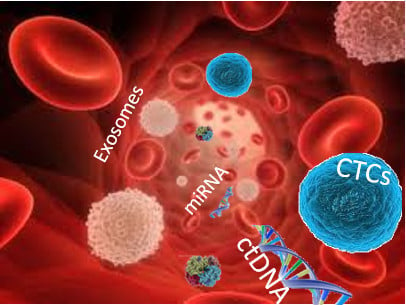
Blood-Based Cancer Biomarkers in Liquid Biopsy: A Promising Non-Invasive Alternative to Tissue Biopsy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
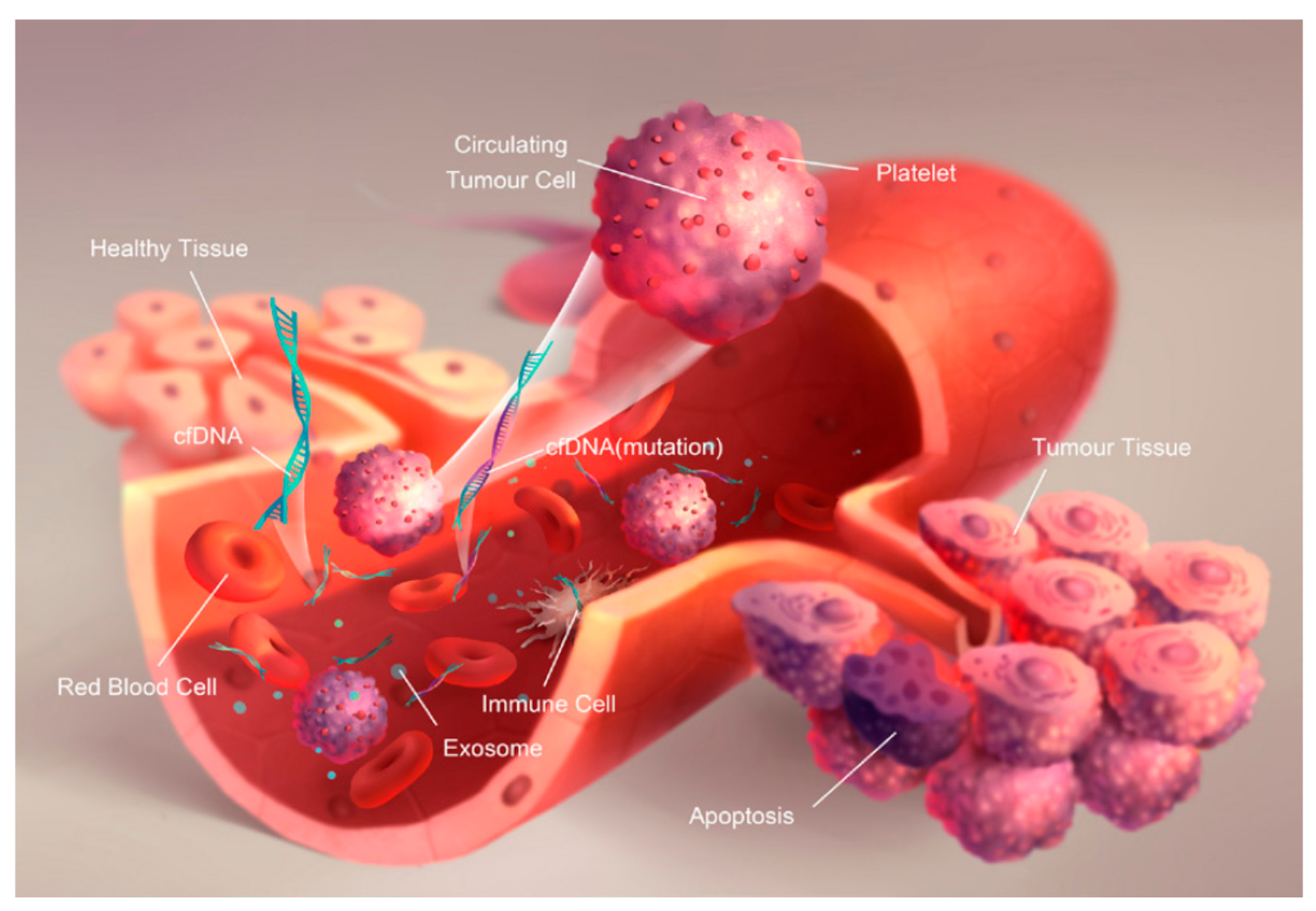
2. Concept of Liquid Biopsy
2.1. Circulant Tumor Cells (CTCs)
2.1.1. Biogenesis
2.1.2. Technologies and Strategies for Detection
Biological Properties
Physical Properties
Density Gradient Separation
Size-Based Filtration
Inertial Sorting
2.1.3. Diagnosis and Recurrence Monitoring for Therapies
Prostate Cancer
Breast Cancer
Pancreatic Cancer
2.2. Circulant Tumor Nucleic Acids (ctNAs)
2.2.1. Biogenesis
2.2.2. Technologies and Strategies for ctNAs Detection
Targeted Approaches (Mutations of ctDNA)
Untargeted Approaches (ctDNA Methylation)
2.2.3. Diagnosis and Recurrence Monitoring for Therapies
Monitoring of MRD
Monitoring Resistance Evolution to Drugs
2.3. Exosomes
2.3.1. Biogenesis
2.3.2. Technologies and Strategies for Detection
2.3.3. Diagnosis and Recurrence Monitoring for Therapies
3. Future Challenges and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malvezzi, M.; Carioli, G.; Bertuccio, P.; Boffetta, P.; Levi, F.; La Vecchia, C.; Negri, E. European cancer mortality predictions for the year 2017, with focus on lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgannezhad, L.; Umer, M.; Islam, M.N.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. Circulating tumor DNA and liquid biopsy: Opportunities, challenges, and recent advances in detection technologies. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1174–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shtivelman, E. Testing for Tumor Mutations: Liquid Biopsy Versus Traditional Biopsy. Available online: https://www.cancercommons.org/uncategorized/testing-for-tumor-mutations-liquid-biopsy-versus-solid-tumor-biopsy/ (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Robertson, E.G.; Baxter, G. Tumour seeding following percutaneous needle biopsy: The real story! Clin. Radiol. 2011, 66, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, E.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Loupakis, F.; Bardelli, A. Liquid biopsy: Monitoring cancer-genetics in the blood. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, F.; Schmidt, K.; Choti, M.A.; Romans, K.; Goodman, S.; Li, M.; Thornton, K.; Agrawal, N.; Sokoll, L.; Szabo, S.A.; et al. Circulating mutant DNA to assess tumor dynamics. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beaver, J.A.; Jelovac, D.; Balukrishna, S.; Cochran, R.L.; Croessmann, S.; Zabransky, D.J.; Wong, H.Y.; Toro, P.V.; Cidado, J.; Blair, B.G.; et al. Detection of cancer DNA in plasma of patients with early-stage breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2643–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siravegna, G.; Marsoni, S.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Integrating liquid biopsies into the management of cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelotto, L.G.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Piscuoglio, S.; Weigelt, B.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Breast cancer intra-tumor heterogeneity. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navin, N.; Krasnitz, A.; Rodgers, L.; Cook, K.; Meth, J.; Kendall, J.; Riggs, M.; Eberling, Y.; Troge, J.; Grubor, V.; et al. Inferring tumor progression from genomic heterogeneity. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadimety, A.; Closson, A.; Li, C.; Yi, S.; Shen, T.; Zhang, J.X.J. Advances in liquid biopsy on-chip for cancer management: Technologies, biomarkers, and clinical analysis. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 55, 140–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xia, W.; Lv, Z.; Ni, C.; Xin, Y.; Yang, L. Liquid Biopsy for Cancer: Circulating Tumor Cells, Circulating Free DNA or Exosomes? Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Bahassi, E.M. Biofluid-Based Circulating Tumor Molecules as Diagnostic Tools for Use in Personalized Medicine. J. Mol. Biomark. Diagn. 