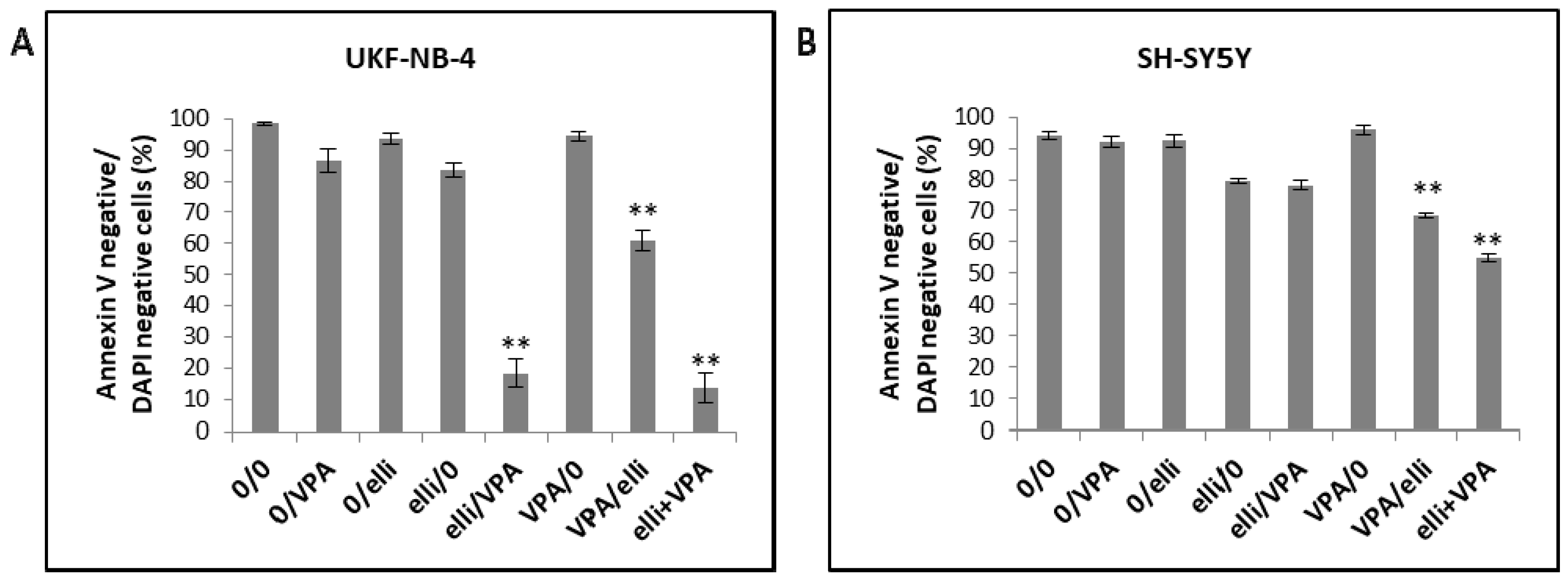

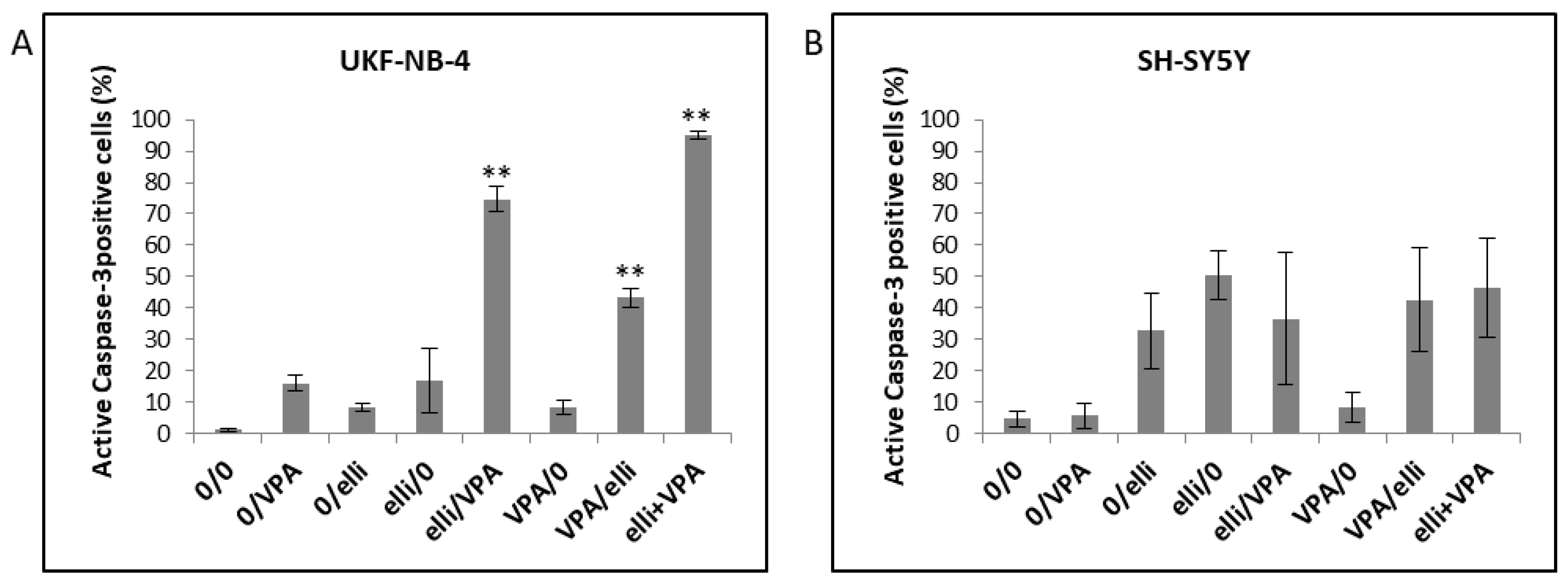





| Designation | 0–24 h | 24–48 h |
|---|---|---|
| 0/0 | medium | |
| 0/VPA | medium | 1 mM VPA |
| 0/elli | medium | 5 µM elli |
| elli/0 | 5 µM elli | |
| elli/VPA | 5 µM elli | 1 mM VPA |
| VPA/0 | 1 mM VPA | |
| VPA/elli | 1 mM VPA | |
| elli + VPA | 5 µM elli + 1 mM VPA | |
| Cells | RAL (Mean ± SD/107 Nucleotides) a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adduct 1 b | Adduct 2 | Adduct 6 | Adduct 7 | Total | |
| UKF-NB-4 | |||||
| elli/0 | 1.86 ± 0.31 | 0.53 ± 0.01 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ±0.005 | 2.91 ± 0.35 |
| elli/VPA | 4.42 ± 0.06 ** | 0.30 ± 0.02 * | 0.47 ± 0.07 ** | 0.74 ± 0.09 * | 5.93 ± 0.87 ** |
| VPA/elli | 2.72 ± 0.02 ** | 0.23 ± 0.06 ** | 0.60 ± 0.04 ** | 0.80 ± 0.10 ** | 4.35 ± 0.52 ** |
| elli + VPA | 6.46 ± 0.05 ** | 0.24 ± 0.02 ** | 1.04 ± 0.02 ** | 1.10 ± 0.07 ** | 8.84 ± 0.34 ** |
| SH-SY5Y | |||||
| elli/0 | 1.50 ± 0.13 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | 0.34 ± 0.07 | 2.22 ± 0.11 |
| elli/VPA | 1.43 ± 0.19 | 0.17 ± 0.02 ** | 0.37 ± 0.02 * | 0.37 ± 0.06 | 2.34 ± 0.16 |
| VPA/elli | 2.37 ± 0.01 ** | 0.26 ± 0.001 ** | 0.37 ± 0.06 * | 0.59 ± 0.07 ** | 3.59 ± 0.19 ** |
