Lowering Low-Density Lipoprotein Particles in Plasma Using Dextran Sulphate Co-Precipitates Procoagulant Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
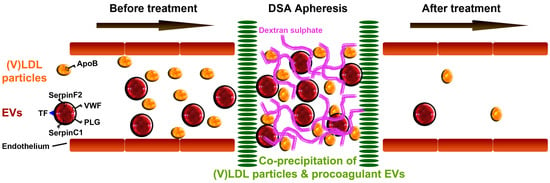
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Coagulation Protein Levels in the (V)LDL (Very-Low- and Low-Density Lipoprotein) Precipitate
2.2. Bilayer EVs Co-Precipitate with Lipoprotein Particles
2.3. Coagulation Proteins in the (V)LDL Precipitate are Present in Extracellular Vesicles (EVs)
2.4. Procoagulant Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Subjects and Sample Preparation
4.2. Sequential Precipitation of (V)LDL Fraction and HDL Fraction
4.3. Proteomics and IPA Analysis
4.4. Quantitative Measurement of Protein Levels
4.5. Apolipoprotein B Measurement
4.6. Density Gradient Centrifugation
4.7. Electron Microscopy
4.8. EV Associated Procoagulant Activity Assay
4.9. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| (V)LDL | Very-low- and low- density lipoproteins |
| DSA | Dextran sulphate adsorption |
| EV | Extracellular vesicle |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
| IPA | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis |
| SA-PE | Streptavidin-phycoerythrin |
| VWF | von Willebrand factor |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ApoB | Apolipoprotein B |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| TF | Tissue factor |
| EM | Electron Microscopy |
| PLG | Plasminogen |
| tPA | Tissue-type plasminogen activator |
| uPA | Urokinase-type plasminogen activator |
References
- Boulanger, C.M.; Loyer, X.; Rautou, P.E.; Amabile, N. Extracellular vesicles in coronary artery disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loyer, X.; Vion, A.C.; Tedgui, A.; Boulanger, C.M. Microvesicles as cell-cell messengers in cardiovascular diseases. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Hoog, V.C.; Timmers, L.; Schoneveld, A.H.; Wang, J.W.; van de Weg, S.M.; Sze, S.K.; van Keulen, J.K.; Hoes, A.W.; den Ruijter, H.M.; de Kleijn, D.P.; et al. Serum extracellular vesicle protein levels are associated with acute coronary syndrome. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2013, 2, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanhai, D.A.; de Kleijn, D.P.; Kappelle, L.J.; Uiterwaal, C.S.; van der Graaf, Y.; Pasterkamp, G.; Geerlings, M.I.; Visseren, F.L.; Group, S.S. Extracellular vesicle protein levels are related to brain atrophy and cerebral white matter lesions in patients with manifest vascular disease: The SMART-MR study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e003824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falati, S.; Liu, Q.; Gross, P.; Merrill-Skoloff, G.; Chou, J.; Vandendries, E.; Celi, A.; Croce, K.; Furie, B.C.; Furie, B. Accumulation of tissue factor into developing thrombi in vivo is dependent upon microparticle P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 and platelet P-selectin. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1585–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Hengel, L.G.; van Steijn-van Tol, A.Q.; Bertina, R.M.; Versteeg, H.H.; Osanto, S. Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity in plasma is unaffected by cytolytic chemotherapy treatment in metastatic testicular cancer patients. Thromb. Res. 2013, 131, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.W.; Gijsberts, C.M.; Seneviratna, A.; de Hoog, V.C.; Vrijenhoek, J.E.; Schoneveld, A.H.; Chan, M.Y.; Lam, C.S.; Richards, A.M.; Lee, C.N.; et al. Plasma extracellular vesicle protein content for diagnosis and prognosis of global cardiovascular disease. Neth. Heart J. 2013, 21, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, K.D.; Willis, G.R.; Datta, D.B.; Ellins, E.A.; Ladell, K.; Price, D.A.; Guschina, I.A.; Rees, D.A.; James, P.E. Lipoprotein-apheresis reduces circulating microparticles in individuals with familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamler, J.; Wentworth, D.; Neaton, J.D. Is relationship between serum cholesterol and risk of premature death from coronary heart disease continuous and graded? Findings in 356,222 primary screenees of the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial (MRFIT). JAMA 1986, 256, 2823–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study Group. Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: The Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet 1994, 344, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, B.R.; Stein, E.; Jones, P.; Illingworth, D.R. Indications for low-density lipoprotein apheresis. Am. J. Cardiol. 1994, 74, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompsen, J.; Thompson, P.D. A systematic review of LDL apheresis in the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2006, 189, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsoni, A.; Villard, E.F.; Bruckert, E.; Robillard, P.; Carrie, A.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Chapman, M.J.