Relevance of MicroRNAs as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. MiRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers
3. MiRNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents
4. MiR-21
5. MiR-29 Family
6. MiR-34 Family
7. MiR-124
8. MiR-130b
9. MiR-155
10. MiR-224
11. MiR-378
12. Other miRNAs
13. MiRNA Panels
14. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3′-UTR | 3′-untranslated region |
| 5-FU | 5-fluorouracil |
| AJCC | American Joint Committee on Cancer |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| BIC | MIR155 host gene |
| CDK6 | cyclin-dependent kinase 6 |
| CEA | carcinoembryonic antigen |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| DCBE | double-contrast barium enema |
| DFS | disease-free survival |
| FISH | fluorescence in situ hybrydization |
| FOBT | fecal occult blood test |
| HCV | hepatitis C virus |
| ISH | in situ hybridization |
| miRNAs | microRNAs |
| mRNA | messenger RNA |
| NGS | next-generation sequencing |
| OS | overall survival |
| PFS | progression-free survival |
| PPV | positive predictive value |
| PTEN | phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| RFS | relapse-free survival |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| ROCK1 | rho-associated protein kinase 1 |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor β |
| TNM | tumor-node-metastasis |
| UICC | Union for International Cancer Control |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| ZEB-1 | zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 protein |
References
- Global Cancer Observatory. Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/today/home (accessed on 16 June 2018).
- Maida, M.; Macaluso, F.S.; Ianiro, G.; Mangiola, F.; Sinagra, E.; Hold, G.; Maida, C.; Cammarota, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Scarpulla, G. Screening of colorectal cancer: Present and future. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2017, 17, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolpin, B.M.; Mayer, R.J. Systemic treatment of colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1296–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tétreault, N.; De Guire, V. miRNAs: Their discovery, biogenesis and mechanism of action. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.-H.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.-G.; Ambs, S.; Cimmino, A.; Petrocca, F.; Visone, R.; Iorio, M.; Roldo, C.; Ferracin, M.; et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Liu, B.; Qu, S.; Liang, G.; Luo, W.; Gong, C. MicroRNAs and cancer: Key paradigms in molecular therapy. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 2735–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlquist, D.A. Molecular detection of colorectal neoplasia. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2127–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniyappa, M.K.; Dowling, P.; Henry, M.; Meleady, P.; Doolan, P.; Gammell, P.; Clynes, M.; Barron, N. MiRNA-29a regulates the expression of numerous proteins and reduces the invasiveness and proliferation of human carcinoma cell lines. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 3104–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eminaga, S.; Christodoulou, D.C.; Vigneault, F.; Church, G.M.; Seidman, J.G. Quantification of microRNA expression with next-generation sequencing. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaby, O.; Svoboda, M.; Fabian, P.; Smerdova, T.; Knoflickova, D.; Bednarikova, M.; Nenutil, R.; Vyzula, R. Altered expression of miR-21, miR-31, miR-143 and miR-145 is related to clinicopathologic features of colorectal cancer. Oncology 2007, 72, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, U.; Romeo, F.; Noonan, D.M.; Albini, A. Prediction of breast cancer metastasis by genomic profiling: Where do we stand? Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2009, 26, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schetter, A.J.; Leung, S.Y.; Sohn, J.J.; Zanetti, K.A.; Bowman, E.D.; Yanaihara, N.; Yuen, S.T.; Chan, T.L.; Kwong, D.L.W.; Au, G.K.H.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA 2008, 299, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-J.; Zhou, Z.-G.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, B.; Gu, J.; Chen, H.-Y.; Sun, X.-F. Clinicopathological significance of microRNA-31, -143 and -145 expression in colorectal cancer. Dis. Markers 2009, 26, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, Y.; Yasunaga, M.; Takahashi, A.; Kuroda, J.; Moriya, Y.; Akasu, T.; Fujita, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Baba, H.; Matsumura, Y. MicroRNA expression profiling of exfoliated colonocytes isolated from feces for colorectal cancer screening. Cancer Prev. Res. 2010, 3, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulda, V.; Pesta, M.; Topolcan, O.; Liska, V.; Treska, V.; Sutnar, A.; Rupert, K.; Ludvikova, M.; Babuska, V.; Holubec, L.; et al. Relevance of miR-21 and miR-143 expression in tissue samples of colorectal carcinoma and its liver metastases. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2010, 200, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, P.; Hultine, S.; Smith, L.M.; Dews, M.; Fox, J.L.; Biyashev, D.; Schelter, J.M.; Huang, Q.; Cleary, M.A.; Volpert, O.V.; et al. p53-responsive miR-194 inhibits thrombospondin-1 and promotes angiogenesis in colon cancers. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7490–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X. Downregulation of miR-195 correlates with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Somlo, G.; Yu, Y.; Palomares, M.R.; Li, A.X.; Zhou, W.; Chow, A.; Yen, Y.; Rossi, J.J.; Gao, H.; et al. De novo sequencing of circulating miRNAs identifies novel markers predicting clinical outcome of locally advanced breast cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oue, N.; Anami, K.; Schetter, A.J.; Moehler, M.; Okayama, H.; Khan, M.A.; Bowman, E.D.; Mueller, A.; Schad, A.; Shimomura, M.; et al. High miR-21 expression from FFPE tissues is associated with poor survival and response to adjuvant chemotherapy in colon cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Qin, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Tian, K.; Deng, S.; Li, X.; Zhu, S.; et al. MiR-130b is a prognostic marker and inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in pancreatic cancer through targeting STAT3. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyazi, M.; Zehentmayr, F.; Niemöller, O.M.; Eigenbrod, S.; Kretzschmar, H.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Tonn, J.-C.; Atkinson, M.; Mörtl, S.; Belka, C. MiRNA expression patterns predict survival in glioblastoma. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krützfeldt, J.; Rajewsky, N.; Braich, R.; Rajeev, K.G.; Tuschl, T.; Manoharan, M.; Stoffel, M. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with “antagomirs”. Nature 2005, 438, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanford, R.E.; Hildebrandt-Eriksen, E.S.; Petri, A.; Persson, R.; Lindow, M.; Munk, M.E.; Kauppinen, S.; Ørum, H. Therapeutic silencing of microRNA-122 in primates with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Science 2010, 327, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, H.L.A.; Reesink, H.W.; Lawitz, E.J.; Zeuzem, S.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Patel, K.; van der Meer, A.J.; Patick, A.K.; Chen, A.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, D.D.; Connelly, C.M.; Grohmann, C.; Deiters, A. Small molecule modifiers of microRNA miR-122 function for the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7976–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Okugawa, Y.; Yang, J.; Liang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Han, H.; et al. Novel evidence for an oncogenic role of microRNA-21 in colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Gut 2016, 65, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Hermeking, H. miR-34a and miR-34b/c Suppress Intestinal Tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2746–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokavec, M.; Öner, M.G.; Li, H.; Jackstadt, R.; Jiang, L.; Lodygin, D.; Kaller, M.; Horst, D.; Ziegler, P.K.; Schwitalla, S.; et al. IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1853–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toiyama, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Hur, K.; Nagasaka, T.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Serum miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, K.; Han, B.; Bai, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L. MicroRNA-21 (Mir-21) Promotes Cell Growth and Invasion by Repressing Tumor Suppressor PTEN in Colorectal Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nana-Sinkam, S.P.; Fabbri, M.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in cancer: Personalizing diagnosis and therapy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1210, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamichi, N.; Shimomura, R.; Inada, K.; Sakurai, K.; Haraguchi, T.; Ozaki, Y.; Fujita, S.; Mizutani, T.; Furukawa, C.; Fujishiro, M.; et al. Locked nucleic acid in situ hybridization analysis of miR-21 expression during colorectal cancer development. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4009–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastaminejad, S.; Taherikalani, M.; Ghanbari, R.; Akbari, A.; Shabab, N.; Saidijam, M. Investigation of MicroRNA-21 Expression Levels in Serum and Stool as a Potential Non-Invasive Biomarker for Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer. Iran. Biomed. J. 2017, 21, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.W.; Ng, S.S.M.; Dong, Y.J.; Ng, S.C.; Leung, W.W.; Lee, C.W.; Wong, Y.N.; Chan, F.K.L.; Yu, J.; Sung, J.J.Y. Detection of miR-92a and miR-21 in stool samples as potential screening biomarkers for colorectal cancer and polyps. Gut 2012, 61, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, A.; Balaguer, F.; Shen, Y.; Nagasaka, T.; Lozano, J.J.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Fecal MicroRNAs as novel biomarkers for colon cancer screening. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 1766–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, Y.; Iinuma, H.; Tsukamoto, M.; Matsuda, K.; Hashiguchi, Y. Clinical significance of microRNA-21 as a biomarker in each Dukes’ stage of colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjaer-Frifeldt, S.; Hansen, T.F.; Nielsen, B.S.; Joergensen, S.; Lindebjerg, J.; Soerensen, F.B.; dePont Christensen, R.; Jakobsen, A.; Danish Colorectal Cancer Group. The prognostic importance of miR-21 in stage II colon cancer: A population-based study. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, B.S.; Jørgensen, S.; Fog, J.U.; Søkilde, R.; Christensen, I.J.; Hansen, U.; Brünner, N.; Baker, A.; Møller, S.; Nielsen, H.J. High levels of microRNA-21 in the stroma of colorectal cancers predict short disease-free survival in stage II colon cancer patients. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, H.; Iinuma, H.; Shimada, R.; Horiuchi, A.; Watanabe, T. Clinicopathological and prognostic value of microRNA-21 and microRNA-155 in colorectal cancer. Oncology 2010, 79, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Yang, B.; Zhai, X.; Liu, X.; Shen, K.; Wu, Z.; Cai, J. Prognostic role of microRNA-21 in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, H.; Jin, W.; Ding, Z.; Zheng, S.; Yu, Y. Tissue microRNA-21 expression predicted recurrence and poor survival in patients with colorectal cancer—A meta-analysis. Oncotargets Ther. 2016, 9, 2615–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Min, M.; Zou, L.; Shen, P.; Zhu, Y. The clinical role of microRNA-21 as a promising biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44893–44909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.K.; Lee, J.K.; Oh, S.T.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, C.K. Stromal expression of miR-21 in T3-4a colorectal cancer is an independent predictor of early tumor relapse. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaan, Z.; Rai, S.N.; Eichenberger, M.R.; Roberts, H.; Keskey, B.; Pan, J.; Galandiuk, S. Plasma miR-21: A potential diagnostic marker of colorectal cancer. Ann. Surg. 2012, 256, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, M.; Iinuma, H.; Yagi, T.; Matsuda, K.; Hashiguchi, Y. Circulating Exosomal MicroRNA-21 as a Biomarker in Each Tumor Stage of Colorectal Cancer. Oncology 2017, 92, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.E.; Ahmed, N.C.; Vos, P.W.; Bonnerup, C.; Atkins, J.N.; Casey, M.; Nuovo, G.J.; Naziri, W.; Wiley, J.E.; Mota, H.; et al. Diagnostic microRNA markers to screen for sporadic human colon cancer in stool: I. Proof of principle. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2013, 10, 93–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; Ren, X. The role of miRNA-29 family in cancer. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 92, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-G.; Gu, J. Serum microRNA-29a is a promising novel marker for early detection of colorectal liver metastasis. Cancer Epidemiol. 2012, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, D.; Ni, S.; Peng, Z.; Sheng, W.; Du, X. Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sheikh, Y.A.; Ghneim, H.K.; Softa, K.I.; Al-Jobran, A.A.; Al-Obeed, O.; Mohamed, M.A.V.; Abdulla, M.; Aboul-Soud, M.A.M. Expression profiling of selected microRNA signatures in plasma and tissues of Saudi colorectal cancer patients by qPCR. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhen, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Jing, C. The Diagnostic Efficacy and Biological Effects of microRNA-29b for Colon Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 15, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basati, G.; Razavi, A.E.; Pakzad, I.; Malayeri, F.A. Circulating levels of the miRNAs, miR-194, and miR-29b, as clinically useful biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, J.; Fu, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Song, C.; Zhu, S.; Leng, Y.; Wang, G.; et al. MicroRNA-29a promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by regulating matrix metalloproteinase 2 and E-cadherin via KLF4. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissmann-Brenner, A.; Kushnir, M.; Lithwick Yanai, G.; Aharonov, R.; Gibori, H.; Purim, O.; Kundel, Y.; Morgenstern, S.; Halperin, M.; Niv, Y.; et al. Tumor microRNA-29a expression and the risk of recurrence in stage II colon cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 2097–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, T.-Y.; Hsi, E.; Yang, I.-P.; Tsai, P.-C.; Wang, J.-Y.; Juo, S.-H.H. Computational analysis of mRNA expression profiles identifies microRNA-29a/c as predictor of colorectal cancer early recurrence. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Uemura, M.; Nishimura, J.; Hata, T.; Takemasa, I.; Ikenaga, M.; Ikeda, M.; Murata, K.; Mizushima, T.; et al. MicroRNA-29b is a Novel Prognostic Marker in Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22 (Suppl. 3), S1410–S1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Zhou, C.; Lu, Y.; Hong, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. IFN-γ-mediated IRF1/miR-29b feedback loop suppresses colorectal cancer cell growth and metastasis by repressing IGF1. Cancer Lett. 2015, 359, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulivi, P.; Canale, M.; Passardi, A.; Marisi, G.; Valgiusti, M.; Frassineti, G.L.; Calistri, D.; Amadori, D.; Scarpi, E. Circulating Plasma Levels of miR-20b, miR-29b and miR-155 as Predictors of Bevacizumab Efficacy in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misso, G.; Di Martino, M.T.; De Rosa, G.; Farooqi, A.A.; Lombardi, A.; Campani, V.; Zarone, M.R.; Gullà, A.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P.; et al. Mir-34: A new weapon against cancer? Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, P.; Chen, K.-Y.; Chen, J.H.; Wang, L.; Walters, J.; Shin, Y.J.; Goerger, J.P.; Sun, J.; Witherspoon, M.; Rakhilin, N.; et al. A microRNA miR-34a-regulated bimodal switch targets Notch in colon cancer stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Song, Y.-C.; Cao, P.-L.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Q.; Yan, R.; Diao, D.-M.; Cheng, Y.; Dang, C.-X. Detection of miR-34a and miR-34b/c in stool sample as potential screening biomarkers for noninvasive diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aherne, S.T.; Madden, S.F.; Hughes, D.J.; Pardini, B.; Naccarati, A.; Levy, M.; Vodicka, P.; Neary, P.; Dowling, P.; Clynes, M. Circulating miRNAs miR-34a and miR-150 associated with colorectal cancer progression. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Li, N.; Dong, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Ng, S.S.; Sung, J.J.; et al. miR-34a-5p suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis and predicts recurrence in patients with stage II/III colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4142–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Bao-Han, W.; Lv, X.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; MacNaughton, W.K.; Wang, H. MicroRNA-34a mediates the autocrine signaling of PAR2-activating proteinase and its role in colonic cancer cell proliferation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siemens, H.; Neumann, J.; Jackstadt, R.; Mansmann, U.; Horst, D.; Kirchner, T.; Hermeking, H. Detection of miR-34a promoter methylation in combination with elevated expression of c-Met and β-catenin predicts distant metastasis of colon cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazawa, H.; Tsuchiya, N.; Izumiya, M.; Nakagama, H. Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15472–15477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Almeida, A.L.N.R.; Bernardes, M.V.A.A.; Feitosa, M.R.; Peria, F.M.; da Tirapelli, D.P.C.; da Rocha, J.J.R.; Feres, O. Serological under expression of microRNA-21, microRNA-34a and microRNA-126 in colorectal cancer. Acta Cir. Bras. 2016, 31 (Suppl. 1), 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, H.; Liang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Song, B. MiR-34a inhibits colon cancer proliferation and metastasis by inhibiting platelet-derived growth factor receptor α. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 7072–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ai, F.; Li, X.; Tian, L.; Wang, X.; Shen, S.; Liu, F. MicroRNA-34a suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis by regulating Notch signaling. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 2325–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiyoshi, Y.; Schetter, A.J.; Okayama, H.; Inamura, K.; Anami, K.; Nguyen, G.H.; Horikawa, I.; Hawkes, J.E.; Bowman, E.D.; Leung, S.Y.; et al. Increased microRNA-34b and -34c predominantly expressed in stromal tissues is associated with poor prognosis in human colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akao, Y.; Noguchi, S.; Iio, A.; Kojima, K.; Takagi, T.; Naoe, T. Dysregulation of microRNA-34a expression causes drug-resistance to 5-FU in human colon cancer DLD-1 cells. Cancer Lett. 2011, 300, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Wang, F.-J.; Zhang, H.-G.; Xu, X.-Z.; Jia, R.-C.; Yao, L.; Qiao, P.