Mutation Analysis in Cultured Cells of Transgenic Rodents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of Big Blue® Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts and Preparation of Cell Cultures
2.2. Cytotoxicity Examination of Test Chemical/Agent
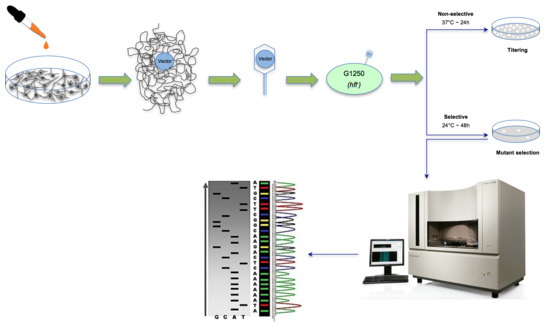
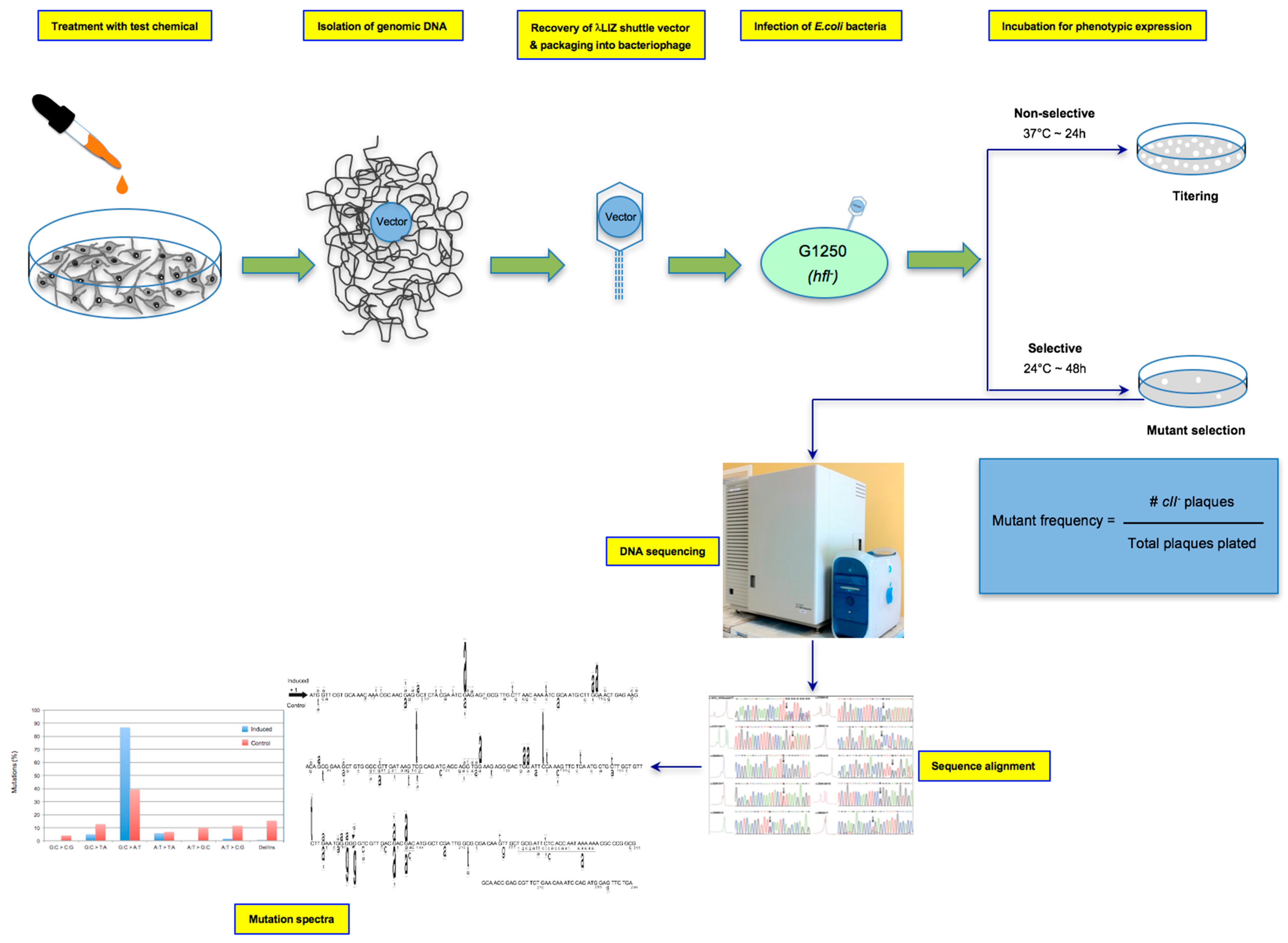
2.3. In Vitro Treatment for Mutagenicity Testing
2.4. Genomic DNA Isolation
2.5. The λ Select cII Assay
2.6. The Induced and Spontaneous cII Mutant Frequencies and Mutation Spectra
3. Data Analysis
3.1. Determining the Mutagenic Potency of a Test Chemical/Agent and Analyzing the Sequence-Specificity of Mutations
3.2. Statistical Analysis and Interpretation of the Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| DMSO | dimethylsulfoxide |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| FBS | fetal calf serum |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
References
- Russell, W.M.S.; Burch, R.L. The Principles of Humane Experimental Technique; Methuen: London, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Besaratinia, A.; Pfeifer, G.P. Investigating human cancer etiology by DNA lesion footprinting and mutagenicity analysis. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 1526–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thybaud, V.; Dean, S.; Nohmi, T.; de Boer, J.; Douglas, G.R.; Glickman, B.W.; Gorelick, N.J.; Heddle, J.A.; Heflich, R.H.; Lambert, I.; et al. In vivo transgenic mutation assays. Mutat. Res. 2003, 540, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, I.B.; Singer, T.M.; Boucher, S.E.; Douglas, G.R. Detailed review of transgenic rodent mutation assays. Mutat. Res. 2005, 590, 1–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiger, R.R. Quantifying in vivo somatic mutations using transgenic mouse model systems. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1105, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jakubczak, J.L.; Merlino, G.; French, J.E.; Muller, W.J.; Paul, B.; Adhya, S.; Garges, S. Analysis of genetic instability during mammary tumor progression using a novel selection-based assay for in vivo mutations in a bacteriophage lambda transgene target. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9073–9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, D.E.; Cunningham, M.L.; Tindall, K.R. Spontaneous and ENU-induced mutation spectra at the cII locus in Big Blue Rat2 embryonic fibroblasts. Mutagenesis 1998, 13, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erexson, G.L.; Watson, D.E.; Tindall, K.R. Characterization of new transgenic Big Blue(R) mouse and rat primary fibroblast cell strains for use in molecular toxicology studies. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1999, 34, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erexson, G.L.; Tindall, K.R. Micronuclei and gene mutations in transgenic big Blue((R)) mouse and rat fibroblasts after exposure to the epoxide metabolites of 1, 3-butadiene. Mutat. Res. 2000, 472, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDiarmid, H.M.; Douglas, G.R.; Coomber, B.L.; Josephy, P.D. 2-Amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (PhIP)-induced mutagenesis in cultured Big Blue rat mammary epithelial and fibroblast cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2002, 39, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp-Szabo, E.; Douglas, G.R.; Coomber, B.L.; Josephy, P.D. Mutagenicity of the oral carcinogen 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide in cultured BigBlue rat tongue epithelial cells and fibroblasts. Mutat. Res. 2003, 522, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, Y.; Gate, L.; Darne, C.; Bottin, M.C.; Langlais, C.; Micillino, J.C.; Goutet, M.; Julien, S.; Stephane, B. In Vitro Study of Mutagenesis Induced by Crocidolite-Exposed Alveolar Macrophages NR8383 in Cocultured Big Blue Rat2 Embryonic Fibroblasts. J. Toxicol. 2010, 2010, 323828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Bates, S.E.; Pfeifer, G.P. Mutational signature of the proximate bladder carcinogen N-hydroxy-4-acetylaminobiphenyl: Inconsistency with the p53 mutational spectrum in bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4331–4338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Pfeifer, G.P. Enhancement of the mutagenicity of benzo(a)pyrene diol epoxide by a nonmutagenic dose of ultraviolet A radiation. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8708–8716. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Pfeifer, G.P. Weak yet distinct mutagenicity of acrylamide in mammalian cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Pfeifer, G.P. Biological consequences of 8-methoxypsoralen-photoinduced lesions: Sequence-specificity of mutations and preponderance of T to C and T to a mutations. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Pfeifer, G.P. Genotoxicity of acrylamide and glycidamide. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Bates, S.E.; Synold, T.W.; Pfeifer, G.P. Similar mutagenicity of photoactivated porphyrins and ultraviolet A radiation in mouse embryonic fibroblasts: Involvement of oxidative DNA lesions in mutagenesis. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 15557–15566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Besaratinia, A.; Feng, Z.; Tang, M.S.; Amin, S.; Luch, A.; Pfeifer, G.P. DNA damage, repair, and mutation induction by (+)-Syn and (−)-anti-dibenzo[a,l]pyrene-11,12-diol-13,14-epoxides in mouse cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7321–7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Synold, T.W.; Xi, B.; Pfeifer, G.P. G-to-T transversions and small tandem base deletions are the hallmark of mutations induced by ultraviolet a radiation in mammalian cells. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 8169–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Pfeifer, G.P. Investigating DNA adduct-targeted mutagenicity of tamoxifen: Preferential formation of tamoxifen-DNA adducts in the human p53 gene in SV40 immortalized hepatocytes but not endometrial carcinoma cells. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 8418–8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.I.; Pfeifer, G.P.; Besaratinia, A. Lack of mutagenicity of acrolein-induced DNA adducts in mouse and human cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11640–11647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Kim, S.I.; Bates, S.E.; Pfeifer, G.P. Riboflavin activated by ultraviolet A1 irradiation induces oxidative DNA damage-mediated mutations inhibited by vitamin C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5953–5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Kim, S.I.; Pfeifer, G.P. Rapid repair of UVA-induced oxidized purines and persistence of UVB-induced dipyrimidine lesions determine the mutagenicity of sunlight in mouse cells. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2008, 22, 2379–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Kim, S.I.; Hainaut, P.; Pfeifer, G.P. In vitro recapitulating of TP53 mutagenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma associated with dietary aflatoxin B1 exposure. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1127–1137, 1137.e1–1137.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Li, H.; Yoon, J.I.; Zheng, A.; Gao, H.; Tommasi, S. A high-throughput next-generation sequencing-based method for detecting the mutational fingerprint of carcinogens. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommasi, S.; Bates, S.E.; Behar, R.Z.; Talbot, P.; Besaratinia, A. Limited mutagenicity of electronic cigarettes in mouse or human cells in vitro. Lung Cancer 2017, 112, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dycaico, M.J.; Provost, G.S.; Kretz, P.L.; Ransom, S.L.; Moores, J.C.; Short, J.M. The use of shuttle vectors for mutation analysis in transgenic mice and rats. Mutat. Res. 1994, 307, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heddle, J.A.; Martus, H.J.; Douglas, G.R. Treatment and sampling protocols for transgenic mutation assays. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2003, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommasi, S.; Besaratinia, A.; Wilczynski, S.P.; Pfeifer, G.P. Loss of Rassf1a enhances p53-mediated tumor predisposition and accelerates progression to aneuploidy. Oncogene 2011, 30, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; He, Q.; Li, J.M.; Azzam, M.M.; Lu, J.J.; Zou, X.T. Evaluation of embryonic age and the effects of different proteases on the isolation and primary culture of chicken intestinal epithelial cells in vitro. Anim. Sci. J. 2015, 86, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellows, M.D.; O’Donovan, M.R.; Lorge, E.; Kirkland, D. Comparison of different methods for an accurate assessment of cytotoxicity in the in vitro micronucleus test. II: Practical aspects with toxic agents. Mutat. Res. 2008, 655, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossman, T.G. Inappropriate cytotoxicity measurements. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2009, 50, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). The OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals: In Vitro Mammalian Cell Micronucleus Test 2014; OECD: Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). OECD Guideline for the Testing of Chemicals: In Vitro Mammalian Cell Gene Mutation Tests Using the Hprt and Xprt Genes; OECD: Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Guidance Document on Revisions to OECD Genetic Toxicology Test Guidelines; OECD: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Agilent Technologies, Stratagene Products Division. λ Select-cII Mutation Detection System for Big Blue Rodents. Instruction Manual; Catalog #720120; Revision B.0. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/cs/library/usermanuals/public/720120.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2018).