2013, 5, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroclawski, M.L.; Serpa-Neto, A.; Fonseca, F.L.A.; Castro-Neves-Neto, O.; Pompeo, A.S.F.L.; Machado, M.T.; Pompeo, A.C.L.; del Giglio, A. Cell-free plasma DNA as biochemical biomarker for the diagnosis and follow-up of prostate cancer patients. Tumor Biol. 2013, 34, 2921–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Stoehlmacher, J.; Pantel, K.; Goekkurt, E. Detection and monitoring of cell-free DNA in blood of patients with colorectal cancer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1137, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozzi, G.; Conte, D.; Mariani, L.; Lo Vullo, S.; Roz, L.; Lombardo, C.; Pierotti, M.A.; Tavecchio, L. Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA in Plasma at Diagnosis and during Follow-Up of Lung Cancer Patients Advances in Brief of Lung Cancer Patients. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4675–4678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Reuben, J.M.; Doyle, G.V.; Allard, W.J.; Terstappen, L.W.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells, Disease Progression, and Survival in Metastatic Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; Li, J. Clinical and biological significance of circulating tumor cells, circulating tumor DNA, and exosomes as biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 55632–55645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosse, S.A.; Pantel, K. Biologic challenges in the detection of circulating tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcdonald, D.M.; Baluk, P. Significance of Blood Vessel Leakiness in Cancer Significance of Blood Vessel Leakiness in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5381–5385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.M.; Ramani, V.C.; Jeffrey, S.S. Circulating tumor cell technologies. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 374–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagrath, S.; Jack, R.M.; Sahai, V.; Simeone, D.M. Opportunities and Challenges for Pancreatic Circulating Tumor Cells. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wit, S.; van Dalum, G.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells. Scientifica 2014, 2014, 819362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, D.F.; Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Miller, M.C.; Matera, J.; Allard, W.J.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.W.M. Circulating Tumor Cells at Each Follow-up Time Point during Therapy of Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Predict Progression-Free and Overall Survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4218–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Circulating tumor cells: Liquid biopsy of cancer. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagrath, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Maheswaran, S.; Bell, D.W.; Irimia, D.; Ulkus, L.; Smith, M.R.; Kwak, E.L.; Digumarthy, S.; Muzikansky, A.; et al. Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 2007, 450, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ozkumur, E.; Shah, A.M.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Emmink, B.L.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Brachtel, E.; Yu, M.; Chen, P.I.; Morgan, B.; Trautwein, J.; et al. Inertial Focusing for Tumor Antigen-Dependent and—Independent Sorting of Rare Circulating Tumor Cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 179ra47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farace, F.; Massard, C.; Vimond, N.; Drusch, F.; Jacques, N.; Billiot, F.; Laplanche, A.; Chauchereau, A.; Lacroix, L.; Planchard, D.; et al. A direct comparison of CellSearch and ISET for circulating tumour-cell detection in patients with metastatic carcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollier, E.; Go, D.E.; Che, J.; Gossett, D.R.; O’Byrne, S.; Weaver, W.M.; Kummer, N.; Rettig, M.; Goldman, J.; Nickols, N.; et al. Size-selective collection of circulating tumor cells using Vortex technology. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danila, D.C.; Fleisher, M.; Scher, H.I. Circulating tumor cells as biomarkers in prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3903–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bono, J.S.; Scher, H.I.; Montgomery, R.B.; Parker, C.; Miller, M.C.; Tissing, H.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.W.M.; Pienta, K.J.; Raghavan, D. Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6302–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, W.J.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.; Connelly, M.C.; Rao, C.; Tibbe, A.G.J.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Tumor cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, D.L.; Pretorius, P.J. Origin, translocation and destination of extracellular occurring DNA—A new paradigm in genetic behaviour. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phallen, J.; Sausen, M.; Adleff, V.; Leal, A.; Hruban, C.; White, J.; Anagnostou, V.; Fiksel, J.; Cristiano, S.; Papp, E.; et al. Direct detection of early-stage cancers using circulating tumor DNA. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y. Circulating Tumor DNA as Biomarkers for Cancer Detection. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 15, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, J.T.Y.; Colognori, D.; Lee, J.T. Long noncoding RNAs: Past, present, and future. Genetics 2013, 193, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, H.; Liu, H.; Xiong, P.; Zhu, M. Long non-coding RNA functions in lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 4027–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, Y.; Rinn, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 2014, 505, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cesana, M.; Cacchiarelli, D.; Legnini, I.; Santini, T.; Sthandier, O.; Chinappi, M.; Tramontano, A.; Bozzoni, I. A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell 2011, 147, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Sun, M.; Liu, H.; Yao, Y.; Song, Y. Long non-coding RNAs: A new frontier in the study of human diseases. Cancer Lett. 2013, 339, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valladares-Ayerbes, M.; Reboredo, M.; Medina-Villaamil, V.; Iglesias-Díaz, P.; Lorenzo-Patiño, M.J.; Haz, M.; Santamarina, I.; Blanco, M.; Fernández-Tajes, J.; Quindós, M.; et al. Circulating miR-200c as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fatima, F.; Nawaz, M. Long distance metabolic regulation through adipose-derived circulating exosomal miRNAs: A trail for RNA-based therapies? Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateescu, B.; Kowal, E.J.K.; van Balkom, B.W.M.; Bartel, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Buzás, E.I.; Buck, A.H.; de Candia, P.; Chow, F.W.N.; Das, S.; et al. Obstacles and opportunities in the functional analysis of extracellular vesicle RNA—An ISEV position paper. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1286095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ba, Y.; Ma, L.; Cai, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, K.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seto, A.G. The road toward microRNA therapeutics. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ashram, S.; Al Nasr, I.; Suo, X. Nucleic acid protocols: Extraction and optimization. Biotechnol. Rep. 2016, 12, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castella, V.; Dimo-Simonin, N.; Brandt-Casadevall, C.; Mangin, P. Forensic evaluation of the QIAshredder/QIAamp DNA extraction procedure. Forensic Sci. Int. 2006, 156, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clausen, F.B.; Krog, G.R.; Rieneck, K.; Dziegiel, M.H. Improvement in fetal DNA extraction from maternal plasma. Evaluation of the NucliSens Magnetic Extraction system and the QIAamp DSP Virus Kit in comparison with the QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit. Prenat. Diagn. 2007, 27, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, C.; Weickmann, S.; Schmidt, B.; Fleischhacker, M. An improved method for the isolation of free-circulating plasma DNA and cell-free DNA from other body fluids. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1137, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Jeon, S.; Seo, J.