-F. miR-34a mediates oxaliplatin resistance of colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting macroautophagy via transforming growth factor-β/Smad4 pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 1816–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Z.-W.; Xin, S.-Y.; Zhou, L.-Q.; Yuan, H.-X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, K.-X. Downregulation of rho-associated protein kinase 1 by miR-124 in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 5454–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Xu, D.; Tu, C.; Li, W.; Ning, Y.; Ding, J.; Wang, S.; Yuan, L.; Xu, N.; Qian, K.; et al. MiR-124 inhibits cell proliferation in breast cancer through downregulation of CDK4. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 5987–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, T.; Yamamoto, E.; Yamano, H.; Nojima, M.; Maruyama, R.; Kumegawa, K.; Ashida, M.; Yoshikawa, K.; Kimura, T.; Harada, E.; et al. Analysis of DNA methylation in bowel lavage fluid for detection of colorectal cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, C.; Kirchner, T.; Hlubek, F. The impact of microRNAs on colorectal cancer. Virchows Arch. Int. J. Pathol. 2009, 454, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, Y.; Ando, T.; Nanjo, S.; Ushijima, T.; Sugiyama, T. DNA methylation of microRNA-124a is a potential risk marker of colitis-associated cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 2444–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.-J.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.-Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Z.-G.; Sun, X.-F. Downregulation of microRNA-124 is an independent prognostic factor in patients with colorectal cancer. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2013, 28, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinushi, T.; Shibayama, Y.; Kinoshita, I.; Oizumi, S.; Jinushi, M.; Aota, T.; Takahashi, T.; Horita, S.; Dosaka-Akita, H.; Iseki, K. Low expression levels of microRNA-124-5p correlated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer via targeting of SMC4. Cancer Med. 2014, 3, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slattery, M.L.; Pellatt, A.J.; Lee, F.Y.; Herrick, J.S.; Samowitz, W.S.; Stevens, J.R.; Wolff, R.K.; Mullany, L.E. Infrequently expressed miRNAs influence survival after diagnosis with colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 83845–83859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colangelo, T.; Fucci, A.; Votino, C.; Sabatino, L.; Pancione, M.; Laudanna, C.; Binaschi, M.; Bigioni, M.; Maggi, C.A.; Parente, D.; et al. MicroRNA-130b promotes tumor development and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 1086–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Tong, K.; Yu, J. MicroRNA-130a is upregulated in colorectal cancer and promotes cell growth and motility by directly targeting forkhead box F2. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 5241–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sempere, L.F.; Preis, M.; Yezefski, T.; Ouyang, H.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Silahtaroglu, A.; Conejo-Garcia, J.R.; Kauppinen, S.; Wells, W.; Korc, M. Fluorescence-based codetection with protein markers reveals distinct cellular compartments for altered MicroRNA expression in solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 4246–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Fan, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhao, D. Investigation of microRNA-155 as a serum diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongliang, C.; Shaojun, H.; Aihua, L.; Hua, J. Correlation between expression of miR-155 in colon cancer and serum carcinoembryonic antigen level and its contribution to recurrence and metastasis forecast. Saudi Med. J. 2014, 35, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Xiao, H.-X.; Tian, H.-P.; Liu, Z.-L.; Xia, S.-S.; Zhou, T. Upregulation of microRNA-155 promotes the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through the regulation of claudin-1 expression. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.-L.; Wang, H.-F.; Sun, Z.-Q.; Tang, Y.; Han, X.-N.; Yu, X.-B.; Liu, K. Up-regulated miR-155-5p promotes cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 6988–6994. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lee, C.G.L. Role of miR-224 in hepatocellular carcinoma: A tool for possible therapeutic intervention? Epigenomics 2011, 3, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, A.; Li, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, G.; Yang, Y.; Cui, L.; Sun, J. Fecal miR-29a and miR-224 as the noninvasive biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark. Sect. Dis. Markers 2016, 16, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, H.-X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, T. Up-regulation of miR-224 promotes cancer cell proliferation and invasion and predicts relapse of colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ling, H.; Pickard, K.; Ivan, C.; Isella, C.; Ikuo, M.; Mitter, R.; Spizzo, R.; Bullock, M.; Braicu, C.; Pileczki, V.; et al. The clinical and biological significance of MIR-224 expression in colorectal cancer metastasis. Gut 2016, 65, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Di, J.; Cui, M.; Xing, J.; Wu, F.; Wu, W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Yao, Z.; et al. Downregulated USP3 mRNA functions as a competitive endogenous RNA of SMAD4 by sponging miR-224 and promotes metastasis in colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, W.-T.; Li, T.-T.; Wang, Z.-G.; Wang, S.-Y.; He, M.-R.; Ye, Y.-P.; Qi, L.; Cui, Y.-M.; Wu, P.; Jiao, H.-L.; et al. microRNA-224 promotes cell proliferation and tumor growth in human colorectal cancer by repressing PHLPP1 and PHLPP2. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4662–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, T.-W.; Hsu, H.-L.; Wu, Y.-H.; Chen, W.T.-L.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Cheng, C.-W. MicroRNA-224 suppresses colorectal cancer cell migration by targeting Cdc42. Dis. Markers 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, L.-S.; Chen, G.; Feng, Z.-B. Potential Targets and Clinical Value of MiR-224-5p in Cancers of the Digestive Tract. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 682–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mosakhani, N.; Sarhadi, V.K.; Borze, I.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.