- Herskowitz, I.; Hagen, D. The lysis-lysogeny decision of phage lambda: Explicit programming and responsiveness. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1980, 14, 399–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, W.T.; Skopek, T.R. Statistical test for the comparison of samples from mutational spectra. J. Mol. Biol. 1987, 194, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.A.; Fellows, M.D.; Hashizume, T.; White, P.A. The utility of metabolic activation mixtures containing human hepatic post-mitochondrial supernatant (S9) for in vitro genetic toxicity assessment. Mutagenesis 2016, 31, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, G.; Martelli, A. Failure of the standard battery of short-term tests in detecting some rodent and human genotoxic carcinogens. Toxicology 2004, 196, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMarini, D.M.; Gudi, R.; Szkudlinska, A.; Rao, M.; Recio, L.; Kehl, M.; Kirby, P.E.; Polzin, G.; Richter, P.A. Genotoxicity of 10 cigarette smoke condensates in four test systems: Comparisons between assays and condensates. Mutat. Res. 2008, 650, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkler, F.; Stolpmann, K.; Luch, A. Exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Bulky DNA adducts and cellular responses. EXS 2012, 101, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, S.; van de Sandt, J.J.; Merk, H.F.; Lockley, D.J.; Pendlington, R.U.; Pease, C.K. Xenobiotic metabolism in human skin and 3D human skin reconstructs: A review. Curr. Drug Metab. 2007, 8, 758–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyborski, D.L.; Malkhosyan, S.; Moores, J.; Perucho, M.; Short, J.M. Development of a rat cell line containing stably integrated copies of a lambda/lacI shuttle vector. Mutat. Res. 1995, 334, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, V. Cell-line authentication demystified. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, G.A.; Bain, L.J. Chronic toxicity of environmental contaminants: Sentinels and biomarkers. Environ. Health Perspect. 1997, 105 (Suppl. 1), 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arlt, V.M.; Stiborova, M.; vom Brocke, J.; Simoes, M.L.; Lord, G.M.; Nortier, J.L.; Hollstein, M.; Phillips, D.H.; Schmeiser, H.H. Aristolochic acid mutagenesis: Molecular clues to the aetiology of Balkan endemic nephropathy-associated urothelial cancer. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 2253–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Pfeifer, G.P. Second-hand smoke and human lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.S.; Urlando, C.; Heddle, J.A. Comparison of somatic mutation in a transgenic versus host locus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10681–10685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, V.E.; Gorelick, N.J.; Andrews, J.L.; Craft, T.R.; deBoer, J.G.; Glickman, B.W.; Skopek, T.R. Frequency and spectrum of ethylnitrosourea-induced mutation at the hprt and lacI loci in splenic lymphocytes of exposed lacI transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 4654–4661. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Aidoo, A.; Manjanatha, M.G.; Mittelstaedt, R.A.; Shelton, S.D.; Lyn-Cook, L.E.; Casciano, D.A.; Heflich, R.H. Comparison of mutant frequencies and types of mutations induced by thiotepa in the endogenous Hprt gene and transgenic lacI gene of Big Blue rats. Mutat. Res. 1998, 403, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, L.; Heddle, J.A. A comparison of the effects of diverse mutagens at the lacZ transgene and Dlb-1 locus in vivo. Mutagenesis 1999, 14, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shane, B.S.; de Boer, J.; Watson, D.E.; Haseman, J.K.; Glickman, B.W.; Tindall, K.R. LacI mutation spectra following benzo[a]pyrene treatment of Big Blue mice. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.I.; Yoon, J.I.; Tommasi, S.; Besaratinia, A. New experimental data linking secondhand smoke exposure to lung cancer in nonsmokers. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2012, 26, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beal, M.A.; Gagne, R.; Williams, A.; Marchetti, F.; Yauk, C.L. Characterizing Benzo[a]pyrene-induced lacZ mutation spectrum in transgenic mice using next-generation sequencing. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaver-Walker, P.M.; Urlando, C.; Tao, K.S.; Zhang, X.B.; Heddle, J.A. Enhanced somatic mutation rates induced in stem cells of mice by low chronic exposure to ethylnitrosourea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 11470–11474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skopek, T.R.; Kort, K.L.; Marino, D.R.; Mittal, L.V.; Umbenhauer, D.R.; Laws, G.M.; Adams, S.P. Mutagenic response of the endogenous hprt gene and lacI transgene in benzo[a]pyrene-treated Big Blue B6C3F1 mice. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1996, 28, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelstaedt, R.A.; Manjanatha, M.G.; Shelton, S.D.; Lyn-Cook, L.E.; Chen, J.B.; Aidoo, A.; Casciano, D.A.; Heflich, R.H. Comparison of the types of mutations induced by 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene in the lacI and hprt genes of Big Blue rats. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1998, 31, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, L.; Heddle, J.A. Differential mutation of transgenic and endogenous loci in vivo. Mutat. Res. 2000, 454, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellon, I.; Spivak, G.; Hanawalt, P.C. Selective removal of transcription-blocking DNA damage from the transcribed strand of the mammalian DHFR gene. Cell 1987, 51, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanawalt, P.C. Transcription-coupled repair and human disease. Science 1994, 266, 1957–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommasi, S.; Denissenko, M.F.; Pfeifer, G.P. Sunlight induces pyrimidine dimers preferentially at 5-methylcytosine bases. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4727–4730. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, G.P.; Besaratinia, A. Mutational spectra of human cancer. Hum. Genet. 2009, 125, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulos, R.C.; Olivier, J.; Wong, J.W.H. The interaction between cytosine methylation and processes of DNA replication and repair shape the mutational landscape of cancer genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 7786–7795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, L.; Heddle, J.A. A test for neutrality of mutations of the lacZ transgene. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1996, 28, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiger, R.R.; Cosentino, L.; Masumura, K.I.; Nohmi, T.; Heddle, J.A. Further characterization and validation of gpt delta transgenic mice for quantifying somatic mutations in vivo. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2001, 37, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiger, R.R.; Cosentino, L.; Shima, N.; Bielas, J.H.; Cruz-Munoz, W.; Heddle, J.A. The cII locus in the MutaMouse system. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1999, 34, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjanatha, M.G.; Cao, X.; Shelton, S.D.; Mittelstaedt, R.A.; Heflich, R.H. In vivo cII, gpt, and Spi(-) gene mutation assays in transgenic mice and rats. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1044, 97–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yatagai, F.; Nohmi, T.; Kusakabe, M.; Masumura, K.; Yoshiki, A.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kurobe, T.; Kuniya, K.; Hanaoka, F.; Yano, Y. Mutation induction by heavy-ion irradiation of gpt delta transgenic mice. Phys. Medica 2001, 17 (Suppl. 1), 192–193. [Google Scholar]
- Bhalli, J.A.; Shaddock, J.G.; Pearce, M.G.; Dobrovolsky, V.N. Sensitivity of the Pig-a assay for detecting gene mutation in rats exposed acutely to strong clastogens. Mutagenesis 2013, 28, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohmi, T.; Masumura, K. Gpt delta transgenic mouse: A novel approach for molecular dissection of deletion mutations in vivo. Adv. Biophys. 2004, 38, 97–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiger, R.R. Just how does the cII selection system work in Muta Mouse? Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2001, 37, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrinello, S.; Samper, E.; Krtolica, A.; Goldstein, J.; Melov, S.; Campisi, J. Oxygen sensitivity severely limits the replicative lifespan of murine fibroblasts. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Adda di Fagagna, F. Living on a break: Cellular senescence as a DNA-damage response. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odell, A.; Askham, J.; Whibley, C.; Hollstein, M. How to become immortal: Let MEFs count the ways. Aging 2010, 2, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommasi, S.; Zheng, A.; Weninger, A.; Bates, S.E.; Li, X.A.; Wu, X.; Hollstein, M.; Besaratinia, A. Mammalian cells acquire epigenetic hallmarks of human cancer during immortalization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Besaratinia, A.; Zheng, A.; Bates, S.E.; Tommasi, S. Mutation Analysis in Cultured Cells of Transgenic Rodents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010262
Besaratinia A, Zheng A, Bates SE, Tommasi S. Mutation Analysis in Cultured Cells of Transgenic Rodents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(1):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010262
Chicago/Turabian StyleBesaratinia, Ahmad, Albert Zheng, Steven E. Bates, and Stella Tommasi. 2018. "Mutation Analysis in Cultured Cells of Transgenic Rodents" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 1: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010262
APA StyleBesaratinia, A., Zheng, A., Bates, S. E., & Tommasi, S. (2018). Mutation Analysis in Cultured Cells of Transgenic Rodents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(1), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010262