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; Le Goff, W.; Guerin, M. Impact of LDL apheresis on atheroprotective reverse cholesterol transport pathway in familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, B.R.; Kelsey, S.F.; Dau, P.C.; Gotto, A.M., Jr.; Graham, K.; Illingworth, D.R.; Isaacsohn, J.; Jones, P.H.; Leitman, S.F.; Saal, S.D.; et al. Long-term effects of low-density lipoprotein apheresis using an automated dextran sulfate cellulose adsorption system. Liposorber Study Group. Am. J. Cardiol. 1998, 81, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambauer, R.; Schiel, R.; Latza, R.; Klinkmann, J. Treatment of severe hyperlipidemia: Six years' experience with low-density lipoprotein apheresis. Artif. Organs 1996, 20, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, S. Low-density lipoprotein apheresis and changes in plasma components. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2001, 5, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knisel, W.; Di Nicuolo, A.; Pfohl, M.; Muller, H.; Risler, T.; Eggstein, M.; Seifried, E. Different effects of two methods of low-density lipoprotein apheresis on the coagulation and fibrinolytic systems. J. Intern. Med. 1993, 234, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julius, U.; Siegert, G.; Gromeier, S. Intraindividual comparison of the impact of two selective apheresis methods (DALI and HELP) on the coagulation system. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2000, 23, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oberhoffer, M.; Eifert, S.; Jaeger, B.; Blessing, F.; Beiras-Fernandez, A.; Seidel, D.; Reichart, B. Postoperative Heparin-Mediated Extracorporeal Low-Density Lipoprotein Fibrinogen Precipitation Aphaeresis Prevents Early Graft Occlusion after Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. Surg. J. 2016, 2, e5–e9. [Google Scholar]
- Aengevaeren, W.R.; Kroon, A.A.; Stalenhoef, A.F.; Uijen, G.J.; van der Werf, T. Low density lipoprotein apheresis improves regional myocardial perfusion in patients with hypercholesterolemia and extensive coronary artery disease. LDL-Apheresis Atherosclerosis Regression Study (LAARS). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1996, 28, 1696–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubba, P.; Iannuzzi, A.; Postiglione, A.; Scarpato, N.; Montefusco, S.; Gnasso, A.; Nappi, G.; Cortese, C.; Mancini, M. Hemodynamic changes in the peripheral circulation after repeat low density lipoprotein apheresis in familial hypercholesterolemia. Circulation 1990, 81, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Song, J.; Cavigiolio, G.; Ishida, B.Y.; Zhang, S.; Kane, J.P.; Weisgraber, K.H.; Oda, M.N.; Rye, K.A.; Pownall, H.J.; et al. Morphology and structure of lipoproteins revealed by an optimized negative-staining protocol of electron microscopy. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Gursky, O. Aggregation and fusion of low-density lipoproteins in vivo and in vitro. Biomol. Concepts 2013, 4, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, F.M.; Alaupovic, P.; Moye, L.A.; Cole, T.G.; Sussex, B.; Stampfer, M.J.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Braunwald, E. VLDL, apolipoproteins B, CIII, and E, and risk of recurrent coronary events in the Cholesterol and Recurrent Events (CARE) trial. Circulation 2000, 102, 1886–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotvall, J.; Hill, A.F.; Hochberg, F.; Buzas, E.I.; Di Vizio, D.; Gardiner, C.; Gho, Y.S.; Kurochkin, I.V.; Mathivanan, S.; Quesenberry, P.; et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 26913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Pol, E.; Boing, A.N.; Gool, E.L.; Nieuwland, R. Recent developments in the nomenclature, presence, isolation, detection and clinical impact of extracellular vesicles. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuana, Y.; Jiang, L.; Lammertink, B.H.A.; Vader, P.; Deckers, R.; Bos, C.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Moonen, C.T. Microbubbles-Assisted Ultrasound Triggers the Release of Extracellular Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andaloussi, S.E.; Mager, I.; Breakefield, X.O.; Wood, M.J. Extracellular vesicles: Biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, G.R. LDL apheresis. Atherosclerosis 2003, 167, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanez-Mo, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borras, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rota, S.; McWilliam, N.A.; Baglin, T.P.; Byrne, C.D. Atherogenic lipoproteins support assembly of the prothrombinase complex and thrombin generation: Modulation by oxidation and vitamin E. Blood 1998, 91, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sadler, J.E. Biochemistry and genetics of von Willebrand factor. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 395–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.W.; Eikenboom, J. Von Willebrand disease and Weibel-Palade bodies. Hamostaseologie 2010, 30, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khor, B.; Van Cott, E.M. Laboratory tests for antithrombin deficiency. Am. J. Hematol. 