-L.; Sundström, J.; Ristamäki, R.; Osterlund, P.; Knuutila, S. MicroRNA profiling differentiates colorectal cancer according to KRAS status. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, B.F.; Yang, C.Q.; Chen, X.M.; Gao, H.J. Initial study of microRNA expression profiles of colonic cancer without lymph node metastasis. J. Dig. Dis. 2010, 11, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ning, J.; Wang, S. MicroRNA-378 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer brain metastasis by promoting cell migration, invasion and tumor angiogenesis. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanutto, S.; Pizzamiglio, S.; Ghilotti, M.; Bertan, C.; Ravagnani, F.; Perrone, F.; Leo, E.; Pilotti, S.; Verderio, P.; Gariboldi, M.; et al. Circulating miR-378 in plasma: A reliable, haemolysis-independent biomarker for colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, B.; Ji, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Gao, H.; Sun, H.; Wu, H.; Chen, X.; et al. MicroRNA-378-5p suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells by targeting BRAF. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, H.-X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, T. MiR-378 is an independent prognostic factor and inhibits cell growth and invasion in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Zhu, L.; Li, L.; Kang, C. miR-378 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer cells by inhibiting SDAD1. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Dai, S.; Zhen, T.; Shi, H.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Y.; Kang, L.; Liang, Y.; Han, A. Clinical and biological significance of miR-378a-3p and miR-378a-5p in colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 1207–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zekri, A.-R.N.; Youssef, A.S.E.-D.; Lotfy, M.M.; Gabr, R.; Ahmed, O.S.; Nassar, A.; Hussein, N.; Omran, D.; Medhat, E.; Eid, S.; et al. Circulating Serum miRNAs as Diagnostic Markers for Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Li, B.; Sun, H.; Zhang, H. The predicted target gene validation, function, and prognosis studies of miRNA-22 in colorectal cancer tissue. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317692257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerimis, D.; Kontos, C.K.; Christodoulou, S.; Papadopoulos, I.N.; Scorilas, A. Elevated expression of miR-24-3p is a potentially adverse prognostic factor in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 50, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Liu, B.; Shan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Jia, L. Tumor-suppressive miR-26a and miR-26b inhibit cell aggressiveness by regulating FUT4 in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elshafei, A.; Shaker, O.; Abd El-Motaal, O.; Salman, T. The expression profiling of serum miR-92a, miR-375, and miR-760 in colorectal cancer: An Egyptian study. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317705765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.-Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-S.; Tsai, W.-S.; You, J.-F.; Lin, G.-P.; Chen, T.-W.; Chen, J.-S.; Chan, E.-C. MicroRNA-223 and microRNA-92a in stool and plasma samples act as complementary biomarkers to increase colorectal cancer detection. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10663–10675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, F.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Z. Circulating Exosomal miR-17-5p and miR-92a-3p Predict Pathologic Stage and Grade of Colorectal Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 11, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, Z. Biological effects and clinical characteristics of microRNA-106a in human colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maierthaler, M.; Benner, A.; Hoffmeister, M.; Surowy, H.; Jansen, L.; Knebel, P.; Chang-Claude, J.; Brenner, H.; Burwinkel, B. Plasma miR-122 and miR-200 family are prognostic markers in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Gao, C.; Li, Y.; Sun, M.; Xu, J.; Li, H.; Jia, L.; Zhao, Y. miR-125a-3p/FUT5-FUT6 axis mediates colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion and pathological angiogenesis via PI3K-Akt pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiala, O.; Pitule, P.; Hosek, P.; Liska, V.; Sorejs, O.; Bruha, J.; Vycital, O.; Buchler, T.; Poprach, A.; Topolcan, O.; et al. The association of miR-126-3p, miR-126-5p and miR-664-3p expression profiles with outcomes of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with bevacizumab. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317709283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, L.; Wan, T.M.-H.; Man, J.H.-W.; Chow, A.K.-M.; Iyer, D.; Chen, G.; Yau, T.C.-C.; Lo, O.S.-H.; Foo, D.C.-C.; Poon, J.T.-C.; et al. Identification of serum miR-139-3p as a non-invasive biomarker for colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27393–27400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, J.; Toden, S.; Yoshida, K.; Toiyama, Y.; Alberts, S.R.; Kusunoki, M.; Sinicrope, F.A.; Goel, A. MiR-139-5p as a novel serum biomarker for recurrence and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baltruskeviciene, E.; Schveigert, D.; Stankevicius, V.; Mickys, U.; Zvirblis, T.; Bublevic, J.; Suziedelis, K.; Aleknavicius, E. Down-regulation of miRNA-148a and miRNA-625-3p in colorectal cancer is associated with tumor budding. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, X.; Jin, R.; Mao, X.; Wang, J.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, G. Prognostic value of miRNA-181a/b in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Biomark. Med. 2018, 12, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, N.; Koga, Y.; Taniguchi, H.; Kojima, M.; Kanemitsu, Y.; Saito, N.; Matsumura, Y. High expression of miR-181c as a predictive marker of recurrence in stage II colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 6970–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hong, X.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, X.; Wang, Z.; Qi, Z.; Hong, X. miR-181d and c-myc-mediated inhibition of CRY2 and FBXL3 reprograms metabolism in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Duan, B.; Hu, J.; Yu, H.; Sheng, H.; Gao, H.; Huang, J. Decreased expression of miR-193a-3p is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Chang, J.; Tong, D.; Peng, J.; Huang, D.; Guo, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. Differential microRNA expression profiling in primary tumors and matched liver metastasis of patients with colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 35783–35791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tayel, S.I.; Fouda, E.A.M.; Gohar, S.F.; Elshayeb, E.I.; El-Sayed, E.H.; El-Kousy, S.M. Potential role of MicroRNA 200c gene expression in assessment of colorectal cancer. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 647, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, P.; Powrózek, T.; Olesiński, T.; Dmitruk, A.; Dziwota, J.; Kowalski, D.; Milanowski, J. Evaluation of miR-506 and miR-4316 expression in early and non-invasive diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2017, 32, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Jiang, T.; Shao, H.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Qin, B.; Zhang, X.; Fan, J. miR-1290 Is a Biomarker in DNA-Mismatch-Repair-Deficient Colon Cancer and Promotes Resistance to 5-Fluorouracil by Directly Targeting hMSH2. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 7, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, I.; Mlčochová, J.; Součková, K.; Fabian, P.; Poprach, A.; Halamkova, J.; Svoboda, M.; Vyzula, R.; Slaby, O. MicroRNAs as outcome predictors in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with bevacizumab in combination with FOLFOX. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, J.; Huang, L.; Cao, Q.; Liu, F. Identification of colorectal cancer-restricted microRNAs and their target genes based on high-throughput sequencing data. Oncotargets Ther. 2016, 9, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koduru, S.V.; Tiwari, A.K.; Hazard, S.W.; Mahajan, M.; Ravnic, D.J. Exploration of small RNA-seq data for small non-coding RNAs in Human Colorectal Cancer. J. Genom. 2017, 5, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, C.; Yan, X.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Yin, M.; Yang, Y.; Gao, R.; Hong, L.; Ma, Y.; Shi, C.; et al. Systematic literature review and clinical validation of circulating microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68317–68328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, H.; Jia, B. A 5-serum miRNA panel for the early detection of colorectal cancer. Oncotargets Ther. 2018, 11, 2603–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, M.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, X.; Shan, X.; Qi, L.-W.; Wu, L.; Cheng, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. A panel of microRNA signature in serum for colorectal cancer diagnosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17081–17091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xiang, J.; Li, Z.; Lu, S.; Hu, J.; Gao, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; et al. A plasma microRNA panel for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaan, Z.; Roberts, H.; Eichenberger, M.R.; Billeter, A.; Ocheretner, G.; Pan, J.; Rai, S.N.; Jorden, J.; Williford, A.; Galandiuk, S. A plasma microRNA panel for detection of colorectal adenomas: A step toward more precise screening for colorectal cancer. Ann. Surg. 2013, 258, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikberg, M.L.; Myte, R.; Palmqvist, R.; van Guelpen, B.; Ljuslinder, I. Plasma miRNA can detect colorectal cancer, but how early? Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, I.-P.; Tsai, H.-L.; Miao, Z.-F.; Huang, C.-W.; Kuo, C.-H.; Wu, J.-Y.; Wang, W.-M.; Juo, S.-H.H.; Wang, J.-Y. Development of a deregulating microRNA panel for the detection of early relapse in postoperative colorectal cancer patients. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-N.; Liu, T.-T.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Tseng, Y.-J.; Yao, C.; Weng, S.-Q.; Dong, L.; Shen, X.-Z. Serum microRNA signatures and metabolomics have high diagnostic value in colorectal cancer using two novel methods. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.K.W.; Fedorak, R.N.; Prosser, C.I.; Stewart, M.E.; van Zanten, S.V.; Sadowski, D.C. The sensitivity and specificity of guaiac and immunochemical fecal occult blood tests for the detection of advanced colonic adenomas and cancer. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2012, 27, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzi, A.; Lenz, H.-J.; Quinn, D.I.; Sadeghi, S. Comparative effectiveness of screening strategies for colorectal cancer. Cancer 2017, 123, 1516–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
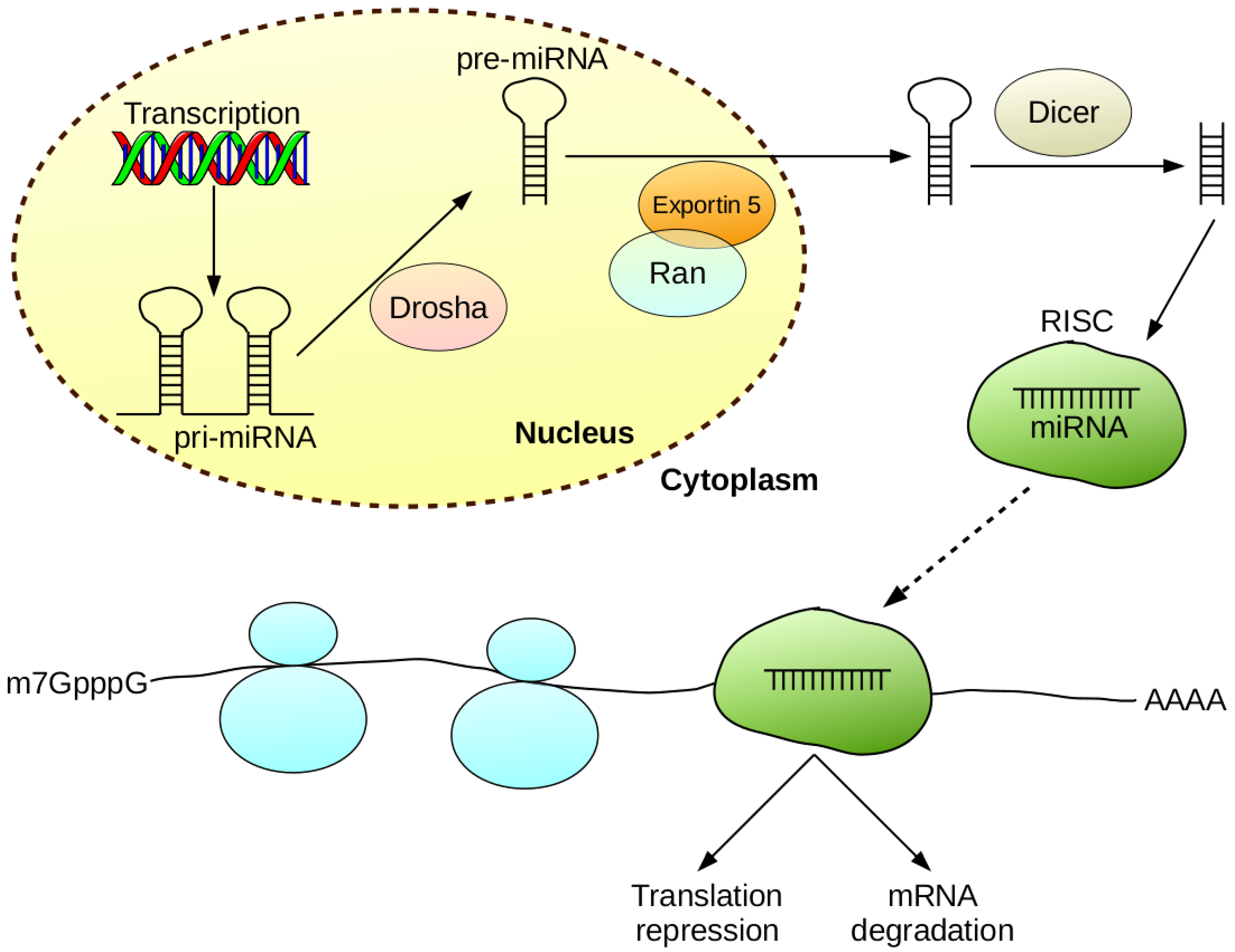
| Possible Applications of miRNA: |
| Predictors of response to therapy and prognostic biomarkers |
| Use of miRNA as a drug—modulation of gene expression |
| Prediction and detection of metastases or non-invasive tumor phenotypes |
| Cancer diagnostics—detection of tumor specific miRNA signatures |
| Advantages of Using miRNA: |
| Easy detection in various biological materials (serum/plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, faeces) |
| High stability of miRNA molecules |
| Ability to determine specific types of cancer, and predict response to therapy and prognosis based on miRNA expression profile |
| Potential for use as antagonists in cancer therapy |
| MiRNA | Biomarker Type | Regulation in CRC | Source of miRNA | Cohort Size | Correlation/Differentiation | Detection Method | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-17 | diagnostic | up-regulation | serum | n = 190 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Zekri et al. [108] |
| miR-17-5p | diagnostic | up-regulation | serum | n = 39 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Fu et al. [114] |
| miR-19a | diagnostic | up-regulation | serum | n = 190 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Zekri et al. [108] |
| miR-20a | diagnostic | up-regulation | serum | n = 190 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Zekri et al. [108] |
| miR-21 | diagnostic | up-regulation | plasma, tissues | n = 116 | control vs. CRC | microfluidic array technology, qRT-PCR | Kanaan et al. [48] |
| miR-21 | diagnostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 73 | control vs. CRC vs. polyps | ISH | Yamamichi et al. [36] |
| miR-21 | diagnostic | up-regulation | serum, stool | n = 80 | TNM stages | qRT-PCR | Bastaminejad et al. [37] |
| miR-21 | diagnostic | up-regulation | stool, tissues | n = 246 | control vs. CRC vs. polyps | qRT-PCR | Wu et al. [38] |