-S.; Goh, S.-H.; Han, J.-Y.; Cho, Y. A novel strategy for highly efficient isolation and analysis of circulating tumor-specific cell-free DNA from lung cancer patients using a reusable conducting polymer nanostructure. Biomaterials 2016, 101, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotti, I.; Bonin, S. Quantification of Nucleic Acids. In Guidelines for Molecular Analysis in Archive Tissues; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 17, pp. 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, M.L.; Medrano, J.F. Real-time PCR for mRNA quantitation. Biotechniques 2005, 39, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A. Real-time, fluorescence-based quantitative PCR: A snapshot of current procedures and preferences. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2005, 5, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Hoon, D.S.B.; Pantel, K. Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahr, S.; Hentze, H.; Englisch, S.; Hardt, D.; Fackelmayer, F.O.; Hesch, R.D.; Knippers, R. DNA fragments in the blood plasma of cancer patients: Quantitations and evidence for their origin from apoptotic and necrotic cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischhacker, M.; Schmidt, B. Circulating nucleic acids (CNAs) and cancer—A survey. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2007, 1775, 181–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinsky, P.F.; Prorok, P.C.; Kramer, B.S. Prostate Cancer Screening—A Perspective on the Current State of the Evidence. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1285–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettegowda, C.; Sausen, M.; Leary, R.J.; Kinde, I.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, N.; Bartlett, B.R.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Alani, R.M.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 224ra24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.D.; Javed, A.A.; Thoburn, C.; Wong, F.; Tie, J.; Gibbs, P.; Schmidt, C.M.; Yip-Schneider, M.T.; Allen, P.J.; Schattner, M.; et al. Combined circulating tumor DNA and protein biomarker-based liquid biopsy for the earlier detection of pancreatic cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10202–10207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J.D.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Thoburn, C.; Afsari, B.; Danilova, L.; Douville, C.; Javed, A.A.; Wong, F.; Mattox, A.; et al. Detection and localization of surgically resectable cancers with a multi-analyte blood test. Science 2018, 359, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Clinical applications of circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA as liquid biopsy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Messaoudi, S.; Rolet, F.; Mouliere, F.; Thierry, A.R. Circulating cell free DNA: Preanalytical considerations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 424, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäbert, K.; Cojoc, M.; Peitzsch, C.; Kurth, I.; Souchelnytskyi, S.; Dubrovska, A. Cancer biomarker discovery: Current status and future perspectives. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2014, 90, 659–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forshew, T.; Murtaza, M.; Parkinson, C.; Gale, D.; Tsui, D.W.Y.; Kaper, F.; Dawson, S.J.; Piskorz, A.M.; Jimenez-Linan, M.; Bentley, D.; et al. Noninvasive identification and monitoring of cancer mutations by targeted deep sequencing of plasma DNA. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 136ra68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Mo, Z.; Ye, D.; Wang, M.; Liu, F.; Jin, G.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Shao, Q.; Chen, Z.; et al. Genome-wide association study in Chinese men identifies two new prostate cancer risk loci at 9q31.2 and 19q13.4. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warton, K.; Mahon, K.L.; Samimi, G. Methylated circulating tumor DNA in blood: Power in cancer prognosis and response. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, R157–R171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.G.; Graff, J.R.; Myohanen, S.; Nelkin, B.D.; Baylin, S.B. Methylation-specific PCR: A novel PCR assay for methylation status of CpG islands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9821–9826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derks, S.; Lentjes, M.H.F.M.; Hellebrekers, D.M.E.I.; de Bruïne, A.P.; Herman, J.G.; van Engeland, M. Methylation-specific PCR unraveled. Cell. Oncol. 2004, 26, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bailey, V.J.; Zhang, Y.; Keeley, B.P.; Yin, C.; Pelosky, K.L.; Brock, M.; Baylin, S.B.; Herman, J.G.; Wang, T.H. Single-tube analysis of DNA methylation with silica superparamagnetic beads. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, I.H.N.; Lo, Y.M.D.; Zhang, J.; Liew, C.T.; Ng, M.H.L.; Wong, N.; Lai, P.B.S.; Lau, W.Y.; Hjelm, N.M.; Johnson, P.J. Detection of aberrant p16 methylation in the plasma and serum of liver cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wimberger, P.; Roth, C.; Pantel, K.; Kasimir-Bauer, S.; Kimmig, R.; Schwarzenbach, H. Impact of platinum-based chemotherapy on circulating nucleic acid levels, protease activities in blood and disseminated tumor cells in bone marrow of ovarian cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 2572–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.T.; Johnstone, R.M. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: Selective externalization of the receptor. Cell 1983, 33, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, A.; Hume, A.N. Exosome signaling in mammary gland development and cancer. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2011, 55, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munson, P.; Shukla, A. Exosomes: Potential in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Medicines 2015, 2, 310–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwar, S.S.; Dunlay, C.J.; Simeone, D.M.; Nagrath, S. Microfluidic device (ExoChip) for on-chip isolation, quantification and characterization of circulating exosomes. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathivanan, S.; Ji, H.; Simpson, R.J. Exosomes: Extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luga, V.; Zhang, L.; Viloria-Petit, A.M.; Ogunjimi, A.A.; Inanlou, M.R.; Chiu, E.; Buchanan, M.; Hosein, A.N.; Basik, M.; Wrana, J.L. Exosomes mediate stromal mobilization of autocrine Wnt-PCP signaling in breast cancer cell migration. Cell 2012, 151, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Hagiwara, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. Neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2)-dependent exosomal transfer of angiogenic micrornas regulate cancer cell metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 10849–10859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, L.; Qian, H.; Xu, W. Exosomes in cancer: Small particle, big player. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lötvall, J.; Hill, A.F.; Hochberg, F.; Buzás, E.I.; Di Vizio, D.; Gardiner, C.; Gho, Y.S.; Kurochkin, I.V.; Mathivanan, S.; Quesenberry, P.; et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 26913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzás, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lässer, C.; Lötvall, J.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J.; et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramirez, M.I.; Amorim, M.G.; Gadelha, C.; Milic, I.; Welsh, J.A.; Freitas, V.M.; Nawaz, M.; Akbar, N.; Couch, Y.; Makin, L.; et al. Technical challenges of working with extracellular vesicles. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 881–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, R.T.; Kim, J.; Jang, S.C.; Choi, E.J.; Gho, Y.S.; Park, J. Microfluidic filtration system to isolate extracellular vesicles from blood. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 5202–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlund, C.J.E.; Eklund, A.; Grunewald, J.; Gabrielsson, S. Pulmonary Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Local and Systemic Inflammation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantin, R.; Diou, J.; Bélanger, D.; Tremblay, A.M.; Gilbert, C. Discrimination between exosomes and HIV-1: Purification of both vesicles from cell-free supernatants. J. Immunol. Methods 2008, 338, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlassov, A.V.; Magdaleno, S.; Setterquist, R.; Conrad, R. Exosomes: Current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.D.; Zacharias, W.; Gercel-Taylor, C. Exosome isolation fro protemic analyses and RNA profiling. In Serum/Plasma Proteomics: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 728, pp. 235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Caby, M.-P.; Lankar, D.; Vincendeau-Scherrer, C.; Raposo, G.; Bonnerot, C. Exosomal-like Vesicles are present in Human Blood Plasma. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Akiyoshi, T.; Kubo, M.; Yamanaka, N.; Tasaki, A.; Nakashima, H.; Nakamura, M.; Kuroki, S.; Tanaka, M.; et al. Purification, characterization and biological significance of tumor-derived exosomes. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 3703–3707. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tauro, B.J.; Greening, D.W.; Mathias, R.A.; Ji, H.; Mathivanan, S.; Scott, A.M.; Simpson, R.J. Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods 2012, 56, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Fine, D.; Schmulen, J.; Hu, Y.; Godin, B.; Zhang, J.X.J.; Liu, X. Ciliated micropillars for the microfluidic-based isolation of nanoscale lipid vesicles. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2879–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Crow, J.; Roth, M.; Zeng, Y.; Godwin, A.K. Integrated immunoisolation and protein analysis of circulating exosomes using microfluidic technology. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3773–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Konishi, Y.; Ohta, H.; Okamoto, H.; Sonoda, H.; Nonaka, R.; Yamamoto, H.; Ishii, H.; Mori, M.; et al. Ultra-sensitive liquid biopsy of circulating extracellular vesicles using ExoScreen. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaidyanathan, R.; Naghibosadat, M.; Rauf, S.; Korbie, D.; Carrascosa, L.G.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Trau, M. Detecting exosomes specifically: A multiplexed device based on alternating current electrohydrodynamic induced nanoshearing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11125–11132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akagi, T.; Kato, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Kosaka, N.; Ochiya, T.; Ichiki, T. On-chip immunoelectrophoresis of extracellular vesicles released from human breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Chung, J.; Lee, K.; Balaj, L.; Min, C.; Carter, B.S.; Hochberg, F.H.; Breakefield, X.O.; Lee, H.; Weissleder, R. Chip-based analysis of exosomal mRNA mediating drug resistance in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveira-Rodríguez, M.; López-Cobo, S.; Reyburn, H.T.; Costa-García, A.; López-Martín, S.; Yáñez-Mó, M.; Cernuda-Morollón, E.; Paschen, A.; Valés-Gómez, M.; Blanco-López, M.C. Development of a rapid lateral flow immunoassay test for detection of exosomes previously enriched from cell culture medium and body fluids. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 31803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagni, P.; Cretich, M.; Benussi, L.; Tonoli, E.; Ciani, M.; Ghidoni, R.; Santini, B.; Galbiati, E.; Prosperi, D.; Chiari, M. Combined mass quantitation and phenotyping of intact extracellular vesicles by a microarray platform. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 902, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webber, J.; Clayton, A. How pure are your vesicles? J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 19861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, Z.J.; Lee, C.; Rojalin, T.; Carney, R.P.; Hazari, S.; Knudson, A.; Lam, K.; Saari, H.; Ibañez, E.L.; Viitala, T.; et al. Single exosome study reveals subpopulations distributed among cell lines with variability related to membrane content. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 28533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Logozzi, M.; De Milito, A.; Lugini, L.; Borghi, M.; Calabrò, L.; Spada, M.; Perdicchio, M.; Marino, M.L.; Federici, C.; Iessi, E.; et al. High levels of exosomes expressing CD63 and caveolin-1 in plasma of melanoma patients. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuana, Y.; Koning, R.I.; Kuil, M.E.; Rensen, P.C.N.; Koster, A.J.; Bertina, R.M.; Osanto, S. Cryo-electron microscopy of extracellular vesicles in fresh plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 21494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Nijman, H.W.; Stoorvogel, W.; Liejendekker, R.; Harding, C.V.; Melief, C.J.; Geuze, H.J. B-Lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Gillespie, B.M.; Palanisamy, V.; Gimzewski, J.K. Quantitative nanostructural and single-molecule force spectroscopy biomolecular analysis of human-saliva-derived exosomes. Langmuir 2011, 27, 14394–14400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Rasool, H.I.; Palanisamy, V.; Mathisen, C.; Schmidt, M.; Wong, D.T.; Gimzewski, J.K. Structural-mechanical characterization of nanoparticle exosomes in human saliva, using correlative AFM, FESEM, and force spectroscopy. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Li, S.; Guo, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, D.; Gu, J.; He, X.; Huang, S. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, K.; Ingram, A.; Austin, R.; Kapoor, A.; Tang, D.; Majeed, F.; Qureshi, T.; Al-Nedawi, K. Regulation of the Tumor Suppressor PTEN through Exosomes: A Diagnostic Potential for Prostate Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Jutzy, J.M.S.; Valenzuela, M.M.A.; Turay, D.; Aspe, J.R.; Ashok, A.; Mirshahidi, S.; Mercola, D.; Lilly, M.B.; Wall, N.R. Plasma-Derived Exosomal Survivin, a Plausible Biomarker for Early Detection of Prostate Cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, R.J.; Pawlowski, T.; Catto, J.W.F.; Marsden, G.; Vessella, R.L.; Rhees, B.; Kuslich, C.; Visakorpi, T.; Hamdy, F.C. Changes in circulating microRNA levels associated with prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Method | Principle | Comment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| QIAamp DNA Mini Kit | NA purification based on a silica membrane | Rapid purification of high-quality DNA | [51] |
| Consistent, high yields | |||
| DNA isolation, including of genomic, mitochondrial, viral, among others. | Contaminants and inhibitors removal | ||
| QIAamp DSP Virus Spin Kit | Copurification of NA, based on a silica membrane, from human plasma serum. | Rapid universal viral NA purification | [52] |
| High-quality viral NAs | |||
| Elution volume: 20–150 µL | |||
| Minimal risk of cross contamination | |||
| NucleoSpin® Plasma XS | Rapid purification of ctDNA from human plasma and serum, based on a silica membrane. | High recovery (DNA > 50 bp) | [53] |
| Elution volume: 5 μL | |||
| Concentrated DNA, even if diluted | |||
| Ready-to-use DNA for downstream | |||
| Agencourt Genfind v2 | Isolation and purification of DNA from whole blood and serum. | Faster separation, easier manipulation and simple automation. | [54] |
| Paramagnetic bead isolation for high recovery of DNA. | The method can be run manually in a 2 mL tube format |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marrugo-Ramírez, J.; Mir, M.; Samitier, J. Blood-Based Cancer Biomarkers in Liquid Biopsy: A Promising Non-Invasive Alternative to Tissue Biopsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102877
Marrugo-Ramírez J, Mir M, Samitier J. Blood-Based Cancer Biomarkers in Liquid Biopsy: A Promising Non-Invasive Alternative to Tissue Biopsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102877
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarrugo-Ramírez, José, Mònica Mir, and Josep Samitier. 2018. "Blood-Based Cancer Biomarkers in Liquid Biopsy: A Promising Non-Invasive Alternative to Tissue Biopsy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102877
APA StyleMarrugo-Ramírez, J., Mir, M., & Samitier, J. (2018). Blood-Based Cancer Biomarkers in Liquid Biopsy: A Promising Non-Invasive Alternative to Tissue Biopsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102877