2010, 85, 947–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, J.; Gerber, S.S. The plasmin-antiplasmin system: Structural and functional aspects. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, C.; Harrison, P.; Belting, M.; Boing, A.; Campello, E.; Carter, B.S.; Collier, M.E.; Coumans, F.; Ettelaie, C.; van Es, N.; et al. Extracellular vesicles, tissue factor, cancer and thrombosis—Discussion themes of the ISEV 2014 Educational Day. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwicker, J.I.; Trenor, C.C.; Furie, B.C.; Furie, B. Tissue factor-bearing microparticles and thrombus formation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Violi, F.; Calvieri, C.; Ferro, D.; Pignatelli, P. Statins as antithrombotic drugs. Circulation 2013, 127, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, H.J.; McKiernan, R.G.; Prehn, J.H. Harnessing system models of cell death signalling for cytotoxic chemotherapy: Towards personalised medicine approaches? J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Vernooij, F.; Ibrahim, I.; Ooi, S.; Gijsberts, C.M.; Schoneveld, A.H.; Sen, K.W.; den Ruijter, H.M.; Timmers, L.; Richards, A.M.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle Proteins Associated with Systemic Vascular Events Correlate with Heart Failure: An Observational Study in a Dyspnoea Cohort. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, M.; Scholnick, H.R.; Morfin, R. Rapid method for the isolation of lipoproteins from human serum by precipitation with polyanions. J. Lipid Res. 1970, 11, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheow, E.S.H.; Sim, K.H.; De Kleijn, D.; Lee, C.N.; Sorokin, V.; Sze, S.K. Simultaneous Enrichment of Plasma Soluble and Extracellular Vesicular Glycoproteins Using Prolonged Ultracentrifugation-Electrostatic Repulsion-hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (PUC-ERLIC) Approach. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 1657–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auwerda, J.J.; Yuana, Y.; Osanto, S.; de Maat, M.P.; Sonneveld, P.; Bertina, R.M.; Leebeek, F.W. Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity and venous thrombosis in multiple myeloma. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 105, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorana, A.A.; Francis, C.W.; Menzies, K.E.; Wang, J.G.; Hyrien, O.; Hathcock, J.; Mackman, N.; Taubman, M.B. Plasma tissue factor may be predictive of venous thromboembolism in pancreatic cancer. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 1983–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Canonical Pathway | −Log (p-Value) | |
|---|---|---|
| (V)LDL | HDL | |
| Coagulation System | 10.26 | 2.93 |
| Extrinsic Prothrombin Activation | 7.34 | 2.39 |
| Intrinsic Prothrombin Activation | 6.01 | 1.92 |
| Sub-Fraction of (V)LDL Precipitate | Factor Xa Generation (fM Xa/min) |
|---|---|
| V1 | 145.67 ± 44.98 |
| V2 | 101.17 ± 30.21 |
| V3 | 124.58 ± 33.16 |
| V4 | 673.75 ± 153.93 |
| V5 | 239.67 ± 57.03 |
| V6 | 1592.17 ± 304.77 * |
| V7 | 2028.33 ± 324.72 ** |
| V8 | 1596.83 ± 272.50 * |
| V9 | 223.25 ± 72.88 |
| V10 | 309.42 ± 148.90 |
| Total | 7034.83 ± 1237.64 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.-W.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Sze, S.K.; Van de Weg, S.M.; Vernooij, F.; Schoneveld, A.H.; Tan, S.-H.; Versteeg, H.H.; Timmers, L.; Lam, C.S.P.; et al. Lowering Low-Density Lipoprotein Particles in Plasma Using Dextran Sulphate Co-Precipitates Procoagulant Extracellular Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010094
Wang J-W, Zhang Y-N, Sze SK, Van de Weg SM, Vernooij F, Schoneveld AH, Tan S-H, Versteeg HH, Timmers L, Lam CSP, et al. Lowering Low-Density Lipoprotein Particles in Plasma Using Dextran Sulphate Co-Precipitates Procoagulant Extracellular Vesicles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(1):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010094
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiong-Wei, Ya-Nan Zhang, Siu Kwan Sze, Sander M. Van de Weg, Flora Vernooij, Arjan H. Schoneveld, Sock-Hwee Tan, Henri H. Versteeg, Leo Timmers, Carolyn S. P. Lam, and et al. 2018. "Lowering Low-Density Lipoprotein Particles in Plasma Using Dextran Sulphate Co-Precipitates Procoagulant Extracellular Vesicles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 1: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010094
APA StyleWang, J.-W., Zhang, Y.-N., Sze, S. K., Van de Weg, S. M., Vernooij, F., Schoneveld, A. H., Tan, S.-H., Versteeg, H. H., Timmers, L., Lam, C. S. P., & De Kleijn, D. P. V. (2018). Lowering Low-Density Lipoprotein Particles in Plasma Using Dextran Sulphate Co-Precipitates Procoagulant Extracellular Vesicles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(1), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010094