| miR-21 | diagnostic | up-regulation | stool | n = 55 | TNM stages | miRNA microarrays, qRT-PCR | Ahmed et al. [50] |
| miR-21 | diagnostic | up-regulation | stool, tissues | n = 37 | control vs. CRC vs. adenomas | qRT-PCR, miRNA microarrays | Link et al. [39] |
| miR-21 | diagnostic, prognostic | up-regulation | serum, tissues | n = 279 | TNM stages, tumor size, distant metastasis, poor survival | qRT-PCR | Toiyama et al. [33] |
| miR-21 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 301 | poor survival | qRT-PCR | Oue et al. [23] |
| miR-21 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 306 | liver metastasis, Dukes’ stage, shorter OS, shorter DFS | qRT-PCR | Fukushima et al. [40] |
| miR-21 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 197 | poor survival, poor therapeutic outcome | miRNA microarrays, qRT-PCR, ISH | Schetter et al. [16] |
| miR-21 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 46 | shorter DFS | qRT-PCR | Kulda et al. [19] |
| miR-21 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 520 | inferior recurrence-free cancer-specific survival | ISH | Kjaer-Frifeldt et al. [41] |
| miR-21 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 234 | shorter DFS | ISH | Nielsen et al. [42] |
| miR-21 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 156 | liver metastasis, shorter OS, shorter DFS | qRT-PCR | Shibuya et al. [43] |
| miR-21 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 277 | shorter RFS | ISH | Kang et al. [47] |
| miR-22 | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 193 | shorter OS | qRT-PCR | Li et al. [109] |
| miR-24-3p | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 268 | shorter OS, shorter DFS | qRT-PCR | Kerimis et al. [110] |
| miR-26a/b | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 58 | shorter OS | qRT-PCR | Li et al. [111] |
| miR-29 | diagnostic | up-regulation | tissues, plasma | n = 40 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Al-Sheikh et al. [54] |
| miR-29a | diagnostic | up-regulation | plasma | n = 209 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Huang et al. [53] |
| miR-29a | diagnostic | down-regulation | stool | n = 131 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Zhu et al. [93] |
| miR-29a | diagnostic | up-regulation | serum | n = 74 | liver metastasis | qRT-PCR | Wang and Gu [52] |
| miR-29a | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 110 | poor prognosis | miRNA microarrays, qRT-PCR | Weissmann-Brenner et al. [58] |
| miR-29b | diagnostic | down-regulation | tissues, plasma | n = 600 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Li et al. [55] |
| miR-29b | diagnostic, prognostic | down-regulation | serum | n = 110 | TNM stages | qRT-PCR | Basati et al. [56] |
| miR-29b | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 245 | shorter OS, shorter DFS | qRT-PCR | Inoue et al. [60] |
| miR-29b | prognostic | down-regulation | plasma | n = 52 | shorter OS, shorter PFS | qRT-PCR | Ulivi et al. [62] |
| miR-34a | diagnostic | up-regulation | plasma | n = 185 | polyps vs. advanced cancer | qRT-PCR | Aherne et al. [66] |
| miR-34a | diagnostic, prognostic | methylation | tissues, stool | n = 142 | lymph metastasis, control vs. CRC | methylation-specific PCR | Wu et al. [65] |
| miR-34a | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 268 | shorter DFS, recurrence | qRT-PCR | Gao et al. [67] |
| miR-34a | prognostic | methylation | tissues | n = 94 | liver metastasis | methylation-specific PCR | Siemens et al. [69] |
| miR-34a | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 176 | poor prognosis | qRT-PCR | Li et al. [72] |
| miR-34a | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 103 | distant metastasis | qRT-PCR, ISH | Zhang et al. [73] |
| miR-34a/b/c | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 272 | poor prognosis | qRT-PCR | Hiyoshi et al. [74] |
| miR-34b/c | diagnostic | methylation | tissues, stool | n = 142 | control vs. CRC | methylation-specific PCR | Wu et al. [65] |
| miR-92a | diagnostic | up-regulation | tissues, stool, plasma | n = 907 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Chang et al. [113] |
| miR-92a | diagnostic, prognostic | up-regulation | serum | n = 91 | control vs. CRC, TNM stages, poor prognosis | qRT-PCR | Elshafei et al. [112] |
| miR-92a-3p | diagnostic | up-regulation | serum | n = 39 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Fu et al. [114] |
| miR-106a | diagnostic | up-regulation | tissues, plasma | n = 84 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | He et al. [115] |
| miR-122 | prognostic | up-regulation | plasma | n = 543 | shorter RFS, shorter OS | qRT-PCR | Maierthaler et al. [116] |
| miR-124 | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 96 | shorter OS, shorter DFS | qRT-PCR | Wang et al. [82] |
| miR-124-3p | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 1893 | increased likelihood of dying | miRNA microarrays | Slattery et al. [84] |
| miR-124-5p | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 71 | shorter OS | qRT-PCR | Jinushi et al. [83] |
| miR-125a-3p | diagnostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 35 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Liang et al. [117] |
| miR-126-3p | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 63 | shorter OS, shorter PFS | qRT-PCR | Fiala et al. [118] |
| miR-126-5p | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 63 | shorter OS, shorter PFS | qRT-PCR | Fiala et al. [118] |
| miR-130b | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 80 | poor prognosis | miRNA microarrays | Colangelo et al. [85] |
| miR-139-3p | diagnostic | down-regulation | tissues, serum | n = 249 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Ng et al. [119] |
| miR-139-5p | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues, serum | n = 433 | shorter RFS | miRNA microarrays, qRT-PCR | Miyoshi et al. [120] |
| miR-148a | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 54 | shorter PFS | qRT-PCR | Baltruskeviciene et al. [121] |
| miR-150 | diagnostic | down-regulation | plasma | n = 185 | adenomas vs. advanced cancer | qRT-PCR | Aherne et al. [66] |
| miR-155 | prognostic | up-regulation | serum | n = 206 | shorter OS, shorter PFS | qRT-PCR | Lv et al. [88] |
| miR-155 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 156 | shorter OS, shorter DFS | qRT-PCR | Shibuya et al. [43] |
| miR-155 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 84 | poor prognosis | qRT-PCR | Hongliang et al. [89] |