| elli + VPA | 2.37 ± 0.01 ** | 0.27 ± 0.01 ** | 0.45 ± 0.01 ** | 0.65 ± 0.006 ** | 3.74 ± 0.02 ** |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cerna, T.; Hrabeta, J.; Eckschlager, T.; Frei, E.; Schmeiser, H.H.; Arlt, V.M.; Stiborová, M. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Valproic Acid Exerts a Synergistic Cytotoxicity with the DNA-Damaging Drug Ellipticine in Neuroblastoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010164
Cerna T, Hrabeta J, Eckschlager T, Frei E, Schmeiser HH, Arlt VM, Stiborová M. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Valproic Acid Exerts a Synergistic Cytotoxicity with the DNA-Damaging Drug Ellipticine in Neuroblastoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(1):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010164
Chicago/Turabian StyleCerna, Tereza, Jan Hrabeta, Tomas Eckschlager, Eva Frei, Heinz H. Schmeiser, Volker M. Arlt, and Marie Stiborová. 2018. "The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Valproic Acid Exerts a Synergistic Cytotoxicity with the DNA-Damaging Drug Ellipticine in Neuroblastoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 1: 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010164
APA StyleCerna, T., Hrabeta, J., Eckschlager, T., Frei, E., Schmeiser, H. H., Arlt, V. M., & Stiborová, M. (2018). The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Valproic Acid Exerts a Synergistic Cytotoxicity with the DNA-Damaging Drug Ellipticine in Neuroblastoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(1), 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010164