| miR-155 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 76 | lymph node and distant metastases | qRT-PCR | Zhang et al. [90] |
| miR-155-5p | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 372 | metastasis | qRT-PCR | Qu et al. [91] |
| miR-155-5p | prognostic | down-regulation | plasma | n = 52 | shorter OS, shorter PFS | qRT-PCR | Ulivi et al. [62] |
| miR-181c | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 147 | shorter RFS | miRNA microarrays, qRT-PCR | Yamazaki et al. [123] |
| miR-181d | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 40 | metastasis | qRT-PCR | Guo et al. [124] |
| miR-193a-3p | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 96 | shorter OS | miRNA microarrays, qRT-PCR | Lin et al. [125] |
| miR-196-5p | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 48 | shorter OS | miRNA microarrays, qRT-PCR | Li et al. [126] |
| miR-200 | prognostic | down-regulation | plasma | n = 543 | shorter RFS, shorter OS | qRT-PCR | Maierthaler et al. [116] |
| miR-200c | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 48 | shorter OS | miRNA microarrays, qRT-PCR | Li et al. [126] |
| miR-200c | prognostic | up-regulation | serum | n = 90 | shorter OS | qRT-PCR | Tayel et al. [127] |
| miR-223 | diagnostic | down-regulation | stool | n = 131 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Zhu et al. [93] |
| miR-223 | diagnostic | up-regulation | serum | n = 190 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Zekri et al. [108] |
| miR-223 | diagnostic | up-regulation | tissues, stool, plasma | n = 907 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Chang et al. [113] |
| miR-224 | diagnostic | down-regulation | stool | n = 131 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Zhu et al. [93] |
| miR-224 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 108 | shorter DFS | qRT-PCR | Zhang et al. [94] |
| miR-224 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 621 | shorter OS | miRNA microarrays, qRT-PCR | Ling et al. [95] |
| miR-224 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 110 | shorter OS | qRT-PCR | Liao et al. [97] |
| miR-375 | diagnostic, prognostic | down-regulation | serum | n = 91 | control vs. CRC, TNM stages, poor prognosis | qRT-PCR | Elshafei et al. [112] |
| miR-378 | diagnostic | up-regulation | plasma | n = 65 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Zanutto et al. [103] |
| miR-378 | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 84 | shorter OS | qRT-PCR | Zhang et al. [105] |
| miR-378a-3p | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 96 | shorter OS | qRT-PCR | Li et al. [107] |
| miR-378a-5p | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 96 | shorter OS | qRT-PCR | Li et al. [107] |
| miR-506 | diagnostic | up-regulation | plasma | n = 126 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Krawczyk et al. [128] |
| miR-625-3p | diagnostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 54 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Baltruskeviciene et al. [121] |
| miR-664-3p | prognostic | down-regulation | tissues | n = 63 | shorter OS, shorter PFS | qRT-PCR | Fiala et al. [118] |
| miR-760 | diagnostic, prognostic | down-regulation | serum | n = 91 | control vs. CRC, TNM stages, poor prognosis | qRT-PCR | Elshafei et al. [112] |
| miR-1290 | prognostic | up-regulation | tissues | n = 291 | shorter OS, shorter DFS | miRNA microarrays, qRT-PCR | Ye et al. [129] |
| miR-4316 | diagnostic | up-regulation | plasma | n = 126 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Krawczyk et al. [128] |
| MiRNA Panel | Biomarker Type | Regulation in CRC | Source of miRNA | Cohort Size | Correlation/Differentiation | Detection Method | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-15b miR-17 miR-21 miR-26b miR-145 | diagnostic | up-regulation | plasma | n = 280 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Pan et al. [133] |
| miR-1246 miR-202-3p miR-21-3p miR-1229-3p miR-532-3p | diagnostic | up-regulation (miR-1246, miR-1229-3p, miR-532-3p) down-regulation (miR-202-3p, miR-21-3p) | serum | n = 575 | control vs. CRC vs. colorectal adenomas | qRT-PCR | Guo et al. [134] |
| miR-19a-3p miR-21-5p miR-425-5p | diagnostic | up-regulation | serum | n = 334 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Zhu et al. [135] |
| miR-409-3p miR-7 miR-93 | diagnostic | up-regulation (miR-409-3p) down-regulation (miR-7, miR-93) | plasma | n = 241 | control vs. CRC | miRNA microarrays, qRT-PCR | Wang et al. [136] |
| miR-431 miR-15b miR-139-3p | diagnostic | up-regulation | plasma | n = 87 | control vs. stage IV CRC | microfluidic array technology, qRT-PCR | Kanaan et al. [137] |
| miR-431 miR-139-3p | diagnostic | up-regulation | plasma | n = 87 | control vs. CRC | microfluidic array technology, qRT-PCR | Kanaan et al. [137] |
| miR-331 miR-15b miR-21 miR-142-3p miR-339-3p | diagnostic | up-regulation | plasma | n = 87 | colorectal adenomas vs. CRC | microfluidic array technology, qRT-PCR | Kanaan et al. [137] |
| miR-18a miR-21 miR-22 miR-25 | diagnostic | up-regulation (miR-18a, miR-21, miR-25) down-regulation (miR-22) | plasma | n = 201 | control vs. CRC | semi-quantitative RT-PCR | Wikberg et al. [138] |
| miR-7 miR-93 miR-195 miR-141 miR-494 let-7b | prognostic | up-regulation (miR-7, miR-141, miR-494) down-regulation (miR-93, miR-195, let-7b)) | tissues | n = 104 | non-early relapsed CRC vs. early relapsed CRC | qRT-PCR | Yang et al. [139] |
| miR-21 miR-15b miR-29a miR-92a miR-125b miR-223 | diagnostic | up-regulation | serum | n = 163 | control vs. CRC | qRT-PCR | Liu et al. [140] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hibner, G.; Kimsa-Furdzik, M.; Francuz, T. Relevance of MicroRNAs as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102944
Hibner G, Kimsa-Furdzik M, Francuz T. Relevance of MicroRNAs as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):2944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102944
Chicago/Turabian StyleHibner, Grzegorz, Małgorzata Kimsa-Furdzik, and Tomasz Francuz. 2018. "Relevance of MicroRNAs as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers in Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 2944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102944
APA StyleHibner, G., Kimsa-Furdzik, M., & Francuz, T. (2018). Relevance of MicroRNAs as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 2944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102944